Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PHENYALANINE
Uploaded by
Margian Erica Taguas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pagesphenyalanine
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentphenyalanine
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pagesPHENYALANINE
Uploaded by
Margian Erica Taguasphenyalanine
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
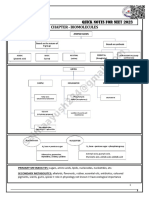
PHENYALANINE- an amino acid widely distributed in plant proteins.
It is an essential
nutrient in the diet of vertebrates.
LEUCINE - a hydrophobic amino acid that is a constituent of most proteins. It is an essential
nutrient in the diet of vertebrates.
ISOLEUCINE - a hydrophobic amino acid that is a constituent of most proteins. It is an
essential nutrient in the diet of vertebrates.
METHIONINE - a sulfur-containing amino acid that is a constituent of most proteins. It
is an essential nutrient in the diet of vertebrates.
VALINE - an amino acid that is a constituent of most proteins. It is an essential nutrient in the
diet of vertebrates.
SERINE - a hydrophilic amino acid that is a constituent of most proteins.
PROLINE - an amino acid that is a constituent of most proteins, especially collagen.
THEREONINE - a hydrophilic amino acid that is a constituent of most proteins. It is an
essential nutrient in the diet of vertebrates.
ALANINE an amino acid that is a constituent of most proteins.
TYROSINE - a hydrophilic amino acid that is a constituent of most proteins and is important
in the synthesis of some hormones.
HISTIDINE - a basic amino acid that is a constituent of most proteins. It is an
essential nutrient in the diet of vertebrates, and is the source from which histamine is
derived in the body.
GLUTAMINE - hydrophilic amino acid that is a constituent of most proteins.
ASPARAGINE - a hydrophilic amino acid that is a constituent of most proteins.
LYSINE - a basic amino acid that is a constituent of most proteins. It is an essential
nutrient in the diet of vertebrates.
ASPARATIC ACID - an acidic amino acid that is a constituent of most proteins
and also occurs in sugar cane. It is important in the metabolism of nitrogen in animals
and also acts as a neurotransmitter.
GLUTAMIC ACID - an acidic amino acid that is a constituent of many
proteins.
CYSTEINE - Cysteine is a semi-essential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula
HOCCHCHSH. It is encoded by the codons UGU and UGC. The thiol side chain in cysteine often
participates in enzymatic reactions, as a nucleophile.
TRYPTOPHAN - Tryptophan is an -amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of
proteins. It contains an -amino group, an -carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it
a non-polar aromatic amino acid.
ARGININE - Arginine is an -amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is
encoded by the codons CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, and AGG.
GLYCINE - Glycine is the amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is
the simplest possible amino acid. The chemical formula of glycine is NHCHCOOH. Glycine is one
of the proteinogenic amino acids.
You might also like
- WorksheetDocument3 pagesWorksheetMargian Erica TaguasNo ratings yet
- 3rd Long Quarter TestDocument3 pages3rd Long Quarter TestMargian Erica TaguasNo ratings yet
- SubjectDocument3 pagesSubjectMargian Erica TaguasNo ratings yet
- National Competency Based Teacher StandardsDocument3 pagesNational Competency Based Teacher StandardsJoboy Fritz75% (4)
- Second Quarter Exam - TOSDocument2 pagesSecond Quarter Exam - TOSMargian Erica TaguasNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Pharmacology Report USYD Semester 2Document12 pagesPharmacology Report USYD Semester 2Joseph ChanNo ratings yet
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of Plasmid DNADocument3 pagesAgarose Gel Electrophoresis of Plasmid DNASindhu LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Albert Tacon Recent Developments in Feeds and Feeding PDFDocument86 pagesAlbert Tacon Recent Developments in Feeds and Feeding PDFAnggaVaiNo ratings yet
- ZN Grade and Tonnage Analysis by ClassDocument10 pagesZN Grade and Tonnage Analysis by ClassJulyans Brousset CornejoNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer PrelimsDocument10 pagesBiology Reviewer PrelimsShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Intl A Levels Biology Unit 2 Wbi12 v1Document14 pagesEdexcel Intl A Levels Biology Unit 2 Wbi12 v1seif nimerNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Crash Course NotesDocument22 pagesBiomolecules Crash Course NotesAayush sainiNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Amylase, Proteases, Lipases, and Cellulase: Applications and ManufacturersDocument3 pagesEnzymes Amylase, Proteases, Lipases, and Cellulase: Applications and ManufacturersKarl Anne DomingoNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms As Research ToolsDocument11 pagesMicroorganisms As Research ToolssajibNo ratings yet
- Q4 W3 4 Sci10 LawDocument8 pagesQ4 W3 4 Sci10 LawBa BengNo ratings yet
- 2&3 - Action Potential and Resting MembraneDocument28 pages2&3 - Action Potential and Resting MembraneTejesswinNo ratings yet
- Estimation & Extraction of DNADocument5 pagesEstimation & Extraction of DNAR .K.BNo ratings yet
- Southern Blotting TechniqueDocument5 pagesSouthern Blotting TechniqueVĩnh Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- Plant & Animal Cells W FunctionsDocument2 pagesPlant & Animal Cells W FunctionsHananel ValerieNo ratings yet
- Institute: Uips Department: PharmacyDocument19 pagesInstitute: Uips Department: Pharmacydeepika bhatiaNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan For Biology Form Four 2021Document29 pagesYearly Lesson Plan For Biology Form Four 2021Azween SabtuNo ratings yet
- Introduction to BP-PK & LADMER SystemsDocument26 pagesIntroduction to BP-PK & LADMER SystemsAbdul Mannan80% (5)
- Laboratory Manual For Genetic EngineeringDocument133 pagesLaboratory Manual For Genetic EngineeringRajesh Patel100% (2)
- Gene StructureDocument5 pagesGene StructureLia TuNo ratings yet
- 20-Dr. M. Hamid Rashid Profile (NIBGE Web Site)Document5 pages20-Dr. M. Hamid Rashid Profile (NIBGE Web Site)zahids2kNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 1 STPM Sem1Document12 pagesBiology Chapter 1 STPM Sem1Jia Hui100% (4)
- Biochem Reviewer ProteinsDocument27 pagesBiochem Reviewer Proteinsram castilloNo ratings yet
- Blessed Sacrament High School Biology AssessmentDocument4 pagesBlessed Sacrament High School Biology AssessmentKPS SHREYASNo ratings yet
- Gel Electrophoresis Separates DNA & Proteins by SizeDocument5 pagesGel Electrophoresis Separates DNA & Proteins by SizeCharm AngelesNo ratings yet
- Dr. Miswar Fattah, M.Si. Kesiapan ATLM Dalam Melakukan Swab Nasofaring Dan Orofaring Dalam Percepatan Diagnostik COVID-19. PDSPatKLIn 18072020Document41 pagesDr. Miswar Fattah, M.Si. Kesiapan ATLM Dalam Melakukan Swab Nasofaring Dan Orofaring Dalam Percepatan Diagnostik COVID-19. PDSPatKLIn 18072020Rini WidyantariNo ratings yet
- BABS1201 Summer 2015-16 ManualDocument157 pagesBABS1201 Summer 2015-16 ManualHi ByeNo ratings yet
- ApoptosisDocument23 pagesApoptosisLavanya Kalapala100% (1)
- SEx Linkage & RecombinationDocument37 pagesSEx Linkage & RecombinationLavander Blush100% (1)
- CAPE Biology Factors Limiting PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesCAPE Biology Factors Limiting PhotosynthesisKashim AliNo ratings yet
- 10 PlasmidsDocument17 pages10 Plasmidsparduman kumarNo ratings yet