Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Process Overview
Uploaded by
Eva Fauziyah AzharyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Process Overview
Uploaded by
Eva Fauziyah AzharyCopyright:
Available Formats
1
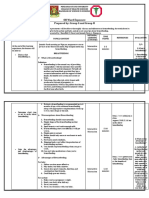
The Nursing Process
The common thread uniting different types of nurses who work in varied areas is the nursing processthe essential core of practice
for the registered nurse to deliver holistic, patient-focused care. One definition of the nursing processan assertive, problem
solving approach to the identification and treatment of patient problems. It provides an organizing framework for the practice of
nursing and the knowledge, judgments, and actions that nurses bring to patient care.
Assessment
An RN uses a systematic, dynamic, rather than static way to collect and analyze data about a client, the first step in delivering
nursing care. Assessment includes not only physiological data, but also psychological, sociocultural, spiritual, economic, and life-
style factors as well. For example, a nurses assessment of a hospitalized patient in pain includes not only the physical causes and
manifestations of pain, but the patients responsean inability to get out of bed, refusal to eat, withdrawal from family members,
anger directed at hospital staff, fear, or request for more pain medication.
Diagnosis
The nursing diagnosis is the nurses clinical judgment about the clients response to actual or potential health conditions or needs.
The diagnosis reflects not only that the patient is in pain, but that the pain has caused other problems such as anxiety, poor nutrition,
and conflict within the family, or has the potential to cause complicationsfor example; respiratory infection is a potential hazard to
an immobilized patient. The diagnosis is the basis for the nurses care plan.
Planning / Goal / Outcome
Based on the assessment and diagnosis, the nurse sets measurable and achievable short- and long-range goals for this patient that
might include moving from bed to chair at least three times per day; maintaining adequate nutrition by eating smaller, more frequent
meals; resolving conflict through counseling, or managing pain through adequate medication.
Assessment data, diagnosis, and goals are written in the patients care plan so that nurses as well as other health
professionals caring for the patient have access to it.
Implementation
Nursing care is implemented according to the care plan, so continuity of care for the patient during hospitalization and in
preparation for discharge needs to be assured. Care is documented in the patients record.
Evaluation
Both the patients status and the effectiveness of the nursing care must be continuously evaluated, and the care plan modified as
needed.
11/26/12 kwb: NP overview - Transfer students
2
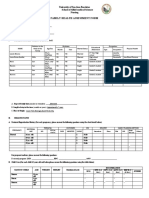
Component and Purpose Activities
Description
Assessment To establish a Establish a database:
database about the Subjective data (not measurable)
Collecting, organizing, clients response to Objective data (measurable)
validating, and documenting health concerns or
client data. illness and the ability Obtain a nursing health history
to manage health Review client records
care needs Review nursing literature
Consult support persons
Consult health professionals
Update data as needed
Organize data
Validate data
Communicate/document data
Diagnosis To identify client Interpret and analyze data:
strengths and health
Cluster, Analyze and problems that can be Compare data against standards
synthesize data. prevented or resolved Cluster or group data (generate tentative
by collaborative and hypotheses)
Problem identification independent nursing Identify gaps and inconsistencies
interventions.
Determine clients strengths, risks, and problems
Nursing diagnosis label To develop a list of
nursing diagnoses
Formulate nursing diagnoses and collaborative
and collaborative
problem statements
problems.
Actual Nursing Diagnosis (3-part)
PES = Problem related to the Etiology (cause) as
evidenced/manifested by the Signs and Symptoms
(defining characteristics).
Potential Nursing Diagnosis/Risk (2-part)
PE = Potential problem related to the Etiology
(cause). There are no signs and symptoms,
because the problem has not occurred yet.
11/26/12 kwb: NP overview - Transfer students
3
Planning/Goal/Outcome To develop and Set priorities and write goals/outcomes in collaboration
individualized care with client. Consult with other health professionals
Determining how to prevent, plan that specifies
reduce, or resolve the client goals/desired Write nursing orders and nursing care plan
identified client problems; how outcomes and related
to support client strengths; nursing interventions. Communicate care plan to relevant healthcare providers
and how to implement nursing
interventions in an organized, Outcome statement
Short term and long term goals
individualized, and goal- must be patient
directed manner centered, specific,
and measurable.
Implementation To assist the client to Select nursing strategies/interventions
meet desired
Carrying out the planned goals/outcomes; Determine need for nursing assistance
nursing interventions promote wellness and
disease; restore
health; and facilitate Perform or delegate planned nursing interventions
coping with altered
functioning. Communicate what nursing actions were
implemented:
Document care and client responses to care
Give verbal reports as necessary
Carry out the plan; DO what it takes to meet
goals.
Nurse initiated Physician initiated
Collaborative.
Evaluation To determine whether Collaborate with client and relate nursing actions to
to continue, modify, or client outcomes
Measuring the degree to terminate the plan of
which goals/outcomes have care. Determine if goals/outcomes have been
been achieved and identifying met/achieved. If not, re-evaluate:
factors that positively or
negatively influence goal Data did you collect enough/correct data?
achievement Diagnosis did you analyze the data
accurately?
Etiology is it accurate?
Outcome patient centered, measurable and
realistic?
Interventions realistic and doable?
Revise/modify the care plan as indicated.
11/26/12 kwb: NP overview - Transfer students
You might also like
- Learning Clinical Reasoning 2nd Edition-KassirerDocument352 pagesLearning Clinical Reasoning 2nd Edition-KassirerRutvik Shah88% (8)
- Case Study, Chapter 70, Management of Patients WithOncologic or Degenerative Neurologic DisordersDocument1 pageCase Study, Chapter 70, Management of Patients WithOncologic or Degenerative Neurologic Disordersclyde i am100% (1)
- Knowledge and Practices of Pregnant Women RegardinDocument13 pagesKnowledge and Practices of Pregnant Women RegardinDrPreeti Thakur ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Family Assessment 3Document9 pagesFamily Assessment 3Georgea Beleni S. AbinesNo ratings yet
- Icd 11Document22 pagesIcd 11Shubhangi Vats100% (1)
- Introduction RevisionDocument50 pagesIntroduction RevisionGracie S. VergaraNo ratings yet
- PICOTDocument8 pagesPICOTRaphael Seke OkokoNo ratings yet
- Student Nursing Care Plan TemplateDocument4 pagesStudent Nursing Care Plan TemplateHaniNo ratings yet
- Theories of Learning 10237Document4 pagesTheories of Learning 10237soniya josephNo ratings yet
- Sub Arachnoid HaemorrageDocument46 pagesSub Arachnoid HaemorrageShitaljit IromNo ratings yet
- nsg-432 Careplan 2Document11 pagesnsg-432 Careplan 2api-521003884No ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy NCP (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Document10 pagesEctopic Pregnancy NCP (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Raiden VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Vasquez - RLE A3 - PCCR (OSMUN Ward)Document16 pagesVasquez - RLE A3 - PCCR (OSMUN Ward)Mari Sheanne M. Vasquez100% (1)
- Knowledge of Contraceptives Methods and Appraisal of Health Education Among Married WomanDocument7 pagesKnowledge of Contraceptives Methods and Appraisal of Health Education Among Married Womanjannatul supti24No ratings yet
- Med Template - NifedipineDocument2 pagesMed Template - NifedipineAshlee KeeferNo ratings yet
- Nurse KeyDocument9 pagesNurse KeyChina De Leon CapispisanNo ratings yet
- Concept Care Map ExampleDocument5 pagesConcept Care Map ExampleNick HaislipNo ratings yet
- CERTIFIED NURSINGS ASSISTANT!!!!! Temperature Pulse and RespirationDocument28 pagesCERTIFIED NURSINGS ASSISTANT!!!!! Temperature Pulse and RespirationJonas VargasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-OBDocument6 pagesDrug Study-OBRibelyne loise Aquisio50% (2)
- Unit 6 Educational ApplicationsDocument10 pagesUnit 6 Educational ApplicationsBea Bianca CruzNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Objective Intervention EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Objective Intervention Evaluationjezreel ibarraNo ratings yet
- Beta ThalaDocument2 pagesBeta ThalaAngie LamoNo ratings yet
- Translational Research: Generating Evidence For PracticeDocument24 pagesTranslational Research: Generating Evidence For Practicebeer_ettaaNo ratings yet
- Zocor (Simvastatin)Document3 pagesZocor (Simvastatin)E100% (1)
- Anticipatory GrievingDocument2 pagesAnticipatory GrievingJamaeka GotisNo ratings yet
- NCM 107-A Lecture 2012Document241 pagesNCM 107-A Lecture 2012Michael Anthony Ermita50% (2)
- A Review On Otitis Media (Karnapaka) : Ayurvedic Aspects and TreatmentDocument4 pagesA Review On Otitis Media (Karnapaka) : Ayurvedic Aspects and TreatmentEditor_IAIMNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan For Newborn ScreeningDocument4 pagesHealth Teaching Plan For Newborn ScreeningPrincess Pauline AbrasaldoNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan School Age: Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing Normal Road, Zamboanga CityDocument12 pagesHealth Teaching Plan School Age: Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing Normal Road, Zamboanga CityJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- The Components of Labor and DeliveryDocument4 pagesThe Components of Labor and DeliveryGwyneth Nicole BudayNo ratings yet
- Sample NURSING PROCESS IN PHARMACOLOGY PDFDocument7 pagesSample NURSING PROCESS IN PHARMACOLOGY PDFVic Intia PaaNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Nursing Care PlanDocument12 pagesObstetric Nursing Care PlanJass Mira Bueno100% (1)
- Persuasive Communication in NursingDocument4 pagesPersuasive Communication in NursingNicole Audrey JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Ethical Dilemma With Using Informatics Technology: March 2019Document10 pagesNursing Ethical Dilemma With Using Informatics Technology: March 2019Ahmed MasoudNo ratings yet
- OB Ward Exposure Prepared By: Group G and Group HDocument10 pagesOB Ward Exposure Prepared By: Group G and Group HJannah Marie A. DimaporoNo ratings yet
- Missed AbortionDocument2 pagesMissed AbortionRyan MulanoNo ratings yet
- The Goal of Disaster NursingDocument13 pagesThe Goal of Disaster NursingPrince Mark BadilloNo ratings yet
- Angeles University Foundation: CholelithiasisDocument1 pageAngeles University Foundation: CholelithiasisKate Laxamana GuinaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Lourlyn's Angels?Document27 pagesLourlyn's Angels?lovelove DayoNo ratings yet
- F Discharge Plan 2019Document1 pageF Discharge Plan 2019Besael BaccolNo ratings yet
- Involving Family, Domestic Relations, Women and Children. (2015) - Philippine JudicialDocument10 pagesInvolving Family, Domestic Relations, Women and Children. (2015) - Philippine JudicialAngel MayNo ratings yet
- Home Birth Setting Versus Hospital Birth SettingDocument4 pagesHome Birth Setting Versus Hospital Birth SettingAmanda Bonita PersaudNo ratings yet
- COPD Secondaryto PTBDocument142 pagesCOPD Secondaryto PTBallexiscampaner100% (2)
- Far Eastern University: Evidence Based NursingDocument5 pagesFar Eastern University: Evidence Based NursingandreaNo ratings yet
- Stressors Nursing StudentsDocument9 pagesStressors Nursing StudentsJamesRGNNo ratings yet
- Remember: Goals and Plan of Care Should Be Base According To Client's Problems/needs NOT According To Your OwnDocument11 pagesRemember: Goals and Plan of Care Should Be Base According To Client's Problems/needs NOT According To Your Ownavinash dhameriyaNo ratings yet
- NCP Knowledge DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP Knowledge DeficitRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- NursingDocument11 pagesNursingNdung'u Wa Mumbi100% (1)
- Case Study For MaternalDocument2 pagesCase Study For MaternalAcohCChaoNo ratings yet
- Normal Vaginal Delivery After One Lower Segment Caesarean Section Can Be Safe Option For Many Women But Not Right Choice For AllDocument6 pagesNormal Vaginal Delivery After One Lower Segment Caesarean Section Can Be Safe Option For Many Women But Not Right Choice For AllRussel Cauton de JesusNo ratings yet
- ECOMAPDocument1 pageECOMAPJay Marie GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Midwifery Pharmacology-38Document1 pageMidwifery Pharmacology-38georgeloto12No ratings yet
- Learning Feedback g2Document8 pagesLearning Feedback g2Darwin DaveNo ratings yet
- Family Health Assessment Form: University of San Jose-Recoletos School of Allied Medical Sciences NursingDocument11 pagesFamily Health Assessment Form: University of San Jose-Recoletos School of Allied Medical Sciences NursingIvan A. EleginoNo ratings yet
- Nursing PaperDocument7 pagesNursing Paperapi-340968056No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan General Objective: To Promote Safety Through Prevention of The Spread of InfectionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan General Objective: To Promote Safety Through Prevention of The Spread of InfectionitsmeayaNo ratings yet
- Review of Literature On Temporary Family Planning MethodsDocument5 pagesReview of Literature On Temporary Family Planning MethodsafdtjozlbNo ratings yet
- Nrg203: Care of Mother, Child, and Adolescent: (StudentDocument6 pagesNrg203: Care of Mother, Child, and Adolescent: (Studentmikhaela sencilNo ratings yet
- NCP Draft - Ectopic PregnancyDocument7 pagesNCP Draft - Ectopic PregnancyD CNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Patient Centered InterviewDocument5 pagesPatient Centered InterviewPatsarachaya ChiewsupphakijNo ratings yet
- 2000 Ford Ranger 4.0l Transfer CaseDocument66 pages2000 Ford Ranger 4.0l Transfer CaseurielferNo ratings yet
- The Psychiatric Review of Symptoms - A Screening Tool For Family Physicians - American Family PhysicianDocument7 pagesThe Psychiatric Review of Symptoms - A Screening Tool For Family Physicians - American Family PhysicianTimothy TurscakNo ratings yet
- Psoas RehabDocument7 pagesPsoas Rehabmtemei4414No ratings yet
- Aya 11 15Document230 pagesAya 11 15Isaac Nana BineyNo ratings yet
- IMCI#1Document89 pagesIMCI#1Rosechelle Baggao Siupan-ElarcoNo ratings yet
- SchizophreniaDocument21 pagesSchizophreniaCLOYD MARVIN100% (1)
- (Oxford American Psychiatry Library) Stephen Strakowski, Erik Nelson - Major Depressive Disorder-Oxford University Press (2015)Document113 pages(Oxford American Psychiatry Library) Stephen Strakowski, Erik Nelson - Major Depressive Disorder-Oxford University Press (2015)Angelica100% (3)
- Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) : Past 3 Months LifetimeDocument1 pageColumbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) : Past 3 Months LifetimeIzabel EstevamNo ratings yet
- Condition Monitoring and Diagnostics of Power TransformersDocument11 pagesCondition Monitoring and Diagnostics of Power TransformersloliveiNo ratings yet
- Chapman's Reflexes and Modern Clinical Applications - Lecture - William H. Devine, DODocument94 pagesChapman's Reflexes and Modern Clinical Applications - Lecture - William H. Devine, DOHermann92% (12)
- Wearable Sensors and SystemsDocument14 pagesWearable Sensors and SystemsArulkarthickNo ratings yet
- LiebowitzDocument10 pagesLiebowitzRalucaButaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Abnormal PsychologyDocument14 pagesJournal of Abnormal PsychologyDiane MxNo ratings yet
- Acquaintance With The Actuality: Community Diagnosis Programme of Kathmandu Medical College at Gundu Village, Bhaktapur, NepalDocument7 pagesAcquaintance With The Actuality: Community Diagnosis Programme of Kathmandu Medical College at Gundu Village, Bhaktapur, Nepalputriaisyahn ainiNo ratings yet
- Somatoform DisorderDocument3 pagesSomatoform DisorderJunar M. BalasbasNo ratings yet
- Maturo MedicalizationDocument12 pagesMaturo MedicalizationJoaquinNo ratings yet
- DID Screening SheetDocument5 pagesDID Screening SheetIsaac CruzNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Complete SOAP2Document2 pagesGuidelines For Complete SOAP2Betsy Brown Byersmith100% (1)
- CHEDDocument83 pagesCHEDKarylle SuriagaNo ratings yet
- Training Manual PsychologistsDocument75 pagesTraining Manual PsychologistsNagarjuna KalimisettyNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptDocument19 pagesNIH Public Access: Author Manuscripta_l_y_nNo ratings yet
- Syndrome in PsychiatryDocument12 pagesSyndrome in Psychiatryrahul KumarNo ratings yet
- English EssayDocument2 pagesEnglish Essayapi-276207402No ratings yet
- Minor Ailments Services: A Starting Point For PharmacistsDocument49 pagesMinor Ailments Services: A Starting Point For PharmacistsacvavNo ratings yet
- Station 1 Abdominal MRCP PACES Practice Mark SheetDocument1 pageStation 1 Abdominal MRCP PACES Practice Mark SheetdoctorebrahimNo ratings yet
- Midterm - Chapter 7Document6 pagesMidterm - Chapter 7mark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Psikosis Dan Gerakan Shaking Sebagai Efek Samping Putus Zat Alkohol Dan Ganja: Laporan KasusDocument5 pagesPsikosis Dan Gerakan Shaking Sebagai Efek Samping Putus Zat Alkohol Dan Ganja: Laporan KasusliaNo ratings yet