Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCERT Chapter 6: Tissues (Plant Tissue and Animal Tissue)
Uploaded by
Chetan GautamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCERT Chapter 6: Tissues (Plant Tissue and Animal Tissue)
Uploaded by
Chetan GautamCopyright:
Available Formats
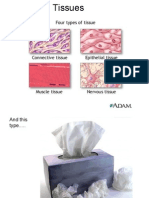
Chapter 6: Tissues
1. Tissue is a group of cells having similar origin, structure& function.
Study of tissues is called Histology
2. In unicellular organism (Amoeba) single cell performs all basic
functions, whereas in multi-cellular organisms (Plants and Animals)
shows division of labour as Plant tissue & Animal tissues.
3. Plant tissues are two types: Meristems & Permanent tissues.
4. Meristems : The Meristems are the tissues having the power of cell
division. It is found on those region of the plant which grows.
5. Types of Meristems :
1. The Apical meristems It is present at the growing tip of the stem
and roots and increases the length.
2. The lateral meristems - present at the lateral side of stem and root
(cambium) and increases the girth.
3. The intercalary meristems - present at internodes or base of the
leaves and increases the length between the nodes.
6. Permanent tissues: Two types such as Simple permanent tissues &
Complex permanent tissues.
Parenchyma: Tissues provide the support to plants. They are
loosely packed and has large intracellular space.
- Parenchyma with chlorophyll which performs photosynthesis is
called as chlorenchyma.
- The parenchyma with large air spaces to give buoyancy is
called as aerenchyma .Parenchyma also stores food and water.
Collenchyma: Tissue provides mechanical support, thickened at
the corners, have very little intercellular space. It allows easy
bending of various parts of a plants without breaking.
Sclerenchyma: Tissue makes the plant hard and stiff, thickened
due to lignin and no intercellular space. Cells of this tissue are
dead and commonly seen in the husk of coconut.
Guard cells& Epidermal tissue: the tissue aids in protection and
exchange of gases. Guard cells kidney shaped in dicots, dumb bell
shaped in monocots to guard the stomata. The epidermal tissues of
roots aid in absorption of water and minerals. The epidermal
tissues in desert plants have a thick waxy coating of Cutin with
waterproof quality. The epidermal tissues form the several layer
thick Cork or the Bark of the tree.
Complex permanent tissues: The complex tissues are made of more
than one type of cells. All these cells coordinate to perform a common
function.
They are subdivided as;
Xylem: It consists of tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem
fibers. The cells have thick walls,
Function - aids in conduction of water and minerals.
Phloem: It consists of sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem
parenchyma, and phloem fibers.
Function - Phloem transports food material to other parts of the plants.
ANIMAL TISSUES
Sub divided as epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue and
nervous tissue.
1. Epithelial tissue: It is a protective covering forming a continuous
sheet. Simple epithelium is the one which is extremely thin in one
layer, whereas stratified epithelium are arranged in pattern of layers.
Depending on shape and function they are classified as:
Squamous epithelium in the lining of mouth and esophagus.
Cuboidal epithelium in the lining of kidney tubules and salivary
glands.
Columnar epithelium in the intestine &Columnar epithelium with
cilia in the lining of respiratory tract.
Glandular epithelium in the Glands aids in a special function as
gland cells, which can secrete at the epithelial surface.
Connective Tissue: Five Types, such as :
1. Blood: The Blood is a fluid connective tissue. Blood plasma has RBCs
(Red Blood Cells) WBCs (White Blood Cells) and platelets. Blood
plasma contains proteins, salts and hormones. Blood flows and
transports gases, digested food, hormones and waste materials.
2. Bone: The bone is a connective tissue with hard matrix, composed of
calcium and phosphorus. A bone is connected by another bone with
another connective tissue called ligaments. A bone is connected by
muscle with another connective tissue called tendon.
3. Cartilage: The cartilage is a connective tissue with solid matrix
composed of proteins and sugars. It is commonly seen in nose, ear,
trachea, and larynx.
4. Areolar Connective Tissue: It is found between the skin and muscles,
around the blood vessels. It supports internal organs and aids in repair
of tissues.
5. Adipose Connective Tissue: It is filled with fat globules for the storage
of fat. It acts as a insulator.
Muscular tissues: They have special contractile proteins responsible for
movements. Three types, such as:
Striated muscles/skeletal muscles/voluntary muscles :
They are cylindrical, un-branched and multinucleated.They have dark
bands and light bands.
Unstriated muscles/smooth muscles/involuntary muscles:
They are commonly called as Smooth muscles, having no striations (dark
bands/ light bands are absent). Commonly found alimentary canal, uterus,
Iris of an Eye. They are spindle shaped. Involuntary in nature.
Cardiac Muscles: They are commonly called as Heart muscles,
cylindrical, branched and uni-nucleate. Involuntary in nature.
Nervous Tissue: The tissue responds to stimuli. The brain, spinal cord and
nerves are composed of nervous tissue or neurons. A neuron consists of
Cell Body, cytoplasm, Nucleus, Dendrite, Axon, nerve ending. The neuron
impulse allow us to move our muscles when we want to respond to
stimuli.
You might also like
- Chapter 6 - Tissues Revision NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 6 - Tissues Revision NotesAbhishek100% (1)
- TissuesDocument74 pagesTissuesMonica Sree100% (1)
- M2 NQ 8 F1 U LUt P@pho T0 ERx Z6 VVQ ZTTS28 QTF SNGD 9 e 68!Document3 pagesM2 NQ 8 F1 U LUt P@pho T0 ERx Z6 VVQ ZTTS28 QTF SNGD 9 e 68!deep.deepkNo ratings yet
- Tissue and Tissue Systems - STD 9Document14 pagesTissue and Tissue Systems - STD 9Syamala Natarajan100% (1)
- Cell Types 1Document28 pagesCell Types 1IngridNo ratings yet
- Tissues NotesDocument7 pagesTissues NotesHarshitNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument13 pagesTissuesAvika Bhardwaj100% (1)
- General Biology IIDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology IIFrederick SantosNo ratings yet
- 642020112334AM-Class 9 Biology Notes-Chapter-6 Plant TissueDocument11 pages642020112334AM-Class 9 Biology Notes-Chapter-6 Plant TissueL Sri Madhi100% (1)
- Tip Growth Girth: Is Stem Bark ForDocument4 pagesTip Growth Girth: Is Stem Bark ForSarvesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal TissuesDocument7 pagesPlant and Animal Tissueskapil100% (1)
- Tissues Just NotesDocument20 pagesTissues Just NotesSudesh Sharma100% (1)
- Tissues Class 9Document13 pagesTissues Class 9Richa Nawani KaushikNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue TypesDocument6 pagesPlant Tissue TypesBhoomika GoyalNo ratings yet
- Different Kind of Tissues in Plant and AnimalsDocument15 pagesDifferent Kind of Tissues in Plant and AnimalsKeerti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Tissues Class 9 Notes (NCERT Book Chapter 6)Document12 pagesDetailed Tissues Class 9 Notes (NCERT Book Chapter 6)suman_das1983100% (7)
- Plant & Animal TissueDocument39 pagesPlant & Animal TissuePrincess Erbie Austria100% (1)
- Class 9 Science CH 6 NotesDocument13 pagesClass 9 Science CH 6 NotesChetan GargNo ratings yet
- Zoology Notes: 007 Chapter 4Document4 pagesZoology Notes: 007 Chapter 4humanupgradeNo ratings yet
- RudrakshDocument3 pagesRudrakshAmartyaNo ratings yet
- Tissues: M.Daisy PrasanthiDocument39 pagesTissues: M.Daisy PrasanthiDinakarKonda100% (1)
- Introduction to Tissues: Types and Functions in 38 CharactersDocument12 pagesIntroduction to Tissues: Types and Functions in 38 CharactersKhushi Agrawal100% (1)
- Tissues: Chapter - 6Document17 pagesTissues: Chapter - 6Aditya Jha100% (1)
- TissuesDocument6 pagesTissuesRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- 9 SC TissueDocument8 pages9 SC Tissuevishesh1997No ratings yet
- Animal Tissue: Chapter - 10 Std. XIDocument110 pagesAnimal Tissue: Chapter - 10 Std. XIYash Soneji100% (2)
- Lesson 4 Cell Types and TissuesDocument36 pagesLesson 4 Cell Types and TissuesKathline Joy DacilloNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesDocument11 pagesCH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesRishabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Tissues NotesDocument3 pagesTissues NotesRajesh Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Science Class 9th Lesson 6 NOTESDocument3 pagesScience Class 9th Lesson 6 NOTESChaitanya Seriouskalhapure100% (1)
- TissuesDocument6 pagesTissuesvaidika.soni12009No ratings yet
- Tissue Types and FunctionsDocument36 pagesTissue Types and FunctionsMinan Fahnanza100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument25 pagesChapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsamit lakraNo ratings yet
- Tissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells and A Complete OrganismDocument7 pagesTissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells and A Complete OrganismErneyann BibeyzNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument14 pagesTissueBarkha Agrawal100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Tissues Class 9Document20 pagesChapter 6 Tissues Class 9anmolmuskan2020No ratings yet
- TissuesDocument16 pagesTissuesDiya sashiniNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 6 Tissue: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 4Document4 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 6 Tissue: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 4lakshya GandhiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 6 Tissue: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 4Document4 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 6 Tissue: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 4lakshya GandhiNo ratings yet
- Tissue Class 9Document40 pagesTissue Class 9Extra AccountNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 TissuesDocument20 pagesChapter 06 TissuesManushi ShahNo ratings yet
- (Preferred) Plant and Animal TissuesDocument20 pages(Preferred) Plant and Animal TissuesHannah CenaNo ratings yet
- Cell TissuesDocument28 pagesCell TissuesStifany Dianne VillasNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6: TissuesDocument20 pagesChapter - 6: TissuesMadhuriNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6: TissuesDocument20 pagesChapter - 6: Tissueskrista leeNo ratings yet
- IX 6 TissuesDocument20 pagesIX 6 Tissuesvaishnav.shrot777No ratings yet
- Human Body Tissues Power PointDocument60 pagesHuman Body Tissues Power PointMaxwell C Jay KafwaniNo ratings yet
- IX Biology Chapter 6 - Types of Plant and Animal TissuesDocument5 pagesIX Biology Chapter 6 - Types of Plant and Animal Tissuessidd230100% (2)
- Tissue - Class 9Document9 pagesTissue - Class 9Rohit Jain100% (1)
- Structural Organization in AnimalsDocument7 pagesStructural Organization in AnimalsVedant BondeNo ratings yet
- Tissues - NotesDocument14 pagesTissues - Notesphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Tissue 11Document5 pagesTissue 11Adnan Al-asbahiNo ratings yet
- TISSUE FORM AND-WPS OfficeDocument8 pagesTISSUE FORM AND-WPS OfficeBasser EsmaelNo ratings yet
- ANIMAL CELL PARTS AND FUNCTIONSDocument5 pagesANIMAL CELL PARTS AND FUNCTIONSNan Fen Jin Sabolarce100% (1)
- Week 2 The Tissues MembranesDocument60 pagesWeek 2 The Tissues MembranesJeqtopher RoaNo ratings yet
- Plant TissueDocument19 pagesPlant TissueKAMESH .G100% (1)
- Animal Tissues 2023Document70 pagesAnimal Tissues 2023yxcz.rzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6.anatonomy of Flowering PlantsDocument12 pagesChapter 6.anatonomy of Flowering PlantsKeerthana IX-C [370]No ratings yet
- Tissue SystemDocument41 pagesTissue Systemrahul royNo ratings yet
- Anemia and Nutritional Deficiency PresentationDocument3 pagesAnemia and Nutritional Deficiency PresentationpriyankaNo ratings yet
- 7c Revision TestDocument7 pages7c Revision TestAdam Amr ElgoharyNo ratings yet
- Hematopoietic System Chapter Provides Overview of Bone Marrow and Lymphoid OrgansDocument275 pagesHematopoietic System Chapter Provides Overview of Bone Marrow and Lymphoid OrgansXochitl ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Troponina IMMULITE 2000Document30 pagesTroponina IMMULITE 2000OFNo ratings yet
- Ninja Nerd AnemiaDocument13 pagesNinja Nerd AnemiaAndra Bauer100% (3)
- Budde (2013) - Current Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches To Patients With Acquired Von Willebrand Syndrome A 2013 UpdateDocument12 pagesBudde (2013) - Current Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches To Patients With Acquired Von Willebrand Syndrome A 2013 UpdateDiego GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Teacher Guide: Muscles and Bones: Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesTeacher Guide: Muscles and Bones: Learning Objectivesabdullah farhanNo ratings yet
- Pathology Haematology AssignmentDocument5 pagesPathology Haematology AssignmentlumpyspacefinesseNo ratings yet
- Kelainan Morfologi EritrositDocument19 pagesKelainan Morfologi EritrositAdel shbelNo ratings yet
- Valores Normales FanaroffDocument13 pagesValores Normales FanaroffLila Calapuja CalsinaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Nervous TissueDocument30 pagesUnderstanding Nervous TissueOtencianoNo ratings yet
- Complication of Blood TransfusionDocument89 pagesComplication of Blood TransfusionyohannesNo ratings yet
- Kidd Blood Group System (2Document4 pagesKidd Blood Group System (2RSH1987100% (1)
- Simple Squamous Epithelial Tissue & Connective Tissue FunctionsDocument10 pagesSimple Squamous Epithelial Tissue & Connective Tissue FunctionsRose CostaNo ratings yet
- Benesphera H33S: Minimum Size, Maximum CapabilityDocument6 pagesBenesphera H33S: Minimum Size, Maximum Capabilitysreedhin awingzNo ratings yet
- Mahmoud Jamil Daher 16/02/2023 12:47 PM M 29/10/1985 16/02/2023 12:47 PM HAM / 00375052Document1 pageMahmoud Jamil Daher 16/02/2023 12:47 PM M 29/10/1985 16/02/2023 12:47 PM HAM / 00375052Mahmoud DaherNo ratings yet
- BLOODDocument46 pagesBLOODLance CarandangNo ratings yet
- Hematology I Intensive Rationale - Louise MDocument20 pagesHematology I Intensive Rationale - Louise MKai YoungNo ratings yet
- CH 05 TissuesDocument50 pagesCH 05 TissuesAlina Ghe100% (1)
- Pregnancy in Thalassemia Trait Carriers An Uneventful JourneyDocument4 pagesPregnancy in Thalassemia Trait Carriers An Uneventful JourneyHendry SusantoNo ratings yet
- BCH 201 AssignmentDocument2 pagesBCH 201 AssignmentSadman RashidNo ratings yet
- Bleeding and ThrombosisDocument27 pagesBleeding and Thrombosisswathi bsNo ratings yet
- LPRF IntroduccionDocument12 pagesLPRF IntroduccionbezinlizeNo ratings yet
- Uncrossmatched Waiver FormDocument2 pagesUncrossmatched Waiver Formjelly aNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of RDW-CV RDW-SD Math 1sd 2013Document8 pagesEvaluation of RDW-CV RDW-SD Math 1sd 2013Gregorio De Las CasasNo ratings yet
- 2.02 TableDocument2 pages2.02 TableMelodieNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Introduction To Forensic Science: by Dr. Ruby L. TamayoDocument42 pagesLecture On Introduction To Forensic Science: by Dr. Ruby L. TamayoApolinar A. TorrijosNo ratings yet
- ISBB Immunology ReviewDocument9 pagesISBB Immunology ReviewNathan DrakeNo ratings yet
- RBC Indices & ESRDocument23 pagesRBC Indices & ESRPamela BesanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Content Review Questions 1-8Document3 pagesChapter 6 Content Review Questions 1-8Rhonique MorganNo ratings yet