Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Magma (From: A Ā Is One of Three Basic Types of Flow Lava. A Ā Is Basaltic Lava Characterized by A Rough or Rubbly
Uploaded by
Albert Magno CaoileOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Magma (From: A Ā Is One of Three Basic Types of Flow Lava. A Ā Is Basaltic Lava Characterized by A Rough or Rubbly
Uploaded by
Albert Magno CaoileCopyright:
Available Formats
Dikes are imaginable as the veins of a volcano, the pathways of rising magma.
A dike is
called a -usually more or less vertical- flat, sheet-like magma body that cuts
unconformingly through older rocks or sediments.
Most dikes can be described as fractures into which magma intrudes or from which they
might erupt. The fracture can be caused by the intrusion of pressurized magma, or vice
versa, the rise of magma can be caused by and exploit existing or tectonically forming
fractures. The point where a dike reaches the surface and erupts lava can be called a
vent.
Magma (from Ancient Greek (mgma) meaning "thick unguent") is a mixture of molten or
semi-molten rock, volatilesand solids[1] that is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and is
expected to exist on other terrestrial planets and some natural satellites. Besides molten rock,
magma may also contain suspended crystals, dissolved gas and sometimes gas bubbles. Magma
often collects in magma chambers that may feed a volcano or solidify underground to form
an intrusion. Magma is capable of intruding into adjacent rocks (forming igneous dikes and sills),
extrusion onto the surface as lava, and explosive ejection as tephra, or fragmented rock, to
form pyroclastic rock.
A is one of three basic types of flow lava. A is basaltic lava characterized by a rough or rubbly
surface composed of broken lava blocks called clinker. The Hawaiian word was introduced as a
technical term in geology by Clarence Dutton.[12]
The loose, broken, and sharp, spiny surface of an a flow makes hiking difficult and slow. The
clinkery surface actually covers a massive dense core, which is the most active part of the flow. As
pasty lava in the core travels downslope, the clinkers are carried along at the surface. At the leading
edge of an a flow, however, these cooled fragments tumble down the steep front and are buried
by the advancing flow. This produces a layer of lava fragments both at the bottom and top of an a
flow.
A fissure vent, also known as a volcanic fissure or eruption fissure, is a linear volcanic
vent through which lava erupts, usually without any explosive activity. The vent is often a few meters
wide and may be many kilometers long. Fissure vents can cause large flood basaltswhich run first
in lava channels and later in lava tubes. After some time the eruption builds up spatter resp. ash
cones and may concentrate on one or some of them. Small fissure vents may not be easily
discernible from the air, but the crater rows (see Laki) or the canyons (see Eldgj) built up by some
of them are.
You might also like
- What Happens Before and After Volcanoes Erupt? Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandWhat Happens Before and After Volcanoes Erupt? Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument3 pagesVolcanoesMizpah OlilaNo ratings yet
- On Earth, Volcanoes Are Generally Found Where Tectonic Plates Are orDocument5 pagesOn Earth, Volcanoes Are Generally Found Where Tectonic Plates Are orrituNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes Everything You Need To KnowDocument5 pagesVolcanoes Everything You Need To KnowDevraj H SNo ratings yet
- Nature and Types of Volcanoes Autosaved 1Document31 pagesNature and Types of Volcanoes Autosaved 1jairolostreNo ratings yet
- CE 203-Class Note 2 (Part 2) - SKSDocument32 pagesCE 203-Class Note 2 (Part 2) - SKSKNOWLEDGE HUBNo ratings yet
- Types of Volcanoes: Shield VolcanoDocument17 pagesTypes of Volcanoes: Shield VolcanoRomeo Gabitanan JrNo ratings yet
- Ch12 Study GuideDocument6 pagesCh12 Study GuideEdjie LluparNo ratings yet
- Ash Emitted by Thevolcanoes. It's The Rock or The Ash That Gets Warm Up and Form To Be A StrongDocument2 pagesAsh Emitted by Thevolcanoes. It's The Rock or The Ash That Gets Warm Up and Form To Be A StrongKyle Hilary MatundingNo ratings yet
- Volcano FormationDocument6 pagesVolcano FormationCrichelle Bustamante BacalsoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Volcanic EruptionsDocument22 pagesChapter 5 Volcanic EruptionsreesespufffNo ratings yet
- Volcanic and Tectonic LandformsDocument8 pagesVolcanic and Tectonic LandformsDiy IdeasNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument42 pagesVolcanoesEllecarg Cenaon CruzNo ratings yet
- How Does Volcano FormDocument2 pagesHow Does Volcano FormIan Dante ArcangelesNo ratings yet
- Zephyria TholusDocument3 pagesZephyria Tholuseric1980_andolanaNo ratings yet
- How Plates Affect Our Planet Volcanoes Passage QuestionsDocument2 pagesHow Plates Affect Our Planet Volcanoes Passage QuestionsIñaki MurNo ratings yet
- Volcanic LandformsDocument16 pagesVolcanic LandformsLielet MatutinoNo ratings yet
- Science DraftDocument4 pagesScience Draftmaster dilucNo ratings yet
- HGGGGDocument8 pagesHGGGGBea Ashley VosotrosNo ratings yet
- VolcanismDocument6 pagesVolcanismKristine MercadoNo ratings yet
- VulcanismDocument35 pagesVulcanismrheeaNo ratings yet
- Types of VolcanoesDocument10 pagesTypes of VolcanoesRobert MestiolaNo ratings yet
- VOLCANO NotesDocument17 pagesVOLCANO NotesAlexander LahipNo ratings yet
- VolvanoDocument6 pagesVolvanoZarinaNo ratings yet
- HussainDocument2 pagesHussainKai JieNo ratings yet
- Types of VolcanoesDocument26 pagesTypes of VolcanoesMatt PayawalNo ratings yet
- What Happens After Magma Is FormedDocument15 pagesWhat Happens After Magma Is Formedjohncarlocanete7No ratings yet
- CH5 VolcanismDocument8 pagesCH5 VolcanismNovie GraceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Volcanic EruptionsDocument19 pagesChapter 5 Volcanic EruptionsreesespufffNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesDocument17 pagesPlate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesChristle NgoveNo ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument5 pagesVolcanokirthmolosNo ratings yet
- Types of VolcanoesDocument15 pagesTypes of VolcanoesSally PocamasNo ratings yet
- CalderaDocument1 pageCalderaApurbo MaityNo ratings yet
- MagmaDocument4 pagesMagmaDP ManguneNo ratings yet
- Power Point Volcanic EruptionDocument18 pagesPower Point Volcanic Eruptionwandi primaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 1st QUARTERDocument6 pagesSCIENCE 1st QUARTERJulia Samantha GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes NomenclatureDocument7 pagesVolcanoes NomenclaturegerztenNo ratings yet
- Microsoft ® Encarta ® 2009. © 1993-2008 Microsoft Corporation. All Rights ReservedDocument1 pageMicrosoft ® Encarta ® 2009. © 1993-2008 Microsoft Corporation. All Rights ReservedJulieta InteNo ratings yet
- 3 Types of VolcanoesDocument8 pages3 Types of Volcanoesjune hetreNo ratings yet
- Dramatic VolcanicDocument2 pagesDramatic VolcanicbNo ratings yet
- Volcanic FeaturesDocument3 pagesVolcanic FeaturesTariNo ratings yet
- B07 Q2 PT EarthsciDocument3 pagesB07 Q2 PT EarthsciJALANDONI, CRIS DWIGHT, O.No ratings yet
- Volcanoes-How It Is FormedDocument55 pagesVolcanoes-How It Is FormedHenry JacobNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes 9d1d91f4Document4 pagesVolcanoes 9d1d91f4KEERTHI MANASA N R GYUA21012No ratings yet
- Disaster Risk Reduction and Readiness ReviewerDocument7 pagesDisaster Risk Reduction and Readiness ReviewerjkierstencvergaraNo ratings yet
- Parts of A VolcanoDocument7 pagesParts of A VolcanoReynielclydeEscoberNo ratings yet
- Earth Sci ReviewerDocument7 pagesEarth Sci ReviewerELSYIANE RICCI D. LAONo ratings yet
- Volcano PPTDocument54 pagesVolcano PPTjocelyn.matigaNo ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument84 pagesVolcanoJM LomoljoNo ratings yet
- Volcano 2014 BBDocument11 pagesVolcano 2014 BBNadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Module SCI101 EARTH SCI VOLCANOS AND MANDocument6 pagesModule SCI101 EARTH SCI VOLCANOS AND MANsm6553151No ratings yet
- Sci ReviewerDocument7 pagesSci ReviewerBxbble BerriNo ratings yet
- Volcano - WikipediaDocument99 pagesVolcano - WikipediaMattyNo ratings yet
- Volcano Erruption.Document12 pagesVolcano Erruption.Andika PutraNo ratings yet
- Geography Volcanic ActivityDocument3 pagesGeography Volcanic ActivityIsabella persadNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes and EarthquakesDocument104 pagesVolcanoes and EarthquakesAlleli AspiliNo ratings yet
- I and S Volcano ReportDocument7 pagesI and S Volcano ReportJASMSJS SkskdjNo ratings yet
- Volcanic LandformDocument12 pagesVolcanic LandformJoseph ZotooNo ratings yet
- 6 - Volcanoes and Related HazardsDocument33 pages6 - Volcanoes and Related HazardsVincent GalleraNo ratings yet
- Wage Order No. RB 1 DW 04Document2 pagesWage Order No. RB 1 DW 04Albert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument60 pagesMotherboardAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- 2022 Annual Financial Report For The National Government Volume IDocument500 pages2022 Annual Financial Report For The National Government Volume IAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- Annex 10Document1 pageAnnex 10Albert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- Praise and WorshipDocument3 pagesPraise and WorshipAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- How To Create R2-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesHow To Create R2-WPS OfficeAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- CSS ScheduleDocument2 pagesCSS ScheduleAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- Device Driver-WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesDevice Driver-WPS OfficeAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- 1stQ Week8Document4 pages1stQ Week8Albert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- TABLE OF SPECIFICATION Grade 10 English 1Document3 pagesTABLE OF SPECIFICATION Grade 10 English 1Albert Magno Caoile100% (1)
- Annex 4 JDVP Certificate of Learners MasteryDocument2 pagesAnnex 4 JDVP Certificate of Learners MasteryAlbert Magno Caoile0% (1)
- Learner-Beneficiaries For The JDVP-TVLDocument2 pagesLearner-Beneficiaries For The JDVP-TVLAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- Educated and Not LearnedDocument11 pagesEducated and Not LearnedAlbert Magno Caoile100% (2)
- Lumpc Holds 27 GADocument12 pagesLumpc Holds 27 GAAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- Tesda-Op-Co-05-F31: Ca-Css0201331719028Document3 pagesTesda-Op-Co-05-F31: Ca-Css0201331719028Albert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment Guide (Performance Assessment) Computer Systems Servicing NC Ii Install and Configure Computer SystemsDocument11 pagesSelf Assessment Guide (Performance Assessment) Computer Systems Servicing NC Ii Install and Configure Computer SystemsAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- Report On The Least Mastered Competetency (LMCS) : Parasapas National High SchoolDocument2 pagesReport On The Least Mastered Competetency (LMCS) : Parasapas National High SchoolAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- La Union SDO Enrollment For SY 2018-2019Document18 pagesLa Union SDO Enrollment For SY 2018-2019Albert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- Deso Tss Ballot IdDocument10 pagesDeso Tss Ballot IdAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- New Graduation Cover 2017-2018Document1 pageNew Graduation Cover 2017-2018Albert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- Empowerment - Mark John Cabutotan and Mary Joy EstimadaDocument4 pagesEmpowerment - Mark John Cabutotan and Mary Joy EstimadaAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- Insight For Today: Identify The Enemy, Part OneDocument2 pagesInsight For Today: Identify The Enemy, Part OneAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- Rizal ControversiesDocument5 pagesRizal ControversiesAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- Locator Slip SampleDocument1 pageLocator Slip SampleAlbert Magno Caoile100% (1)
- 2017 ArapaapDocument13 pages2017 ArapaapAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument2 pagesVolcanoFreddie AbulenciaNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes Igcse Notes FreeDocument10 pagesVolcanoes Igcse Notes FreeAkashNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Volcano and Its Relation To Plate TectonicsDocument42 pagesScience: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Volcano and Its Relation To Plate TectonicsMASH50% (4)
- Plate Tectonics Poster KS2 KS3Document1 pagePlate Tectonics Poster KS2 KS3Maul GeofisikaNo ratings yet
- Romanian Journal of Mineral Deposits Vol 85 Issue 1Document105 pagesRomanian Journal of Mineral Deposits Vol 85 Issue 1Tzontonel100% (1)
- Science9 Q3 SLM2Document15 pagesScience9 Q3 SLM2Zandra Musni Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Geochemistry of Tertiary Igneous Rocks of Northern Luzon Philippines Evidence For A BackArc Setting For Alkalic Porphyry Copper Gold Deposits and A Case For Slab RollBack - PETE HOLLINGS, 1, ROHANDocument21 pagesGeochemistry of Tertiary Igneous Rocks of Northern Luzon Philippines Evidence For A BackArc Setting For Alkalic Porphyry Copper Gold Deposits and A Case For Slab RollBack - PETE HOLLINGS, 1, ROHANJaime Renato Abanto NovoaNo ratings yet
- Endapan MagmatikDocument22 pagesEndapan MagmatikRio CendrajayaNo ratings yet
- Volcano Paper Mache ModelDocument7 pagesVolcano Paper Mache ModelSabrina LavegaNo ratings yet
- Geology of Trans HimalayasDocument20 pagesGeology of Trans HimalayasRavindra Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Grain-Size Distribution of Pyroclastic Rocks - Granulometric and Stereology Analysis On Determining The Depositional Process of Pyroclastic Deposits in Bandung RegionDocument10 pagesGrain-Size Distribution of Pyroclastic Rocks - Granulometric and Stereology Analysis On Determining The Depositional Process of Pyroclastic Deposits in Bandung Regionbarry majeedNo ratings yet
- Science9 Q3 SLM4Document17 pagesScience9 Q3 SLM4Zandra Musni Delos Reyes100% (1)
- AdvDocument4 pagesAdvMonica D Grigore100% (1)
- Gold, Silver, and Copper Metallogeny of The Eastern Sunda Magmatic Arc IndonesiaDocument15 pagesGold, Silver, and Copper Metallogeny of The Eastern Sunda Magmatic Arc Indonesiaiqbal maratama100% (1)
- Textural Characterization of Unidirectional Solidification TexturesDocument25 pagesTextural Characterization of Unidirectional Solidification TexturesJack RamirezNo ratings yet
- Volcano Acrostic Poem: V O L C A N ODocument4 pagesVolcano Acrostic Poem: V O L C A N OMdpn. SalvadorNo ratings yet
- 101 - Volcanic Eruptions in The PhilippinesDocument1 page101 - Volcanic Eruptions in The PhilippinesSeagullian DaveNo ratings yet
- Ore Deposirs Related To Intermediate To Felsic Igneous RocksDocument15 pagesOre Deposirs Related To Intermediate To Felsic Igneous RocksKamalNo ratings yet
- Why No Porphry Copper Deposit in Japan & KoreaDocument19 pagesWhy No Porphry Copper Deposit in Japan & KoreaJulian I SwandiNo ratings yet
- en The Origin of Cihara Granodiorite From SDocument10 pagesen The Origin of Cihara Granodiorite From SAhmad SaepullahNo ratings yet
- POWERPOINT - Volcanic HazardsDocument18 pagesPOWERPOINT - Volcanic HazardsCherry GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes and Volcanic ActivityDocument45 pagesVolcanoes and Volcanic ActivityatikaNo ratings yet
- Muta M Edited BelayDocument32 pagesMuta M Edited Belaygizachew100% (1)
- Document For FreeDocument3 pagesDocument For FreePrecious Nicole J. DariaNo ratings yet
- Archaean Greenstone Belts and Associated Granitic Rocks - A ReviewDocument50 pagesArchaean Greenstone Belts and Associated Granitic Rocks - A Reviewnelson.damascenoNo ratings yet
- Igneous Textures PDFDocument3 pagesIgneous Textures PDFCarolina Castro CardonaNo ratings yet
- Temporal Variation in The Lavas of Mayon Volcano, PhilippinesDocument23 pagesTemporal Variation in The Lavas of Mayon Volcano, PhilippinesrajaderyNo ratings yet
- Phy. Geol.5Document24 pagesPhy. Geol.5Salman Bin TariqNo ratings yet
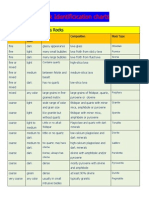
- Rock Identificication ChartsDocument3 pagesRock Identificication ChartsSan ShweNo ratings yet
- Lithochemistry of The Alpala Cu-Au Porphyry Deposit, Northern Andes of EcuadorDocument6 pagesLithochemistry of The Alpala Cu-Au Porphyry Deposit, Northern Andes of EcuadorAlexander DavydNo ratings yet
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessFrom EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo ratings yet
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (597)
- Water to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesFrom EverandWater to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (21)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsFrom EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (65)
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersFrom EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersNo ratings yet
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorFrom EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (137)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutFrom EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (142)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterFrom EverandThe Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterNo ratings yet
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsFrom EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeFrom EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (19)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignFrom EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (19)
- The Soul of an Octopus: A Surprising Exploration into the Wonder of ConsciousnessFrom EverandThe Soul of an Octopus: A Surprising Exploration into the Wonder of ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (254)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsFrom EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (223)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogFrom EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)