Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mitosis Meiosis Study Guide 2 Answers
Uploaded by
api-366982317Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mitosis Meiosis Study Guide 2 Answers
Uploaded by
api-366982317Copyright:
Available Formats
Mitosis & Meiosis Quiz Study Guide
PART 1:
Questions to think about for this quiz
1. What is a prokaryote and how does it reproduce?
Single cell that does not contain a nucleus; like bacteria.
Reproduces through a form of mitosis (asexual reproduction) called binary fission
2. What is a eukaryote and how does it reproduce?
Cell that contains a nucleus
Multi-cellular organisms (plant and animals) reproduce through meiosis by producing gametes
or sex cells
Multi-cellular organisms can also carry out mitosis in order to grow and repair old or
damaged cells
3. How do mitosis, meiosis 1, and meiosis 2 differ in number of cells produced?
Mitosis produces two identical cells
Meiosis I produces two cells with different genetic combinations
Meiosis II produces four cells with different genetic combinations (which is the final part
of meiosis)
4. Be able to generally describe what occurs during prophase, metaphase, anaphase &
telophase.
Prophase - nuclear membrane breaks down, chromosomes become visible, spindles form
Metaphase chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase chromosomes are pulled to opposite ends of the cell
Telophase nuclear membrane reforms, cell pinches in half, cleavage furrow or cell plate
form
Cytokinesis cytoplasm divides and cell splits into two (part of telophase)
5. What happens to the chromosome number after mitosis and meiosis?
The chromosome number remains the same as the parent cell after mitosis
The chromosome number is half the amount as the parent cell after meiosis
6. Why do mitosis and meiosis take place?
Mitosis produces identical cells; is a form of reproduction in single celled organisms and
used for growth and repair in multi-cellular organisms
PART 2:
Other questions to further your course of study
Match each term with its description.
A. cytoplasm divided between the two daughter cells
B. final phase of mitosis; daughter nuclei reform
C. two sister chromatids are joined here
D. chromosomes condense and mitotic spindle begins to form
E. chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
F. sister chromatids separate, move away to opposite poles
G. half of a chromosome in prophase
H. another name for sex cell that is formed through meiosis
I. daughter cell produced with half the number of chromosomes as parent cell
J. daughter cell produced with the same number of chromosomes as parent cell
__C__ 1. centromere __D__ 6. prophase
__G__ 2. chromatid __I__ 7. haploid
__A__ 3. cytokinesis __B__ 6. telophase
__E__ 4. metaphase __F__ 7. anaphase
__H__ 5. gamete __J__ 8. diploid
PART 3:
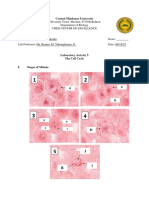
Stages of Mitosis Plus Interphase
The stages of mitosis plus interphase are listed under a-e below. Answer the following
questions with reference to these phases.
A. Interphase B. Prophase
C. Metaphase D. Anaphase
E. Telophase
1. During this stage, homologous pairs of chromosomes are lined up in the middle of the cell.
C (metaphase)
2. Chromosomes replicate during this phase. A (Interphase)
3. Condensation and shortening of chromosomes occurs during this phase. B (prophase)
4. Spindle fibers first appear during this stage. B (prophase)
5. During this phase, the centromeres break apart as the separated sister chromatids begin
to move to opposite poles. D (anaphase)
6. Cytokinesis occurs as this phase of mitosis proceeds. E (telophase)
7. During this phase two identical diploid cells are produced. E (telophase)
8. This is the longest part of the cell cycle. A (interphase)
PART 4:
Stages of Meiosis
A. Prophase I B. Prophase II
The stages of meiosis are
C. Metaphase II D. Anaphase II
listed in the box. Answer the
E. Telophase II F. Anaphase I
following questions with
reference to these phases of
meiosis.
1. The centromere of each chromosome split, which allows for the sister chormatids to move
to opposite ends of the cell. D (Anaphase II)
2. Recombination via crossing over occurs during this stage. A (Prophase I)
3. By the end of this phase, the homologous chromosomes separate. F (Anaphase I)
4. Following this phase, each individual cell is haploid. E (Telophase II)
5. During this phase, the chromosomes line up in the center of the cell. C (Metaphase II )
6. New genetic combinations, upon which natural selection can act, are present after this
stage. A (prophase I)
You might also like
- Genetics Study Guide AnswersDocument23 pagesGenetics Study Guide Answersapi-366982317No ratings yet
- Paguagan Almira Bea E. Cell CycleDocument3 pagesPaguagan Almira Bea E. Cell CycleAlmira Bea Eramela PaguaganNo ratings yet
- Mitosis - Worksheet KEYDocument4 pagesMitosis - Worksheet KEYGeorgia0% (1)
- Xiang Xiang Li - MeiosisSEDocument8 pagesXiang Xiang Li - MeiosisSEXiang Xiang Li100% (1)
- Cellular Reproduction and GeneticsDocument47 pagesCellular Reproduction and GeneticsJean Marie Macadaeg OrdinarioNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Cell Cycle ReviewDocument3 pagesKami Export - Cell Cycle ReviewAchionta Nandy100% (3)
- Science IV - Self TestDocument5 pagesScience IV - Self TestAries MuraoNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: Understanding Mitosis and MeiosisDocument14 pagesCell Division: Understanding Mitosis and MeiosisNezuko Chan100% (1)
- LAB - Meiosis ModelingDocument7 pagesLAB - Meiosis ModelingDaniel CondreayNo ratings yet
- Overcome Blushing PDFDocument108 pagesOvercome Blushing PDFManelsensteinerbergton50% (2)
- 7th Grade Unit 7 Ecosystems Assessment PKTDocument16 pages7th Grade Unit 7 Ecosystems Assessment PKTapi-366982317No ratings yet
- Nutrition Diet Therapy for Cardiac PatientDocument27 pagesNutrition Diet Therapy for Cardiac PatientTina TalmadgeNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Osmeña Q4 - Week 2Document48 pagesGrade 8 Osmeña Q4 - Week 2SHAIRA LYN CUMILANGNo ratings yet
- Meiosis GIZMODocument9 pagesMeiosis GIZMOYeet ThisbichemptyNo ratings yet
- 4th Year Write Up 2 - Int. MedDocument11 pages4th Year Write Up 2 - Int. MedLoges TobyNo ratings yet
- Cell Division PDFDocument11 pagesCell Division PDFMrinal SharmaNo ratings yet
- DLaboratory Actiivty 5 - Integumentary System AnswerDocument6 pagesDLaboratory Actiivty 5 - Integumentary System AnswerSYDNEY JILL ACHAINo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument52 pagesCell DivisionRamachandran Ram100% (1)
- Meiosis WorksheetDocument4 pagesMeiosis WorksheetCarl ReyesNo ratings yet
- Human Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsFrom EverandHuman Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument2 pagesMitosis Worksheetkatherine corvera100% (2)
- Miniongenetics 002Document2 pagesMiniongenetics 002api-366982317No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument12 pagesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionMajid Al-hachami100% (1)
- Gen Bio 1 Lesson 4Document2 pagesGen Bio 1 Lesson 4Ric SantosNo ratings yet
- Science 8 - Q4Document15 pagesScience 8 - Q4Lance Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Quarter 4 Module 2 Week 2 Cell Division Let's UnderstandDocument4 pagesScience 8 Quarter 4 Module 2 Week 2 Cell Division Let's Understandabadloraine0331No ratings yet
- Module 4-The Cell's Life CycleDocument5 pagesModule 4-The Cell's Life CycleGoogle BackupNo ratings yet
- Answers-Worksheet 9.2 Meiosis and Sexual ReproductionDocument6 pagesAnswers-Worksheet 9.2 Meiosis and Sexual ReproductionJO XS7No ratings yet
- Cell Division: Better Your DreamsDocument11 pagesCell Division: Better Your DreamsDouglas MusinguziNo ratings yet
- Module 4-The Cell's Life CycleDocument4 pagesModule 4-The Cell's Life Cycle10. Briol AlvinNo ratings yet
- Key CellDivDocument6 pagesKey CellDivMichael Ryan EreseNo ratings yet
- Sixth Grade Work For Cell Reproduction and MitosisDocument8 pagesSixth Grade Work For Cell Reproduction and MitosisaiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-10: Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument13 pagesChapter-10: Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionAlvianiNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle Activity: Fill in The BlankDocument4 pagesThe Cell Cycle Activity: Fill in The BlankJexi Angeli Geron Macaraig100% (1)
- Gen. Bio 1 Q 1 - Week 4 Module 4Document24 pagesGen. Bio 1 Q 1 - Week 4 Module 4Gyeon Dae-HoNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division Class 11 Notes. " (Cbse)Document8 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division Class 11 Notes. " (Cbse)i uploadNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Sexual ReproductionDocument48 pagesMeiosis and Sexual Reproductionerdayu86100% (1)
- 11.10 Cell cycle and cell divisionDocument7 pages11.10 Cell cycle and cell divisionMoonesh MKNo ratings yet
- 7354216Document2 pages7354216Christopher JosephNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesCell DivisionNusrat ShoshiNo ratings yet
- Corrina Pledger - Mitosis - Worksheet - 2Document2 pagesCorrina Pledger - Mitosis - Worksheet - 2Corrina PledgerNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument12 pagesCell DivisionLeona TittleNo ratings yet
- Cell Division A Level.Document14 pagesCell Division A Level.AJ Sagg. Cann.No ratings yet
- Ayomisola EmbryologyDocument12 pagesAyomisola EmbryologyAkinsola AyomidotunNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle (Module)Document11 pagesThe Cell Cycle (Module)Cel Callao Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 12 Meiosis and Alternation of GenerationsDocument2 pages12 Meiosis and Alternation of GenerationsqrqewNo ratings yet
- Gametes Chromosomes Mitosis Different From Mitosis: Key TakeawaysDocument9 pagesGametes Chromosomes Mitosis Different From Mitosis: Key TakeawaysRishikesh BhintadeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (Organic)Document10 pagesChemistry (Organic)Julia Mibuy Mba OyanaNo ratings yet
- Science: Cell Division: Mitosis and MeiosisDocument16 pagesScience: Cell Division: Mitosis and MeiosisMichelle Casayuran - RegalaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Student Exploration SheetDocument5 pagesMeiosis Student Exploration SheetLyen Queen AmpoonNo ratings yet
- MeiosisSEDocument10 pagesMeiosisSEtheodougy17No ratings yet
- Genbio1 Exam 2 Print To Be SendDocument4 pagesGenbio1 Exam 2 Print To Be SendMohammad Rex MuharramNo ratings yet
- C C C D: ELL Ycle AND ELL IvisionDocument5 pagesC C C D: ELL Ycle AND ELL IvisionBur ChattaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle ExplainedDocument35 pagesCell Cycle ExplainedHimanshi ShrresthaNo ratings yet
- Wk.2.module 2 .QRT.4 Mitosis & Meiosis, Phenotypic ExpressionDocument34 pagesWk.2.module 2 .QRT.4 Mitosis & Meiosis, Phenotypic ExpressionShanikMendozaNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 10Document11 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 10Purva YadgireNo ratings yet
- Biology MitosisDocument11 pagesBiology MitosisLesther ChiengNo ratings yet
- Quick Test MeiosisDocument1 pageQuick Test MeiosisJacqueline Levana HuliselanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5Document5 pagesExercise 5holie madroneroNo ratings yet
- Biology CH 5Document10 pagesBiology CH 5Ali MohsinNo ratings yet
- Homework HandoutDocument2 pagesHomework Handoutabdalla abdelhamidNo ratings yet
- Explore Learning MeiosisDocument7 pagesExplore Learning MeiosisAmarna BarnesNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document11 pagesWeek 2IRIS CHRISTINE SENONo ratings yet
- U4 - Study Guide - CELL DIVISION & GROWTHDocument7 pagesU4 - Study Guide - CELL DIVISION & GROWTHJuan CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Science8 Q4 M2Document6 pagesScience8 Q4 M2Arabella BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell DivisionSsonko EdrineNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument6 pagesMeiosisericaNo ratings yet
- Biomes 1Document3 pagesBiomes 1api-366982317No ratings yet
- BiomesDocument51 pagesBiomesapi-366982317No ratings yet
- EcologyreviewkeyDocument3 pagesEcologyreviewkeyapi-366982317No ratings yet
- Invasive SpeciesDocument2 pagesInvasive Speciesapi-366982317No ratings yet
- ECOLOGY Open Notes AssessmentDocument3 pagesECOLOGY Open Notes Assessmentapi-366982317No ratings yet
- Evolution FoldableDocument7 pagesEvolution Foldableapi-366982317No ratings yet
- Skeletal System PowerpointDocument44 pagesSkeletal System Powerpointapi-366982317No ratings yet
- An AlienDocument5 pagesAn Alienapi-366982317No ratings yet
- Peppered Moth SimulationDocument3 pagesPeppered Moth Simulationapi-3669823170% (1)
- Human Body Systems-BwdoitDocument2 pagesHuman Body Systems-Bwdoitapi-366982317No ratings yet
- Skeletal System2Document34 pagesSkeletal System2api-366982317No ratings yet
- Naturally Selected To Survive 1110 Passage and QuestionsDocument5 pagesNaturally Selected To Survive 1110 Passage and Questionsapi-366982317No ratings yet
- Genetics Webquest2Document3 pagesGenetics Webquest2api-366982317No ratings yet
- Genetics SitesDocument1 pageGenetics Sitesapi-366982317No ratings yet
- Genetics Webquest1Document1 pageGenetics Webquest1api-366982317No ratings yet
- Genetics WebquestDocument2 pagesGenetics Webquestapi-366982317No ratings yet
- ClassificationworkbookDocument40 pagesClassificationworkbookapi-366982317No ratings yet
- Genetics I CanDocument6 pagesGenetics I Canapi-366982317No ratings yet
- Study Guide 2017 B 003Document3 pagesStudy Guide 2017 B 003api-366982317No ratings yet
- Oswreindeergenetics 4Document2 pagesOswreindeergenetics 4api-366982317No ratings yet
- Punnett Square PracticeDocument5 pagesPunnett Square Practiceapi-366982317No ratings yet
- MiniongeneticsDocument1 pageMiniongeneticsapi-366982317No ratings yet
- Genetics VocabularyDocument3 pagesGenetics Vocabularyapi-366982317No ratings yet
- Punnett SquaresDocument6 pagesPunnett Squaresapi-366982317No ratings yet
- Hs 4 Genetics Practice Problems 2Document2 pagesHs 4 Genetics Practice Problems 2api-366982317No ratings yet
- Hs 4 Genetics Practice Problems 2Document1 pageHs 4 Genetics Practice Problems 2api-366982317No ratings yet
- 9966 Cons enDocument225 pages9966 Cons enOmz DonNo ratings yet
- Psychology Prelim Exam 1st Sem 2016-17Document2 pagesPsychology Prelim Exam 1st Sem 2016-17Monroe Ortizano100% (1)
- Unit 11 Arterial PunctureDocument34 pagesUnit 11 Arterial PunctureZoe Rodriguez100% (1)
- A Simplified Technique For Determining The Occlusal Plane in Full Denture ConstructionDocument4 pagesA Simplified Technique For Determining The Occlusal Plane in Full Denture ConstructionAlejandro García ArmentaNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATES CHEMISTRY, Lecture For 1st Year M B B S - Delivered by DR Mohammad Waseem KausarDocument22 pagesCARBOHYDRATES CHEMISTRY, Lecture For 1st Year M B B S - Delivered by DR Mohammad Waseem KausarIMDCBiochem60% (5)
- Thesis Reza Salman Roghani PDFDocument76 pagesThesis Reza Salman Roghani PDFscoopyNo ratings yet
- Potassium BalanceDocument13 pagesPotassium BalancePhysiology by Dr Raghuveer100% (1)
- Transportation in Plants and AnimalsDocument7 pagesTransportation in Plants and AnimalsDivyansh JhaNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Infant or Child With Nausea and Vomiting - UpToDateDocument47 pagesApproach To The Infant or Child With Nausea and Vomiting - UpToDatemayteveronica1000No ratings yet
- Cell Division MCQ Questions & AnswersDocument17 pagesCell Division MCQ Questions & Answersmurali.prionsgm100% (1)
- Chronic Renal Failure Case StudyDocument29 pagesChronic Renal Failure Case StudyMary Shine GonidaNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt-17-18 XI Zoo Study-Package-1 SET-1 Chapter-1A PDFDocument14 pagesCLS Aipmt-17-18 XI Zoo Study-Package-1 SET-1 Chapter-1A PDFChunnu BishtNo ratings yet
- Cooperative Activity 3-1 Through 3-3Document3 pagesCooperative Activity 3-1 Through 3-3Thalia Sanders100% (2)
- Lecture 11 Nursing Care of A Family During Labor and Birth 2021Document105 pagesLecture 11 Nursing Care of A Family During Labor and Birth 2021مؤمن شطناويNo ratings yet
- Basic Human AnatomyDocument43 pagesBasic Human AnatomyZirah Lee ValledorNo ratings yet
- Anabolism of CarbohydratesDocument31 pagesAnabolism of CarbohydrateszhekinangeneNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis WorksheetDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis WorksheetByambazaya E100% (2)
- GCSE Triple Biology 2023Document91 pagesGCSE Triple Biology 2023Ramy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Esthetic Management of Anterior Teeth with GiomerDocument7 pagesEsthetic Management of Anterior Teeth with GiomerFoysal Sirazee100% (1)
- CNS Stimulants 2023Document10 pagesCNS Stimulants 2023ManWol JangNo ratings yet
- Glucocorticoid Signaling From Molecules to Mice to ManDocument387 pagesGlucocorticoid Signaling From Molecules to Mice to ManKuldeepSinghBanaNo ratings yet
- Thanksgiving Sleep Questions and AnswersDocument4 pagesThanksgiving Sleep Questions and Answersapi-420563491No ratings yet
- 3.0 Cytology-CELL CYCLE UphmoDocument43 pages3.0 Cytology-CELL CYCLE UphmoPatrick DingcoNo ratings yet
- Angliski Kniga VezbiDocument6 pagesAngliski Kniga VezbiMartina JovevskaNo ratings yet
- VPB 111Document3 pagesVPB 111Dr-Ashok KeerNo ratings yet