Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ship Stability Nomenclature
Uploaded by
Roderick Estrella0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
229 views6 pagesship stability nomenclature
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentship stability nomenclature
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
229 views6 pagesShip Stability Nomenclature
Uploaded by
Roderick Estrellaship stability nomenclature
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Nomenclature of
ship terms
aft terminal the aftmost point on a ship’s floodable length.
air draft the vertical distance from the waterline to
the highest point on the ship.
amidships a position midway between the aft
perpendicular (AP) and the forward
perpendicular (FP).
angle of list an angle of heel where G is transversely
offset from the ship’s centreline and
transverse GM is positive.
angle of loll an angle of heel where G is on the ship’s
centreline and transverse GM is zero.
angle of repose an angle created by a shift of grain.
apparent trim the difference between the drafts observed
at the for’d and aft draft marks.
appendage a small attachment to a main area or body.
assigned freeboard the ship’s freeboard, after corrections have
been made to the DfT Tabular Freeboard
value.
blockage factor area of ship’s midship section divided by
the cross-sectional area of a river or canal.
boot-topping the vertical distance between the lightdraft
and the SLWL.
bow height a vertical distance measured at the FP, from
the waterline to the uppermost deck
exposed to the weather.
bulk carriers workhorse vessels, built to carry such
cargoes as ore, coal, grain, sugar, etc. in large
quantities.
calibrated tank a tank giving volumes or weights at vertical
increments of say one centimetre in the
tank’s depth.
404 Ship Stability for Masters and Mates
cargo-passenger ship a vessel that carries cargo and up to 12
paying passengers.
Cb block coefficient: linking the volume of
displacement with LBP, breadth mld and
draft.
compressive stress stress that is forcing the fibres in the
material to be crushed together.
computer packages packages for estimating stability, trim, end
drafts, shear forces and bending moments
for a condition of loading.
confined channel a river or canal where there is a nearby
presence of banks.
continuous girder a girder that runs continuously from say
main transverse bulkhead to main
transverse bulkhead.
Cw waterplane area coefficient: linking the
waterplane area with the LBP and the ship’s
breadth mld.
deadweight the weight that a ship carries.
deck camber transverse curvature of a deck, measured
from deck height at centreline to deck height
at side, at amidships.
deck sheer longitudinal curvature of a deck, measured
vertically from amidships to the deck, at Aft
Perp or Forward Perp.
depth moulded measured from top of keel to underside
of uppermost continuous deck, at
amidships.
DfT Department for Transport.
displacement for all conditions of loading, it is the
lightweight plus any deadweight.
domain of ship mainly the area in which the pressure bulbs
exist on a moving vessel.
draft moulded distance from the waterline to the top of
keel, measured at amidships.
dwt abbreviation for deadweight, the weight
that a ship carries.
dynamical stability the area under a statical stability curve
multiplied by the ship’s displacement.
even keel a vessel with no trim: where the aft draft has
the same value as the forward draft.
factor of subdivision Fs the floodable length ordinates times Fs gives
the permissible length ordinates.
FB breadth of influence in open water conditions.
forward terminal the foremost most point on a ship’s
floodable length.
Nomenclature of ship terms 405
free surface effects loss of stability caused by liquids in partially
filled tanks.
freeboard ratio freeboard to the margin line @
amidships/ship’s draft moulded.
general particulars LBP, Br. Mld, depth mld, Draft Mld,
Lightweight, Deadweight, Displacement,
Cb, Service Speed, etc.
grain cargo this covers wheat, maize, corn, oats, rye,
barley, seeds, rice, etc.
grain heeling moments transverse moments caused by the
transverse movement of grain in a
compartment.
heaving motion the vertical movement of a ship’s VCG.
hydrometer an instrument used to measure the density
of a liquid.
hydrostatic curves used for calculating the trim and stability
values for various conditions of loading.
hydrostatic table a tabular statement of values on hydrostatic
curves.
icing allowances must be considered when dealing with loss
of stability and change of trim.
IMO International Maritime Organisation.
inertia coefficient used for obtaining moments of inertias of
waterplanes.
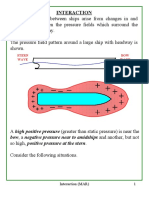
interaction action and reaction of ships when they get
too close to one another or too close to a
river bank.
intercostal girder a girder that is non-continuous.
knot 1852 m per hour.
lightship draft draft of ship when ship is empty, with a
deadweight of zero.
lightweight empty ship, with boilers topped up to
working level.
LNG ships liquefied natural gas carrier with cargo
at ⫺161 degrees C.
LOA length overall, from the foremost part of the
bow to the aftermost part of the stern.
longitudinal running from bow to stern in a fore and aft
direction.
LPG ships liquefied petroleum gas carrier with cargo
at ⫺42 degrees C.
margin line a line that is 75 mm below the bulkhead
deck @ side.
MCA Marine Coastguard Agency
moment an area times a lever or a weight times a
lever.
406 Ship Stability for Masters and Mates
Murray’s method a method for estimating longitudinal
bending moments.
NA data ‘not available’ or ‘not applicable’.
NK data ‘not known’.
open water a stretch of water where there are no
adjacent river or canal banks.
P&S port and starboard.
Panamax vessel a vessel having a breadth mld of 32.26 m.
parametric rolling additional rolling of a ship, caused by
having a bluff stern in interacting with a
sharp streamlined bow form.
passenger liners vessels travelling between definite ports,
with timetabled departure and arrival dates.
passenger-cargo ship a vessel that carries cargo and more than 12
paying passengers.
permeability the amount of water that can enter a bilged
compartment, usually expressed as a
percentage.
pitching motion vertical see-saw movement of a ship at the
bow and at the stern.
Plimsoll disc centre of this disc is in line with the SLWL
and its centre is spot on amidships.
port left side of a ship when looking forward.
pressure bulbs bulbs of pressure that build up around a
moving vessel and disappear when vessel
stops.
retrofit a structure later added or deducted after the
delivery of the ship to the shipowner.
righting lever a lever that will bring a stable ship back to
the upright after being displaced by
temporary external forces.
righting moment a moment that will bring a stable ship back
to the upright.
rolling motion a ship roll from extreme port to extreme
starboard and back again to extreme port.
RO-RO ships roll-roll vessels that carry cars/lorries and
passengers.
shallow water where the depth of water reduces the ship
speed and prop revs, increases squat,
reduces rolling motions, etc.
sheer ratio deck sheer forward or aft/ship’s draft
moulded.
shifting boards used to prevent a transverse shift of grain.
ship surgery lengthening, deepening or widening a ship
after cutting her transversely, along or
longitudinally.
Nomenclature of ship terms 407
Simpson’s Rules used for calculating areas, moments, volumes
and inertias, without needing to use calculus.
SLWL summer load waterline similar to
draft moulded, in a density of water of
1.025 t/cu. m.
sounding a vertical distance measured from the
bottom of a tank to the surface of a liquid in
the tank.
sounding pad a steel pad at the base of a sounding pipe.
sounding pipe a pipe of about 37.5 mm that can be used for
taking soundings with a steel sounding
tape.
sounding tube/glass a vertical tube used for reading calibrated
values of a liquid in a tank.
SQA Scottish Qualifications Authority.
squat loss of underkeel clearance as a ship moves
forward from rest.
St Lawrence Seaway max where the ship’s breadth mld is 23.8 m.
Starboard right side of a ship when looking forward.
stiff ship a vessel with a quick rapid rolling period.
stowage factor volume per unit weight for a grain cargo.
stringer plate the line of deck plates nearest to the
shearstrake or gunwhale plating.
Summer freeboard the minimum freeboard for a ship floating
in water with a density of salt water of
1.025 t/cu. m.
supertanker similar to a VLCC: having a dwt of 100 000 t
to 300 000 t.
synchronous rolling the roll of the ship being in phase with the
action of the waves.
tabular freeboard minimum Summer freeboard for a DfT
standard ship.
tender ship a vessel with a long slow lazy rolling period.
tensile stress stress that is forcing the fibres in the
material to be pulled apart.
timber loadlines marked on ships that carry timber on the
main deck.
tonne equivalent to 1000 kg.
transverse running from port to starboard across the
ship.
transverse squat squat at the bilge plating, caused by ships
overtaking or passing in a river.
trim the difference between the forward draft
and the aft draft.
true trim the difference between the drafts at for’d
perpendicular and after perpendicular.
408 Ship Stability for Masters and Mates
Type ‘A’ ship a ship that carries liquid in bulk.
Type ‘B’ ship a ship other than Type ‘A’ ship.
ukc underkeel clearance, being depth of water
minus a ship’s draft.
ULCC ultra large crude carrier, say over 300 000 t dwt.
ullage vertical distance from surface of a liquid in
the tank to top of the sounding pipe or top
of ullage plug.
VLCC very large crude carrier, say 100 000 t to
300 000 t dwt.
wind heel moments moments caused by the wind on side of the
ship causing ship to have angle of heel.
Young’s modulus the value obtained by stress/strain.
You might also like
- Yamaha T135 HC (Manual) Parts CatalogueDocument61 pagesYamaha T135 HC (Manual) Parts CatalogueHafidz Rosly81% (100)
- Magnetic Compass - Oral COCDocument10 pagesMagnetic Compass - Oral COCNaeem100% (1)
- Ship Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesFrom EverandShip Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Patel, Anita - Super Indian Snack and Street Food Recipes PDFDocument117 pagesPatel, Anita - Super Indian Snack and Street Food Recipes PDFBella ImèneNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument3 pagesDefinitionsAhmed AboelmagdNo ratings yet
- Word Ship HandlingDocument9 pagesWord Ship Handlingrigel100% (1)
- D1MC Semester 1 / Ship Stability / April 2006/capt - MARDocument37 pagesD1MC Semester 1 / Ship Stability / April 2006/capt - MARMohd Azril NaharudinNo ratings yet
- GRAINCALCNCBDocument8 pagesGRAINCALCNCBwaleedyehia100% (1)
- Unit 1 - Ships Magnetism Part 1Document13 pagesUnit 1 - Ships Magnetism Part 1The SinghNo ratings yet
- Squat CalculationDocument2 pagesSquat CalculationAjay SinghNo ratings yet
- Maniobra de BuquesDocument401 pagesManiobra de BuquesPablo VeraNo ratings yet
- Navigational WatchkeepingDocument2 pagesNavigational WatchkeepingManos Kalikis100% (1)
- Measures To Consider When Assisting A VesselDocument7 pagesMeasures To Consider When Assisting A VesselMico SantosNo ratings yet
- Wet Damage On Bulk Carriers: With You at All TimesDocument32 pagesWet Damage On Bulk Carriers: With You at All TimesDerfliw John Valenzuela Gayanoche100% (1)
- Damage StabilityDocument11 pagesDamage Stabilitypolaris25100% (1)
- Stability Theory IIIDocument32 pagesStability Theory IIISergio RuedaNo ratings yet
- P020213 Stability BookDocument115 pagesP020213 Stability BookPETERNo ratings yet
- 2.ship ConstDocument74 pages2.ship ConstArjun AchuNo ratings yet
- 02-Ship Manouvring Part 2Document17 pages02-Ship Manouvring Part 2Ashok Chhetri100% (2)
- 15 Precise PilotingDocument32 pages15 Precise PilotingErnestoDom100% (3)
- Dynamic UKC BookletDocument19 pagesDynamic UKC BookletOllivier AmaruNo ratings yet
- What Is International Grain CodeDocument3 pagesWhat Is International Grain CodeJames JarabeloNo ratings yet
- Initial Transverse Metacenter CugalDocument19 pagesInitial Transverse Metacenter CugalPete KatipunanNo ratings yet
- Seamanship - DefinitionDocument2 pagesSeamanship - DefinitionFrenzie Mae Vasquez Rivera0% (1)
- Safe Navigation in The Kanmon Kaikyo PDFDocument19 pagesSafe Navigation in The Kanmon Kaikyo PDFQuân Nguyễn100% (1)
- Mandatory Emergency Towing Systems in Ships Other Than Tankers of Not Less Than 20,000 DWTDocument6 pagesMandatory Emergency Towing Systems in Ships Other Than Tankers of Not Less Than 20,000 DWTnawanNo ratings yet
- 2 Reefer Cargo ManifestDocument3 pages2 Reefer Cargo Manifestjimmy_shroffNo ratings yet
- INTERACTION and SQUATDocument48 pagesINTERACTION and SQUATمرتضى جبار السودانيNo ratings yet
- Stability FormulaeDocument4 pagesStability FormulaePaul Ashton100% (1)
- MSC.1-Circ.707 - Guidance To The Master For Avoiding DangerousSituations in Following and Quartering Seas (Secretariat) PDFDocument14 pagesMSC.1-Circ.707 - Guidance To The Master For Avoiding DangerousSituations in Following and Quartering Seas (Secretariat) PDFhugh7777No ratings yet
- Scotvec (Stabiltiy) Theory: Table of ContentsDocument25 pagesScotvec (Stabiltiy) Theory: Table of ContentsMohan KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Damage Control Plan N BookletDocument2 pagesDamage Control Plan N BookletAbu Nawshad100% (1)
- Module 24 Damage StabilityDocument9 pagesModule 24 Damage StabilitySippu SifathullahNo ratings yet
- 4 - ManevraDocument44 pages4 - ManevraIulian Sandru100% (1)
- SQEMARINEPassage PlanningDocument3 pagesSQEMARINEPassage PlanningCapt. Lakhi Narayan Mandal IMU Navi Mumbai Campus100% (2)
- ROTIDocument7 pagesROTIcaptyashpalNo ratings yet
- Mooring TopicsDocument3 pagesMooring Topicsjoeven64No ratings yet
- A Guide To The Influence of Ground Reaction On Ship PDFDocument12 pagesA Guide To The Influence of Ground Reaction On Ship PDFamr_tarek_26No ratings yet
- Handout of SHIP CONSTRUCTION (NASC) GMEDocument52 pagesHandout of SHIP CONSTRUCTION (NASC) GMEInderjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- ANCHOR and CABLEDocument16 pagesANCHOR and CABLEMitanshu Chadha100% (1)
- Phase 1 Naval Arch Theory QuestionsDocument6 pagesPhase 1 Naval Arch Theory QuestionsSam UelNo ratings yet
- B1b StabilityDocument17 pagesB1b StabilityDarwin Neil MoranoNo ratings yet
- Tonnage MeasurementDocument5 pagesTonnage Measurementbhaswath2000No ratings yet
- Ship Stability Center of Gravity and Center of BuoyancyDocument8 pagesShip Stability Center of Gravity and Center of BuoyancyAmin Al QawasmehNo ratings yet
- Letter FlagsDocument6 pagesLetter FlagsAnamaria Daniela100% (1)
- How Squat, Bank and Bank Cushion Effects Influence Ships in Restricted WatersDocument6 pagesHow Squat, Bank and Bank Cushion Effects Influence Ships in Restricted Watersconcrete designNo ratings yet
- Fse On Ship StabilityDocument34 pagesFse On Ship StabilityVinodh KumarNo ratings yet
- 02 Seamanship and Ship Handling 03Document20 pages02 Seamanship and Ship Handling 03Oleg Kuchorenko100% (1)
- D-101 Master Standing OrdersDocument9 pagesD-101 Master Standing Orderszainav100% (1)
- Radar and ARPA Automatic Radar Plotting AidsDocument7 pagesRadar and ARPA Automatic Radar Plotting Aidszeropenn00100% (1)
- BP 3 The International Maritime Dangerous Goods Imdg CodeDocument20 pagesBP 3 The International Maritime Dangerous Goods Imdg CodepavithranrohanNo ratings yet
- Ship Stability OOW Basic PrincipleDocument17 pagesShip Stability OOW Basic PrincipleAmin Al QawasmehNo ratings yet
- 6 Final KGDocument44 pages6 Final KGCap Karim ElSherbiniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Levels of Tides at Standard and Secondary PortsDocument28 pagesLesson 3 Levels of Tides at Standard and Secondary PortsEljay Lance Daguno Flores100% (1)
- Interaction: Bow, A Negative Pressure Near To Amidships and Another, But NotDocument5 pagesInteraction: Bow, A Negative Pressure Near To Amidships and Another, But NotBharatiyulam100% (1)
- ANCHOR SystemDocument32 pagesANCHOR SystemenglisgoNo ratings yet
- Marine Gyro-Compasses and Automatic Pilots: A Handbook for Merchant Navy OfficersFrom EverandMarine Gyro-Compasses and Automatic Pilots: A Handbook for Merchant Navy OfficersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Tanker Disasters: IMO's Places of Refuge and the Special Compensation Clause; Erika, Prestige, Castor and 65 CasualtiesFrom EverandTanker Disasters: IMO's Places of Refuge and the Special Compensation Clause; Erika, Prestige, Castor and 65 CasualtiesNo ratings yet
- Embassy and Attached Agencies Hotlines 1 PDFDocument1 pageEmbassy and Attached Agencies Hotlines 1 PDFRoderick EstrellaNo ratings yet
- M-08-CI-A6-01 REV 02 Customer Pressure Selection Chart For The A6 Valve PDFDocument1 pageM-08-CI-A6-01 REV 02 Customer Pressure Selection Chart For The A6 Valve PDFRoderick EstrellaNo ratings yet
- GNTabloid - 040119 Issuu PDFDocument3 pagesGNTabloid - 040119 Issuu PDFRoderick EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Splice BookDocument30 pagesSplice BooklmantuanoNo ratings yet
- PSCRB Day 1 (Edited) (3 Files Merged) PDFDocument390 pagesPSCRB Day 1 (Edited) (3 Files Merged) PDFRoderick Estrella100% (1)
- Good Maintenance On Board Ships e 2015Document83 pagesGood Maintenance On Board Ships e 2015harunNo ratings yet
- CvoroviDocument82 pagesCvoroviAna Lekan100% (2)
- PSCRB Day 1 (Edited) (3 Files Merged) PDFDocument390 pagesPSCRB Day 1 (Edited) (3 Files Merged) PDFRoderick Estrella100% (1)
- Rider's Manual: BMW MotorradDocument136 pagesRider's Manual: BMW MotorradAlex Quintana100% (1)
- SBB Product NoteDocument3 pagesSBB Product NoteFilipe MartinsNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Praktikum Dasar-Dasar Pemisahan Kimia Pembuatan Membran Polysulfon (PSF)Document9 pagesJurnal Praktikum Dasar-Dasar Pemisahan Kimia Pembuatan Membran Polysulfon (PSF)Rizki AuNo ratings yet
- Colegio de San Gabriel Arcangel of Caloocan, IncDocument7 pagesColegio de San Gabriel Arcangel of Caloocan, IncKIRITO SALINASNo ratings yet
- All About CupcakesDocument4 pagesAll About CupcakesRevtech RevalbosNo ratings yet
- Saturated Salt Solutions and %RHDocument2 pagesSaturated Salt Solutions and %RHsamman149686100% (1)
- Annual Report 2016Document171 pagesAnnual Report 2016Angel GrilliNo ratings yet
- What Is New in API 610 11th EdDocument6 pagesWhat Is New in API 610 11th EdAnonymous 1XHScfCINo ratings yet
- The Tenth House in AstrologyDocument6 pagesThe Tenth House in AstrologytratakNo ratings yet
- Updated CBRN - Guideline - Final - Dec 16 - 2021Document110 pagesUpdated CBRN - Guideline - Final - Dec 16 - 2021Mohammed AbdillahiNo ratings yet
- 4864.21 - Optics System 2Document39 pages4864.21 - Optics System 2Edgar Jose Aponte MartinezNo ratings yet
- Tadabbur I Qur'ānDocument43 pagesTadabbur I Qur'ānamjad_emailNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On TurbojetDocument6 pagesResearch Paper On Turbojetqptwukrif100% (1)
- Nokia 6131 NFCDocument5 pagesNokia 6131 NFCvetvetNo ratings yet
- Maximizing Bass Reflex System Performance Through Optimization ofDocument32 pagesMaximizing Bass Reflex System Performance Through Optimization ofGilberto MontaniNo ratings yet
- Coronary Stents: Current StatusDocument42 pagesCoronary Stents: Current StatusMANSI SALUNKENo ratings yet
- Papr114 SpectralDocument4 pagesPapr114 Spectrallilivaca28No ratings yet
- Case IH Farmall B - Brochure - 0717Document7 pagesCase IH Farmall B - Brochure - 0717nadeemmohamed555No ratings yet
- Supplier S Documentation of Equipment PDFDocument32 pagesSupplier S Documentation of Equipment PDFzhangjieNo ratings yet
- Allegheny Power Planning CriteriaDocument19 pagesAllegheny Power Planning Criteriaksdp1No ratings yet
- Design & Fabrication of Low Cost Small-Scale Fatigue Testing MachineDocument12 pagesDesign & Fabrication of Low Cost Small-Scale Fatigue Testing MachinekshitijNo ratings yet
- Zbus and Symmetrical Fault AnalysisDocument20 pagesZbus and Symmetrical Fault Analysishj203800No ratings yet
- MantrasDocument45 pagesMantrasharibhakta100% (1)
- Poem Summary - Keeping QuietDocument3 pagesPoem Summary - Keeping QuietVignesh Mohan100% (2)
- Concrete Tunnel Design and Calculation Spreadsheet Based On AASHTO and ACIDocument3 pagesConcrete Tunnel Design and Calculation Spreadsheet Based On AASHTO and ACIFirat PulatNo ratings yet
- GENII - Nissan Patrol GQ & GU - RE4 4 Speed Diesel & Petrol - Lock Up Instructions-1Document14 pagesGENII - Nissan Patrol GQ & GU - RE4 4 Speed Diesel & Petrol - Lock Up Instructions-1Trav GilesNo ratings yet
- System Substation Commissioning TestsDocument8 pagesSystem Substation Commissioning TestsCvijayakumar100% (1)
- AidsDocument22 pagesAidsVicky Singh100% (2)
- 06 Brakes PDFDocument6 pages06 Brakes PDFAKILI PSINo ratings yet