Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pre-Lab 3
Uploaded by
SaulS.DiazOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pre-Lab 3
Uploaded by
SaulS.DiazCopyright:
Available Formats
Austin Community College Chemistry
Saul Sanchez Experiment 8
Title: Determination of Equilibrium Constant (Method 1)
Goal: To determine the value of Kc for the equilibrium reaction below and to verify that Kc is
constant at constant temperature. This will be done by mixing various concentrations of the
reactants, and determining Kc in each case.
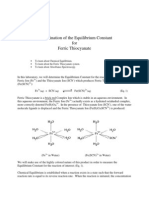
Fe3+(aq) + SCN-(aq) <____> FeSCN2+(aq)
Since this complex ion is red, we can measure the intensity of the red color using a
spectrophotometer. Specifically, we will measure absorbance, which is a measure of how much
light at the specified wavelength is absorbed.
Now, we need to relate the measured absorbance to concentration. Data for a calibration
curve will be provided. The student will graph this data, and will result in a straight-line curve.
Procedure:
Method I:
1) Label 5 test tubes. Pour about 30 ml 2.00x10-3 M Fe(NO3)3 in 1 M HNO3 into a dry 100
ml beaker.
2) Pipet 5.00 ml of that solution into each test tube. Then add about 20 ml 2.0x10-3 M KSCN
to another dry 100 ml beaker.
3) Pipet 1,2,3,4 and 5 ml from the KSCN beaker into each of the corresponding test tubes
labeled 1 to 5. Then pipet the proper number of milliliters of water into each test tube to
bring the total volume in each tube to 10.00 ml. Mix each solution with a glass-stirring
rod.
4) Place a portion of the mixture in tube 1 in a spectrophotometer cell, and measure the
absorbance of the solution at 447 nm. Determine the concentration of FeSCN2+ from the
calibration curve provided for each instrument or from your equation. Record the value
on the data sheet.
Test Tube No.
1 2 3 4 5
Volume of Fe(NO3)3 ml 5.00 3.00 5.00 5.00 5.00
Volume of KSCN ml 1.00 2.00 3.00 4.00 5.00
Volume of H2O ml - - - - -
Austin Community College Chemistry
Method II:
1) Prepare a solution of known [FeSCN2+] by pipetting 10.00 ml 0.200 M Fe(NO3)3 in 1 M
HNO3 into a test tube and adding 2.00 ml 0.00200 M KSCN and 8.00 ml water. Mix the
solution with stirring rod.
2) Assuming that all SCN- is converted to FeSCN2+ calculate [FeSCN2+] in the standard
solution and record the value on the data page.
3) The [FeSCN2+] in the unknown mixture in test tubes 1 to 5 is found by comparing the red
color intensity in there mixtures with that of the standard solution.
4) Pour out the standard solution into a dry, clean beaker until the color intensity you see
down the tube containing the standard matches what you see when looking down the tube
with the unknown. Use a wall-lit piece of white paper as your background.
5) When the colors match the following relation is valid:
[FeSCN2+]unknown x depth of unknown solution = [FeSCN2+] x depth of standard solution.
6) Measure the depths of the matching solutions with a ruler and record them. Repeat
measurements for mixtures 2-5, recording the depth of each unknown and that of the
standard solution which matches its intensity.
You might also like
- Lab 4 Determination of An Equilibrium Constant 1Document7 pagesLab 4 Determination of An Equilibrium Constant 1Mohammad IzadiNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry - Chemical Equilibrium LabDocument4 pagesAP Chemistry - Chemical Equilibrium LabJonathan Chen100% (1)
- Experiment 7 - KC DeterminationDocument12 pagesExperiment 7 - KC DeterminationDan Chen0% (1)
- Spectrophotometric Determination of An Equilibrium ConstantDocument6 pagesSpectrophotometric Determination of An Equilibrium ConstantJett CanoyNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometric Determination of The Equilibrium Constant of A ReactionDocument5 pagesSpectrophotometric Determination of The Equilibrium Constant of A Reactionnarras11100% (1)
- Experiment 6: Determination of An Equilibrium Constant: PurposeDocument8 pagesExperiment 6: Determination of An Equilibrium Constant: PurposedenciopoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium: Finding A Constant, K: LabquestDocument5 pagesChemical Equilibrium: Finding A Constant, K: LabquestSandra SaidNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium ConstantDocument12 pagesEquilibrium ConstantMs azmat100% (2)
- Chemical Equilibrium Experiment: Name: Licheng Zheng ID: 30662751 Date: 2/8/13Document5 pagesChemical Equilibrium Experiment: Name: Licheng Zheng ID: 30662751 Date: 2/8/13Licheng ZhengNo ratings yet
- 4 Equilibrium PDocument6 pages4 Equilibrium PbettersideofmeNo ratings yet
- Complete Report Exp 2Document9 pagesComplete Report Exp 2Puvaneswari ParanjodiNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Constant LabDocument10 pagesEquilibrium Constant LabAarsh Sachdeva100% (1)
- ManualDocument7 pagesManualVijay TarangeNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Keq LabDocument4 pagesUnit 6 Keq Labjh4540No ratings yet
- Specttrometric LabManual Equilibrium 3bDocument8 pagesSpecttrometric LabManual Equilibrium 3bPande AdnyanaNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Lab ReportDocument10 pagesEquilibrium Lab ReportJimin Son100% (1)
- FR Experiment 5 Chem17Document9 pagesFR Experiment 5 Chem17Emanuel VallejeraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 2: The Equilibrium Constant For The Formation of The Iron (III) Thiocyanate ComplexDocument7 pagesLaboratory 2: The Equilibrium Constant For The Formation of The Iron (III) Thiocyanate ComplexBrandon MutongorewaNo ratings yet
- Ferric Thio Cyan AteDocument16 pagesFerric Thio Cyan AtePablo BernalNo ratings yet
- Determination of Equilibrium Constant For Iron ThiocyanateDocument6 pagesDetermination of Equilibrium Constant For Iron ThiocyanatePablo Bernal100% (2)
- Equilibrium Constant PDFDocument12 pagesEquilibrium Constant PDF3cutelittlebirdiesNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 16 Determination of An Equilibrium Constant: Use of The Spectrophotometer The PipetDocument13 pagesExperiment # 16 Determination of An Equilibrium Constant: Use of The Spectrophotometer The PipetPablo BernalNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometric Determination of The Equilibrium Constant of A ReactionDocument8 pagesSpectrophotometric Determination of The Equilibrium Constant of A ReactionKim Tan100% (1)
- Spectrophotometric Determination of The Equilibrium Constant of A Reaction DraftDocument3 pagesSpectrophotometric Determination of The Equilibrium Constant of A Reaction DraftFem T. BartolomeNo ratings yet
- 20 Equilibrium ConstantDocument5 pages20 Equilibrium Constantgardarr11No ratings yet
- Determination of An Equilibrium ConstantDocument10 pagesDetermination of An Equilibrium ConstantStephanie100% (1)
- Equilibrium Formal Report 2Document11 pagesEquilibrium Formal Report 2I Dont CareNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 Determination of An Equilibrium Constant: OutcomesDocument5 pagesExperiment 8 Determination of An Equilibrium Constant: OutcomesnicoleNo ratings yet
- EquilibriumDocument5 pagesEquilibriumShafeeq IbraheemNo ratings yet
- FR-Spectrophotometric Determination of The Equilibrium Constant of A ReactionDocument10 pagesFR-Spectrophotometric Determination of The Equilibrium Constant of A ReactionStella Maris BautistaNo ratings yet
- 3+ (Aq) - (Aq) 2+ (Aq) 2+Document5 pages3+ (Aq) - (Aq) 2+ (Aq) 2+Ferguie SolisNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Constant For FeSCNDocument5 pagesEquilibrium Constant For FeSCNhdlee8880% (1)
- The Determination of K For Fescn: "Your Safer Source For Science Supplies"Document8 pagesThe Determination of K For Fescn: "Your Safer Source For Science Supplies"Pablo Bernal0% (1)
- Spectrophotometric Determination of The Equilibrium Constant of A Reaction Chem 17Document7 pagesSpectrophotometric Determination of The Equilibrium Constant of A Reaction Chem 17Frances Abegail QuezonNo ratings yet
- Chem 17 FR 1 Expt 5 FinalDocument14 pagesChem 17 FR 1 Expt 5 FinalMarrod CruzNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Constant Report Example 4Document17 pagesEquilibrium Constant Report Example 4jim gorman94% (17)
- Lab #11: Determination of A Chemical Equilibrium Constant: ObjectivesDocument0 pagesLab #11: Determination of A Chemical Equilibrium Constant: ObjectivesPablo BernalNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Chemical Equilibrium Determination of An Equilibrium Constant by SpectrophotometryDocument6 pagesExperiment 2 Chemical Equilibrium Determination of An Equilibrium Constant by SpectrophotometryApollo Montecillo FilipinoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium Three Stooges in Chemical ReactionsDocument11 pagesChemical Equilibrium Three Stooges in Chemical ReactionsKhud SarNo ratings yet
- ChemEquilibrium Experiment 2022NDocument20 pagesChemEquilibrium Experiment 2022NDaniela Solórzano PantojaNo ratings yet
- S D E C R / E 5: Pectrophotometric Etermination OF THE Quilibrium Onstant OF A Eaction XperimentDocument14 pagesS D E C R / E 5: Pectrophotometric Etermination OF THE Quilibrium Onstant OF A Eaction XperimentKenneth Dionysus SantosNo ratings yet
- CH 101: Physical Chemistry Practicals: Determination of The Equilibrium Constant For A Chemical ReactionDocument34 pagesCH 101: Physical Chemistry Practicals: Determination of The Equilibrium Constant For A Chemical ReactionEvelyn MushangweNo ratings yet
- Soriano CHM242 FR1Document8 pagesSoriano CHM242 FR1Aladha SorianoNo ratings yet
- 4 3Document8 pages4 3Johnny Woods0% (1)
- Exp. 2 c230 S - 07 Keq of FeSCNDocument10 pagesExp. 2 c230 S - 07 Keq of FeSCNdenciopoNo ratings yet
- Applied Chemistry Lab - CHEM-320: Lab Report # 10 (Semester 6 2021) Submission Date: 30-May, 2021Document6 pagesApplied Chemistry Lab - CHEM-320: Lab Report # 10 (Semester 6 2021) Submission Date: 30-May, 2021AeeshaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report For Chemical Equilibrium Pre-Lab QuestionsDocument11 pagesLab Report For Chemical Equilibrium Pre-Lab QuestionsKhud SarNo ratings yet
- 3 Equilib. LeChat. Principle 2012Document4 pages3 Equilib. LeChat. Principle 2012Jennifer HuNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Ii SCH2106 PDFDocument13 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Ii SCH2106 PDFAndrew May NcubeNo ratings yet
- Fe SCNDocument6 pagesFe SCNmksayshiNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of The Iron Thiocyanate ReactionDocument6 pagesEquilibrium of The Iron Thiocyanate ReactionwaitmanffNo ratings yet
- 14 CHEL17 - Chemistry Lab ManualDocument60 pages14 CHEL17 - Chemistry Lab ManualAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 6: Photometric Determination of An Equilibrium ConstantDocument9 pagesEXPERIMENT 6: Photometric Determination of An Equilibrium ConstantdenciopoNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 2 SheetDocument5 pagesLab Activity 2 SheetLianne OhNo ratings yet
- Chem 17 - SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC DETERMINATION OF THE EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT OF A REACTIONDocument7 pagesChem 17 - SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC DETERMINATION OF THE EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT OF A REACTIONWilfredo LlanaNo ratings yet
- Formal Report (Experiment 5 RDR)Document8 pagesFormal Report (Experiment 5 RDR)Jay Jay0% (1)
- Selected Constants: Oxidation–Reduction Potentials of Inorganic Substances in Aqueous SolutionFrom EverandSelected Constants: Oxidation–Reduction Potentials of Inorganic Substances in Aqueous SolutionNo ratings yet
- Recommended Reference Materials for Realization of Physicochemical Properties: Pressure–Volume–Temperature RelationshipsFrom EverandRecommended Reference Materials for Realization of Physicochemical Properties: Pressure–Volume–Temperature RelationshipsE. F. G. HeringtonNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsFrom EverandElectrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsAndrzej LewenstamNo ratings yet
- Computational Pharmaceutics: Application of Molecular Modeling in Drug DeliveryFrom EverandComputational Pharmaceutics: Application of Molecular Modeling in Drug DeliveryDefang OuyangNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials Problem 8-7Document1 pageMechanics of Materials Problem 8-7SaulS.DiazNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials Problem 8-6Document1 pageMechanics of Materials Problem 8-6SaulS.DiazNo ratings yet
- Problem 8-5 PDFDocument1 pageProblem 8-5 PDFSaulS.DiazNo ratings yet
- Problem 8-3 PDFDocument1 pageProblem 8-3 PDFSaulS.DiazNo ratings yet
- Calc 3 Project 1Document12 pagesCalc 3 Project 1SaulS.DiazNo ratings yet
- Calculus 3 Project 2 - Contour Plots Describing Functions in The Third DimensionDocument19 pagesCalculus 3 Project 2 - Contour Plots Describing Functions in The Third DimensionSaulS.DiazNo ratings yet
- Title: Goal:: (Aq) - + (Aq) - (Aq)Document2 pagesTitle: Goal:: (Aq) - + (Aq) - (Aq)SaulS.DiazNo ratings yet
- Title: Goal:: (Aq) - + (Aq) - (Aq)Document2 pagesTitle: Goal:: (Aq) - + (Aq) - (Aq)SaulS.DiazNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab 8Document1 pagePre-Lab 8SaulS.DiazNo ratings yet
- Pledge Parent DeclarationDocument2 pagesPledge Parent Declarationabc xyz100% (3)
- Knowledge Representation and Reasoning: University "Politehnica" of Bucharest Department of Computer ScienceDocument25 pagesKnowledge Representation and Reasoning: University "Politehnica" of Bucharest Department of Computer Scienceusman kebatoNo ratings yet
- Outline: Optimum Spray Cooling in Continuous Slab Casting Process Under Productivity ImprovementDocument5 pagesOutline: Optimum Spray Cooling in Continuous Slab Casting Process Under Productivity ImprovementKiatkajohn WorapradyaNo ratings yet
- Types of Plagiarism IDocument9 pagesTypes of Plagiarism IUdiana Puspa Dewi100% (1)
- Kali Lunix CommandDocument7 pagesKali Lunix CommandSubhash BhalekarNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry - Exp 1Document8 pagesAnalytical Chemistry - Exp 1Zharifah Bari'ah Basa'ah100% (1)
- Life Cycle AnalysisDocument14 pagesLife Cycle AnalysisAshesh PradhanNo ratings yet
- Wuthering HeightsDocument26 pagesWuthering HeightsAbubakarr SankohNo ratings yet
- Bibliografi Full TesisDocument6 pagesBibliografi Full TesisHabibah Mohamad RejabNo ratings yet
- Alekha Gaddam: Education Level Institution/College Board/University Year of Passing Aggregate (In %)Document2 pagesAlekha Gaddam: Education Level Institution/College Board/University Year of Passing Aggregate (In %)veenadhari koppulaNo ratings yet
- Soil Survey Mapping - LectureNotes2Document132 pagesSoil Survey Mapping - LectureNotes2Udaya KumarNo ratings yet
- Pid Good Tuning A Pocket GuideDocument120 pagesPid Good Tuning A Pocket GuideHeidi HillNo ratings yet
- Heat Flux Thermocouple MCTDocument2 pagesHeat Flux Thermocouple MCTIziNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Variance (F-Test) : Name: Jonalyn M. Cerilo Subject: Statistics Professor: Dr. Maria Dela Vega TopicDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Variance (F-Test) : Name: Jonalyn M. Cerilo Subject: Statistics Professor: Dr. Maria Dela Vega TopicKim NoblezaNo ratings yet
- SINAMICS S120 Commissioning Manual 0306 EngDocument412 pagesSINAMICS S120 Commissioning Manual 0306 Engwww.otomasyonegitimi.com100% (1)
- 89c51 MCUDocument16 pages89c51 MCUyuvakiraniNo ratings yet
- Endnote X8: Research SmarterDocument9 pagesEndnote X8: Research SmarterMuhajir BusraNo ratings yet
- SAMI-using FibermetDocument15 pagesSAMI-using FibermetAnonymous MwAZh7ripLNo ratings yet
- Nstp1 Quiz 1 Quiz To Prelim by Jezza Amacalamba 1 CompressDocument12 pagesNstp1 Quiz 1 Quiz To Prelim by Jezza Amacalamba 1 CompressHiro GamerNo ratings yet
- Release Notes RobotStudio 6.01.01Document36 pagesRelease Notes RobotStudio 6.01.01Razvan Theodor AncaNo ratings yet
- LSP Writeshop Guide 2014Document84 pagesLSP Writeshop Guide 2014Michelle de los Santos100% (2)
- 5 Year Development Plan 1Document10 pages5 Year Development Plan 1Che Morales100% (2)
- BalakaniayanDocument4 pagesBalakaniayanmanuel5No ratings yet
- Molinos Eolicos VestasDocument41 pagesMolinos Eolicos VestasOscar Männlich100% (1)
- FL Pocket Book-1Document19 pagesFL Pocket Book-1IISCIrelandNo ratings yet
- DisksDocument3 pagesDisksYogesh C GangadharanNo ratings yet
- Catatan Statisktik FIXDocument59 pagesCatatan Statisktik FIXAndrian WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Mod Loop 1Document12 pagesMod Loop 1Juan carlos Sotelo merazNo ratings yet
- 4-9a York NPLV ArticleDocument4 pages4-9a York NPLV Articlekah178No ratings yet