Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cha 2
Uploaded by
ShammimBegum0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views5 pagesecommerce
Original Title
Cha2 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentecommerce
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views5 pagesCha 2
Uploaded by
ShammimBegumecommerce
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Electronic Data Interchange(EDI):
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) - interposes communication of business
information in standardized electronic form.
Prior to EDI, business depended on postal and phone systems that restricted
communication to those few hours of the workday that overlap between time zones.
Why EDI?
Reduction in transaction costs
Foster closer relationships between trading partners
EDI & Electronic Commerce
Electronic commerce includes EDI & much more
EDI forges boundary less relationships by improving interchange of information
between trading partners, suppliers, & customers.
EDI layered architecture:
Semantic (or application) layer
Standards translation layer
Packing (or transport) layer
Physical network infrastructure layer
EDI semantic layer:
Describes the business application
Procurement example
– Requests for quotes
– Price quotes
– Purchase orders
– Acknowledgments
– Invoices
Specific to company & software used
Standards translation:
Specifies business form structure so that information can be exchanged
Two competing standards
– American National Standards Institute(ANSI)X12
– EDIFACT developed by UN/ECE, Working Party for the Facilitation of
International Trade Procedures
EDI transport layer
How the business form is sent, e.g. post, UPS, fax
Increasingly, e-mail is the carrier
Differentiating EDI from e-mail
– Emphasis on automation
– EDI has certain legal status
Physical network infrastructure layer
Dial-up lines, Internet, value-added network, etc.
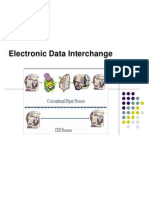
Information flow with EDI:
Buyer sends purchase order to seller computer
Seller sends purchase order confirmation to buyer
Seller sends booking request to transport company
Transport company sends booking confirmation to seller
Seller sends advance ship notice to buyer
Transport company sends status to seller
Buyer sends Receipt advice to seller
Seller sends invoice to buyer
Buyer sends payment to seller
Applications of EDI:
Role of EDI in international trade:
Reduced transaction expenditures
Quicker movement of imported & exported goods
Improved customer service through ―track & trace‖ programs
Faster customs clearance & reduced opportunities for corruption, a huge problem
in trade
Interbank Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT)
EFTS is credit transfers between banks where funds flow directly from the payer‘s
bank to the payee‘s bank.
• The two biggest funds transfer services in the United States are the Federal
Reserve‘s system, Fed wire, & the Clearing House Interbank Payments System
(CHIPS) of the New York clearing house
Health care EDI for insurance EDI
Providing good & affordable health care is a universal problem
EDI is becoming a permanent fixture in both insurance & health care industries
as medical provider, patients, & payers
Electronic claim processing is quick & reduces the administrative costs of
health care.
Using EDI software, service providers prepare the forms & submit claims via
communication lines to the value-added network service provider
• The company then edits sorts & distributes forms to the payer. If necessary,
the insurance company can electronically route transactions to a third-party for
price evaluation
Claims submission also receives reports regarding claim status & request for
additional Information
Manufacturing & retail procurement using EDI
These are heavy users of EDI.In manufacturing, EDI is used to support just-in-time.
In retailing, EDI is used to support quick response
EDI Protocols:
1. ANSI X12
2. EDIFACT
Comparison of EDIFACT & X.12 Standards:
These are comprised of strings of data elements called segments.
A transaction set is a set of segments ordered as specified by the standard.
ANSI standards require each element to have a very specific name, such as order date
or invoice date.
EDIFACT segments, allow for multiuse elements, such as date.
EDIFACT has fewer data elements & segments & only one beginning segment
(header),but it has more composites.
It is an ever-evolving platform.
You might also like
- Inter Organizational Commerce and EDIDocument11 pagesInter Organizational Commerce and EDIstavyag100% (1)
- Electronic Data Interchange: DefinitionsDocument5 pagesElectronic Data Interchange: Definitionskhanwasim0519623No ratings yet
- E - CommerceDocument34 pagesE - CommerceMohit SainiNo ratings yet
- Ecommerce Unit-IiDocument11 pagesEcommerce Unit-Ii21ucm165No ratings yet
- Electronic Data InterchangeDocument35 pagesElectronic Data Interchangeanki31taNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Management and Administrative Science: Assignment No. 1 "Electronic Data Interchange "Document10 pagesFaculty of Management and Administrative Science: Assignment No. 1 "Electronic Data Interchange "shuja002No ratings yet
- Electronic Data Interchange (An in Depth Analysis of Technological and Security Issues)Document30 pagesElectronic Data Interchange (An in Depth Analysis of Technological and Security Issues)Mustafa HussainNo ratings yet
- 04 Electronic Data InterchangeDocument16 pages04 Electronic Data InterchangeSushil KarkiNo ratings yet
- EDI FundamentalsDocument19 pagesEDI FundamentalsSowmya NadimintiNo ratings yet
- E CommerceDocument10 pagesE CommerceShruti SinghNo ratings yet
- Electronic Data InterchangeDocument20 pagesElectronic Data Interchangeshaikshaa007100% (3)
- Electronic Data Interchange: Deepti KhannaDocument21 pagesElectronic Data Interchange: Deepti KhannaVanshika PandeyNo ratings yet
- E Commerce Unit 3Document9 pagesE Commerce Unit 3Abhishek kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document31 pagesUnit 4Mahesh NannepaguNo ratings yet
- Electronic Data Interchange : Defining EDI. EDI Layered Architecture. EDI Implementation. Financial EDI Benefits of EDIDocument14 pagesElectronic Data Interchange : Defining EDI. EDI Layered Architecture. EDI Implementation. Financial EDI Benefits of EDIKrishna VeerNo ratings yet
- Unit-IV: SYLLABUS: Electronic Data Interchange, EDI Applications in Business, EDIDocument10 pagesUnit-IV: SYLLABUS: Electronic Data Interchange, EDI Applications in Business, EDIJyotsnaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Data Interchange EDIDocument13 pagesElectronic Data Interchange EDIKumari anju bharatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 (Structured Electronic Documents)Document22 pagesChapter 7 (Structured Electronic Documents)Atik Israk LemonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Electronic Data NterchangeDocument54 pagesChapter 3 - Electronic Data NterchangeRajan SubediNo ratings yet
- EDI Unit Four CompleteDocument5 pagesEDI Unit Four Completebhanu pratap singhNo ratings yet
- Interorganizational Commerce and Edi: ObjectiveDocument15 pagesInterorganizational Commerce and Edi: ObjectivefopivNo ratings yet
- EDI Basic TrainingDocument42 pagesEDI Basic Trainingvenkateswarlu mandalapuNo ratings yet
- Electronic Data Interchange (Edi)Document2 pagesElectronic Data Interchange (Edi)mahesh_gottapuNo ratings yet
- A New Business ParadigmDocument31 pagesA New Business ParadigmChandrikaBajoriaNo ratings yet
- EDI Session 1Document33 pagesEDI Session 1Dileep Kumar Naidu RayalaNo ratings yet
- Presented by Rashmi.RDocument14 pagesPresented by Rashmi.RRASHUNo ratings yet
- Electronic Data InterchangeDocument14 pagesElectronic Data InterchangeKabindra KoiralaNo ratings yet
- What Is EDI Electronic Data Interchange IBMDocument2 pagesWhat Is EDI Electronic Data Interchange IBMJ B Akhil DevNo ratings yet
- MCAECommerce 3Document9 pagesMCAECommerce 3dante saprNo ratings yet
- Marketing Information System Chapter FiveDocument7 pagesMarketing Information System Chapter Fivefilimonkinfe47No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 SlidesDocument43 pagesChapter 3 SlidesHay JirenyaaNo ratings yet
- 01 EDI Definitions Standards and Messaging Marianna MihelsonDocument13 pages01 EDI Definitions Standards and Messaging Marianna MihelsonCesare RotundoNo ratings yet
- EDIDocument3 pagesEDIAtharvaNo ratings yet
- EdiDocument37 pagesEdikuku288100% (1)
- What Is EDIDocument5 pagesWhat Is EDIZeeshan ch 'Hadi'No ratings yet
- Unit-3 E-Commerce EDI SRGDocument48 pagesUnit-3 E-Commerce EDI SRGLuitel ShaneNo ratings yet
- (Year) : Submitted By: Prabhat Kumar Jha Roll-No-18, Div - B, TybbaDocument11 pages(Year) : Submitted By: Prabhat Kumar Jha Roll-No-18, Div - B, Tybbamniraula3No ratings yet
- Electronic Data Interchange (Edi)Document65 pagesElectronic Data Interchange (Edi)V.F.MUHAMMED ISMAIL THOUHEEDNo ratings yet
- EDI Through A Distributed Information Systems Approach: IncompatibleDocument10 pagesEDI Through A Distributed Information Systems Approach: IncompatibleADRIAN OSPINA SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Unit-3: Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)Document4 pagesE-Commerce Unit-3: Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)Pramila PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Electronic Data Interchange: Nature, Benefits of E.D.I, Demerits of E.D.IDocument36 pagesElectronic Data Interchange: Nature, Benefits of E.D.I, Demerits of E.D.IutkaljyotiNo ratings yet
- Electronic Data InterchangeDocument16 pagesElectronic Data InterchangeGauravNo ratings yet
- Advantages of EDIDocument6 pagesAdvantages of EDIKhalid JamalNo ratings yet
- EdiDocument25 pagesEdiDebdatta ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Eb Group 1Document38 pagesEb Group 1Danica ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)Document39 pagesElectronic Data Interchange (EDI)bhadoria9No ratings yet
- Purpose and Function of EDI: Faster Transactions: Paper Documents Take Time To Transport FromDocument5 pagesPurpose and Function of EDI: Faster Transactions: Paper Documents Take Time To Transport Fromayusha dasNo ratings yet
- Electronic Data InterchangeDocument17 pagesElectronic Data Interchangesudha_adventNo ratings yet
- Electronic Data InterchangeDocument15 pagesElectronic Data InterchangeShivam DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)Document23 pagesChapter-3 Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)Suman BhandariNo ratings yet
- EDIDocument9 pagesEDISwati HansNo ratings yet
- Electronic Data Interchange (Edi)Document2 pagesElectronic Data Interchange (Edi)Seenu HkNo ratings yet
- Complete EDI MaterialDocument81 pagesComplete EDI MaterialSivaramakrishnan Muthukrishnan100% (1)
- What Is EDIDocument8 pagesWhat Is EDIGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- EcomDocument13 pagesEcomVineet PathakNo ratings yet
- Electronic Data InterchangeDocument35 pagesElectronic Data Interchangesameer7mohammad100% (1)
- aRPIT EdiDocument6 pagesaRPIT EdiArpit BatraNo ratings yet
- Essay Template in All EssaysDocument1 pageEssay Template in All EssaysShammimBegumNo ratings yet
- MIT 2 AppDocument2 pagesMIT 2 AppShammimBegumNo ratings yet
- Network FundamentalsDocument1 pageNetwork FundamentalsShammimBegumNo ratings yet
- Free ESL Phrases and Idioms English Lesson - Bored To DeathDocument2 pagesFree ESL Phrases and Idioms English Lesson - Bored To DeathShammimBegumNo ratings yet
- About ContentDocument1 pageAbout ContentShammimBegumNo ratings yet
- About ContentDocument2 pagesAbout ContentShammimBegumNo ratings yet
- PHD Program IITKanpur SmartCity PalaniDocument1 pagePHD Program IITKanpur SmartCity PalaniShammimBegumNo ratings yet
- Color ComboDocument1 pageColor ComboShammimBegumNo ratings yet
- Employ M EN AG R E E M ENTDocument2 pagesEmploy M EN AG R E E M ENTShammimBegumNo ratings yet
- P. Swathi 2. M.Ram Teja 3. V.Sriraj 4. G.Sai Rohit: Winners: Team - 1 (IT IV/IV)Document1 pageP. Swathi 2. M.Ram Teja 3. V.Sriraj 4. G.Sai Rohit: Winners: Team - 1 (IT IV/IV)ShammimBegumNo ratings yet
- MBAOGSem3 5Document226 pagesMBAOGSem3 5ShammimBegumNo ratings yet
- IdlyDocument4 pagesIdlysshammim585No ratings yet
- MCQ OSCM Unit 1Document22 pagesMCQ OSCM Unit 1ShammimBegum67% (6)
- Assignment 1Document17 pagesAssignment 1ShammimBegumNo ratings yet
- UGC NET JRF Study MaterialDocument16 pagesUGC NET JRF Study MaterialExamrace62% (26)
- List of Famous Cities On River Banks in The WorldDocument2 pagesList of Famous Cities On River Banks in The WorldDiptangshu DeNo ratings yet
- Spike Magazine Cup PackDocument5 pagesSpike Magazine Cup PackBungle MarleyNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter SUMMATIVE TEST in MAPEHDocument3 pages3rd Quarter SUMMATIVE TEST in MAPEHzaile felineNo ratings yet
- José Guadalupe PosadaDocument19 pagesJosé Guadalupe PosadaJudy Baca100% (1)
- K To 12 Math 7 Curriculum Guide PDFDocument15 pagesK To 12 Math 7 Curriculum Guide PDFEdmar Tan Fabi100% (1)
- Edug 899 - Grade 2 Forces and Motion Unit - CompletedDocument37 pagesEdug 899 - Grade 2 Forces and Motion Unit - Completedapi-241358660No ratings yet
- 2 Beats Per Measure 3 Beats Per Measure 4 Beats Per MeasureDocument24 pages2 Beats Per Measure 3 Beats Per Measure 4 Beats Per MeasureArockiya StephenrajNo ratings yet
- Epidemiological Triad of HIV/AIDS: AgentDocument8 pagesEpidemiological Triad of HIV/AIDS: AgentRakib HossainNo ratings yet
- Test Cases: Project Name: Virtual ClassroomDocument5 pagesTest Cases: Project Name: Virtual ClassroomTina HernandezNo ratings yet
- Ijrpr2741 Study On Investor Perception Towards Stock Market InvestmentDocument19 pagesIjrpr2741 Study On Investor Perception Towards Stock Market InvestmentAbhay RanaNo ratings yet
- AC MachinesDocument32 pagesAC Machinesjoeney guardiarioNo ratings yet
- Luyện nghe Tiếng Anh có đáp án: I/ Listen and complete the textDocument3 pagesLuyện nghe Tiếng Anh có đáp án: I/ Listen and complete the textVN LenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Mine Ventialtion ProblemDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Mine Ventialtion ProblemfahimNo ratings yet
- Englis 123Document39 pagesEnglis 123Cindy EysiaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Profile of Multimode GroupDocument6 pagesCorporate Profile of Multimode GroupShaheen RahmanNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Neural-Network - Genetic Algorithm Technique For Aircraft Engine Performance Diagnostics Developed and DemonstratedDocument4 pagesHybrid Neural-Network - Genetic Algorithm Technique For Aircraft Engine Performance Diagnostics Developed and Demonstratedmohamad theibechNo ratings yet
- NUFLO Low Power Pre-Amplifier: SpecificationsDocument2 pagesNUFLO Low Power Pre-Amplifier: SpecificationsJorge ParraNo ratings yet
- Castle CrashesDocument21 pagesCastle Crasheswicked wolfNo ratings yet
- HBS - Zara Fast Fashion Case Write UpDocument4 pagesHBS - Zara Fast Fashion Case Write Upaaronhwalton100% (1)
- Practical CS ProcessingDocument483 pagesPractical CS ProcessinganAMUstudent100% (2)
- Shaft DeflectionDocument15 pagesShaft Deflectionfreek_jamesNo ratings yet
- Pu3-Mo A1 MoversDocument40 pagesPu3-Mo A1 MoversMiss María José SalasNo ratings yet
- RSM222.f22.CourseOutline v3 2022-09-05Document9 pagesRSM222.f22.CourseOutline v3 2022-09-05Kirsten WangNo ratings yet
- Pesud Abadi Mahakam Company Profile Abdul Basith-DikonversiDocument48 pagesPesud Abadi Mahakam Company Profile Abdul Basith-DikonversiAndi HafizNo ratings yet
- Lahainaluna High School Cafeteria: Lahaina, Maui, HawaiiDocument42 pagesLahainaluna High School Cafeteria: Lahaina, Maui, HawaiiKeerthy MoniNo ratings yet
- Program Logic FormulationDocument69 pagesProgram Logic FormulationIan OffemariaNo ratings yet
- Nokia 3g Full Ip CommissioningDocument30 pagesNokia 3g Full Ip CommissioningMehul JoshiNo ratings yet
- Kitchen Equipment Handling and Maintaining Standard Procedure and PoliciesDocument2 pagesKitchen Equipment Handling and Maintaining Standard Procedure and PoliciesChef Chef75% (4)
- CR-805 Retransfer PrinterDocument2 pagesCR-805 Retransfer PrinterBolivio FelizNo ratings yet
- Lecture 08Document32 pagesLecture 08SusovanNo ratings yet
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindFrom EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo ratings yet
- Defensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityFrom EverandDefensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveFrom EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveNo ratings yet
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsFrom EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (722)
- AI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderFrom EverandAI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (398)
- Cyber War: The Next Threat to National Security and What to Do About ItFrom EverandCyber War: The Next Threat to National Security and What to Do About ItRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (66)
- Chaos Monkeys: Obscene Fortune and Random Failure in Silicon ValleyFrom EverandChaos Monkeys: Obscene Fortune and Random Failure in Silicon ValleyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (111)
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Digital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyFrom EverandDigital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Scary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldFrom EverandScary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (55)
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumFrom EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (12)
- ChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessFrom EverandChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessNo ratings yet
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansFrom EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansNo ratings yet
- The Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyFrom EverandThe Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyNo ratings yet
- Mini Farming: Self-Sufficiency on 1/4 AcreFrom EverandMini Farming: Self-Sufficiency on 1/4 AcreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (76)
- Reality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyFrom EverandReality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (24)
- The Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldFrom EverandThe Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (107)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (227)
- The Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationFrom EverandThe Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)