Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes 04 - Block Manipulation
Uploaded by
Man JaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes 04 - Block Manipulation
Uploaded by
Man JaCopyright:
Available Formats
Data Acquisition & Control Systems
DAG Lecture 4 Block manipulation
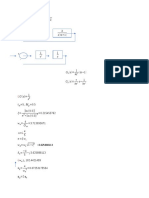
Blocks in Series
Block Diagram Manipulation
GA(s) GB(s) = GA(s)GB(s)
The idea is to use a set of rules to gradually
reduce a complex system consisting of a
number of subsystems down to a single block
that contains the transfer function for the whole Proof
system. U(s) X(s) Y(s)
GA (s) GB (s)
Y(s)= GB (s)X(s)
Y(s)= GB (s) GA (s)U(s)
X(s)= GA (s)U(s)
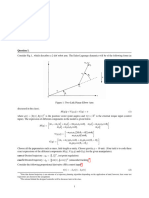
Two Water Tanks in Series (Problem 1 Q3a) Z(s) Y(s)
U(s) +
Proof for G(s)
Closed Loop Rule -
q1
H(s)
X(s)
Tank 1
q12 Y(s) = G(s) Z(s)
Y(s) = G(s)U(s) - G(s)H(s)Y(s)
Tank 2 Z(s) = U(s) - X(s)
q2 {1 + G(s)H(s)}Y(s) = G(s)U(s)
Hence;
Y(s) = G(s) {U(s) - X(s)}
q1 q2 G(s)
X(s) = H(s)Y(s) 1 + G(s)H(s)
Flow rate Control Flow rate Control
qd
qd + qi 1 qo
10 1+100s
Gear box Motor
-
Controller
qi
Tap Flow rate sensor
qd + qo
Tank
qo
-
D.A.Germany - School of Engineering & Technology
Data Acquisition & Control Systems
DAG Lecture 4 Block manipulation
Flow rate Control Interlocking Loops
3
1+s 3
10
qd 1+100s qo + 1
+
+ 1
+
1+s 1+s
+ +
- -
1+ 10
1+100s 10 10
1+s 3
+
+ 1
1+s
1
+
? ?
-
10
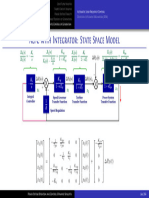
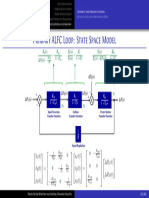
Satellite Tracking Antenna
Moving a block round a summer
= J d + B
+ + dt
G(s) G(s)
=
- - K
G(s) 1 + sT Angular
Torque
T = J/B, K = 1/B velocity
+ + resolver Antenna Integrator
Motor + Gears
G(s) = G(s)
d + K 1
- - Kr Kmg
1/G(s) 1 + sT s
- resolver
Kr
+
d K 1
Kmg
Kr
1 + sT s Summary of Lecture 4
-
Transfer Function = Y(s)/U(s)
1
Kr Block manipulation = reducing a block diagram
Kr
down to a single block
d
+ Multiply blocks in series
Add blocks in Parallel
-
Feedback Rule: G/(1+GH)
Directed Independent Learning for this week:
d Try Problems 3
D.A.Germany - School of Engineering & Technology
You might also like
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Lecture 05 - Block Diagram ManipulationDocument53 pagesLecture 05 - Block Diagram ManipulationMunkhbileg UlNo ratings yet
- KOM 3781 Discrete-Time Control Systems: Veysel GaziDocument72 pagesKOM 3781 Discrete-Time Control Systems: Veysel GaziFatih CanbolatNo ratings yet
- Ch11-Dynamic Behavior & Stability of Closed-Loop Control System.Document15 pagesCh11-Dynamic Behavior & Stability of Closed-Loop Control System.Mark GoodmoreNo ratings yet
- FOC Lect5 FeedbackDocument16 pagesFOC Lect5 FeedbackErhan ÖZNo ratings yet
- L4 1st 2nd Order CharacteristicsDocument28 pagesL4 1st 2nd Order Characteristicsalex carterNo ratings yet
- 2012 20 Traf Signal Design 2Document32 pages2012 20 Traf Signal Design 2刘国庆No ratings yet
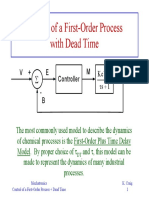
- G(s) = k s (τs+1) G s) = τs+1) : = 5 ; M = 0.5 ln (0.5) + ln (0.5) = 0.215453762Document8 pagesG(s) = k s (τs+1) G s) = τs+1) : = 5 ; M = 0.5 ln (0.5) + ln (0.5) = 0.215453762Diana UlloaNo ratings yet
- Controller DesignDocument116 pagesController DesignShlok MishraNo ratings yet
- Modern Control Engineering Systems RepresentationDocument30 pagesModern Control Engineering Systems RepresentationBrooklynPrinceNo ratings yet
- 13 - Digital Controller DesignDocument22 pages13 - Digital Controller DesignEverton CollingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document37 pagesChapter 3Izzat AiresNo ratings yet
- T T 0 T T D T: 2 I S 2 I IDocument28 pagesT T 0 T T D T: 2 I S 2 I IzeldaikNo ratings yet
- 5 Block Diagram Representation of LTI Systems: U (T) G(S) y (T)Document3 pages5 Block Diagram Representation of LTI Systems: U (T) G(S) y (T)Yassine DjillaliNo ratings yet
- AFLC with IntegratorDocument1 pageAFLC with IntegratorCharandeep TirkeyNo ratings yet
- Robotics1 B 10.01.12Document7 pagesRobotics1 B 10.01.12Ammar BendjeddouNo ratings yet
- 446-08 Block Diagrams (N) - HandoutDocument7 pages446-08 Block Diagrams (N) - HandoutFrancisco HurtadoNo ratings yet
- EN530.678 Nonlinear Control and Planning in Robotics Lecture 2: System Models January 29, 2020Document6 pagesEN530.678 Nonlinear Control and Planning in Robotics Lecture 2: System Models January 29, 2020SAYED JAVED ALI SHAHNo ratings yet
- 5 Lecture 5: Fluid Models: 5.1 Stability of Uid and Stochastic Processing NetworksDocument8 pages5 Lecture 5: Fluid Models: 5.1 Stability of Uid and Stochastic Processing NetworksAala SinghNo ratings yet
- Solution Assignment 7Document5 pagesSolution Assignment 7sushant sharmaNo ratings yet
- Ders11 IngDocument16 pagesDers11 IngjgenNo ratings yet
- Linear Control Methods For Robots: Berke GürDocument40 pagesLinear Control Methods For Robots: Berke GürOmar Seraj Ed-DeenNo ratings yet
- 5 Block Diagram Representation of LTI SystemsDocument7 pages5 Block Diagram Representation of LTI SystemsDj OoNo ratings yet
- Part-A: All AllDocument15 pagesPart-A: All AllMaharshiGohelNo ratings yet
- Unit 09 Digital Controller Design - Part 1 - Lead - Lag Using W - Transform and PIDDocument68 pagesUnit 09 Digital Controller Design - Part 1 - Lead - Lag Using W - Transform and PIDJeff BobNo ratings yet
- CPC Solution W4 PDFDocument4 pagesCPC Solution W4 PDFAmal GSNo ratings yet
- Assignment_1__Robotics_2023 (1)Document2 pagesAssignment_1__Robotics_2023 (1)dsuyash57No ratings yet
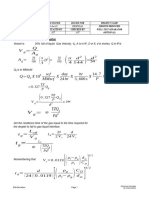
- Formulae For The Examination: Control Engineering Laboratory AS-74.2112 Digital ControlDocument11 pagesFormulae For The Examination: Control Engineering Laboratory AS-74.2112 Digital ControlbalkyderNo ratings yet
- DC Analysis: and Discuss Solution TechniquesDocument27 pagesDC Analysis: and Discuss Solution Techniquesx moodNo ratings yet
- Set6 PDFDocument8 pagesSet6 PDFNITISH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Primary ALFC LoopDocument1 pagePrimary ALFC LoopCharandeep TirkeyNo ratings yet
- On Integral Representations of Q - Gamma and Q-Beta FunctionsDocument16 pagesOn Integral Representations of Q - Gamma and Q-Beta Functionsyip90No ratings yet
- Coupled Pipe-Annulus Calculations: Da DP K DP DT A Da DP DP DT A QDocument1 pageCoupled Pipe-Annulus Calculations: Da DP K DP DT A Da DP DP DT A QJia Jun GooNo ratings yet
- First-Order Process Time Delay 2002Document47 pagesFirst-Order Process Time Delay 2002Hazeq Azahar100% (1)
- 1-2P-Flash Separator - SokaDocument27 pages1-2P-Flash Separator - Sokaahmad santosoNo ratings yet
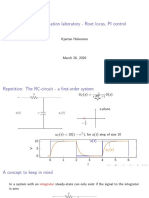
- Process Automation Laboratory - Root Locus, PI Control: Kjartan HalvorsenDocument20 pagesProcess Automation Laboratory - Root Locus, PI Control: Kjartan HalvorsenBryan Badillo RamosNo ratings yet
- What Are Polynomial Models - MATLAB & SimulinkDocument4 pagesWhat Are Polynomial Models - MATLAB & Simulinknicanor rodolfoNo ratings yet
- Epl 21 Supp2Document2 pagesEpl 21 Supp2horaciowioNo ratings yet
- New Galois Hulls of Generalized Reed-Solomon CodesDocument12 pagesNew Galois Hulls of Generalized Reed-Solomon CodesMarvin OlavidesNo ratings yet
- Vector Derivatives: Ds DX 1 ( Det G)Document5 pagesVector Derivatives: Ds DX 1 ( Det G)Peter He ZhengNo ratings yet
- Practical Aspects in Adaptive ControlDocument35 pagesPractical Aspects in Adaptive ControlSam KhanNo ratings yet
- Confirming Pages: Q (T) A AreaDocument2 pagesConfirming Pages: Q (T) A AreaChelsea MartinezNo ratings yet
- Rotating Waves in Parabolic SystemsDocument1 pageRotating Waves in Parabolic SystemsneomindxNo ratings yet
- Notes 4Document13 pagesNotes 4lili aboudNo ratings yet
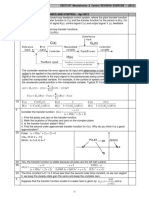
- T FN, Pole-Zeros, Block Diagram & SFGDocument28 pagesT FN, Pole-Zeros, Block Diagram & SFGArsal AslamNo ratings yet
- FORMULA SHEETDocument3 pagesFORMULA SHEETJibin K JacobNo ratings yet
- Control SystemDocument10 pagesControl SystemMand TamNo ratings yet
- 1 72 Lecture 10Document6 pages1 72 Lecture 10Mars TinNo ratings yet
- KJM - Volume 9 - Issue 2 - Pages 288-299Document12 pagesKJM - Volume 9 - Issue 2 - Pages 288-299Theepa Gayathri SanthoshNo ratings yet
- Lect 6 Extra Examples PDFDocument5 pagesLect 6 Extra Examples PDFZaidoon MohsinNo ratings yet
- Frequency Response Method (Continue)Document37 pagesFrequency Response Method (Continue)Edo SunardyNo ratings yet
- Lecture06 Macro LWRDocument44 pagesLecture06 Macro LWREduardo HerreraNo ratings yet
- Models for Control Part IDocument99 pagesModels for Control Part I이정우No ratings yet
- Suggested Solution To Past Papers PDFDocument20 pagesSuggested Solution To Past Papers PDFMgla AngelNo ratings yet
- Transport Processes: - CONDUCTION (Part 2&3)Document37 pagesTransport Processes: - CONDUCTION (Part 2&3)DivyeshNo ratings yet
- Exact Controllability For Stochastic Transport Equations: D 1 1 D 1 2 1 2 R X, X G 1 2 RDocument24 pagesExact Controllability For Stochastic Transport Equations: D 1 1 D 1 2 1 2 R X, X G 1 2 RJacques KazakuNo ratings yet
- QM2 2223 Formulas Math IBDocument2 pagesQM2 2223 Formulas Math IBholden.mortaxeNo ratings yet
- Chapter3_2Document12 pagesChapter3_2hailegebreselassie24No ratings yet
- Block Diagram Simplification TechniquesDocument22 pagesBlock Diagram Simplification TechniquesAhmed SaidNo ratings yet
- AND Optimization OF Three Existing Ethylbenzene Dehydrogenation Reactors in SeriesDocument5 pagesAND Optimization OF Three Existing Ethylbenzene Dehydrogenation Reactors in SeriesMuhammad Ridwan TanjungNo ratings yet
- Onishi T Ed Quantum Science The Frontier of Physics and ChemDocument498 pagesOnishi T Ed Quantum Science The Frontier of Physics and ChemStrahinja DonicNo ratings yet
- Admix Load CellDocument6 pagesAdmix Load Cellmanil_5No ratings yet
- F 2786538d6cdc0bb1Document245 pagesF 2786538d6cdc0bb1Daniel HarutyunyanNo ratings yet
- Matlab programs to fit common curves using least squares methodDocument5 pagesMatlab programs to fit common curves using least squares methodRavi ParkheNo ratings yet
- Zarlino-On The ModesDocument150 pagesZarlino-On The ModesPartituraDireccion100% (1)
- Baidu - LeetCodeDocument2 pagesBaidu - LeetCodeSivareddyNo ratings yet
- Data Structures and AlgorithmsDocument45 pagesData Structures and AlgorithmsKeith Tanaka MagakaNo ratings yet
- Employee performance factors analysis electronic companyDocument10 pagesEmployee performance factors analysis electronic companyAmrithaNo ratings yet
- Hot Rolled Sheet Pile SHZ Catalogue PDFDocument2 pagesHot Rolled Sheet Pile SHZ Catalogue PDFkiet eelNo ratings yet
- Hawking-Brief History of TimeDocument336 pagesHawking-Brief History of TimeAlbert Kristian0% (1)
- 04.protection of 33KV Feeder.Document16 pages04.protection of 33KV Feeder.gnpr_10106080No ratings yet
- Handout 06 - Geothermometry PDFDocument7 pagesHandout 06 - Geothermometry PDFOg LocabaNo ratings yet
- Cold Backup and Recovery From Archivelog - OrACLE-HELPDocument4 pagesCold Backup and Recovery From Archivelog - OrACLE-HELPadelarduarteNo ratings yet
- Serial Port InterfacingDocument5 pagesSerial Port Interfacingyampire100% (1)
- Determination of Voltage DropDocument6 pagesDetermination of Voltage DropFahmi CumiNo ratings yet
- ASP Flashcards - QuizletDocument36 pagesASP Flashcards - QuizletRehman MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- Drager Fabius Gs Technical Service ManualDocument350 pagesDrager Fabius Gs Technical Service ManualLeonardo Chirinos100% (3)
- Propeller forces and typesDocument2 pagesPropeller forces and typesEdison Gutierrez CapunoNo ratings yet
- RelativedensityipgDocument2 pagesRelativedensityipgapi-310625232No ratings yet
- This HandoutDocument11 pagesThis HandoutAnonymous QM0NLqZONo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry Practce PDFDocument6 pagesStereochemistry Practce PDFFerminNo ratings yet
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument22 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationJGD123No ratings yet
- Development of A Highway Performance Index For Upgrading Decision Making - Case Study For A Provincial Road Network in A Developing CountryDocument6 pagesDevelopment of A Highway Performance Index For Upgrading Decision Making - Case Study For A Provincial Road Network in A Developing CountryAshen MinolNo ratings yet
- h6541 Drive Sparing Symmetrix Vmax WPDocument19 pagesh6541 Drive Sparing Symmetrix Vmax WPsantoshNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 5 Mathematics Sample Paper Set NDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 5 Mathematics Sample Paper Set NRamanjeet KaurNo ratings yet
- Blowfish Encryption AlgorithmDocument3 pagesBlowfish Encryption AlgorithmParkerAllisonNo ratings yet
- PVC PLasticisersDocument2 pagesPVC PLasticisersKrishna PrasadNo ratings yet
- Simultaneous EquationsDocument11 pagesSimultaneous EquationsSaleena AurangzaibNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Tyres: CMR Engineering CollegeDocument17 pagesPneumatic Tyres: CMR Engineering CollegeHemanth Rama Krishna YernagulaNo ratings yet