Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ihl Protein Chart
Uploaded by
Mahmoud Alnsour0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views9 pagesproteins
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentproteins
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views9 pagesIhl Protein Chart
Uploaded by
Mahmoud Alnsourproteins
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
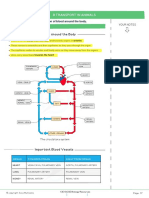
Protein Function Pathway
CD34 On all Hemopoetic Stem cells
CD21 (CR2) -iC3b + C3d co-receptor Involved in Complement
Connects the B cell to the cascade and B cell activation
complement cascade
-CR2+ C3d allows intercellular
stimulation which is an increase
in overall signaling
CD19 Signaling chain of co- Involved in B cell marking
receptor/B-cell marker
CD 81 BCR/ Co-receptor interaction Entry point for HCV (hep C)
CR1 Recognizer of C3b
CCL 21/19 Cytokines that attract cells to B cell activation
the LN, ones with CCR 7 T cell activation
Immature DC cells without
antigens
CXCL 13 Allows B-cells to enter, B-cells
follow a gradient of CXCL-13
CD 69 Expressed after Antigen B cell activation
encounter on B-cells blocks
S1P
S1P A chemotactic lipid that binds to
a receptor on Naive T-cell.
Blocked by CD69.**** [verify]
IL-5 Involved in Plasma cell
formation [derived from B cell]
Produced from Th2
IL-6 -Secreted by T-cells to induce
plasma formation
-FDC’s secrete this in
centroblast formation
-In combination with IL-1 and
TNF-α, it leads to a high
inflammatory response
IL-15 FDC’s secrete this in centroblast
formation
Involved in the proliferation and
growth of NK cells as well
[book]
BAFF FDC’s secrete this in centroblast
formation
BCL-xL Survival signal originating from
the ligation of MH-II and CD40
on B cell and T-cell combination
IL-10 Used in the differentiation of
plasma cells in centrocytes
Produced by T-regulatory Cells
IL-4 Used in Centrocyte
differentiation into memory B-
cells Produced from Th2
FcRn It is involved in the movement
of IgG from the blood stream to
the inside of the tissue.
It binds the Ab within the cell
and protects from the lysosome
by the binding to the Fc Region
pIg Is involved in the transport of
IgA across membrane
It is cleaved during this process
and keeps a piece of itself
attached to the A
FcεR1 Allows for the readily binding of
IgE to allow an allergic reaction
Found on: neutrophils, Mast
cells, Eosinophils
CRP Involved in the binding of IgM
FcγR Binds IgG
CD16 Binds to FcγRIII on NK cells and
tells it to kill
FcγRIII Binds CD16, found on NK cells
RAG Recombination protein gene
necessary for the formation of
different classes of Ig’s.
-Issues found with this gene
leads to a deficiency in Ig
Production
-Mechanism is a Dimer
formation for initiation of
recombination
RSS One/both ends of VDJ
recognition by the RAG-1 and
RAG-2
-It follows this recognition by
direction of recombination,
ensuring that correct processes
occur
CD3 Complex CD3ε(2) + CD38+CD3γ+ζ
IL-7 Required for further B-cell
growth and proliferation with
receptors found on both late
pro and pre-B cell
-Cytokine necessary in T-Cell
development produced by
thymic stroma and bind to the
CD34 expressing progenitor
cells
pTα β chain test for ability for ability
to bind to its Ag (β – won at this
point
L-Selectin T-cell binder to to sialyl-lewisx of
CD34 and GlyCAM-1
CD34 Used to carry T cells in rolling
mechanism
GlyCAM-1 Found on HEV, used to carry the
T-cell to its destination
ICAM1 and ICAM2 Binds to LFA to stop movement
when the T-cell arrives to the LN
DC cell binding T-Cell - DC cell
CD2 LFA3
LFA-1 ICAM 1 / 2
ICAM 3 DC SIGN
TNF-α Massive increase in production
leads to septic shock
IL-1+TNF-α are key to an
inflammatory response
IL-1β Fibroblast interferon production
that is key in viral infection
resistance
Increases inflammation
IL-1 In concert with TNF-, it plays a
key to an inflammatory
response
IL-12 Macrophage cytokine that acts
on NK cells
Produced by Th1
Dectin -1 Phagocytosis macrophage
receptor that recognizes
carbohydrate ligands
Mannose receptor Dendritic cell[non-follicular] and
macrophage receptor that
pushes for pathogen
phagocytosis
MARCO Scavenger receptor on
macrophage that binds to both
gram negative and positive
Selectin Required by neutrophils to
enter into inflammatory
response
NLR’s Coreceptors, Nod-1 and Nod 2
Its function is to detect the
products derived from
intracellular degraded
phagocytosed pathogens
B7 A B-cell Receptor that binds to
CD28 on a T-cell that allows
further growth
IL-2 Get produced in in an autocrine
way, acts on IL-2R for higher
proliferation
Cyclosporine A, FK506 Inhibits IL-2
Rapamycin IL-2 Receptor inhibition
TH1+TH7 In patients with a lack of IL-10
receptor, patients produce this
combo to be mediated on
subsets of CD4-T cells
CD4 Tfh They remain in the secondary
lymph node and proliferate B-
cells with the receptors of CD28
–B7 and CD40L
VLA-4 Replaces CD62C on L-selelctin
and binds to VCAM-1 On T-Cell
for the purpose of homing into
the inflamed tissue.
CD2+LFA-1 Effector T cells use this to
become more sensitive to tissue
than Niave T-cells
Th1 Cells produces IFNγ and IL-12 (in a
positive feedback loop) in a
feedback loop for pro immune
responses to in order for
macrophages to suppress
intracellular infections
IFNγ -Produced by Th1 cells to
stimulate immune response
Will stimulate macrophages and
remain in the synapses.
-Combined with MHCII it
induces transcription of class II
cells
-Combined with protostomes it
causes a high production of
proteasomes in LMPC, as well
as an increase in p28 release
-Combined with DO under
states of noninfection, DM in
states of infection
-combination of CD40 leads to
increased expression of IL-12 on
DC cells which leads to more NK
T cells
Th17 Produces IL-17,21,22,26 to
enhance the neutrophil
response to fungal and
extracellular bacterial infections
It is induced by IL-6 and TGF-β
Th2: Antagonist to Th1(anti-
inflammatory)
Helps in allergic reactions with
mast cells, eosinophils,
basophils, and B cell IgE
responses
Induced by IL-4
Produces IL-4 and IL-5
TfH Helps B cells differentiate and
class switch
It is induced by IL-16, TGF-β,and
IL-23
T regulatory cells Down Regulates T-cell Function
Induces by: TGF-β
Produces TGF-β and IL-10
JAKs Non-binding cytokine receptors
that Allow Stats to bind upon
phosphorylation
And activates transcription
STATS Activate transcription upon JAK
phosphorylation
SOC’s Bind tyrosine on the cytokine
receptor
Th2 secretion TGF-β + IL4+IL-10 +IL-13
CD25 Expressed on T-regulatory cells
in order to suppress T-cells
FOXD3- It is a transcription suppressor
produced by T-regulatory cells
Perorin+granulysin+serlycin Hole formation in the cell
Grazymes Degenerate nucleus and cause
shrinkage by CD8
NKg2D Expressed by NK cells upon
activation.
Activates MHC-Like structures
It is found in high quantities
during stress
CD16a[FCγRIIIA] Receptor found on NK cells
Only receptor needed for
activation during adaptive
immunity
IgG specific
CD94: NKG2A Ligated by HLA-E [Corralated
with HLA- [A-C]
MIC glycoproteins Activated during stressed
allowing NKG2D to bind
KIR Inhibitory receptor that
recognizes diff forms of HLA
receptors
CD94: NKG2C Predominant during CMV
infection, high cytotoxic activity,
and low responsiveness to
cytokines
Type matching MHC complexes HLA: A,B, and DR
required:
HLA-[A,B,C] Highly polymorphic, Ag to CD8
NK ligands
MHI
MHCII DP, DQ, DR
AG to CD4 T-cell
DM +DO Oligimorphic regulate peptide
FCyRI Receptor of IgC3
Pentaxins Access of protein in the blood
that targets pathogens for
destruction
C-reactive proteins
CD-14 Co-receptors to TLR4, its making
macrophage
CXCL8 Macrophages secrete it upon
activation to attract necessary
cells to migrate from blood to
tissue
IL-1β
Calnexin Stabilizes MHC1 after synthesis
to prevent mis-folding of till the
attachment of β2 microglobin
Taposin Stabilizes MHC to receive
peptides
ERAP Acts like pacman to shorten
long peptides bound to MHC1
till its ready to present itself
iI It is th einvariant chain and
blocks MHCII from binding to
class I peptides
CLIP Broken down iI that remains
attached to MHC2 till it binds to
till HLA-DM binds
HLA-DM Similar to MHC2 and acts to free
up CLIP from MHC2
Remains bound till MH2 bound
to right antigen
HLA-DO Reversibly binds to MHC2 to
inhibit Ag presentation
CCR7 “seeker protein” receptor on
B/T cell that seeks out gradients
of CCL 21 and 19
CCL 21/19 Released by DC’s to attract T
and B cells
IPP Stress molecule that at normal
physiological levels illicit no
response
HMBPP Stronger than IPP made by
bacteria and parasites
BHPP Bind with FCrs at the same time
to induce a T-like cell Vγ:Vδ to
perform ADCC and kill B cell
lymphoma
Zolendronate High Ipp, allows therapeutic
function to fix bone
BTN3A1 Found on all sells, and is
structurally similar to B7,
allowing T like cells to bind.
Specific cobinding from Vγ9:Vδ2
Vγ9:Vδ2 Recognizes phosphoten and not
peptides, binds using BTN3A1
EPCR Ligand for Vγ4:Vδ5 similar to
MH! And allows its cell ti bind
directly
CD1D Group 2 of the CD1 and binds to
Vγ:Vδ
Vγ:Vδ Binds long hydrophibic alkyl
chains.
Ag presented by CD1d
α:β T cells that are non polymorphic
MHC1
Bind CD1a, b, c
NKT cells Bind CD1d
MAIT cells Small organic molecules on MR1
is how it recognizes stuff
CD8 like,
Il12R Activated by IL-18, 23, 25
IgG4 High affinity for all IgG’s
It stimulates FcRIIβ
FCγRIIB Activates macrophages and
neutrophils by antibodies
IGE Most likely picked up by mast
cells on the FcεRI
FcεRII 2 receptor for IgE on mast cells
Each binding domain will bind
single IgG molecule
Can directly bind to IgE, BCR,
BCR co receptor, CR2
ADAM-10 cleaves FcεRII at different sigts
Produces monomeric/ Trimeric
FcεRII
Prostaglandins Promotes BV diliation
Chemoattractors for PMNs
Mast Cells Will synthesize IL-4, TNFα
Eosinophils CCL5. CCL7, CCL11, CCL13
CD27 Marker on B cell
FCγRIIBI Niave B cells suppressor
(Ag+Ab)
You might also like
- Soap NoteDocument4 pagesSoap NoteMahmoud AlnsourNo ratings yet
- Soap NoteDocument1 pageSoap NoteMahmoud AlnsourNo ratings yet
- REview of NeuroanatmyDocument10 pagesREview of NeuroanatmyMahmoud AlnsourNo ratings yet
- CNS Response To InjuryDocument10 pagesCNS Response To InjuryMahmoud AlnsourNo ratings yet
- PHYS Review CardioDocument16 pagesPHYS Review CardioMahmoud AlnsourNo ratings yet
- Hemaliths ObjectivesDocument3 pagesHemaliths ObjectivesMahmoud AlnsourNo ratings yet
- Mahmoud Alnsour - 8-28-17 - MuscleDocument7 pagesMahmoud Alnsour - 8-28-17 - MuscleMahmoud AlnsourNo ratings yet
- AddictionDocument3 pagesAddictionMahmoud AlnsourNo ratings yet
- Final Composition For TranspalantDocument30 pagesFinal Composition For TranspalantMahmoud AlnsourNo ratings yet
- Micro Object 1Document4 pagesMicro Object 1Mahmoud AlnsourNo ratings yet
- Anatomy NotesDocument2 pagesAnatomy NotesMahmoud AlnsourNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Notes 2Document2 pagesAnatomy Notes 2Mahmoud AlnsourNo ratings yet
- Soap NoteDocument1 pageSoap NoteMahmoud AlnsourNo ratings yet
- Soap NoteDocument1 pageSoap NoteMahmoud AlnsourNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- LAMPIRAN RET PELAYANAN KESEHATAN (Rev)Document167 pagesLAMPIRAN RET PELAYANAN KESEHATAN (Rev)RafliNo ratings yet
- Mary Lyons The Passionate EscapeDocument108 pagesMary Lyons The Passionate Escapekausarpshaikh88% (8)
- 8.3.2 SPEAKING - Oral Presentation Rubric NAMEDocument4 pages8.3.2 SPEAKING - Oral Presentation Rubric NAMEapi-197465646No ratings yet
- Extinction Level: Jurassic ParkDocument146 pagesExtinction Level: Jurassic ParkArjan BosNo ratings yet
- CEVA ISAP2008 Sassi Et AlDocument48 pagesCEVA ISAP2008 Sassi Et AlJef SassiNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Exam Grade 10 Animal ProductionDocument4 pages3rd Quarter Exam Grade 10 Animal Productionbella flor villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic MethodsDocument93 pagesDiagnostic MethodsSyukri La Ranti100% (3)
- Motor Neurone Disease and HomoeopathyDocument8 pagesMotor Neurone Disease and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD HomNo ratings yet
- Canine WorkbookDocument48 pagesCanine Workbookrosy_verenice100% (1)
- Grade 9 Sex Ed - Youtube LinksDocument16 pagesGrade 9 Sex Ed - Youtube Linksapi-204719782No ratings yet
- Spirulina Improves Growth - Egg Production and Meat Quality - 2012Document15 pagesSpirulina Improves Growth - Egg Production and Meat Quality - 2012julesverneNo ratings yet
- Cancer Tongue Cured With HomoeopathyDocument6 pagesCancer Tongue Cured With HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD HomNo ratings yet
- February 17, 2017 Strathmore TimesDocument24 pagesFebruary 17, 2017 Strathmore TimesStrathmore TimesNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY RevisionNotes SaveMyExamsDocument7 pagesBIOLOGY RevisionNotes SaveMyExamsAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- Quiz Report-2Document12 pagesQuiz Report-2Nadiya RashidNo ratings yet
- Vital Spots 10 - Taranaki ITF Taekwondo PDFDocument54 pagesVital Spots 10 - Taranaki ITF Taekwondo PDFMaria Elisa MonclusNo ratings yet
- Marshall, 2006 Robinson, 2005 Swan and Papp, 1972: Geographic RangeDocument24 pagesMarshall, 2006 Robinson, 2005 Swan and Papp, 1972: Geographic Rangeanggit prihatnoloNo ratings yet
- Periodontal LigamentDocument3 pagesPeriodontal LigamentCzarina DavidNo ratings yet
- Organ Systems 1 NBC ReviewerDocument39 pagesOrgan Systems 1 NBC ReviewerJames ChavezNo ratings yet
- Dental Pulp TissueDocument77 pagesDental Pulp TissueJyoti RahejaNo ratings yet
- 2012.11.18 - Donald Marshall - Vril Lizards Underground Reptilians Who Bodysnatch HumansDocument15 pages2012.11.18 - Donald Marshall - Vril Lizards Underground Reptilians Who Bodysnatch HumansJFBr100% (1)
- A Queen ManualDocument25 pagesA Queen ManualAle BioleNo ratings yet
- OBDocument4 pagesOBCharlie Cotoner FalgueraNo ratings yet
- 03 Biosecurity Jit PPT FinalDocument20 pages03 Biosecurity Jit PPT FinalReza WratsongkoNo ratings yet
- How PETCO Manages Ethical Concerns of StakeholdersDocument2 pagesHow PETCO Manages Ethical Concerns of Stakeholdersyashnegi.847268No ratings yet
- HTTP: - WWW - Gurumann.com - High-BP - DIET - Ebook - by - Guru - Mann PDFDocument8 pagesHTTP: - WWW - Gurumann.com - High-BP - DIET - Ebook - by - Guru - Mann PDFVardanNo ratings yet
- Chest TubesDocument3 pagesChest TubesKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Surgery For Cerebral Contusions: Rationale and Practice: Review ArticleDocument4 pagesSurgery For Cerebral Contusions: Rationale and Practice: Review ArticleIshan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Iam MahavetnetDocument13 pagesIam MahavetnetVet_ashishtklNo ratings yet
- Principles of Spine Trauma and Spinal Deformities PDFDocument34 pagesPrinciples of Spine Trauma and Spinal Deformities PDFVirlan Vasile CatalinNo ratings yet