Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Different Laboratory Service Models
Uploaded by
Gerald John PazCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Different Laboratory Service Models
Uploaded by
Gerald John PazCopyright:
Available Formats
FEU-IAS –Medical Technology Department on Laboratory Management 1st Sem.
2012-2013
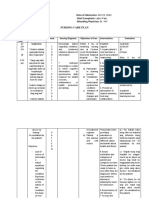
DIFFERENT LABORATORY SERVICE Characteristics Remarks
MODELS
1.Traditional “closed” laboratory has discrete sections in hematology, chemistry,
microbiology, and blood bank, generally separated into
rooms or sections.
2. “Open” laboratory discrete services are placed in one large room with portable
walls that can be adjusted as needed based on volume.
3. Core laboratory common type of consolidation has been hematology and Advantages include handling stat
chemistry laboratories (“chematology”) requests, improving off-shift workflow,
and avoiding chronic staffing problems
4. Regional laboratory Specific low-volume or expensive laboratory services For example, consolidation of all virology
currently provided by more than one regional hospital or PCR testing into one hospital
laboratory, that are consolidated into one hospital laboratory.
laboratory.
5. Reference laboratory Traditional full service laboratory that handles all types of
testing, especially esoteric tests.
6. Point-of-care Laboratory testing that is brought to the patient's bedside. (e.g., glucose, pregnancy, activated
Test menu is generally limited to a few basic chemistry and clotting time, blood gases).
hematology tests
Rapid response laboratory that is often located in or near Provides critical laboratory tests such as
7. Stat laboratory an emergency department or surgical suite. hematocrits and blood gases.
8. Limited service Laboratory provides limited menu of routine (like CBC,
chemistry panel, prothrombin time) and/or specialty
services (like fertility testing) on a stat or non-stat basis.
Includes downsized hospital labs that retain stats and some
routine tests but send most work to an off-site core
laboratory.
Reference Topic: Functions of Management- Planning
You might also like
- RA 4688 (Clinical Laboratory Law)Document7 pagesRA 4688 (Clinical Laboratory Law)Danielle Anne Zamora-Matillosa Lamban100% (1)
- Administrative Orders of Ra 4688Document40 pagesAdministrative Orders of Ra 4688Joshua BacunawaNo ratings yet
- PMLS 1 Lesson 8 Nature of Clinical LabDocument200 pagesPMLS 1 Lesson 8 Nature of Clinical Labangelica fayeNo ratings yet
- Doctors ListDocument212 pagesDoctors ListSaranya Chandrasekar33% (3)
- Maam Lita and Sir Patrick LessonsDocument15 pagesMaam Lita and Sir Patrick Lessonsroxannegarcelaso10No ratings yet
- Laboratory Management 2ND Year 1Document57 pagesLaboratory Management 2ND Year 1allawigantrish13No ratings yet
- Laboratory Management Compiled Lecture GuideDocument79 pagesLaboratory Management Compiled Lecture GuideRach ReyesNo ratings yet
- DHA Laboratory Guidelines 2019: Laboratory UnitDocument33 pagesDHA Laboratory Guidelines 2019: Laboratory UnitRafat ElshemiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8Document48 pagesLesson 8Xigna Milano AmoresNo ratings yet
- The Clinical LaboratoryDocument24 pagesThe Clinical LaboratoryRomar Durian100% (2)
- The Clinical LaboratoryDocument24 pagesThe Clinical LaboratoryRomar DurianNo ratings yet
- Lab Scope of ServicesDocument10 pagesLab Scope of Servicessabir osmanNo ratings yet
- كورس اللابDocument110 pagesكورس اللابgaber 230No ratings yet
- Finals Notes (PMLS-1)Document5 pagesFinals Notes (PMLS-1)Una Kaya CabatinganNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Laboratory Automation On Performance ImprovementDocument6 pagesThe Impact of Laboratory Automation On Performance ImprovementChris V-PandaNo ratings yet
- Meeting 1 - The Clinical LabDocument19 pagesMeeting 1 - The Clinical LabSofwatul MunjiyatNo ratings yet
- Handouts MTLB 4688 The Clinical Lab LawDocument6 pagesHandouts MTLB 4688 The Clinical Lab LawFait Hee100% (1)
- Clinical LaboratoriesDocument24 pagesClinical Laboratoriespdamodar200788% (8)
- Clinical Laboratory Tests and FunctionsDocument61 pagesClinical Laboratory Tests and FunctionsQuimson KennethNo ratings yet
- Lab PlanningDocument7 pagesLab PlanningrakeshkaydalwarNo ratings yet
- PMLS Lesson 8Document14 pagesPMLS Lesson 8Althea EspirituNo ratings yet
- Point-Of-Care Testing in Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care - An OverviewDocument9 pagesPoint-Of-Care Testing in Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care - An OverviewDelladuasatu stellaNo ratings yet
- Quality Standards For Sample Processing, Transportation, and Storage in Hemostasis TestingDocument11 pagesQuality Standards For Sample Processing, Transportation, and Storage in Hemostasis TestingGunay AliyevaNo ratings yet
- CM Intro Laboratory Equipment PPDocument21 pagesCM Intro Laboratory Equipment PPGeronimoNo ratings yet
- Lab. Man - Cris Joshua Archibido, RMTDocument2 pagesLab. Man - Cris Joshua Archibido, RMTCris Joshua ArchibidoNo ratings yet
- ClinicalLaboratory StatPearls NCBIBookshelfDocument2 pagesClinicalLaboratory StatPearls NCBIBookshelfKhadim HussainNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction About The Study A) Feasibility StudyDocument19 pages1.introduction About The Study A) Feasibility StudyDiscov Singh100% (8)
- Tissue Pathways For Breast Pathology: September 2010Document9 pagesTissue Pathways For Breast Pathology: September 2010fadoNo ratings yet
- Assignment in RA 4688 Clinical Laboratory LawsDocument3 pagesAssignment in RA 4688 Clinical Laboratory LawsErin HernaNo ratings yet
- 2010 Sturgeon Taking A New Biomarker Into Routine UseDocument12 pages2010 Sturgeon Taking A New Biomarker Into Routine UsemarciliomeiraNo ratings yet
- CHEM LEC - PRELIMSDocument19 pagesCHEM LEC - PRELIMScherrycayari13No ratings yet
- BT26 Anatomic PathologyDocument2 pagesBT26 Anatomic PathologyProduktemeuljeNo ratings yet
- Types of Labs and Equipment OverviewDocument4 pagesTypes of Labs and Equipment OverviewmuncadamonicaNo ratings yet
- Ajcpath140 0193Document10 pagesAjcpath140 0193Marinelle TumanguilNo ratings yet
- Clinical Lab. (Transes)Document3 pagesClinical Lab. (Transes)MLS1C - PLARISAN, VALENT DAVENo ratings yet
- Improve Lab Workflow PerformanceDocument18 pagesImprove Lab Workflow PerformanceKaye TacocongNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Management Module5BDocument4 pagesLaboratory Management Module5BLezel Joy R. MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Analytical VariationDocument5 pagesPre-Analytical VariationREMAN ALINGASANo ratings yet
- Clinical Laboratory Personnel and FunctionsDocument11 pagesClinical Laboratory Personnel and FunctionsLNU SHS SSCNo ratings yet
- MIGUEL, VANESSA L. - Core vs Hospital LabsDocument2 pagesMIGUEL, VANESSA L. - Core vs Hospital LabsChin ChinNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 MedtechDocument17 pagesCHAPTER 8 MedtechKisen DiazNo ratings yet
- LMGT311 Lecture-Week 17Document22 pagesLMGT311 Lecture-Week 17Princheska TallaNo ratings yet
- Medical Laboratory - WikipediaDocument9 pagesMedical Laboratory - WikipediaTYAS PAMILUNINGSIHNo ratings yet
- Classification of clinical labs in the PhilippinesDocument2 pagesClassification of clinical labs in the PhilippinesKitty OrtxNo ratings yet
- The Clinical Laboratory and Its LawsDocument1 pageThe Clinical Laboratory and Its LawsAldren BeliberNo ratings yet
- NablDocument46 pagesNablGupta AtulNo ratings yet
- Bertholf2017 Chapter LaboratoryStructureAndFunctionDocument23 pagesBertholf2017 Chapter LaboratoryStructureAndFunctionci8084102No ratings yet
- Clinical BiochemistryDocument25 pagesClinical Biochemistrymirzafahad82005No ratings yet
- Nature of the Clinical Laboratory T19Document21 pagesNature of the Clinical Laboratory T19nicoNo ratings yet
- Maximizing the Clinical Utility of Laboratory TestingDocument4 pagesMaximizing the Clinical Utility of Laboratory TestingDETECTIVE CONANNo ratings yet
- Automation in The Clinical Microbiology Laboratory PAPERDocument7 pagesAutomation in The Clinical Microbiology Laboratory PAPERobakhit91No ratings yet
- Point-of-Care and Physician Office LaboratoriesDocument7 pagesPoint-of-Care and Physician Office LaboratoriesSNo ratings yet
- Pmls ReviewerDocument8 pagesPmls ReviewerElis DreNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Lab Sciences - QuDocument66 pagesFundamentals of Lab Sciences - QueebookachipNo ratings yet
- PMTP Unit 3:: Regulations Governing Laboratory PersonnelDocument12 pagesPMTP Unit 3:: Regulations Governing Laboratory PersonnelARVINE JUSTINE CORPUZNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Utilization in The Emergency Department - Are The Requested Tests Patient-Oriented?Document3 pagesLaboratory Utilization in The Emergency Department - Are The Requested Tests Patient-Oriented?djebrutNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0165993611000860 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S0165993611000860 MainHamza IqbalNo ratings yet
- PMLS 1 Topic 8.0 TransDocument6 pagesPMLS 1 Topic 8.0 TranslalaNo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide to Lab Technician Work: Overview and Interview Q&AFrom EverandThe Complete Guide to Lab Technician Work: Overview and Interview Q&ANo ratings yet
- Practical Manual for Detection of Parasites in Feces, Blood and Urine SamplesFrom EverandPractical Manual for Detection of Parasites in Feces, Blood and Urine SamplesNo ratings yet
- Drug Abuse Video GuidelinesDocument1 pageDrug Abuse Video GuidelinesGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Problem Based Learning PDFDocument1 pageProblem Based Learning PDFGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Culture MediaDocument1 pageConcepts of Culture MediaGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Biobanking For Human Microbiome Research Promise, Risks, and EthicsDocument15 pagesBiobanking For Human Microbiome Research Promise, Risks, and EthicsGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Phlebotomy: Phlebos - Greek Word Meaning "Vein" & Tome - "To Cut"Document5 pagesPhlebotomy: Phlebos - Greek Word Meaning "Vein" & Tome - "To Cut"Gerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Geopolitical Challenges For Infectious Disease Prevention and ControlDocument17 pagesGeopolitical Challenges For Infectious Disease Prevention and ControlGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Teacher Presentation Style: (Please Email Me at For A References List.)Document5 pagesThe Impact of Teacher Presentation Style: (Please Email Me at For A References List.)kashanpirzadaNo ratings yet
- Problem BasedDocument3 pagesProblem BasedLady KweeNo ratings yet
- GROUP11 Section1 PBL2 Gerald John PazDocument1 pageGROUP11 Section1 PBL2 Gerald John PazGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Gene Therapy May Prevent Retinoschisis in Boys: ReviewDocument2 pagesGene Therapy May Prevent Retinoschisis in Boys: ReviewGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0167701216302627 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0167701216302627 MainGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Case Studies On CoagulationDocument3 pagesCase Studies On CoagulationGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Host Microbiomes and Their Interactions With Immune SystemDocument9 pagesHost Microbiomes and Their Interactions With Immune SystemGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Role of Microbiota in Immunity and InflammationDocument12 pagesRole of Microbiota in Immunity and InflammationGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 022Document100 pagesChapter 022Gerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 021Document49 pagesChapter 021Gerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 023Document34 pagesChapter 023Gerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Managment and Planning PDFDocument53 pagesManagment and Planning PDFGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 023Document34 pagesChapter 023Gerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 024Document49 pagesChapter 024Gerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 001Document83 pagesChapter 001Gerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 025Document31 pagesChapter 025Gerald John PazNo ratings yet
- The First Blind Man On Top of The WorldDocument1 pageThe First Blind Man On Top of The WorldGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Safety ChapterDocument39 pagesLaboratory Safety ChapterGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Papa Bear of The Berenstain BearsDocument1 pagePapa Bear of The Berenstain BearsGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- GROUP 6-Micro Biochem ResultsDocument2 pagesGROUP 6-Micro Biochem ResultsGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 002Document68 pagesChapter 002Gerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Short Report: Genetics Islet Autoantibodies Can Discriminate Maturity-Onset Diabetes of The Young (MODY) From Type 1 DiabetesDocument7 pagesShort Report: Genetics Islet Autoantibodies Can Discriminate Maturity-Onset Diabetes of The Young (MODY) From Type 1 DiabetesGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Managment and PlanningDocument53 pagesManagment and PlanningGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine Residency BrochureDocument23 pagesInternal Medicine Residency Brochuredanskip1025No ratings yet
- Lim Vs ChincoDocument3 pagesLim Vs ChincoAlyanna ChangNo ratings yet
- Test 3Document2 pagesTest 3FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Diagnosa PneumoperitoniumDocument5 pagesJurnal Diagnosa PneumoperitoniumMustafa HolidiNo ratings yet
- 2014 PN Fundamental Surgical DrainsDocument14 pages2014 PN Fundamental Surgical DrainsklossmaddyNo ratings yet
- A. Examine A Healthcare Organization That Has SignificanceDocument5 pagesA. Examine A Healthcare Organization That Has SignificanceDrogNo ratings yet
- 102721.MCRO - 34 CR 20 658 - Order Other - 2020 10 27 - 20210318153105Document3 pages102721.MCRO - 34 CR 20 658 - Order Other - 2020 10 27 - 20210318153105West Central TribuneNo ratings yet
- Nurse Guide April09Document136 pagesNurse Guide April09api-256209231No ratings yet
- Sno Membership Number Name of Doctor Address 1 Address 2 City State Pin CodeDocument44 pagesSno Membership Number Name of Doctor Address 1 Address 2 City State Pin CodeAartiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Monir Hossain CV2Document3 pagesDr. Monir Hossain CV2antoniolopeez176No ratings yet
- Communicating Effectively During Drug AdministrationDocument2 pagesCommunicating Effectively During Drug AdministrationNayla FerdianaNo ratings yet
- Tanjung RhuDocument22 pagesTanjung RhuAimanTajuddin70% (10)
- Clinical Skill Books PDFDocument384 pagesClinical Skill Books PDFnamitaNo ratings yet
- SURGICAL CARE COMPLEX POLICY (OsMak-CLN-SD-SCC) PDFDocument2 pagesSURGICAL CARE COMPLEX POLICY (OsMak-CLN-SD-SCC) PDFpatientsafetyNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Materials and WastesDocument4 pagesHazardous Materials and WastesShofiaNo ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument8 pagesAnnotated Bibliographyapi-495941898No ratings yet
- Name: XYZ Age: 27 Y.O Chief Complaint: Labor Pain Room: 1 (CLMMRH) Attending Physician: Dr. YYY Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesName: XYZ Age: 27 Y.O Chief Complaint: Labor Pain Room: 1 (CLMMRH) Attending Physician: Dr. YYY Nursing Care PlanCheska Mae PalicNo ratings yet
- Paediatrica Indonesiana: Hindra Irawan Satari, Agus Firmansyah, TheresiaDocument8 pagesPaediatrica Indonesiana: Hindra Irawan Satari, Agus Firmansyah, TheresiaLestari Indah PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment ReportDocument8 pagesAccomplishment ReportKevin Fernandez MendioroNo ratings yet
- Capstone Clinical Nursing JudgementDocument7 pagesCapstone Clinical Nursing Judgementapi-544889322No ratings yet
- Colostomy Irrigation ProcedureDocument3 pagesColostomy Irrigation Proceduresenyorakath0% (1)
- Guide Standardised MmseDocument8 pagesGuide Standardised MmsecinthyaaaNo ratings yet
- PleuraFlow Brochure ML004 I FINALDocument4 pagesPleuraFlow Brochure ML004 I FINALxergiogcNo ratings yet
- LBWF News 20th April 2015Document24 pagesLBWF News 20th April 2015ChingfordCCNo ratings yet
- Thank you for the dialogue. It helps me understand better about emergency situation in hospital. I appreciate your sharingDocument28 pagesThank you for the dialogue. It helps me understand better about emergency situation in hospital. I appreciate your sharingnyoman pastikaNo ratings yet
- Define Ostensible Agency Act orDocument3 pagesDefine Ostensible Agency Act orArvin RobertNo ratings yet
- Medical Drill Report (Kualakurun)Document8 pagesMedical Drill Report (Kualakurun)Harry Cuayo100% (1)
- Service Quality of Hospital Outpatient Departments: Patients' PerspectiveDocument2 pagesService Quality of Hospital Outpatient Departments: Patients' Perspectivelouie john abilaNo ratings yet
- Keeping Preemies Warm, Breathing Well and EnergizedDocument8 pagesKeeping Preemies Warm, Breathing Well and Energizedindirinoor5No ratings yet