Professional Documents
Culture Documents
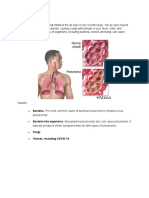
Bronchitis, Tracheitis, Lobular Pneumonia, Pulmonary Tuberculosis, Rheumatic Endocarditis
Uploaded by
Anastasia S. RusuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bronchitis, Tracheitis, Lobular Pneumonia, Pulmonary Tuberculosis, Rheumatic Endocarditis
Uploaded by
Anastasia S. RusuCopyright:
Available Formats
Bonchitis
-temperature about 38C
-a short painful dry cough associated with rapid respiration
-the pain in the throat ans behind the breastbone
-dry moist rales hearted in the lungs
-respiratory rate increased
-discomfort in the chest
The amount of the discharge from the bronchial mucous membrane was lare.
It accumulated in the bronchial tubes and made the patient cough.Passing
through this fluid in the bronchial tubes the air which was breathed in and
out produced moist and dry rales.
Treatment-bed regimen and light diet. Recommend to drink either warm milk
or have warm applications on his chest. Patient has to take two tablets of
tetracyclin to be taken orally and a cough mixture to be taken three times a day.
Tracheites
-cough, usually dry at first,but in a doy or two it becomed productive
-pain in the substernal area, in the throat
-general condition becames worse
-a bad headache may develop
-in the adult the temperature may not be high,but in the children
it may be as high as 39
Is the disease in wich the mucous membrane of the trachea is impared.In
such conditions the microorganism such as pneumococci staphylococci ans
streptococci multiply rapidly and produce the inflammation of the mucouc membrane.
Treatment-patient must be in a warm room,well aired. Wil be administrated
aspirin or codein which gives relief. Recommended to have warm milk with soda several times a day.
Lobular Pneumonia
-fever persistin for two weeks (caused by the appearance of the new foci of inflammatipon
in the pulmonary tussue.
-rapid breathing
-breathlessness and cyanosis
-decrease in the respiratory syrface and occlusion of numerous bronchioles and alveoli
-paint in the chest
-cough with purulent sputum
-accelerated pulse rate
-arterial pressure reduced
-dullness
-abnormal respiration
-numerous rales and crepitation
-increased number of leucocytosis and an accelerated erythrocyte sedimentation rate
-numerous foci of inflammation in the lungs
enlargement of the lymphatic glands
Treatment the first day of the dsease the patient was administered a 2gr dose of nursulphazol
which was followed by a 1 gr dose every four hours during that day.In addition to nursulphazol
the patient had been receiving streptomycin in doses of 500 000 units twice daily during
8 days. To improve patient sleep he had been taken bromide and luminal during whole course.
Cough tans chest pain were relieved by the administration of codein, cough mixture xups and
other necessary procedures. When the body temperature come to normal he was allowed to walk a little.
Pulmonary Tuberculosis
-general malaise,fatigue,loss of appetite and weight
-cough with sputum dischare
-blood in sputum
-fever
-cold profuse perspiration at night
Pulmonary tuberculosis is caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease
may also affect other organs;bones, joints, lymphatic glands.
Rheumatic Endocarditis
-general malaise, early fatiue on exertion,
-cardiac discomfort and palpitation
-fever
-irregular pulse rate
-heart is slightly enlarged
-soft systolic murmur is heard at the heart apex
-diastole murmur is heard at the apex and base of the heart
-organic changes in the mitral aortic and tricuspid valves
Treatment- is administrated antibiotic therapy to eliminate the primary focus of infection.
Adonis preparations to control cardiovascular insufficiency. The patient took aspirin in
the dosage of 1 gr four times a day. Diet should be nourishing with many vitamins but limited
in salt. The patient was allowed only a limited amount of fluid.
You might also like
- Expanded 3P Study Guide YasminaIrinaDocument79 pagesExpanded 3P Study Guide YasminaIrinaikNo ratings yet
- The Flu: A Guide for Prevention and TreatmentFrom EverandThe Flu: A Guide for Prevention and TreatmentRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bronchitis 170709131740Document28 pagesBronchitis 170709131740Viji MNo ratings yet
- MedSurgATI1Document97 pagesMedSurgATI1LeelanRamphal100% (1)
- Bacteria. The Most Common Cause of Bacterial Pneumonia Is StreptococcusDocument4 pagesBacteria. The Most Common Cause of Bacterial Pneumonia Is StreptococcusLouise OpinaNo ratings yet
- Med Surg ATI1Document97 pagesMed Surg ATI12Ghzchapter88% (17)
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory Physiology LectureDocument31 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory Physiology LectureMeryl RamosNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument104 pagesRespiratory SystemKatisha JosephNo ratings yet
- The patient's breathing has improved. She is able to take deep breaths without difficulty and her respiratory rate has decreased. Lung sounds are clearDocument42 pagesThe patient's breathing has improved. She is able to take deep breaths without difficulty and her respiratory rate has decreased. Lung sounds are clearNikko MelencionNo ratings yet
- ASTHMADocument16 pagesASTHMANavneet GillNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for PneumoniaDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for PneumoniaJazzmin Angel ComalingNo ratings yet
- Acute Asthma ExacerbationDocument2 pagesAcute Asthma ExacerbationBrial Faith Venice C. TibongNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument14 pagesBronchitisNyakie MotlalaneNo ratings yet
- Segui NCPDocument4 pagesSegui NCPRichelle TalaguitNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesTuberculosis Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceCyrus De Asis86% (36)
- Approach To SOBDocument25 pagesApproach To SOBabdiyare7134No ratings yet
- PNEUMONIADocument33 pagesPNEUMONIAgabrielle panganNo ratings yet
- BronchoPulmonary Hygiene TechniquesDocument88 pagesBronchoPulmonary Hygiene Techniques私 シャーロットNo ratings yet
- COPD Introduction: Types, Risk Factors, and Nursing CareDocument36 pagesCOPD Introduction: Types, Risk Factors, and Nursing Carejho_No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument15 pagesNursing Care PlanZhel Geron MercadoNo ratings yet
- Respi DisorderDocument14 pagesRespi DisorderErika ArceoNo ratings yet
- PBL Scriber OriginalDocument2 pagesPBL Scriber OriginalNik Nur 'AlyaNo ratings yet
- Febrile SeizuresDocument39 pagesFebrile SeizuresOwoupele Ak-GabrielNo ratings yet
- Acute Bronchitis Symptoms Causes TreatmentDocument5 pagesAcute Bronchitis Symptoms Causes TreatmentDianne LegionNo ratings yet
- Women's Pneumonia ReportDocument9 pagesWomen's Pneumonia ReportNohaira SADANGNo ratings yet
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocument79 pagesChest PhysiotherapyRabab Ahmed100% (2)
- COPD and Asthma Guide - Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument21 pagesCOPD and Asthma Guide - Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentEdmund RufinoNo ratings yet
- SEMI Final Coverage Fundamentals of NursingDocument14 pagesSEMI Final Coverage Fundamentals of NursingGlory NeriNo ratings yet
- History SummaryDocument233 pagesHistory SummarymaybeNo ratings yet
- NCP PleuralDocument5 pagesNCP Pleuraljanine_valdezNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs NotesDocument4 pagesVital Signs NoteslorNo ratings yet
- MEDICAL SURGICAL (MS) RLE PULMONARY ASSESSMENTDocument8 pagesMEDICAL SURGICAL (MS) RLE PULMONARY ASSESSMENTYman Gio BumanglagNo ratings yet
- P1 Medworld Academy: Respiratory SystemDocument123 pagesP1 Medworld Academy: Respiratory SystemThenunda തേനുണ്ടNo ratings yet
- Pleno Scenario 1: Group 2Document44 pagesPleno Scenario 1: Group 2tiok widodoNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia 10Document13 pagesPneumonia 10Dina M Elbakary100% (1)
- 4i4 (L@pq2b50ya1ku4Document16 pages4i4 (L@pq2b50ya1ku4Kristel AnneNo ratings yet
- Respiratory EMDocument51 pagesRespiratory EMMwalimu Hachalu FayeNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors & TreatmentDocument12 pagesPneumonia: Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors & TreatmentDina M ElbakaryNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process and Midwifery AssessmentDocument20 pagesNursing Process and Midwifery AssessmentGreggy Francisco LaraNo ratings yet
- Patho Respiratory - KatherineDocument9 pagesPatho Respiratory - KatherineKayla MayerNo ratings yet
- PulmonologyDocument22 pagesPulmonologyPepa KaradzhovaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument14 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationJennifer ArdeNo ratings yet
- MED SURG OUTLINE Chapter 14 Care of Patients With Disorders of Upper Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesMED SURG OUTLINE Chapter 14 Care of Patients With Disorders of Upper Respiratory SystemMichaela LemanNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument16 pagesPneumoniamalope mahlatseNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs-Temp, PRDocument54 pagesVital Signs-Temp, PRmags_abad09No ratings yet
- RD in Newborn by Yong Part 2Document37 pagesRD in Newborn by Yong Part 2semangat akreNo ratings yet
- Week 9 MCN 1Document7 pagesWeek 9 MCN 1Zxiayieee JeonNo ratings yet
- A Mini Case Presentation On Influenza VirusDocument22 pagesA Mini Case Presentation On Influenza Virusangelo100% (1)
- ASTHMA IN CHILDRENDocument5 pagesASTHMA IN CHILDRENRenjie ElizardeNo ratings yet
- 2nd Lecture Chest and LowerDocument18 pages2nd Lecture Chest and LowerChucky VergaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Respiratory AssessmentDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Respiratory AssessmentKathleen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Langston University Adult Health Nursing Final Exam Study GuideDocument19 pagesLangston University Adult Health Nursing Final Exam Study GuideRin noharaNo ratings yet
- Understanding MeningitisDocument16 pagesUnderstanding MeningitisJessa BorreNo ratings yet
- Case Report "Hidrocephalus With Broncopneumonia + TB"Document24 pagesCase Report "Hidrocephalus With Broncopneumonia + TB"Indah LindianaNo ratings yet
- Management of COPD: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentDocument47 pagesManagement of COPD: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentMegha VadanereNo ratings yet
- Cough: 1 - Productive (Wet, Chesty) CoughDocument6 pagesCough: 1 - Productive (Wet, Chesty) CoughEkhlas K. HasanNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia PamphletDocument2 pagesPneumonia PamphletMairiz Jem Santos100% (6)
- Language EssayDocument1 pageLanguage EssayAnastasia S. RusuNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis, Tracheitis, Lobular Pneumonia, Pulmonary Tuberculosis, Rheumatic EndocarditisDocument1 pageBronchitis, Tracheitis, Lobular Pneumonia, Pulmonary Tuberculosis, Rheumatic EndocarditisAnastasia S. RusuNo ratings yet
- Industry 4.0 Revolution PowerPointDocument48 pagesIndustry 4.0 Revolution PowerPointHasan mubarokNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis, Tracheitis, Lobular Pneumonia, Pulmonary Tuberculosis, Rheumatic EndocarditisDocument1 pageBronchitis, Tracheitis, Lobular Pneumonia, Pulmonary Tuberculosis, Rheumatic EndocarditisAnastasia S. RusuNo ratings yet
- 2019 Medical Plan PowerPoint TemplatesDocument48 pages2019 Medical Plan PowerPoint TemplatesAnonymous 0XjTzZf1f100% (1)
- History of ArtDocument921 pagesHistory of ArtAnastasia S. Rusu100% (1)
- Package - Insert - 08586 - H - en - 30427 - CA 19-9 PDFDocument8 pagesPackage - Insert - 08586 - H - en - 30427 - CA 19-9 PDFadybaila4680No ratings yet
- 2016 - Byk FotoDocument7 pages2016 - Byk FotoSyifa IKNo ratings yet
- Web KFOG-jan-11Document16 pagesWeb KFOG-jan-11kutra3000No ratings yet
- Dental Caries IndexDocument35 pagesDental Caries Indexdr parveen bathla100% (1)
- Submission For The Reclassification of A Medicine: Topical MinoxidilDocument33 pagesSubmission For The Reclassification of A Medicine: Topical MinoxidilMoneimul IslamNo ratings yet
- AIIMS (MBBS) Solved Question Paper 2010Document34 pagesAIIMS (MBBS) Solved Question Paper 2010cbsestudymaterialsNo ratings yet
- DSM-IV Introduction: Understanding the Multiaxial Assessment SystemDocument3 pagesDSM-IV Introduction: Understanding the Multiaxial Assessment SystemRoci ArceNo ratings yet
- TeresaDocument2 pagesTeresaapi-435131948No ratings yet
- Psychoeducation: 19 July 2018 Unit VI Topic DiscussionDocument26 pagesPsychoeducation: 19 July 2018 Unit VI Topic DiscussionDana Franklin100% (1)
- Dialog Roleplay Bahasa Inggris: Disusun Oleh Kelompok 3Document4 pagesDialog Roleplay Bahasa Inggris: Disusun Oleh Kelompok 3Desma LindaNo ratings yet
- TTTTDocument26 pagesTTTTMoataz TrabehNo ratings yet
- Brain Health Assessment by Dr. Daniel Amen #1 Brain Type QuizDocument1 pageBrain Health Assessment by Dr. Daniel Amen #1 Brain Type Quiz03.wizenedwasterNo ratings yet
- Option Volume Ventilation Pi 9066364 en 1506 3Document2 pagesOption Volume Ventilation Pi 9066364 en 1506 3Abdullah AlsafiNo ratings yet
- C1963 D 01Document116 pagesC1963 D 01Драган Столовић25% (4)
- PPM Action Plan - 13 - 01 - 2022Document128 pagesPPM Action Plan - 13 - 01 - 2022whoosh2008No ratings yet
- Poster PresentationDocument1 pagePoster PresentationVency KatiraNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip and Cleft PalateDocument27 pagesCleft Lip and Cleft Palatenamah odatNo ratings yet
- Cryptogenic StrokeDocument17 pagesCryptogenic StrokeIRENA GENINo ratings yet
- EMDR Scripted Protocols Index by Marilyn Luber PHDDocument4 pagesEMDR Scripted Protocols Index by Marilyn Luber PHDcebanova1994No ratings yet
- NBME Answer With Explanation in DepthDocument10 pagesNBME Answer With Explanation in DepthDejan Zolak100% (3)
- Consider Nursing School for a Fulfilling and In-Demand CareerDocument2 pagesConsider Nursing School for a Fulfilling and In-Demand CareerTangerine DianeNo ratings yet
- Goku Notes - Phasmids 2Document9 pagesGoku Notes - Phasmids 2Joulo YabutNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goals: Independent: Short Term GoalsDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goals: Independent: Short Term GoalskyawNo ratings yet
- Quiz Hospital DocumentationDocument5 pagesQuiz Hospital DocumentationJessica EdiosNo ratings yet
- HealthDocument6 pagesHealthAngel Bernal PinedaNo ratings yet
- OSCE Subcutaneous Injection SkillsDocument2 pagesOSCE Subcutaneous Injection SkillsvishnuNo ratings yet
- I. Bedsores A. What Are Bedsores?Document3 pagesI. Bedsores A. What Are Bedsores?peter911xNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care for High-Risk Pregnant MothersDocument40 pagesNursing Care for High-Risk Pregnant MothersAllyza EspirituNo ratings yet
- Ericksonian Approaches To Pain ManagementDocument6 pagesEricksonian Approaches To Pain Managementosher2650% (2)
- Psychosocial Aspect of Critical Nursing Pak JoDocument9 pagesPsychosocial Aspect of Critical Nursing Pak JoYuli Permata SARINo ratings yet