Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lower Completion - Juan Tovar PDF
Uploaded by
Mahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lower Completion - Juan Tovar PDF
Uploaded by
Mahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikCopyright:
Available Formats
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
Well Completion Design
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
DEFINITION
Well Completion Design is the process of converting a drilled
wellbore into a safe and efficient production/injection system
Can be divided into:
Lower(reservoir) section and
Upper completion
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CONTENTS
Introduction
Open Hole Wells
Cased & Perforated Wells
Sand Control Options
Casing / Tubing Configurations
Perforation Design
Expandables
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
INTRODUCTION
The lower completion must consider
Equipment requirements for open and cased and perforated wells
Methods of preventing or reducing the ingress of sand
Equipment configurations with regards to both the well design and the
properties of the fluids to be produced
In cased wells, careful consideration should be given to the design of
perforations to maximise production rates
The use of new technologies (such as expandables) to reduce rig time and
improve production economics
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
There are two basic well configurations for oil and gas wells:
Open Hole
The reservoir rock across the producing interval is left exposed to the wellbore.
Fluid are produced directly through the reservoir rock along the wellbore and
into the well.
Cased & Perforated
Casing is set across the producing interval, and perforated (where required).
Hydrocarbons are then produced through the perforation tunnels and into the
cased wellbore.
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
OPEN HOLE
The lowest casing string or liner is set above the reservoir - the lower section of the
wellbore is uncased
Generally only be in a consolidated formation
It is the simplest and cheapest because no equipment has to be installed
HOWEVER:
No selectivity of the reservoir zones (for production or injection)
Water or gas break-through cannot be controlled in producers
Permeability variations will result in fluid preferentially entering the most permeable
zone preventing an effective reservoir sweep in injectors
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
OPEN HOLE WELLS
The main features and limitations of the open hole completion are:
Advantages Lower equipment and operating costs
Maximum well productivity and minimum
formation damage
Preferred option for horizontal wells
Limitations Should only be used in consolidated
formations
No zone selectivity or flow control of gas
or water production
Wellbore may require periodic cleaning
and maintenance
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CASED & PERFORATED WELLS
Casing or liner string is run and cemented across the production
interval, and perforated in selected zones
This is a more complicated method, hence time consuming and
expensive
It offers good zonal isolation and wellbore integrity with flow control
of produced water or gas
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CASED & PERFORATED WELLS
The main features and limitations are:
Advantages Better zonal isolation and flow
control
Reduced productivity
Limitations Time consuming and expensive
Greater potential for formation
damage and impaired productivity
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
SAND CONTROL OPTIONS
There are several ways in which sand production can be mitigated in oil and gas
wells:
Slotted Liners
Stand Alone Screens
Frac Pack
Gravel Pack
Expandable Sand Screens
Chemical Consolidation
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
SLOTTED LINERS
The most basic mechanical sand control methods is the slotted liner.
Tubing sections with a series of slots cut through the tubing wall
The slot width is designed to initiate inter-particle bridging
Originally considered it should be twice the diameter of the D10.
More conservative present view is they should be about the same size as D10
The main limitation of slotted liners is their flow area an average of 3%
The flow area, it can be calculated using the following equation:
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
SLOTTED LINERS
There are two types of slot available - keystone and straight.
Keystone slots are considered better due
to their self cleaning ability
They are generally twice as expensive as
straight cuts
Slotted liners are only slightly cheaper
than wire-wrap and often more expensive
They are considered to be stronger -
improved handling
They have much less open flow area than
wire wrapped screens
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
STAND ALONE SCREENS
There are three main types of stand-alone screens:
WIRE WRAPPED PREMIUM PRE-PACKED
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
STAND ALONE SCREENS WIRE WRAPPED
Perforated
Wire wrapped screens are made from API Based
Pipe
triangular shaped wrap wire.
Rectangular wires may result in jamming
Rib Wires
of grains plugging the screen and
reducing the flow area.
Wrap Wire
The triangular shape of the wrap wire
reduces the chance of sand grains from
getting trapped in the slots and hence
plugging the screen.
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
STAND ALONE SCREENS WIRE WRAPPED
Sand bridges restrict passage of other
grains
Formation of this structure critical to
controlling the sand
The fine particles are able to pass Gap
If the fines were stopped they would plug
smaller pores reducing the system
permeability.
If sand grain size varies considerably, the
filter cake has a reduced permeability
hence little control poorly sorted sands
In general terms, wire-wrap screens are
used behind gravel packs,
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
STAND ALONE SCREENS PRE-PACKED
The pre-pack gravel is the main filtration medium
and the wire-wrap jackets are designed to retain
the proppant in place
The pre-packed screens provide insurance
against voids in the gravel pack
Pre-pack screens are used in horizontal wells or
marginal wells where the use of a gravel pack
would be uneconomic
Slimmer pre-pack screens are primarily used
behind frac packs or high rate water packs in
horizontal wells
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
STAND ALONE SCREENS PRE-PACKED
A concern for operators is the difference
between cured and uncured resins and its
affect on screen permeability
The less precise sorting and non-sphericity Resin Coated Gravel
of sand results in t a tighter and less porous
pack
Cured resin was thought to blind off some
pore throats reducing permeability
Ceramic proppants this is not an issue as,
the difference is not significant at normal
Resin Coated Proppant
levels
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
STAND ALONE SCREENS PREMIUM
All metal design, with metal mesh filtration and
protective outer metal shroud
Filter media is metal weave, metal fibres or
powder particles embedded within square mesh
Apertures vary from 60 micron to 300 micron
Mesh prevents larger particles passing but allows
formation fines to pass
Run in long horizontals, behind gravel packs
Similar sand control properties to pre-pack screens
Improved plugging resistance and ability to flow
back drilling muds through the screens
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
FRAC PACK
The objective of frac packs is to improve productivity by creating a
short, wide fracture close to the wellbore
A proppant is placed inside the fracture to hold open the fracture and
control sand production
In frac packing the fracture widths can be 1 inch or larger and lengths
usually in the region of 20 to 50 feet
Cross-linked gels are used for optimum fracture size
The majority of wells have a conventional gravel pack in the central
wellbore area in addition to the frac pack
A more recent development is to have a resin coated frac pack along
with a screenless completion in the wellbore
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
FRAC PACK
Fracture filled with
gravel /proppant
wellbore packed
with screen in
wellbore
Fracture filled with
resin coated gravel
/proppant Wellbore free
of equipment
FRAC-PAC WITH SCREEN FRAC-PAC WITHOUT SCREEN
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
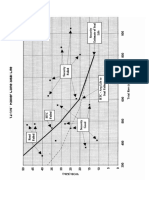
FRAC PACK
The well performance benefits of frac packing, below, shows the typical skin
behaviour of a frac pack.
In terms of sand control this improved well performance will limit the drawdown
required to obtain a particular rate and as the flow comes from a larger area
the rates will be lower thus, reducing the fluid drag
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
FRAC PACK
The major advantages of frac packs are that
They bypass near wellbore damage
They offer a larger effective wellbore radius
They can connect multiple thin layers
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
GRAVEL PACK
Gravel Packs (GP) are useful for completing sand prone reservoirs in a
wide variety of reservoir sand types and completions.
GP systems have been in common use for many years, and on their
application exists a wealth of experience and knowledge
Gravel packing in open-hole (EGP External Gravel Pack) is useful for
preventing annular flow and controlling sand in heterogeneous
formations.
Gravel packing in cased-holes (IGP Internal Gravel Pack) is useful for
protecting the sand screens from erosional flow.
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
GRAVEL PACK
TUBING
PACKER
Cemented
and
perforated
casing/line
r
SCREEN
Gravel
Squeezed
into
perforations Under-reamed
Open hole
section with
gravel pack
CASED HOLE (INTERNAL) OPEN HOLE (EXTRNAL)
GRAVEL PACK GRAVEL PACK
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
GRAVEL PACK
Gravel packing is more complex with increased hole angle and length
In open hole, high permeability streaks / washouts can interfere with uniform
gravel placement
Low net to gross pays can also intermix with the gravel during pumping and
impair the gravel pack permeability and hence productivity
To counteract these problems, the industry has responded by developing
specialised techniques and equipment - alternative path technology
Some systems use shunt tubes on the exterior of the screens and allows the
gravel to by-pass blockages in the well-bore annulus
Alternative approaches are offered by other service companies, which aim
to achieve the same result
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CHEMICAL CONSOLIDATION
Used in formations with little or no cementaceous material
Can also be used as a remedial technique
The principle is to bond the quartz grains together using a liquid resin
This provides artificial cementing material between the grains
A major benefit is that the wellbore is left free of obstructions
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CHEMICAL CONSOLIDATION
In order for chemical consolidation to be effective the resin must:
Fully coat the grains of the formation
Concentrate the resin at the grains contact points
Leave the majority of pore space available for flow
Grain to Grain
contact points
Resin coated
grain
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CHEMICAL CONSOLIDATION
Sand grains must be coated with resin to wet the exposed
sand surface to form a good adhesive bond
The resin will concentrate in the grain contact points
Before the resin can harden a non-reactive fluid (usually oil) is
placed in the pore space to partially displace the resin
Typical volume ratios leave 35% of the pore space filled with
resin
The remainder that has been displaced to oil will be open for
flow once the resin has set
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CASING AND TUBING CONFIGURATIONS
For the two basic well configurations (open hole and cased and
perforated) there are a number of lower completion options:
Horizontal
Multi Laterals
Multi Zone
Injectors
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CASING AND TUBING CONFIGURATIONS HORIZONTAL
Horizontal wells have an increased borehole contact area with the formation
This could be as much as 6000 feet or more of completed reservoir zone
Productivity is a function of well length and interval height
Horizontal wells may have the following completion configurations:
Open hole
Cased and perforated
Slotted liner
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CASING AND TUBING CONFIGURATIONS HORIZONTAL
Applications for horizontal wells are predominantly based around more effective
and efficient drainage of the reservoir, while minimising production problems
which may have been encountered had a vertical well been used.
They include:
Intersection of naturally fractured reservoirs
Minimisation of gas and water coning
Low permeability gas wells improved drainage area
High permeability gas well reduce near wellbore velocities
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CASING AND TUBING CONFIGURATIONS MULTI LATERALS
Multilateral technology was developed to increase reservoir exposure
by using complex drainage architecture connecting one or many lateral
wellbores to the main borehole at the multilateral junction
The junction can be designed in a new well application or created in an
existing wellbore for re-entry. The main and lateral bore designs can
be vertical, directional, or horizontal and are based on individual
reservoir requirements
From the lateral bore, additional laterals, branches, or splays can be
added to tie back additional reservoir targets.
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CASING AND TUBING CONFIGURATIONS MULTI LATERALS
Increase well-bore leverage
Developed to increase reservoir exposure
Reduce surface infrastructure
Obviate requirement for slot recovery
Commingle production from different zones or
reservoirs
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CASING AND TUBING CONFIGURATIONS MULTI LATERALS
Multi lateral applications include:
Reservoir exposure
Multiple targets
Comingled flow
Auto gas lift
Dump flood
Slot reductions / infrastructure
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CASING AND TUBING CONFIGURATIONS MULTI LATERALS
Six levels of multilateral completion technology
Multilateral
Completion
Open / Mother Bore Mother Bore Mother Bore
Unsupported Cased & Cemented Cased & Cemented & Lateral
Junction Lateral Open Lateral Cased Cased & Cemented
Pressure Integrity Pressure Integrity at Downhole Splitter
at Junction Junction with Casing
(Not Cement)
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CASING AND TUBING CONFIGURATIONS MULTI LATERALS
Six levels of multilateral completion technology
Level 1
Open Unsupported Junction
Consolidated formations
Lateral access limited
Production control limited
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CASING AND TUBING CONFIGURATIONS MULTI LATERALS
Six levels of multilateral completion technology
Level 2
Mother Bore Cased & Cemented, Lateral Open
Consolidated formations
Can straddle for production control
Full opening in main bore
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CASING AND TUBING CONFIGURATIONS MULTI LATERALS
Six levels of multilateral completion technology
Level 3
Mother Bore Cased & Cemented, Lateral
Cased
Consolidated formation preferred, but
completions made in unconsolidated
formations
Junction is the weak point of completion
(no integrity or control)
Full bore access to main and lateral
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CASING AND TUBING CONFIGURATIONS MULTI LATERALS
Six levels of multilateral completion technology
Level 4
Mother Bore & Lateral Cased & Cemented
Mechanically supported junction
No hydraulic integrity
Full bore access to mother bore and lateral
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CASING AND TUBING CONFIGURATIONS MULTI LATERALS
Six levels of multilateral completion technology
Level 5
Pressure Integrity at Junction Not Cement
Consolidated or unconsolidated formations
Pressure isolation is provided by mechanical
seal (not cement)
Access preserved for re-entry but may not
be full bore
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CASING AND TUBING CONFIGURATIONS MULTI LATERALS
Six levels of multilateral completion technology
Level 6
Pressure Integrity at Junction with Casing
Consolidated or unconsolidated formations
Pressure isolation is provided by
mechanical seal (not cement)
Access preserved for re-entry an is full bore
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CASING AND TUBING CONFIGURATIONS MULTI ZONE
Multi zone completions utilised where more than one distinct reservoir layer
is encountered.
The depletion of multiple zones can be achieved by:
Co-mingled flow from various layers
Segregated but multi-zone completion
Alternate well completion strategy
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CASING AND TUBING CONFIGURATIONS MULTI ZONE
Multi zone completion options are based on the number of zones to be
produced and the properties of the reservoir fluids, and the flow path of the
zones.
Dual Zone
Casing / Tubing Upper Zone Lower Zone Dual Tubing
Flow Annular Flow Annular Flow Flow
One zone produces Where the upper zone Where the lower zone Here two tubing
through the tubing fluid is non-corrosive fluid is non-corrosive strings are utilised to
string while the other or abrasive, it can be or abrasive it can be produced each layer
produces through the produced through the produced through the independently
casing annulus annulus annulus
Can also use single string selective completion
can produce from one zone or the other
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CASING AND TUBING CONFIGURATIONS MULTI ZONE
Triple Zone
3 Tubing 2 Tubing Strings Single String 2 Strings
Strings and Casing Triple Selective Co-mingled Flow
Completion
Four or More Zones
Triple String Dual String Single String Triple String
with Selective Quad Selective with
Annular Completion Completion Annular
Production Production
Normally never run more than 3 tubing strings
Multi-zones become complex and expensive
Difficult to run, retrieve and susceptible to failure
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
CASING AND TUBING CONFIGURATIONS INJECTORS
The use of injection wells to restore or help maintain reservoir
pressure within the field is widely utilised, however the following
considerations should be made:
Identification of layers suitable for water migration
Impact of water production on the rest of the producing system
Associated production problems scaling fines migration etc.
Sand control requirements for injectors
Water shut off options timing and strategy
Thermal Induced Fracturing (TIF)
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
PERFORATION DESIGN
The purpose of perforating a well is to create a series of communication tunnels,
known as perforations, between the wellbore and the formation
The characteristics and placement of perforations influences the productivity of a
well
Careful consideration must be given to the design and execution of the perforation
programme and operation
Perforations are the only means by which production fluids enter the wellbore and
they must provide an adequate inflow area
The perforations must be deep enough to penetrate any mud damaged zone
around the well bore as well be free of any debris which would impair productivity
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
PERFORATION DESIGN
The following well condition factors should be
considered in the perforation programme: Damage zone
Phase angle Tubing/Casing
Type of completion Crushed zone
Cement
Cement thickness and casing /
formation bond integrity
Type and level of wellbore fluid
Shot
density
Specification (and conditions) of
wellbore tubulars and equipment
Formation permeability, characteristics
Perforation
and type length
Post perforation stimulation and/or
completion programs
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
PERFORATION TYPES DEEP PENETRATING
Overburden
Fluid viscous
drag Turbulence
Plastic zone
WOR Cement & Casing
support
Pr
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
PERFORATION TYPES BIG HOLE
Wellbore
Damaged
zone
Steel casing
Entrance
Hole
Perforation
cavity
Debris
Cement sheat
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
PERFORATION DESIGN
Four main factors must be considered to achieve optimum perforation of a
particular reservoir.
The factors vary in importance depending on the reservoir and completion
type, they are:
Shot Density the number of shots per foot
Perforation Diameter dependant on the gun type
Perforation Phasing the angel of the perforations around the wellbore
Perforation Length dependant on the gun type
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
STRESS DISTRIBUTION AROUND THE WELLBORE
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
PERFORATION DESIGN UNDERBALANCED PERFORATING
Underbalanced perforation - the wellbore pressure is less than the
formation pressure
Improved well productivities due to flow out of the formation immediately
on perforating
This flow removes crushed materials from the perforations, ensuring
clean perforation tunnels
Well performance is greatly affected by well cleanliness, underbalanced
perforating can give better productivity
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
PERFORATION DESIGN UNDERBALANCED PERFORATING
Underbalance Perforation
Damaged formation
Cement Reservior formation
Tubing/Casing Perforation
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
PERFORATION DESIGN TECHNIQUES
Perforating Methods
Through Tubing Tubing / Drill Pipe
/ Casing Conveyed
Wireline Coiled Tubing
Conveyed Conveyed
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
PERFORATION DESIGN TECHNIQUES
Wireline Conveyed Perforating
Economic over short intervals
Multiple runs required for longer intervals
Can pull out immediately after perforating
Suitable for low angle wells only
Limit level of underbalance
Mainly used for re-perforating
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
PERFORATION DESIGN TECHNIQUES
Coiled Tubing Conveyed Perforating
Perforation in high angle wells
Increased underbalance level
Length limited by rig up restrictions
Long intervals require multiple runs
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
PERFORATION DESIGN TECHNIQUES
Tubing / Drill Pipe Conveyed Perforating
Use more rig time to run but can perforate long intervals.
Can be run at same time as part of the completion
Important to ensure that guns can be run to depth and
space out is correct
Can be left in situ once perforating is complete
Can run larger guns increased phasing or higher shot
densities
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
PERFORATION DESIGN - GUIDELINES
Consider all parameters and conditions when choosing guns
Check that charge performance is sufficient:
Check performance with rock strength and confining stress
Check quality control of charges
Investigate entire perforating operation before choosing guns:
Removal of perforation debris
Sufficient underbalance
Will TCP guns have to be pulled after killing the well
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
PERFORATION DESIGN - GUIDELINES
Perforate in filtered inhibited brine do not induce formation damage
by perforating in dirty fluids
If more than four wireline runs are required, TCP will be cheaper.
Check QA / QC on shaped charges:
Check origin / source
Check storage
Test fire in lab?
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
PERFORATION DESIGN - GUIDELINES
GUIDELINES
METHOD
Selective Oriented
Applications All sandstones, rock not completely unconsolidated
Typical skins 2 - 10
Strength > 500 psi TWC for gas wells Strength > 300 psi TWC for gas wells
Selection
> 800 psi TWC for oil wells ( isotropic) > 600 psi TWC for oil wells
criteria
Kv/Kh > 0.7 (Anisotropic) > 3000 psi TWC all wells
DP, any orientation (isotropic only) DP, oriented
Perforation
Density [ 4 8 ] spf Density [ 4 10 ] spf
strategy
EH < 0.4 inches, L = 5 longer than skin EH < 0.5 inches, L = maximum
Method Underbalance if possible Pcrit + 100 psi, larger gun size possible
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
EXPANDABLES
New / developing technology
Slotted expandables (e.g. ESS) for sand control
Solids expandables (e.g. Metalskin) for other applications
Allow reduced running OD while maximising
production ID
Provide improved inflow performance with
with additional borehole support
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
EXPANDABLES - SLOTTED
1 EST Base Pipe 2 Woven Filter Media 3 Outer Shroud
1
2 1
2
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
EXPANDABLES - SLOTTED
ESS Screen Expansion
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
EXPANDABLES - SOLID
Repair existing casing strings
Suitable for cladding
Operationally simple
Suitable for zonal isolation
(LC or swelling shales)
Reduced mechanical properties
after expansion
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
EXPANDABLES - SOLID
Solid Tubular Expansion
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
ARTIFICIAL LIFT METHODS
Gas lift
Hydraulic pumps
Sucker rod
Electrical submersible pumps
Progressive cavity pumps
Jet pumps
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
GAS LIFT
Gas lift works by reducing the hydrostatic head of the reservoir fluids by adding
gas.
Gas lift will be at its most efficient if injected at the maximum depth
Install/recover gas lift valves at deviations beyond 60 may be troublesome
Lift gas will displace the annular contents down to the deepest injection point
The casing must be designed for higher loads
The lift gas must be dry if corrosion of the tubing / casing is to be avoided.
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
GAS LIFT Typical configurations
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
HYDRAULIC PUMPS
Turbine type of pumps rotating at high speed
A pump section and a power section(turbine)
Can accommodate very high rates and high GOR
Very sensitive to solids in the power fluid
Fixed pump setting depth
Texaco Mariner, BP forties.
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
SUCKER ROD PUMPS
Positive displacement pump
Moderate to low rate
Pump activated from surface using a metal rod 1/8 5/8 sizes
Good for heavy crudes and tolerant of solids
Require proper design
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
ESPs
Centrifugal pumps
All rate ranges up to +60000 bfpd
Pump activated from surface using a metal rod 1/8 5/8 sizes
Good for heavy crudes and tolerant of solids
Require proper design
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
TYPICAL CONFIGURATIONS
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
ESPs
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
ESPs SURFACE SET UP
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
ESPs POWER CABLE
Optimum cable selection depends on the current capacity of the cable and the
environment in which the cable will be operating
Cable type can be round or flat
Cable components are : Armour
Jacket
Insulation
Conductor
Insulation material depends on the type of environment
Temperature limits can be as high as ~ 420 o F
Cable ODs, up to 1.8 , conductors are made of cooper or aluminium, solid or
stranded
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
ESPs CABLE CLAMPS
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
MSc Drilling & Well Engineering
Well Design, Drilling & Completions
Lower Completion
JET PUMPS
Jet pumps are simple devices which use a Venturi to pump fluids from the
reservoir.
The power fluid can be any liquid.
The jet pump creates a low pressure at the suction may generate scale
Likewise mixing of power fluid and reservoir fluid may precipitate scale.
The power fluid flow path creates a potential leak to surface.
The high energy mixing of water and oil in the pump can create emulsions
The power fluid is produced to surface.
The casing rating must be checked if the pump is powered from the annulus
The tubing stress analysis must be checked with a higher external pressure.
There will be a hole angle limitation for wireline installation.
Univation/Innovative Knowledge Ltd
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Drillsim PDFDocument4 pagesDrillsim PDFMahmoud Ahmed Ali Abdelrazik0% (1)
- Daily HSE Summary Report 28-03-2018Document1 pageDaily HSE Summary Report 28-03-2018Mahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- 6 - Stability Sign ConventionsDocument2 pages6 - Stability Sign ConventionsMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- 8 Steps To Finding Your Dream Job CoverDocument51 pages8 Steps To Finding Your Dream Job CoverMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- SmithRedBaron Visit QuestionsDocument1 pageSmithRedBaron Visit QuestionsMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Afternoon Report 26-03-18Document1 pageAfternoon Report 26-03-18Mahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Daily HSE Summary Report 25-03-2018Document1 pageDaily HSE Summary Report 25-03-2018Mahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Hassan Abdel-Aziz Galal Abdel-Aal: ContactDocument2 pagesHassan Abdel-Aziz Galal Abdel-Aal: ContactMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Ades - Admarine III - We019 Issued 26-03-2018 at 0401 LTDocument3 pagesAdes - Admarine III - We019 Issued 26-03-2018 at 0401 LTMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Daily HSE Summary Report 27-03-2018Document1 pageDaily HSE Summary Report 27-03-2018Mahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Ades - Admarine III - We019 Issued 27-03-2018 at 0401 LTDocument3 pagesAdes - Admarine III - We019 Issued 27-03-2018 at 0401 LTMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Stuck 1 2 3 4 AnswersDocument7 pagesStuck 1 2 3 4 AnswersMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Avg Downhole Losses: 4 BBLS/HR.: G.P.C Daily Drilling Report Att. Eastern Desert Rig Heading: 206°Document1 pageAvg Downhole Losses: 4 BBLS/HR.: G.P.C Daily Drilling Report Att. Eastern Desert Rig Heading: 206°Mahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Daily HSE Summary Report 26-03-2018Document1 pageDaily HSE Summary Report 26-03-2018Mahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Ades - Admarine III - We019 Issued 28-03-2018 at 0401 LTDocument3 pagesAdes - Admarine III - We019 Issued 28-03-2018 at 0401 LTMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- ADM III Rig Safety Report 28-03-2018Document1 pageADM III Rig Safety Report 28-03-2018Mahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Cement Calcs 12.25Document2 pagesCement Calcs 12.25Mahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Ades - Admarine III - We019 Issued 29-03-2018 at 0401 LTDocument3 pagesAdes - Admarine III - We019 Issued 29-03-2018 at 0401 LTMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- BHA Drilling StiffDocument1 pageBHA Drilling StiffMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Roller Cone Bit Seal LifeDocument1 pageRoller Cone Bit Seal LifeMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Trip Sheet: Following Data Is AvailableDocument2 pagesTrip Sheet: Following Data Is AvailableMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Coring Trip and Stuck PipeDocument3 pagesCoring Trip and Stuck PipeMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Cement Calcs 12.25Document2 pagesCement Calcs 12.25Mahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- BHA #2 Length in FT Cum Length in FTDocument1 pageBHA #2 Length in FT Cum Length in FTMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Workover Operations (Ok)Document6 pagesWorkover Operations (Ok)Mahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge (Ok)Document5 pagesGeneral Knowledge (Ok)Mahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Rig Equipment (Ok)Document25 pagesRig Equipment (Ok)Mahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Sept 15 (Ok)Document3 pagesHydraulics Sept 15 (Ok)Mahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- HSE Sept 15Document2 pagesHSE Sept 15Mahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Stuck Pipe and Fishing Sept 15 (Ok)Document2 pagesStuck Pipe and Fishing Sept 15 (Ok)Mahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- FRABA - Absolute - Encoder / PLC - 1 (CPU 314C-2 PN/DP) / Program BlocksDocument3 pagesFRABA - Absolute - Encoder / PLC - 1 (CPU 314C-2 PN/DP) / Program BlocksAhmed YacoubNo ratings yet
- Bonding in coordination compoundsDocument65 pagesBonding in coordination compoundsHitesh vadherNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Mold RemediationDocument2 pagesChecklist For Mold Remediation631052No ratings yet
- Newton Raphson Method MCQDocument15 pagesNewton Raphson Method MCQmd junaidNo ratings yet
- Unitary Small Air-Conditioners and Air-Source Heat Pumps (Includes Mixed-Match Coils) (RATED BELOW 65,000 BTU/H) Certification ProgramDocument65 pagesUnitary Small Air-Conditioners and Air-Source Heat Pumps (Includes Mixed-Match Coils) (RATED BELOW 65,000 BTU/H) Certification ProgramAmer GaladNo ratings yet
- Machine Tools Cutting FluidsDocument133 pagesMachine Tools Cutting FluidsDamodara MadhukarNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework For Group Processing of Lyric Analysis Interventions in Music Therapy Mental Health PracticeDocument9 pagesConceptual Framework For Group Processing of Lyric Analysis Interventions in Music Therapy Mental Health Practiceantonella nastasiaNo ratings yet
- Bosch Committed to Outsourcing to Boost CompetitivenessDocument4 pagesBosch Committed to Outsourcing to Boost CompetitivenessPriya DubeyNo ratings yet
- Modification Adjustment During Upgrade - Software Logistics - SCN WikiDocument4 pagesModification Adjustment During Upgrade - Software Logistics - SCN Wikipal singhNo ratings yet
- Wei Et Al 2016Document7 pagesWei Et Al 2016Aline HunoNo ratings yet
- Working With Session ParametersDocument10 pagesWorking With Session ParametersyprajuNo ratings yet
- 021SAACK Burner Operating Instructions PDFDocument136 pages021SAACK Burner Operating Instructions PDFmekidmu tadesse100% (1)
- Complex Numbers GuideDocument17 pagesComplex Numbers GuideGus EdiNo ratings yet
- Paygilant - Frictionless Fraud PreventionDocument17 pagesPaygilant - Frictionless Fraud PreventionGlobalys LtdNo ratings yet
- Assessment (L4) : Case Analysis: Managerial EconomicsDocument4 pagesAssessment (L4) : Case Analysis: Managerial EconomicsRocel DomingoNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation - Bipolar Affective Disorder 2Document73 pagesCase Presentation - Bipolar Affective Disorder 2Hemant's galaxy All is hereNo ratings yet
- Ace3 1122.03 GB PDFDocument16 pagesAce3 1122.03 GB PDFArpit VermaNo ratings yet
- Lignan & NeolignanDocument12 pagesLignan & NeolignanUle UleNo ratings yet
- Cisco Lab 2.2.4.3Document5 pagesCisco Lab 2.2.4.3vcx100100% (6)
- 001 Gace Early Childhood TestDocument3 pages001 Gace Early Childhood Testapi-265795386No ratings yet
- Offshore Wind Turbine 6mw Robust Simple EfficientDocument4 pagesOffshore Wind Turbine 6mw Robust Simple EfficientCristian Jhair PerezNo ratings yet
- Rev F AvantaPure Logix 268 Owners Manual 3-31-09Document46 pagesRev F AvantaPure Logix 268 Owners Manual 3-31-09intermountainwaterNo ratings yet
- Networks Lab Assignment 1Document2 pagesNetworks Lab Assignment 1006honey006No ratings yet
- EE114-1 Homework 2: Building Electrical SystemsDocument2 pagesEE114-1 Homework 2: Building Electrical SystemsGuiaSanchezNo ratings yet
- List of StateDocument5 pagesList of StatedrpauliNo ratings yet
- Contract To Sell LansanganDocument2 pagesContract To Sell LansanganTet BuanNo ratings yet
- Basics of Duct DesignDocument2 pagesBasics of Duct DesignRiza BahrullohNo ratings yet
- Shell Omala S2 G150 DatasheetDocument3 pagesShell Omala S2 G150 Datasheetphankhoa83-1No ratings yet
- Women Safety AppDocument18 pagesWomen Safety AppVinod BawaneNo ratings yet
- Exercise C: Cocurrent and Countercurrent FlowDocument6 pagesExercise C: Cocurrent and Countercurrent FlowJuniorNo ratings yet