Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Expectancy Theory (Or Expectancy Theory of Motivation) Proposes An Individual Will Behave or
Uploaded by
nadyaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Expectancy Theory (Or Expectancy Theory of Motivation) Proposes An Individual Will Behave or
Uploaded by
nadyaCopyright:
Available Formats
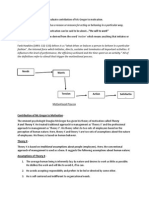
Expectancy theory (or expectancy theory of motivation) proposes an individual will behave or
act in a certain way because they are motivated to select a specific behavior over other
behaviors due to what they expect the result of that selected behavior will be.[1] In essence, the
motivation of the behavior selection is determined by the desirability of the outcome. However, at
the core of the theory is the cognitive process of how an individual processes the different
motivational elements. This is done before making the ultimate choice. The outcome is not the
sole determining factor in making the decision of how to behave.[1]
Expectancy theory is about the mental processes regarding choice, or choosing. It explains the
processes that an individual undergoes to make choices. In the study of organizational behavior,
expectancy theory is a motivation theory first proposed by Victor Vroom of the Yale School of
Management.
"This theory emphasizes the needs for organizations to relate rewards directly to performance
and to ensure that the rewards provided are those rewards deserved and wanted by the
recipients."[2]
Victor H. Vroom (1964) defines motivation as a process governing choices among alternative
forms of voluntary activities, a process controlled by the individual. The individual makes choices
based on estimates of how well the expected results of a given behavior are going to match up
with or eventually lead to the desired results. Motivation is a product of the individual's
expectancy that a certain effort will lead to the intended performance, the instrumentality of this
performance to achieving a certain result, and the desirability of this result for the individual,
known as valence.[3]
teori harapan (atau harapan teori motivasi) mengusulkan seorang individu akan berperilaku
atau bertindak dengan cara tertentu karena mereka termotivasi untuk memilih perilaku
tertentu atas perilaku lain karena apa yang mereka harapkan hasil bahwa perilaku yang
dipilih akan. [1] Pada dasarnya, motivasi pemilihan perilaku ditentukan oleh keinginan
hasilnya. Namun, pada inti dari teori ini adalah proses kognitif tentang bagaimana seorang
individu memproses elemen motivasi yang berbeda. Hal ini dilakukan sebelum membuat
pilihan utama. Hasilnya bukan faktor penentu satu-satunya dalam membuat keputusan
tentang bagaimana berperilaku. [1] teori harapan adalah tentang proses mental mengenai
pilihan, atau memilih. Ini menjelaskan proses-proses yang seorang individu mengalami
untuk membuat pilihan. Dalam studi perilaku organisasi, teori harapan adalah teori motivasi
pertama kali diusulkan oleh Victor Vroom dari Yale School of Management. "Teori ini
menekankan kebutuhan bagi organisasi untuk berhubungan imbalan langsung dengan
kinerja dan untuk memastikan bahwa imbalan yang disediakan adalah mereka imbalan
layak dan diinginkan oleh penerima." [2] Victor H. Vroom (1964) mendefinisikan motivasi
sebagai proses yang mengatur pilihan di antara bentuk-bentuk alternatif kegiatan sukarela,
suatu proses yang dikendalikan oleh individu. individu membuat pilihan berdasarkan
perkiraan seberapa baik hasil yang diharapkan dari perilaku tertentu akan cocok dengan
atau akhirnya mengarah pada hasil yang diinginkan. Motivasi adalah produk dari harapan
individu bahwa upaya tertentu akan menyebabkan kinerja dimaksudkan, perantaraan kinerja
ini untuk mencapai hasil tertentu, dan keinginan untuk hasil ini bagi individu, yang dikenal
sebagai valensi. [3]
You might also like
- Expectancy Theory: Key ElementsDocument3 pagesExpectancy Theory: Key ElementsKanwar Preet SinghNo ratings yet
- Expectancy TheoryDocument6 pagesExpectancy TheoryKarl Chin Io Leong100% (1)
- MBA - Motivation Theory TwoDocument6 pagesMBA - Motivation Theory TwoAbdul LateefNo ratings yet
- MBA - Motivation Theory OneDocument6 pagesMBA - Motivation Theory OneAbdul LateefNo ratings yet
- Vrooms Expectancy TheoryDocument3 pagesVrooms Expectancy Theoryazazel28No ratings yet
- The InstinctDocument2 pagesThe InstinctRhialee FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Chapter No.1Document4 pagesChapter No.1ashnajananNo ratings yet
- Expectancy Theory of MotivationDocument7 pagesExpectancy Theory of MotivationAkanksha SinghNo ratings yet
- Positive Psychology Theories Applied in Positive PsychologyDocument56 pagesPositive Psychology Theories Applied in Positive PsychologysoraruNo ratings yet
- Expectancy Theory: 2 Key ElementsDocument6 pagesExpectancy Theory: 2 Key ElementsAnonymous 7v9J4WaNo ratings yet
- Session 3 Motivation Part2Document16 pagesSession 3 Motivation Part2Kaye QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- MBA - Motivation Theory ThreeDocument6 pagesMBA - Motivation Theory ThreeAbdul LateefNo ratings yet
- Motivation Is The Psychological Feature That Arouses An Organism To Action Toward A Desired Goal and ElicitsDocument15 pagesMotivation Is The Psychological Feature That Arouses An Organism To Action Toward A Desired Goal and ElicitsAsad KhanNo ratings yet
- Motivation TheoryDocument17 pagesMotivation Theoryruin_2832No ratings yet
- LESSON10 Topic 36Document5 pagesLESSON10 Topic 36Matthew MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document2 pagesLecture 3Noshaba SharifNo ratings yet
- University of Jammu: Topic: MotivationDocument22 pagesUniversity of Jammu: Topic: Motivationharshit mahajanNo ratings yet
- Motivation of IndividualsDocument18 pagesMotivation of IndividualsJames IshakuNo ratings yet
- Types of Theories and ModelsDocument26 pagesTypes of Theories and ModelsRichard AlboroNo ratings yet
- Expectancy Theory OverviewDocument27 pagesExpectancy Theory OverviewGeraldine Pajudpod100% (1)
- Jemarie ReportDocument7 pagesJemarie ReportEvelyn EscobalNo ratings yet
- Group 3. MotivationDocument21 pagesGroup 3. MotivationRizky AlmazeinaNo ratings yet
- Motivation TheoryDocument67 pagesMotivation TheoryadjibayuNo ratings yet
- Self Determination TheoryDocument13 pagesSelf Determination Theoryalejandroh_2100% (2)
- Bandura, Albert (Social Learning / Social Cognitive Theory)Document4 pagesBandura, Albert (Social Learning / Social Cognitive Theory)Bhell Mendiola100% (1)
- Act4181 Induvidual Assignment PDFDocument6 pagesAct4181 Induvidual Assignment PDFMuadz KamaruddinNo ratings yet
- Act4181 Induvidual AssignmentDocument6 pagesAct4181 Induvidual AssignmentMuadz KamaruddinNo ratings yet
- Intrinsic MotivationDocument2 pagesIntrinsic MotivationNarmin AbidaNo ratings yet
- Perilaku Kepemimpinan & Perilaku OrganisasiDocument30 pagesPerilaku Kepemimpinan & Perilaku OrganisasiAndy EddyNo ratings yet
- VroomDocument34 pagesVroomkemimeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 Topic 36Document4 pagesLesson 10 Topic 36Matthew MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Research Humms 12cDocument20 pagesResearch Humms 12cUltimate PlayNo ratings yet
- ETHICSDocument4 pagesETHICSrolly coronelNo ratings yet
- Organisational BehaviourDocument27 pagesOrganisational BehaviouryadfghNo ratings yet
- VariablesDocument17 pagesVariablesmoazNo ratings yet
- Theoretical FrameworkDocument16 pagesTheoretical FrameworkKayceej PerezNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument14 pagesMotivationnieotyagiNo ratings yet
- Motivation and Motivation Cycle in PsychologyDocument10 pagesMotivation and Motivation Cycle in PsychologyShahrear Mahmood Sagar80% (5)
- A Project Report On Validation of Expectancy TheoryDocument57 pagesA Project Report On Validation of Expectancy TheoryRohan BahlNo ratings yet
- Process Theories of Motivation & Its Implication in The Indian Bollywood Movie GoalDocument10 pagesProcess Theories of Motivation & Its Implication in The Indian Bollywood Movie GoalSRK HONEYNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument73 pagesLiterature ReviewAkshay JiremaliNo ratings yet
- Lecture Five. Theories of Motivation (Part 04)Document5 pagesLecture Five. Theories of Motivation (Part 04)Ma LakNo ratings yet
- What Is Motivation?Document5 pagesWhat Is Motivation?jerusalem nigussieNo ratings yet
- Maslow's TheoryDocument7 pagesMaslow's Theoryzee100% (2)
- Social Emotional Learning Self-Regulation. Education Presentation Colorful Illustrative StyleDocument23 pagesSocial Emotional Learning Self-Regulation. Education Presentation Colorful Illustrative StyledoitulabingNo ratings yet
- Fank Hawkins (1993: 132-133) Defines It As "What Drives or Induces A Person To Behave in A ParticularDocument8 pagesFank Hawkins (1993: 132-133) Defines It As "What Drives or Induces A Person To Behave in A Particularsend2rasheedNo ratings yet
- The Support of Autonomy and The Control of BehaviorDocument15 pagesThe Support of Autonomy and The Control of BehaviorSushil PaudelNo ratings yet
- MotivationalDocument43 pagesMotivationallybrakissNo ratings yet
- The Problem and Its ScopeDocument38 pagesThe Problem and Its ScopeSusan DenoreNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Organisational ChoiceDocument3 pagesLecture 6 Organisational ChoicePatricia NjeriNo ratings yet
- Theory of Motivation - Insight Into Expectancy Theory: Harihar Panigrahi Roll No.: U211029 Ex-PGP 2011-14, XIMBDocument14 pagesTheory of Motivation - Insight Into Expectancy Theory: Harihar Panigrahi Roll No.: U211029 Ex-PGP 2011-14, XIMBHarihar Panigrahi100% (7)
- Ob Chap 6.1Document6 pagesOb Chap 6.1SHAHID AHMEDNo ratings yet
- 5Document10 pages5ramos sngiNo ratings yet
- Motivation, Job Satisfacton and Job InvolvementDocument49 pagesMotivation, Job Satisfacton and Job InvolvementHar Quin100% (1)
- Self-Determination TheoryDocument19 pagesSelf-Determination TheoryAnonymous IGrPMnSBjNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument31 pagesMotivationsubhartipsychiatryNo ratings yet
- The Cognitive Basis of Institutions: A Synthesis of Behavioral and Institutional EconomicsFrom EverandThe Cognitive Basis of Institutions: A Synthesis of Behavioral and Institutional EconomicsNo ratings yet
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Value- and Incentive-Theories of MotivationFrom EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Value- and Incentive-Theories of MotivationNo ratings yet
- Reflexive Questioning As A Means To Enable Intimacy With CouplesDocument20 pagesReflexive Questioning As A Means To Enable Intimacy With CouplesAlejandro Arquillos ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- Common PUA AcronymsDocument10 pagesCommon PUA AcronymsTheTvdHNo ratings yet
- Science Form 2 Chapter 1 NotesDocument19 pagesScience Form 2 Chapter 1 NotesAngie Kong Su Mei100% (2)
- Hill Et Al 2013 Evol Hum BehavDocument8 pagesHill Et Al 2013 Evol Hum BehavMike WillieNo ratings yet
- Shine From Within - Konko GuidebookDocument80 pagesShine From Within - Konko GuidebookStephen Willis100% (1)
- Movie Analysis TemplateDocument4 pagesMovie Analysis TemplateUdisha Merwal100% (3)
- What Is at Stake When You WriteDocument1 pageWhat Is at Stake When You Writeapi-264600919No ratings yet
- The Elements of DramaDocument1 pageThe Elements of DramaRomy Sales Grande Jr.No ratings yet
- Saharan and North African Toy and Play Cultures: The Animal WorldDocument221 pagesSaharan and North African Toy and Play Cultures: The Animal WorldJean-Pierre RossieNo ratings yet
- Mahatria RaDocument2 pagesMahatria Ramechanical_lecturer100% (1)
- Cognitive DevelopmentDocument8 pagesCognitive Developmentshiela valdemoroNo ratings yet
- Habitats Project Content RubricDocument1 pageHabitats Project Content Rubricapi-233214359No ratings yet
- Ex2 SystemDocument78 pagesEx2 SystemAllan B80% (5)
- Trainers Record Book NewDocument9 pagesTrainers Record Book NewEm Israel Jr.100% (2)
- Bhavana Meditation & Mental CultivationDocument55 pagesBhavana Meditation & Mental CultivationPiya_TanNo ratings yet
- Advantage and Disadvantage of Living in The Boarding HouseDocument3 pagesAdvantage and Disadvantage of Living in The Boarding HouseAngel Refamonte75% (4)
- Positive Psychology BooksDocument6 pagesPositive Psychology BooksSelectical infotech100% (1)
- Digital FootprintsDocument2 pagesDigital FootprintsOfelia OredinaNo ratings yet
- INJF Pesonality Tends To Be Excellent DoctorsDocument1 pageINJF Pesonality Tends To Be Excellent DoctorsDony Wajar AdiyantoNo ratings yet
- Ai Question BankDocument5 pagesAi Question BankManjunath YadavNo ratings yet
- Parenting Style Quiz-Printable PDFDocument4 pagesParenting Style Quiz-Printable PDFYvan Paez0% (1)
- Challenges of The ManagementDocument7 pagesChallenges of The ManagementFizaMurghoobNo ratings yet
- Language Modernization in Four AspectsDocument6 pagesLanguage Modernization in Four AspectsYeni Purtika100% (1)
- Every Child Is Special KhoDocument3 pagesEvery Child Is Special KhoJune Khorien NuñezNo ratings yet
- Communication and Its Process: Presented by Sushilkumar Rane Group - Power Plant ChemistryDocument12 pagesCommunication and Its Process: Presented by Sushilkumar Rane Group - Power Plant ChemistryRavi JoshiNo ratings yet
- Why It Is Always Better To Cease To ExistDocument26 pagesWhy It Is Always Better To Cease To ExistDNo ratings yet
- Fine Motor Skills Towards Independence Series-2Document25 pagesFine Motor Skills Towards Independence Series-2blossomcygnetNo ratings yet
- Leadership Theory and PracticeDocument25 pagesLeadership Theory and Practicepatilpratik021100% (5)
- M4.11 Eng102 Apa PDFDocument34 pagesM4.11 Eng102 Apa PDFjeanninestankoNo ratings yet
- StA Extra Language Practice Worksheet Unit 10Document3 pagesStA Extra Language Practice Worksheet Unit 10ana maria csalinasNo ratings yet