Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gait Pattern
Uploaded by
peakiew0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
374 views2 pagesThe document describes four different types of gait or walking patterns: hemiplegic gait, spastic paraparesis gait, Parkinson's disease gait, and cerebellar gait. Hemiplegic gait involves circumduction of the leg and is caused by upper motor neuron lesions from conditions like stroke or spinal cord injury. Spastic paraparesis gait has a scissors-like motion of the legs and is associated with spastic leg paresis and caused by conditions like multiple sclerosis or spinal cord lesions. Parkinson's disease gait is hesitant with shuffling steps and freezing, and is due to insufficient dopamine. Cerebellar gait is unsteady with short, wide steps and is caused
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes four different types of gait or walking patterns: hemiplegic gait, spastic paraparesis gait, Parkinson's disease gait, and cerebellar gait. Hemiplegic gait involves circumduction of the leg and is caused by upper motor neuron lesions from conditions like stroke or spinal cord injury. Spastic paraparesis gait has a scissors-like motion of the legs and is associated with spastic leg paresis and caused by conditions like multiple sclerosis or spinal cord lesions. Parkinson's disease gait is hesitant with shuffling steps and freezing, and is due to insufficient dopamine. Cerebellar gait is unsteady with short, wide steps and is caused
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
374 views2 pagesGait Pattern
Uploaded by
peakiewThe document describes four different types of gait or walking patterns: hemiplegic gait, spastic paraparesis gait, Parkinson's disease gait, and cerebellar gait. Hemiplegic gait involves circumduction of the leg and is caused by upper motor neuron lesions from conditions like stroke or spinal cord injury. Spastic paraparesis gait has a scissors-like motion of the legs and is associated with spastic leg paresis and caused by conditions like multiple sclerosis or spinal cord lesions. Parkinson's disease gait is hesitant with shuffling steps and freezing, and is due to insufficient dopamine. Cerebellar gait is unsteady with short, wide steps and is caused
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
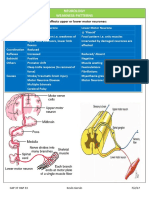
Gait Description Associated signs Causes
Hemiplegia Circumduction gait Difficulty with balance, Upper motor neuron
The foot is plantar flexed motor activities, speech, lesion from any of
and the leg is swung in a swallowing, stiffness of the causes: Stroke
lateral arc (semicircle) muscles, muscle spasm, (especially of the
depression. Problems corticospinal tract),
with developmental spinal cord injury
milestones, behavioural (specifically Brown-
problem, mental Sequard syndrome),
development in children. traumatic brain
injury, encephalitis,
meningitis,
haemorrhages,
neoplasms, cerebral
palsy, MS
Spastic paraparesis Scissors gait Spastic leg paresis, MS, spinal cord
Combined effects of hyperreflexia, clonus, lesions, trauma,
spasticity, unco- extensor plantar hereditary, herniated
ordination and weakness reflexes, arms affected IV discs, infections
of both legs. as well. Tropical Spastic
The legs are flexed may also have paraparesis (HTLV-
slightly at the hip, thighs extraspinal neurological associated
are adducted and legs deficits (eg. myelopathy or
bump together and cross Spinocerebellar, ocular chronic progressive
over each other in a symptoms, mental myelopathy), caused
scissors movement. retardation, dementia, by Human T-
There are short steps, polyneuropathy) lymphotropic virus
side-to-side trunk
movements and
circumduction of legs.
The toes never seem to
leave the floor.
Parkinson’s disease Hesitation in starting. Tremor, bradykinesia, Insufficient
Shuffling instability, lead pipe, dopamine
Freezing: May freeze in cog-wheel rigidity production by the
mid-stride substantial nigra
Festination: Small
shuffling steps
Propulsion: stiff with
head and neck bent,
Retropulsion: patient is
easily pushed backward
and may fall backward
spontaneously
Diminished arm swing,
appear to fall forward as
they walk and have
difficulty making a turn
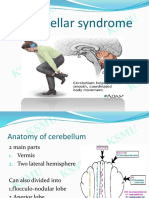
Cerebellar Ataxic gait Asynergy, dysmetria, Focal: stroke,
Unsteady drunken gait dyschronometria, infection, tumour
with cautious short dysdiadochokinesia, Exogenous: alcohol,
steps, which is wide- postural instability, antiepileptics,
based or reeling on a intention tremor, cannabis
narrow base, the patient dysarthria, peculiar B12 deficiency,
staggers towards the writing hereditary, Arnold
affected side if there is a Chiari malformation,
unilateral cerebellar brain degeneration
hemisphere lesion from alcohol, normal
pressure
hydrocephalus etc
Hemiplegic gait
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y160w4sAQNw&feature=related
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BtqWxBUd94I
Spastic gait
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UDgxjRyPe2w&feature=related
Parkinsonian Gait
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j86omOwx0Hk&feature=related
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ylHZWO17W70&feature=related
ataxic gait
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CBlrp-Ok38E&feature=related
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FpiEprzObIU
You might also like
- Lec 2 - Cerebellar AtaxiaDocument2 pagesLec 2 - Cerebellar AtaxiaEmily MurrayNo ratings yet
- Parkinson'S Disease: by - Nikita Borade BPT Final YearDocument42 pagesParkinson'S Disease: by - Nikita Borade BPT Final YearNikks BoradeNo ratings yet
- Neurorehabilitation 1Document439 pagesNeurorehabilitation 1Duncan D'AmicoNo ratings yet
- Back Spine ConditionsDocument2 pagesBack Spine ConditionsNinjaNo ratings yet
- Comparison of UMN & LMN SyndromesDocument2 pagesComparison of UMN & LMN SyndromesPJHGNo ratings yet
- Parkinson-Plus SyndromeDocument2 pagesParkinson-Plus SyndromeRuth May de VillaNo ratings yet
- AtaxiaDocument10 pagesAtaxiaosakaNo ratings yet
- Gait Abnormalities Assessment and CausesDocument12 pagesGait Abnormalities Assessment and CausesMudassar SattarNo ratings yet
- Floppy InfantDocument48 pagesFloppy InfantAlexNo ratings yet
- Neurology Clerkship UWORLD: Brain TumoursDocument13 pagesNeurology Clerkship UWORLD: Brain TumoursHaadi AliNo ratings yet
- Neurology - Weakness PatternsDocument2 pagesNeurology - Weakness PatternsAnisah AliNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument38 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyEka HayatiNo ratings yet
- I. Primary (Idiopathic) ParkinsonismDocument104 pagesI. Primary (Idiopathic) ParkinsonismNathasia SuryawijayaNo ratings yet
- Movement DisordersDocument4 pagesMovement DisordersKeerthikanthGubbalaNo ratings yet
- Pick's Disease Parkinsonian Features Dementia (FluctuationDocument3 pagesPick's Disease Parkinsonian Features Dementia (FluctuationJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- NBME CMS Forms NotesDocument4 pagesNBME CMS Forms NotesJack Guccione100% (7)
- StrokeDocument27 pagesStrokeJASON KO CHIA SHENGNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Syndromes: The Neurosurgical AtlasDocument8 pagesCerebrovascular Syndromes: The Neurosurgical AtlasEduardo Reyna MartínezNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of WeaknessDocument6 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of WeaknessAna LydiaNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy: Dr. Sri Hastuti, SP.S (K) KSM Neurologi Rsudza/Fk Unsyiah 2019Document14 pagesCerebral Palsy: Dr. Sri Hastuti, SP.S (K) KSM Neurologi Rsudza/Fk Unsyiah 2019Afifah NaurahNo ratings yet
- Disease/syndrome Inciting Incident Structures Affected PoliomyelitisDocument12 pagesDisease/syndrome Inciting Incident Structures Affected PoliomyelitismrhemmatNo ratings yet
- Ataxia PresentationDocument11 pagesAtaxia PresentationS RiarNo ratings yet
- Common Conditions of The Lumbar SpineDocument4 pagesCommon Conditions of The Lumbar SpineJames KNo ratings yet
- Neuro Year 3 MedEd Rehaan Khokar 2Document91 pagesNeuro Year 3 MedEd Rehaan Khokar 2Sugoi SagaNo ratings yet
- Where Da Lesion atDocument5 pagesWhere Da Lesion atDeeWallyNo ratings yet
- Neurology Made Easy FinalDocument18 pagesNeurology Made Easy FinalDevin Swanepoel100% (1)
- Alteración Movimientos en Sistémicas Clinic 2015Document29 pagesAlteración Movimientos en Sistémicas Clinic 2015Kharen VerjelNo ratings yet
- Paralysis in Dogs and CatsDocument56 pagesParalysis in Dogs and Catscat clinic pdhbNo ratings yet
- Neurology SheetDocument4 pagesNeurology SheetSyximsh FPNo ratings yet
- Resident Tutorial: AtaxiaDocument50 pagesResident Tutorial: AtaxiaNEuRoLoGisT CoFFeeCuP100% (4)
- Ataxia and Movement Disorders: Clinical Manifestations TreatmentDocument6 pagesAtaxia and Movement Disorders: Clinical Manifestations TreatmentMahfouzNo ratings yet
- Extrapyramidal DiseaseDocument54 pagesExtrapyramidal Diseasemirabel IvanaliNo ratings yet
- Parkinsons - Disease Curs NR 5Document37 pagesParkinsons - Disease Curs NR 5Iliescu DenisaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord DS C1Document76 pagesSpinal Cord DS C1Dagmawi BahiruNo ratings yet
- Neurological Examination SummaryDocument90 pagesNeurological Examination SummaryAlida Taranu TernströmNo ratings yet
- Multiple Cranial NeuropathyDocument13 pagesMultiple Cranial NeuropathyChaerani SalamNo ratings yet
- AthetosisDocument2 pagesAthetosisapi-19973386No ratings yet
- Spinal Cord SyndromeDocument36 pagesSpinal Cord SyndromeSarath ChandranNo ratings yet
- Ataxia: Pediatric Neurology Quick TalksDocument18 pagesAtaxia: Pediatric Neurology Quick TalksAlex GasnasNo ratings yet
- Meded Emq Revision Course Notes Set 1Document44 pagesMeded Emq Revision Course Notes Set 1py siraNo ratings yet
- Lesions of The Motor PathwayDocument28 pagesLesions of The Motor PathwaykehindekolapoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Dioszeghy Peter MononeuropathiesDocument52 pagesDr. Dioszeghy Peter MononeuropathiesAhmad abu-dayyehNo ratings yet
- Neurology: Apprauching and Localizing Neurological LesionDocument53 pagesNeurology: Apprauching and Localizing Neurological LesionMahad IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care For Patient With Neurological DiseaseDocument8 pagesNursing Care For Patient With Neurological DiseaseWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- 002 - Cerebellum PDFDocument45 pages002 - Cerebellum PDFLucas Victor AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Boala ParkinsonDocument16 pagesBoala Parkinsonionut1ilie-1100% (1)
- An Approach To A Floppy InfantDocument33 pagesAn Approach To A Floppy InfantayunisallehNo ratings yet
- 0) Disordersofgaitandbalance - handoutERDocument26 pages0) Disordersofgaitandbalance - handoutERAkim KapsalyamovNo ratings yet
- Extrapyramidal System DisordersDocument41 pagesExtrapyramidal System DisordersAyshe SlocumNo ratings yet
- Stroke RehabilitationDocument57 pagesStroke RehabilitationWahyu FajarNo ratings yet
- Movement DisordersDocument127 pagesMovement DisordersDayanithi AnnamalaiNo ratings yet
- Movement Disorders II "Dyskinesias": Nasser HospitalDocument30 pagesMovement Disorders II "Dyskinesias": Nasser HospitalMahmoud Abu Al AmrainNo ratings yet
- Spastic Paraplegia With Sensory LevelDocument11 pagesSpastic Paraplegia With Sensory LevelHshzggafsNo ratings yet
- Approach To AtaxiaDocument6 pagesApproach To AtaxiaVivek KumarNo ratings yet
- CerebullamDocument2 pagesCerebullamMahmoud Abu MayalehNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examination of A Case of ParaplegiaDocument27 pagesClinical Examination of A Case of Paraplegiaswathi bs0% (2)
- The Nervous System EditedDocument7 pagesThe Nervous System EditedFev BanataoNo ratings yet
- Neurology Topics: Degenerative DiseasesDocument57 pagesNeurology Topics: Degenerative Diseasesलुकास विडालNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy (CP) : Epidemiology and EtiologyDocument5 pagesCerebral Palsy (CP) : Epidemiology and EtiologyMuhammad MohsinNo ratings yet
- Bengaluru BDA RMP 2031 PD Index MapDocument206 pagesBengaluru BDA RMP 2031 PD Index MapmyskmeNo ratings yet
- Start DateDocument2 pagesStart DateHussainNo ratings yet
- Production Technology of Cow PeaDocument20 pagesProduction Technology of Cow PeaMUHAMMAD AQEELNo ratings yet
- Annexure 5.14 BC Mix DesignDocument10 pagesAnnexure 5.14 BC Mix Designmiesty50% (2)
- Your Ights: MR Simrat Singh ARORADocument4 pagesYour Ights: MR Simrat Singh ARORAsimratsingh01No ratings yet
- Assignment Arts Appreciation: Submitted To: Mam Sana Submitted By: Mahnoor Akhter Session: 2018-2022 Semester: 1Document16 pagesAssignment Arts Appreciation: Submitted To: Mam Sana Submitted By: Mahnoor Akhter Session: 2018-2022 Semester: 1Mahnoor AkhterNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Characteristics of A Good Civil Engineer: D. Blockley and RobertsonDocument4 pagesAnalysis of The Characteristics of A Good Civil Engineer: D. Blockley and RobertsonsujupsNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Ko Drum 43-401Document14 pagesData Sheet Ko Drum 43-401sokrat sebtiNo ratings yet
- BS EN 1992 PART 4-2018 Design of Concrete Structures - Design of Fastenings For Use in ConcreteDocument132 pagesBS EN 1992 PART 4-2018 Design of Concrete Structures - Design of Fastenings For Use in Concrete陈辕100% (2)
- ITC Johnston Complete Family Pack Font ListDocument2 pagesITC Johnston Complete Family Pack Font ListSenthuTu0% (1)
- Tutorial 5 - Flexural Members - Lateral Torsional BucklingDocument32 pagesTutorial 5 - Flexural Members - Lateral Torsional BucklingChan Keng ChunNo ratings yet
- PTE Academic - Strategies For Summarize The Written TextDocument9 pagesPTE Academic - Strategies For Summarize The Written TextPradeep PaudelNo ratings yet
- Edla English Unit 2019Document44 pagesEdla English Unit 2019api-506409356No ratings yet
- One Plus Case StudyDocument9 pagesOne Plus Case StudyShubham Shimpi50% (2)
- Reasearch ProposalDocument9 pagesReasearch Proposalamel amoulaNo ratings yet
- Bài Kt 2 Biên Dịch 1-LiêmDocument10 pagesBài Kt 2 Biên Dịch 1-LiêmNguyen Loan100% (1)
- Short Story Analysis RubricDocument3 pagesShort Story Analysis RubricLorybelle CastilloNo ratings yet
- Brdy 6ed Ch12 SolutionDocument128 pagesBrdy 6ed Ch12 SolutionAchmad RochliadiNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Examination in Household Services 9Document3 pages1st Quarter Examination in Household Services 9Aubrey Lynn Joyohoy100% (1)
- Abstract Yessy Marzona Icge VDocument21 pagesAbstract Yessy Marzona Icge VYessy MarzonaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Foundation of ControlDocument25 pagesChapter 18 Foundation of Controlhalka2314No ratings yet
- Design of Septic TankDocument6 pagesDesign of Septic TankJanissaries NivercaNo ratings yet
- Animal ExtinctionDocument2 pagesAnimal Extinctionaliah hudaNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument6 pagesReadmecamiloNo ratings yet
- Cs2252 - MPMC 16 M With Answers Upto 2Document40 pagesCs2252 - MPMC 16 M With Answers Upto 2archumeenabaluNo ratings yet
- Spotifyum V4 PDFDocument12 pagesSpotifyum V4 PDFBrzina1921No ratings yet
- Fundraising Guide For Rescue TeamsDocument5 pagesFundraising Guide For Rescue TeamsDecisions For HeroesNo ratings yet
- Garden Namkeen TestDocument12 pagesGarden Namkeen Testramakrishna.goliNo ratings yet
- MAX232Document4 pagesMAX232janakiram473No ratings yet
- Winitzki - Heidelberg Lectures On Advanced General Relativity 2007Document156 pagesWinitzki - Heidelberg Lectures On Advanced General Relativity 2007winitzkiNo ratings yet