Professional Documents
Culture Documents
42
Uploaded by
Vince Bagsit PolicarpioCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
42
Uploaded by
Vince Bagsit PolicarpioCopyright:
Available Formats
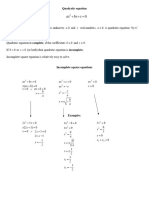
§4-2 QUADRATIC INEQUALITIES
Definition Quadratic inequalities in one variable are inequalities which can be written in one of
the following forms: ax 2 + bx + c > 0 ,
2
ax + bx + c < 0 ,
2
ax + bx + c ≥ 0 or
2
ax + bx + c ≤ 0 where a, b and c are real numbers.
Procedure Solving Quadratic Inequalities
1. Move all terms to one side.
2. Simplify and factor the quadratic expression.
3. Find the roots of the corresponding quadratic equation.
4. Use the roots to divide the number line into regions.
5. Test each region using theinequality.
2
Example 1 Solve the inequality, x > x + 2 .
2
Solution x > x+2
2
x − x−2 > 0
(x - 2)(x + 1) > 0
The corresponding equation is (x - 2)(x + 1) = 0 so…
x-2 = 0 or x+1 = 0
x = 2 x = -1
I II III
-7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Now we test one point in each region.
Region Test Point Inequality Status
I x = -2 (x - 2)(x + 1) = (-2 - 2)(-2 + 1) = 4 > 0 True
II x = 0 (x - 2)(x + 1) = (0 - 2)(0 + 1) = -2 > 0 False
III x = 3 (x - 2)(x + 1) = (3 - 2)(3 + 1) = 4 > 0 True
-7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
So the solution to this inequality is x < -1 or x > 2.
Copyright©2007 by Lawrence Perez and Patrick Quigley
Example 2 Solve the inequality, (x + 3)2 ≥ 2(x 2 + 7).
Solution (x + 3)2 ≥ 2(x 2 + 7)
2 2
x + 6x + 9 ≥ 2 x + 14
2
− x + 6x − 5 ≥ 0
−(x 2 − 6x + 5) ≥ 0
− (x 2 − 6x + 5) 0
≤
−1 −1
2
x − 6x + 5 ≤ 0
(x - 1)(x - 5) ≤ 0
The corresponding equation is (x - 1)(x - 5) = 0 so…
x-1 = 0 or x-5 = 0
x = 1 x = 5
I II III
-7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Now we check one point in each region.
Region Test Point Inequality Status
I x=0 (x - 1)(x - 5) = (0 - 1)(0 - 5) = 5 < 0 False
II x=2 (x - 1)(x - 5) = (2 - 1)(2 - 5) = -3 < 0 True
III x=6 (x - 1)(x - 5) = (6 - 1)(6 - 5) = 5 < 0 False
-7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
So the solution to this inequality is 1 ≤ x ≤ 5.
Copyright©2007 by Lawrence Perez and Patrick Quigley
§4-2 PROBLEM SET
Solve each quadratic inequality, and graph the solution on a number line.
y 2 − 17y + 70 < 0 x + 9x + 13 > −7
2
1. 2.
3. x(x + 1) > 112 − 5x 4. a 2 + 3a + 2 < −3(a + 2)
5. 2x ≤ 5x − 2
2
6. 10 − 9y ≥ −2y 2
7. b(b + 3) ≥ −2 8. a 2 ≤ 4(2a − 3)
y 2 − 17y + 70 < 0 x + 9x + 13 > −7
2
9. 10.
x(x + 1) > 112 − 5x a + 25 < 10a
2
11. 12.
13. 2d + 5d ≤ 12
2
14. a 2 + 3a + 2 ≥ −3(a + 2)
15. 10 − 9y ≥ −2y 2 2x ≤ 5x − 2
2
16.
17. c(c + 4) < 3 + 3(9 + c) 18. 2a(a + 6) > 5 − a(a + 2)
19. b(b + 3) > −2 20. a 2 < 4(2a − 3)
21. (x + 3)2 ≤ 6(x + 15) 22. 2x + 7 ≥ 9x
2
7x 2 ≥ 4(1+ 3x) 3x + 7x ≤ −2
2
23. 24.
−8 < 4(x − x 2 ) x − x−2> 0
2
25. 26.
2k + 3k − 2 > 0 t + 2t − 3 < 0
2 2
27. 28.
29. 4x + 8 ≤ 33x
2
30. x 2 ≥ 4(x − 5)
x + 4 ≥ 2x − 3x 32. 10 − 3x ≤ x 2
2 2
31.
33. 4 < 13x − 3x
2
34. 6(x 2 + 1) > −13
6x − x > 8 20a < 1 − a
2 2
35. 36.
37. 8x ≤ −3(1 − x 2 ) 38. y 2 ≥ 25
t + 18 ≥ 11t 3x(x + 1) ≤ x(x + 5)
2
39. 40.
x <8 x + 3x > 12
2 2
41. 42.
2t > 9t + 18 4x − 9x + 2 < 0
2 2
43. 44.
Copyright©2007 by Lawrence Perez and Patrick Quigley
§4-2 PROBLEM SOLUTIONS
1. 7 < y < 10 2. x < -5 or x > -4 3. x < -14 or x > 8
1 5
4. -4 < a < -2 5. ≤ x ≤2 6. y ≤ 2 or y ≥
2 2
7. b ≤ -2 or b ≥ -1 8. 2≤a≤6 9. 7 < y < 10
10. x < -5 or x > - 11. x < -14 or x > 8 12. no solution
3 5
13. −4 ≤ d ≤ 14. x ≤ -4 or x ≥ -2 15. y ≤ 2 or y ≥
2 2
1 1
16. ≤ x ≤2 17. -6 < c < 5 18. a < -5 or a >
2 3
19. b ≤ -2 or b ≥ -1 20. 2<a<6 21. -9 ≤ x ≤ 9
7 2 1
22. x < 1 or x ≥ 23. x≤− or x ≥ 2 24. −2 ≤ x ≤ −
2 7 3
1
25. -1 < x < 2 26. x < -1 or x > 2 27. k < -2 or k >
2
1
28. -3 < t < 1 29. ≤ x ≤8 30. all real numbers
4
1
31. -1 < x < 4 32. x ≤ -5 or x ≥ 2 33. <x<4
3
1 1
34. no real solutions 35. 2 < x < 4 36. − <x<
4 5
1
37. x≤− or x ≥ 3 38. x ≤ -5 or x ≥ 5 39. t ≤ 2 or t ≥ 9
3
40. 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 41. −2 2 < x < 2 2
−3 − 57 −3 + 57
42. x< or x >
2 2
3 1
43. t <− or t > 6 44. < x <2
2 4
Copyright©2007 by Lawrence Perez and Patrick Quigley
You might also like
- Laptop Power SequenceDocument16 pagesLaptop Power SequenceDelwar Hossain90% (10)
- Green Antz Eco BricksDocument10 pagesGreen Antz Eco BricksVince Bagsit Policarpio75% (4)
- BS en 12583 - 2014 - Gas Infrastructure. Compressor Stations. Functional Requirements.Document56 pagesBS en 12583 - 2014 - Gas Infrastructure. Compressor Stations. Functional Requirements.SDP02No ratings yet
- Quadratic Inequalities: + BX + C 0, Ax Ax AxDocument5 pagesQuadratic Inequalities: + BX + C 0, Ax Ax AxDominic Dalton CalingNo ratings yet
- Eas Workbook Ncea 3 Calculus 1421359238Document27 pagesEas Workbook Ncea 3 Calculus 1421359238Rachel SimNo ratings yet
- Ecuaciones Algebraicas 4ºesoDocument3 pagesEcuaciones Algebraicas 4ºesokkkkkNo ratings yet
- A Level Preparation - Equations and Inequalities (Answers)Document7 pagesA Level Preparation - Equations and Inequalities (Answers)mhacunaNo ratings yet
- Serie EquationsDocument2 pagesSerie EquationsZA9OF FFNo ratings yet
- Guà - A à - LgebraDocument4 pagesGuà - A à - LgebraSofia OgaldeNo ratings yet
- Nama: Muhamad Aldy Akbar Nim: 41520110042 Teknik InformatikaDocument3 pagesNama: Muhamad Aldy Akbar Nim: 41520110042 Teknik InformatikaDYBAR 1415No ratings yet
- SolJul2022 3Document4 pagesSolJul2022 3joshuathepapuNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Solving Quadratic Equations by Factorization and Completing The SquareDocument3 pages3.5 Solving Quadratic Equations by Factorization and Completing The SquareAanya RalhanNo ratings yet
- Jorge RDZ LimitesDocument3 pagesJorge RDZ LimitesoscarNo ratings yet
- ECUACIONES Y INECUACIONES DE SEGUNDO GRADO Y SUPERIORDocument5 pagesECUACIONES Y INECUACIONES DE SEGUNDO GRADO Y SUPERIORJuan JoséNo ratings yet
- A. Desigualdades Polinomiales y Racionales: Obtenga El Conjunto de Soluciones de Las Siguientes Desigualdades. 1 3)Document7 pagesA. Desigualdades Polinomiales y Racionales: Obtenga El Conjunto de Soluciones de Las Siguientes Desigualdades. 1 3)eryaque1004No ratings yet
- I. Repasando Lo Aprendido: Guía de InecuacionesDocument2 pagesI. Repasando Lo Aprendido: Guía de InecuacionesNicolás PerićNo ratings yet
- AM SLN 01 (E)Document23 pagesAM SLN 01 (E)api-3842687100% (1)
- Pertemuan 2 Kalkulus IDocument4 pagesPertemuan 2 Kalkulus IMirandaa Sukma NNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Calculus An Applied Approach 10Th Edition by Larson Isbn 1305860918 9781305860919 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Calculus An Applied Approach 10Th Edition by Larson Isbn 1305860918 9781305860919 Full Chapter PDFbenjamin.smith112100% (12)
- X X X X X X: Problemas Por Factorización Problema #1Document3 pagesX X X X X X: Problemas Por Factorización Problema #1Jose Esteban MonroyNo ratings yet
- HIGH School IV REAL NUMBERS-LINEAR EQUATIONS IN ONE VARIABLEDocument7 pagesHIGH School IV REAL NUMBERS-LINEAR EQUATIONS IN ONE VARIABLENenad JanicijevicNo ratings yet
- Math Module 3Document4 pagesMath Module 3Cristina AmantiadNo ratings yet
- 1.HIGH School VIII QUADRATIC EQUATIONS AND QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS-Quadratic EquationDocument8 pages1.HIGH School VIII QUADRATIC EQUATIONS AND QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS-Quadratic Equationkhrr7brbpcNo ratings yet
- Level NS Calculus I Course Questions Solutions UpdatedDocument158 pagesLevel NS Calculus I Course Questions Solutions UpdatedssNo ratings yet
- 9 Lesson 1Document2 pages9 Lesson 1Sarah SaraelNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Resueltos Unidad IiiDocument13 pagesEjercicios Resueltos Unidad IiiGrecia HauNo ratings yet
- 1 Quadratic Equations in One Unknown (I) : Review Exercise 1 (P. 1.5)Document34 pages1 Quadratic Equations in One Unknown (I) : Review Exercise 1 (P. 1.5)HarryNo ratings yet
- Math Prep 2020 Module 3.3: Quadratic Inequalities: What Makes An Inequality Quadratic?Document4 pagesMath Prep 2020 Module 3.3: Quadratic Inequalities: What Makes An Inequality Quadratic?Fons Roxas-ChuaNo ratings yet
- Gr 10 TEST Memo T1 2024Document5 pagesGr 10 TEST Memo T1 2024fezekanxumalo254No ratings yet
- F4 Textbook Answer C2 (ENG)Document45 pagesF4 Textbook Answer C2 (ENG)Hui Ern SeeNo ratings yet
- GenMath LAS-4 Venze, Adrianne D. MacadayDocument6 pagesGenMath LAS-4 Venze, Adrianne D. MacadayVenze Adrianne Damasco MNo ratings yet
- Rational Function, Equation and InequalityDocument12 pagesRational Function, Equation and InequalityJohnNo ratings yet
- Solving rational inequalitiesDocument21 pagesSolving rational inequalitiesZyra Mae VeranoNo ratings yet
- Basic Maths AssignmentsDocument15 pagesBasic Maths AssignmentsKunalNo ratings yet
- Completing The Square (A 1)Document6 pagesCompleting The Square (A 1)Alexander BautistaNo ratings yet
- QuadEquations PPT Alg2Document25 pagesQuadEquations PPT Alg2Joyce JuarezNo ratings yet
- Límites Y Continuidad: Nombre: Sánchez Álvarez Jorge Arturo Nivel: Primer Semestre ParaleloDocument12 pagesLímites Y Continuidad: Nombre: Sánchez Álvarez Jorge Arturo Nivel: Primer Semestre ParaleloJorge SnchzNo ratings yet
- Ekuazio ArrazionalakDocument1 pageEkuazio ArrazionalakAinaraNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 5 - Quadratic EquationsDocument111 pagesSelina Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 5 - Quadratic Equationsdinesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Limites y ContinuidadDocument121 pagesLimites y ContinuidadJonathan ArenasNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Paper 1: I X II X+ y 4 III y 4 XDocument4 pagesAdd Maths Paper 1: I X II X+ y 4 III y 4 XAishey AshNo ratings yet
- Fracciones AlgebraicasDocument2 pagesFracciones AlgebraicasJuan Manuel CasinoNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1esoDocument3 pagesAlgebra 1esoalberto580ANo ratings yet
- 5 Grado AlgebraDocument1 page5 Grado AlgebraRubenDionicioCisnerosNo ratings yet
- National University of Singapore: X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X XDocument5 pagesNational University of Singapore: X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X XdkNo ratings yet
- 10th Science Ex 1 1 Amir ShehzadDocument8 pages10th Science Ex 1 1 Amir ShehzadShoaib ChNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS SOLUTIONSDocument8 pagesMATHEMATICS SOLUTIONSAsiaNo ratings yet
- Important Notes of 10th Class Math Exercise 1.1Document8 pagesImportant Notes of 10th Class Math Exercise 1.1Tayyabah ShahNo ratings yet
- Class 11th ch-15 Linear InequationsDocument1 pageClass 11th ch-15 Linear InequationsSamarjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Algebra by Vikas Gupta SolutionsDocument263 pagesAlgebra by Vikas Gupta Solutionspqgfd4qjv4No ratings yet
- Y11 Mid Year 2022 p1Document6 pagesY11 Mid Year 2022 p1Let's hit 100k sub without any videosNo ratings yet
- KOLOKVIJUMDocument19 pagesKOLOKVIJUMalminamahovkic1No ratings yet
- P6 Maths Unit-6 (Algebraic Expansion)Document4 pagesP6 Maths Unit-6 (Algebraic Expansion)pyizawbhoneNo ratings yet
- Desarrollo Guia 2Document4 pagesDesarrollo Guia 2Maria Fernanda YaupiNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 2 Kalkulus IDocument4 pagesPertemuan 2 Kalkulus IBintang BintangNo ratings yet
- 35 PDFDocument4 pages35 PDFAce RoiNo ratings yet
- Solucion de Las EcuacionesDocument3 pagesSolucion de Las EcuacionesLaura Camila Bejarano CifuentesNo ratings yet
- Trabajo de Mate 2parcialDocument1 pageTrabajo de Mate 2parcialElizabeth MezaNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Q1 Module2bDocument13 pagesMath 9 Q1 Module2bEDUARDO MALABAGNo ratings yet
- LimitDocument11 pagesLimitKristan Glen PulidoNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 3 - Limits of Algebraic FunctionsDocument4 pagesActivity No. 3 - Limits of Algebraic FunctionsMarielle Dale SolanoNo ratings yet
- Maths IIT-JEE exercise functionsDocument459 pagesMaths IIT-JEE exercise functionsPlato PhilosopherNo ratings yet
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- A' A D C B: Produced by An Autodesk Educational ProductDocument1 pageA' A D C B: Produced by An Autodesk Educational ProductVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Schedule of RC beams for 2F, roof deck and upper roof deckDocument1 pageSchedule of RC beams for 2F, roof deck and upper roof deckVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Civil / Structural Construction Notes: Nearest Faultline Site Location FromDocument1 pageCivil / Structural Construction Notes: Nearest Faultline Site Location FromVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- ASEP FORUM on seismic protectionDocument1 pageASEP FORUM on seismic protectionVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- 364 419 PDFDocument56 pages364 419 PDFVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument87 pagesNotesVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- SC01 SC02 PDFDocument1 pageSC01 SC02 PDFVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Floor Plans 3fDocument1 pageFloor Plans 3fVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- MFDocument134 pagesMFVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Gantry Cranes Brochure PDFDocument40 pagesGantry Cranes Brochure PDFVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Bit CoinDocument59 pagesBit CoinChitradeep Dutta RoyNo ratings yet
- StairsDocument21 pagesStairstomnubiNo ratings yet
- Slab DesignDocument15 pagesSlab DesignLawrence Arellano FernandezNo ratings yet
- R-C-D-C FE Download LinkDocument1 pageR-C-D-C FE Download LinkVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Framing PlanDocument1 pageFraming PlanVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- PDF With Dimensions 062518Document1 pagePDF With Dimensions 062518Vince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Warehouse Storage Warehouse Storage: Parking AreaDocument1 pageWarehouse Storage Warehouse Storage: Parking AreaVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- 01 Additional Excavation in Shaded AreasDocument1 page01 Additional Excavation in Shaded AreasVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- 02 Bottom Bar and FTB Bar Arrangement (Rev 1)Document1 page02 Bottom Bar and FTB Bar Arrangement (Rev 1)Vince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Tondo 3 Story TownhouseDocument1 pageTondo 3 Story TownhouseVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- S02 Stair Rebars ArrangementDocument1 pageS02 Stair Rebars ArrangementVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Slab DesignDocument15 pagesSlab DesignLawrence Arellano FernandezNo ratings yet
- Ground FLR PlanDocument1 pageGround FLR PlanVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Acceptance Letter for ICCPM 2018 Conference PresentationDocument1 pageAcceptance Letter for ICCPM 2018 Conference PresentationVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- 01 Certificate of Engagement in GTechDocument1 page01 Certificate of Engagement in GTechVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- AssigDocument2 pagesAssigVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- 314 02Document7 pages314 02Vince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Lim Is 5 Divided by 3 PDFDocument1 pageLim Is 5 Divided by 3 PDFVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Convergence of eDocument2 pagesConvergence of eVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Earning Elivery Odalities Study Notebook: Guinayangan North DistrictDocument48 pagesEarning Elivery Odalities Study Notebook: Guinayangan North DistrictLORENA CANTONG100% (1)
- Product PlanningDocument23 pagesProduct PlanningGrechen CabusaoNo ratings yet
- Snel White Paper 2020Document18 pagesSnel White Paper 2020Zgodan NezgodanNo ratings yet
- Installation Procedure for Castwel Supercast-II CastableDocument3 pagesInstallation Procedure for Castwel Supercast-II CastableRAJKUMARNo ratings yet
- Series Portable Oscilloscopes: Keysight DSO1000A/BDocument15 pagesSeries Portable Oscilloscopes: Keysight DSO1000A/BNestor CardenasNo ratings yet
- "Smart Attendance Using F Ttendance Management Using Face Recognition" Anagement SystemDocument13 pages"Smart Attendance Using F Ttendance Management Using Face Recognition" Anagement Systemamer HNo ratings yet
- Bio-Climatic Tower/Eco-Tower: Bachelor of ArchitectureDocument12 pagesBio-Climatic Tower/Eco-Tower: Bachelor of ArchitectureZorawar Singh Basur67% (3)
- Standard OFR NATIONAL L13A BDREF Ed1.1 - 24 - JanvierDocument640 pagesStandard OFR NATIONAL L13A BDREF Ed1.1 - 24 - JanvierosmannaNo ratings yet
- Flutter Layout Cheat SheetDocument11 pagesFlutter Layout Cheat SheetJarrett Yew0% (1)
- mf8240 160824142620 PDFDocument698 pagesmf8240 160824142620 PDFArgopartsNo ratings yet
- Air Blue E-TicketDocument1 pageAir Blue E-TicketMuneeb Ahmed100% (3)
- English Test 03Document6 pagesEnglish Test 03smkyapkesbi bjbNo ratings yet
- Industrial Visit Report - 08 09 2018Document11 pagesIndustrial Visit Report - 08 09 2018HARIKRISHNA MNo ratings yet
- Materials Selection For Engineering DesignDocument31 pagesMaterials Selection For Engineering Designsyamsudin2006No ratings yet
- Operator Interface SERIES 300 Device Platform EAGLE OS ET-316-TXDocument6 pagesOperator Interface SERIES 300 Device Platform EAGLE OS ET-316-TXDecoNo ratings yet
- Duration of LTMDocument3 pagesDuration of LTMsamueldaNo ratings yet
- IGNOU FEG-02 (2011) AssignmentDocument4 pagesIGNOU FEG-02 (2011) AssignmentSyed AhmadNo ratings yet
- E-Governance in KeralaDocument10 pagesE-Governance in KeralaRahmath SafeenaNo ratings yet
- False CeilingDocument70 pagesFalse CeilingBharti Sikri93% (15)
- Drilling RisersDocument13 pagesDrilling Risersadvantage025No ratings yet
- UAE Branch AGM 2018/19 ElectionsDocument6 pagesUAE Branch AGM 2018/19 ElectionsDavidNo ratings yet
- Bid ProcessDocument85 pagesBid ProcessRobiatol Adawiah Mohammad ShamsidiNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 2 Original TestDocument6 pagesPhysics Chapter 2 Original TestJanina OrmitaNo ratings yet
- Understand Shell and Rib Feature - Creo Elements ProDocument8 pagesUnderstand Shell and Rib Feature - Creo Elements ProWaqas AhmadNo ratings yet
- T5N 630 PR221DS-LS/I in 630 3p F FDocument3 pagesT5N 630 PR221DS-LS/I in 630 3p F FDkalestNo ratings yet
- Spatial Personality For Human Space InteractionDocument10 pagesSpatial Personality For Human Space Interactionavijitsaha bornoNo ratings yet
- Let's Mingle Chat Invite ExamplesDocument22 pagesLet's Mingle Chat Invite ExamplesCarmen BalbuenaNo ratings yet
- BrainSpace - January 2024 CADocument46 pagesBrainSpace - January 2024 CARafal ZawadkaNo ratings yet