Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TCIS Study Guide PDF
Uploaded by
AndrewOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TCIS Study Guide PDF
Uploaded by
AndrewCopyright:
Available Formats
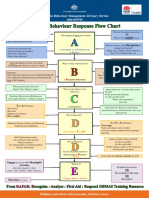
Successful TCIS implementation 4 stages of a Power Struggle Crisis
• Leadership & Administration
• Stressful Incident
Communication
• Social Work & Clinical Services
• Student’s Feelings
is 55% facial
• Data driven incident monitoring
• Student’s Behavior
expressions,
• Supervision and post crisis response
38% Tone of
• Adult’s Response
• Training Voice, and only
7% is your
Setting Conditions words.
Strategies to avoid a power struggle
• Organizational
• Self talk
• Personal
• Listening & Validating Feelings
Goals of Emotional
• Environmental
First Aid
• Manage Environment
• Instructional
• Student Choices
• Promote
• Community Culture
• Change Expectations
immediate help to
“A setting condition is anything that reduce emotional
intensity
makes a crisis more of less likely.”
Active Listening • Resolve the crisis
• Validates Feelings
• Keep the student
Stress Model of Crisis in the activity
• Reduces Defensiveness
1. Pre-crisis - Baseline
• Promotes Change
2. Trigger - Agitated
Strategies of
• Shows you care
3. Escalation - Aggressive
Emotional First Aid
Non-verbal techniques include
4. Outburst - Violence
• Drain off Emotions
nodding, eye-contact, silence, and • Clarify Events
5. Recovery - Return to Baseline
your facial expressions. • Maintain
Relationship
Educator • Remind students
Behavior Support Techniques of expectations
• Manage Environment
Outcomes Firefighter
• Prompting
Types of Anger
Abuser • Hurdle Help
Reactive anger is
• Redirection
uncontrolled,
• Proximity
emotional, and
Self Awareness Questions
• Directive Statement
impulsive.
1. How am I Feeling?
Proactive Anger is
• Time Away
2. What the the child want/need/feel?
deliberate,
“The key to using Behavioral Support
3. How is the environment affecting methodical, and
Techniques is to match them to student
calm
the child?
needs.”
4. How do I best respond?
Crisis co-regulation Pain Based
L.S.I. (Life Space Intervention)
• Self Awareness (Think) Behaviors
• Isolate the conversation
• Use positive self talk
• Aggressivness
• Ask yourself the 4 questions
• Explore the child’s P.O.V.
• Impulsivity
• Verbal Strategies (Say) • Summarize their feelings • Defiance
• Say very little
• Connect feelings to behavior • Running Away
• L.S.I.
• Alternative behaviors discussed • Inability to
• Monitor your tone of voice
• Plan developed & practiced regulate emotions
• Use understanding responses
• Enter student back into activity
• Re-enacting
such as:
trauma
• I can see. . .
“L.S.I. is a therapeutic verbal strategy
• When you. . .
for young people”
• I know we. . .
• I am sorry that. . .
“Remember, all
Goals of L.S.I.
• Non-Verbal Strategies (Do) behaviors have
• Take a deep breath
• Return the child to baseline
meaning, therefore
• Have an open stance
• Clarify the events
• Repair & restore the relationship
student’s behaviors
• Step back
• Give it time
• Teach coping skills
reflect their needs."
• Sit down
• Reintegrate back into the class
• Control your body language
4 elements that make an incident potentially violent
Trigger Target Weapon Motivation
“To reduce the risk of violence remove one of these.”
You might also like
- Saying Goodbye to Your Family Pet: A Parent's Guide to Pet LossFrom EverandSaying Goodbye to Your Family Pet: A Parent's Guide to Pet LossNo ratings yet
- Point of Entry: The Preschool-to-Prison PipelineDocument25 pagesPoint of Entry: The Preschool-to-Prison PipelineCenter for American ProgressNo ratings yet
- Communication Choice Board BundleDocument5 pagesCommunication Choice Board BundleMadhu sudarshan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Iep Impact Examples 3Document3 pagesIep Impact Examples 3api-539726271100% (1)
- P.S.S.T. Public School Speech Therapist: (The Best Kept Secret in the Public Schools)From EverandP.S.S.T. Public School Speech Therapist: (The Best Kept Secret in the Public Schools)No ratings yet
- Evidence+Based+Practices+for+Early+R+Therapy Full+Handout Lindsey+HockelDocument45 pagesEvidence+Based+Practices+for+Early+R+Therapy Full+Handout Lindsey+HockelNoha Ibraheem Helmy100% (1)
- A Year of Core: Week 1: WantDocument13 pagesA Year of Core: Week 1: WantElizabeth SullivanNo ratings yet
- Parents School Therapy Guide PDFDocument18 pagesParents School Therapy Guide PDFMarta MartNo ratings yet
- IPA Chart and Places of ArticulationDocument3 pagesIPA Chart and Places of ArticulationKelyne LeeNo ratings yet
- Days of The WeekDocument4 pagesDays of The WeekPatrícia Argôlo RosaNo ratings yet
- De-Escalation Techniques: Strategies For Preventing The Escalation of Behavior in The School SettingDocument52 pagesDe-Escalation Techniques: Strategies For Preventing The Escalation of Behavior in The School SettingPablo escorcheNo ratings yet
- Iep Guidance ResourcesDocument4 pagesIep Guidance Resourcesapi-343665078100% (1)
- Within Word Stage BrochureDocument2 pagesWithin Word Stage Brochureapi-514989921No ratings yet
- Putting It Into PersepectiveDocument4 pagesPutting It Into PersepectiveAngelaNo ratings yet
- Expected and Unexpected Behavior Sorts FreebieDocument7 pagesExpected and Unexpected Behavior Sorts FreebieSeemaNoorNo ratings yet
- Speak OutDocument44 pagesSpeak OutJackie MurtaghNo ratings yet
- Leadership Personality QuizesDocument1 pageLeadership Personality Quizesapi-546585538No ratings yet
- Self Assessment Zones PDFDocument1 pageSelf Assessment Zones PDFRachelNo ratings yet
- AAC Technologies For Young Children PDFDocument18 pagesAAC Technologies For Young Children PDFDayna DamianiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan SDocument38 pagesLesson Plan SLuis SeixasNo ratings yet
- Circle Under Berry Educator GuidesDocument5 pagesCircle Under Berry Educator GuidesChronicleBooksNo ratings yet
- WWW Helpguide Org Mental Effective Communication Skills HTMDocument9 pagesWWW Helpguide Org Mental Effective Communication Skills HTMPrakhar KumarNo ratings yet
- 24AnimalSightWordChants PDFDocument7 pages24AnimalSightWordChants PDFRachelNo ratings yet
- FREESightWordMiniBook 1Document13 pagesFREESightWordMiniBook 1Ach LeadNo ratings yet
- Are You Getting Enough? (3) The Supervision ProcessDocument2 pagesAre You Getting Enough? (3) The Supervision ProcessSpeech & Language Therapy in Practice100% (1)
- A Guide For Middle School Students With Autism in College Readiness - FinalDocument2 pagesA Guide For Middle School Students With Autism in College Readiness - Finalapi-447504969No ratings yet
- Strategy 13 Presentation - Social Emotional LearningDocument29 pagesStrategy 13 Presentation - Social Emotional Learningapi-588940234No ratings yet
- Jennifer Eazells Ascl 599 Assignment 2 - Community Handbook CompressedDocument148 pagesJennifer Eazells Ascl 599 Assignment 2 - Community Handbook Compressedapi-242610364No ratings yet
- DBTDocument46 pagesDBTDiana Davis100% (1)
- Behaviour Response Flow Chart 5 Nov 2012Document1 pageBehaviour Response Flow Chart 5 Nov 2012jakilaNo ratings yet
- Dialectical Behavior TherapyDocument44 pagesDialectical Behavior TherapyRavitejaNo ratings yet
- Strss Mannagement & COPING SKILLSDocument36 pagesStrss Mannagement & COPING SKILLSImon PaulNo ratings yet
- Dialectical Behavioural TherapyDocument47 pagesDialectical Behavioural TherapyAthul Raj100% (1)
- SIEGEL - Tailoring MindfulneDocument16 pagesSIEGEL - Tailoring Mindfulnejohannquesada100% (1)
- Stress Management by AlankarDocument26 pagesStress Management by AlankaralankarmathurNo ratings yet
- Stress Management: Counseling AssignmentDocument8 pagesStress Management: Counseling Assignmenthr4everNo ratings yet
- Adlerian TherapyDocument21 pagesAdlerian TherapyMA. ESPERANZA ORDANEZANo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Family and Consumer SkillsDocument15 pagesReviewer in Family and Consumer SkillsKevin Nichols Abacan100% (2)
- Psych Reg Disruptive Behavioural Disorders 2009Document79 pagesPsych Reg Disruptive Behavioural Disorders 2009hopeIshanzaNo ratings yet
- Reflective Questions on Identifying, Understanding and Managing EmotionsDocument1 pageReflective Questions on Identifying, Understanding and Managing EmotionsAndreasNo ratings yet
- DBT OverviewtDocument2 pagesDBT OverviewtKrysta DonnellyNo ratings yet
- Health Ed # 4 OnlineDocument2 pagesHealth Ed # 4 OnlineRam AugustNo ratings yet
- Coaching For A Personal Best PerformanceDocument35 pagesCoaching For A Personal Best PerformanceJohn DacanayNo ratings yet
- Stress Management by SumitDocument26 pagesStress Management by Sumitanurag_2011No ratings yet
- GROUPXDocument6 pagesGROUPXNaila DannNo ratings yet
- New Personal Effectiveness 1Document32 pagesNew Personal Effectiveness 1kenneth jajaNo ratings yet
- 28 CounselingDocument91 pages28 CounselingLany T. CataminNo ratings yet
- 7 Anxiety & Depression Reducing Techniques For AdolescentsDocument8 pages7 Anxiety & Depression Reducing Techniques For AdolescentsLILIANA VALDOVINOSNo ratings yet
- HFLE Presentation - NSC SecondaryDocument29 pagesHFLE Presentation - NSC SecondaryGervent GayleNo ratings yet
- Keterampilan Dasar KonselingDocument47 pagesKeterampilan Dasar KonselingNadiah CahyaniNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1566963562973Document4 pagesOrca Share Media1566963562973Anne Martha Acuña NeronaNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Theories of CounselingDocument114 pagesTopic 7 Theories of Counselingdicksandayo8No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Workplace AttitudeDocument46 pagesChapter 4 Workplace AttitudeSiti Sarah Zalikha Binti Umar BakiNo ratings yet
- PsychodynamicDocument49 pagesPsychodynamicManvi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy Webinar SlidesDocument49 pagesDialectical Behavior Therapy Webinar SlidesJanelle100% (1)
- Sociology PrsentationDocument31 pagesSociology PrsentationSYED ARSALANNo ratings yet
- Act With Choice v12.05.2021Document2 pagesAct With Choice v12.05.2021Ami LengadeNo ratings yet
- Session Goals: Understanding Psychosocial Development of Children With Hearing LossDocument14 pagesSession Goals: Understanding Psychosocial Development of Children With Hearing LossravibhargavaraamNo ratings yet
- Numberblock Fives Band PowerPointDocument15 pagesNumberblock Fives Band PowerPointAndrewNo ratings yet
- Numberblocks Seven PowerPointDocument17 pagesNumberblocks Seven PowerPointAndrewNo ratings yet
- Numberblocks Number 6 PowerPointDocument24 pagesNumberblocks Number 6 PowerPointAndrewNo ratings yet
- Endoftheyear Magic TricksDocument13 pagesEndoftheyear Magic TricksAndrewNo ratings yet
- Numberblocks Three PowerPointDocument14 pagesNumberblocks Three PowerPointAndrewNo ratings yet
- Freestyle Book Test by Greg ArceDocument83 pagesFreestyle Book Test by Greg ArceAndrew100% (4)
- What Can You See? Picture Observation and CountingDocument15 pagesWhat Can You See? Picture Observation and CountingAndrewNo ratings yet
- Numberblocks Number 4 PowerPointDocument15 pagesNumberblocks Number 4 PowerPointAndrewNo ratings yet
- Text Features - SmallDocument6 pagesText Features - SmallAndrewNo ratings yet
- Numberblocks Number Two PowerPointDocument19 pagesNumberblocks Number Two PowerPointAndrewNo ratings yet
- Eugene Burger Lecture NotesDocument14 pagesEugene Burger Lecture NotesAndrew75% (4)
- Dragon Magazine #031 PDFDocument56 pagesDragon Magazine #031 PDFAndrew100% (2)
- TCIS Study GuideDocument2 pagesTCIS Study GuideAndrew100% (2)
- Mental Health Brain Scan Report from May 2006Document68 pagesMental Health Brain Scan Report from May 2006Carl FernandesNo ratings yet
- Woman of Kleenex - by Larry NivenDocument4 pagesWoman of Kleenex - by Larry NivenAndrewNo ratings yet
- Doctor Strange - Eternal SagaDocument171 pagesDoctor Strange - Eternal SagaAndrew100% (3)
- The Value of Nothing - Caleb LarsenDocument84 pagesThe Value of Nothing - Caleb LarsenAndrewNo ratings yet
- The Substitute Magician - A Short StoryDocument3 pagesThe Substitute Magician - A Short StoryAndrewNo ratings yet
- Gladiator 2 by Nick CaveDocument103 pagesGladiator 2 by Nick Cavequinntessential100% (6)
- The Tony Clifton Story - by Andy Kaufman and Bob ZmudaDocument149 pagesThe Tony Clifton Story - by Andy Kaufman and Bob ZmudaAndrewNo ratings yet
- An Info-Hippie's ManifestoDocument2 pagesAn Info-Hippie's ManifestoAndrew100% (2)
- Indiana Jones and The City of The Gods - Frank DarabontDocument140 pagesIndiana Jones and The City of The Gods - Frank DarabontguionistaenfurecidoNo ratings yet
- Dragon Magazine #143Document108 pagesDragon Magazine #143Andrew100% (3)
- Chris CapeHart's 3 Ring RoutineDocument16 pagesChris CapeHart's 3 Ring RoutineAndrew100% (2)
- The Advanced Theory of AdvancementDocument4 pagesThe Advanced Theory of AdvancementAndrewNo ratings yet
- Financial Times Europe 14 November 2023Document18 pagesFinancial Times Europe 14 November 2023Nikola JovanovNo ratings yet
- Xerosis CutisDocument6 pagesXerosis CutisHadi FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspect of BusinessDocument4 pagesLegal Aspect of BusinessABHISHEK YADAVNo ratings yet
- Tendernotice 2Document133 pagesTendernotice 2Pratik GuptaNo ratings yet
- Natural Disaster in Indonesia: Risty Khoirunisa Presentation SkillDocument11 pagesNatural Disaster in Indonesia: Risty Khoirunisa Presentation SkillRisty KhoirunisaNo ratings yet
- 25 0 - Command RefDocument632 pages25 0 - Command RefVitaly KroivetsNo ratings yet
- PaliLossy PDFDocument408 pagesPaliLossy PDFtemp100% (2)
- Marketing Management Assignment On MelitaDocument17 pagesMarketing Management Assignment On MelitaarjunNo ratings yet
- Inventory Costs and ControlDocument7 pagesInventory Costs and ControlEden Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - Financial Accounting - February 4Document7 pagesAssignment 3 - Financial Accounting - February 4Ednalyn PascualNo ratings yet
- TENDA Wifi RepeaterDocument45 pagesTENDA Wifi RepeaterZsolt MarkóNo ratings yet
- ISC - Actualtests.cissp ISSAP.v2015!03!13.by - Adella.237qDocument68 pagesISC - Actualtests.cissp ISSAP.v2015!03!13.by - Adella.237qdeewanandNo ratings yet
- The Art of Dying by Neville GoddardDocument4 pagesThe Art of Dying by Neville GoddardhabiotoNo ratings yet
- Application 1 (Basic Steps in Accounting)Document2 pagesApplication 1 (Basic Steps in Accounting)Maria Nezka Advincula86% (7)
- TurbineDocument14 pagesTurbineArjit GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Pike County Sheriff Forms Major Crimes Task Force For Unsolved MurdersDocument2 pagesPike County Sheriff Forms Major Crimes Task Force For Unsolved MurdersAndy Burgoon100% (1)
- NDA Strategic PlanDocument222 pagesNDA Strategic PlanJudith AinembabaziNo ratings yet
- Aff K - Deleuze - Michigan7 2020 K LabDocument305 pagesAff K - Deleuze - Michigan7 2020 K LabEvan JackNo ratings yet
- International Aerospace Olympiad 2020: Group C Study MaterialDocument13 pagesInternational Aerospace Olympiad 2020: Group C Study Material8D Audio TuneNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument10 pagesProject ProposalMuhammad Ammar SohailNo ratings yet
- Training Design TaekwondoDocument5 pagesTraining Design Taekwondoalexander100% (3)
- Mgt554 Business EnvironmentDocument8 pagesMgt554 Business EnvironmentHimank GuptaNo ratings yet
- Essay Assessment CriteriaDocument1 pageEssay Assessment CriteriaNguyen Quynh AnhNo ratings yet
- 6446 Gibson PBD - HR WebDocument192 pages6446 Gibson PBD - HR WebKoke Colil Benavente100% (1)
- VisitAberdeen City Centre MapDocument2 pagesVisitAberdeen City Centre MapZarko MikicNo ratings yet
- Komunikasi Melalui Aplikasi Whatsapp Dalam Rangka Pembelajaran Anak Sekolah Dasar Masa Pandemi Covid-19 Di Lingkungan Medan DenaiDocument8 pagesKomunikasi Melalui Aplikasi Whatsapp Dalam Rangka Pembelajaran Anak Sekolah Dasar Masa Pandemi Covid-19 Di Lingkungan Medan DenaiErwin ErlanggaNo ratings yet
- Process Analyzer Sampling System TrainingDocument3 pagesProcess Analyzer Sampling System TrainingPhilNo ratings yet
- Billy: Bookcase SeriesDocument4 pagesBilly: Bookcase SeriesDImkaNo ratings yet
- RecipesDocument102 pagesRecipesmajaklipa100% (3)