Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formulation and Evaluation of Oral Fast Dissolving Film of Cinnarizine
Uploaded by
Baru Chandrasekhar RaoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formulation and Evaluation of Oral Fast Dissolving Film of Cinnarizine
Uploaded by
Baru Chandrasekhar RaoCopyright:
Available Formats
IAJPS 2018, 05 (04), 2316-2325 Mahesh Shinde et al ISSN 2349-7750
CODEN [USA]: IAJPBB ISSN: 2349-7750
INDO AMERICAN JOURNAL OF
PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES
http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1218075
Available online at: http://www.iajps.com Research Article
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF ORAL FAST
DISSOLVING FILM OF CINNARIZINE
Mahesh Shinde*1, Vikas Choure1, Shahadev Rathod1, Arvind Birajdar1, Amit Jadhav2
1
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, R.T.M. Nagpur University, Nagpur, M.S. India.
2
Sandip Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences , Savitribai Phule Pune University, Trimbakeshwar
Road, Nashik, M.S. India.
Abstract:
Cinnarizine is a H1 anti-histaminic drug and it can be used in the treatment of nausea, vomiting, motion sickness,
vertigo and in menier’s disease. The purpose of present work was a development of fast dissolving oral film of
cinnarizine, to overcome the limitation of current routes of administration to provide faster dissolution rate and
increase the patient compliance. The amount of dose of drug calculate according to the area covered by the 15ml
formulation without drug. The amount of drug was then used for the preparation of film by using solvent casting
method utilizing HPMC E5 as a film forming polymer and PEG 400 as a plasticizer. The 32 factorial design was
applied for optimization of concentration of polymer HPMC E5 and plasticizer PEG 400. The prepared film were
evaluated for various parameters like film thickness, folding endurance, drug content, dispersion test, uniformity of
weight, surface pH measurement, moisture loss study, in vitro drug dissolution study, disintegration time and
stability study.in vitro drug dissolution studies were carried out using simulated salivary fluid (pH 6.8 phosphate
buffer).among all the formulation, formulation (F5) which contain HPMC E5 (15%)and PEG400( 6%) were
released upto 98.17% of the drug from the film within 25 sec. which exhibit faster absorption and also shows
desirable characteristics of film than other formulation.
Keywords: Oral fast dissolving film, cinnarizine, motion sickness, menier’s disease, HPMC E5, PEG 400, solvent
casting method.
Corresponding author:
Mahesh P. Shinde, QR code
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences,
R.T.M. Nagpur University, Nagpur, Pin
Code-440033, Maharastra, India.
E-Mail: maheshshinde9404@gmail.com
(Mob.No.)-9404484830
Please cite this article in press Mahesh P. Shinde et al., Formulation and Evaluation of Oral Fast Dissolving Film
of Cinnarizine, Indo Am. J. P. Sci, 2018; 05(04).
www.iajps.com Page 2316
IAJPS 2018, 05 (04), 2316-2325 Mahesh Shinde et al ISSN 2349-7750
INTRODUCTION: A systemic action can be achieved via drug
Cinnarizine is chemically 1-benzhydryl 1-4-cinnamyl permeation through the mucosal epithelium. The
piperazine. It acts as histamine H1 antagonist and concept of fast dissolving drug delivery emerged
calcium channel blocker. It bind to histamine H1 from the desired to provide patient with more
receptor and to muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. conventional means of taking that medication. Fast
Cinnarizine also inhibit contraction of vascular dissolving films recently have acquired great
smooth muscle cells by blocking calcium channels. It importance in the pharmaceutical industry due to
is used for the treatment of nausea, vomiting, vertigo, their unique property and specific advantages like no
motion sickness, menier’s disease. Among all the need of water for disintegration, accurate dosing,
routes of drug administration the oral route is most rapid onset of action, easy of transportability, easy of
advisable route in the designing the formulation of handling, pleasant taste and improve the patient
dosage form than drug delivery design by other compliance. Fast dissolving oral film are useful in the
routes of administration. The oral mucosa is patient such as pediatric, geriatric, bedridden, emetic
conveniently and easily accessible and therefore patient, diarrhea, sudden episode of allergic attack or
allows uncomplicated application of various dosage coughing for those who have an active life style. It is
form. Furthermore, the oral mucosa is robust against also useful whether local action desired such as local
local stress or damage and shows fast cellular anaesthetic for toothache, oral ulcer, cold sore or
recovery. Active substances can be administered teething.
locally to treat oral diseases such as periodontal
disease, fungal, bacterial infection.
Fig 1: cinnarizine loaded oral fast dissolving film.
MATERIAL AND METHODS:
Table 1: List of chemicals
Sr.no. Name of chemicals use
1 Cinnarizine In the treatment of Motion
sickness, menier’s disease, nausea,
vomiting.
2 HPMC E5 polymer
3 PEG 400 plasticizer
4 Citric acid Buffering agent
5 Mannitol Sweetning agent
6 Pipermint oil Flavouring agent
7 Water Solvent
www.iajps.com Page 2317
IAJPS 2018, 05 (04), 2316-2325 Mahesh Shinde et al ISSN 2349-7750
Table 2: List of instruments
Sr.no. Name of instrument Model/Manufacturer
1 Analytical weighing balance Labine analytical balance,Mumbai
2 Magnetic stirrer Remi equipment, Mumbai
3 Sonicator Bio-techniques,Mumbai
4 Film former V.J.instrument,Mumbai
5 Franz diffusion cell Orchid
6 Digital pH meter Hanna instrument
7 UV spectrophotometer Jasco
according to different formulation as shown in table
Preparation of fast dissolving oral films 3. Then add plasticiser (0.4ml, 0.5ml, 0.6ml) for
1)Calculation of drug loaded in film different formulation (f1 to f9) which shown in table
15 ml of placebo formulation (without drug) which 3 and mixed well till clear solution was obtained.
can be covered the 10×30cm=300 cm2 area. i.e.10cm- Then the drug was added to the polymeric solution.
width of film and 30cm-length of the film. Remaining ingredient citric acid, mannitol, pipermint
Now dose of cinnarizine is 25mg in 2×2cm film oil are add and then continuously stirring for 15
i.e.4cm2 area. minute in the magnetic stirrer. After that the solution
Then the 4cm2→25mg drug is placed on the ultrasonicator for 30 minute, to
300cm2→ ‘x’ mg of drug remove the air bubble from the formulation. After
X=300×25/4 that clear solution can be pour on the film former
X=1875 mg of drug with the help of dragger with the maintaining specific
Hence the 1875 mg of drug required in 15ml thickness 0.4mm. film former temperature
formulation. maintained at 40ºc. after that film allow to dry, then
2)Procedure the dried film were carefully removed from the film
Solvent casting method former, checked in any imperfection or air bubbles
Polymer HPMC E5 (1400mg, 1500mg, 1600mg) and cut to pieces of 2×2cm i.e. 4cm2.
were weight accurately and dispersed in water
Table 3: Composition of factorial design formulations of cinnarizine of different batches
Batch Drug (mg) HPMC E5 PEG 400 Citric acid Mannitol Pipermint Water (ml)
(mg) (ml) (mg) (mg) oil (ml)
F1 1875 1400 0.5ml 200 200 0.5 10
(14%)* (5%)*
F2 1875 1500 0.5ml 200 200 0.5 10
(15%)* (5%)*
F3 1875 1600 0.5ml 200 200 0.5 10
(16%)* (5%)*
F4 1875 1400 0.6ml 200 200 0.5 10
(14%)* (6%)*
F5 1875 1500 0.6ml 200 200 0.5 10
(15%)* (6%)*
F6 1875 1600 0.6ml 200 200 0.5 10
(16%)* (6%)*
F7 1875 1400 0.7ml 200 200 0.5 10
(14%)* (7%)*
F8 1875 1500 0.7ml 200 200 0.5 10
(15%)* (7%)*
F9 1875 1600 0.7ml 200 200 0.5 10
(16%)* (7%)*
*Polymer and plasticiser concentration in percentage
www.iajps.com Page 2318
IAJPS 2018, 05 (04), 2316-2325 Mahesh Shinde et al ISSN 2349-7750
Fig.2: Initial mixture of all ingredient Fig. 3: Formulation place in ultrasonicator
to remove air bubble
Fig. 4: Formulation after the ultrasonicator Fig. 5: Film former
clear solution form
Fig. 6: Formulation pour on the film former Fig. 7: Formulation spread on the
film former
www.iajps.com Page 2319
IAJPS 2018, 05 (04), 2316-2325 Mahesh Shinde et al ISSN 2349-7750
Fig. 8: After the drying film removed Fig. 9: Film cut into 2×2cm
from the film former
films should have nearly constant weight. It is useful
Evaluation of oral fast dissolving film of to ensure that a film contains the proper amount of
cinnarizine excipient and API.
Film thickness Surface pH measurement
A thickness of the film was calculated by using The surface pH of film was determined in order to
digital vernier caliper. Film was measured at five investigate the possibility of any side effects in vivo.
position i.e. central and four corners and the mean As an acidic an alkaline pH may cause irritation to
thickness was calculated. the oral mucosa. It is determined to keep the surface
Folding endurance pH as close to neutral as possible. Film is slightly wet
Folding endurance was determined repeatedly by with the help of water. The pH is measured by using
folding a small strip of the film at the same place till digital pH meter to determined the surface pH. The
number of times the film could be folded at the same procedure was performed in triplicate and average
place without cracking was noted as folding with standard deviation was calculated.
endurance. The film was folded at an angle of 180º at Moisture loss studies
the same place till it broke or folded up to 100 times The percent moisture loss study was carried out to
without breaking. The studies were performed in trice check the physical stability and integrity of the films.
and the average mean was calculated. In the present study the moisture loss capacity of the
Drug content film was determined by placing the known weight
Drug content of all the batches was determined by and predetermined size of the film in desiccator
UV spectrophotometric method. For this 2×2cm strip containing anhydrous calcium chloride for three days.
from each batch was cut and dissolve in 50ml of The film were removed and reweight and the percent
phosphate buffer pH 6.8. then the solution was moisture loss of the films was measured by using
filtered through whatman filter paper and diluted if following formula.
necessary. The resulting solution was measured Percent moisture loss = initial weight – final weight
spectrophotometrically at 253nm. /final weight ×100
Uniformity of drug content In vitro drug dissolution study
For determining the uniformity of drug content in the In vitro drug dissolution studies were performed on
film 10 films were taken and assayed same procedure all the film formulation by using an apparatus called
was repeated for the batches as above. franz diffusion cell apparatus maintained a volume
Dispersion test capacity of 15ml was used for dissolution study. The
A film equivalent to 25mg of cinnarizine was placed film equivalent to 25mg of cinnarizine was placed in
in 200ml of 6.8 pH phosphate buffer and was stirred between the two compartment of an apparatus and
for 3 minutes. Then the resulting solution was passed pipette 15ml of 6.8 pH buffer ( pH of saliva) was
through sieve number 22. The film passed the added to receptor compartment. Cell is kept on
dispersion test only when no residue is left on the magnetic stirrer and bead in the cell is maintained at a
screen. speed of 50 revolution per minute and medium
Uniformity weight maintained at a temperature of nearly 32ºc ±0.5ºc and
Three films were randomly selected and weight withdraw 1ml of sample at various time intervals and
individually, then the mean weight and standard the sample were diluted with 6.8 pH phosphate buffer
deviation of films was calculated. It is desired that and measured absorbance at 253nm against 6.8 pH
www.iajps.com Page 2320
IAJPS 2018, 05 (04), 2316-2325 Mahesh Shinde et al ISSN 2349-7750
buffer as blank. The various dissolution profiles for concentration of polymer. The folding endurance was
films were given in shown in figure 10 and the in found to vary between 93 ±5 to 105 ±5 fold indicate
vitro dissolution parameter were given in table that the films have good flexibility. The formulation
number 6. with high concentration of polymer have low value of
folding endurance because after specific increase in
In vitro disintegration time concentration of polymer decrease in folding
The disintegration time reported was the time when endurance is observed due to film thickness. More
the film starts to break. In vitro disintegration time thickness lower will be folding endurance
was determined visually in a petri-dish containing Disintegration time was found to vary between 25 to
20ml of pH 6.8 phosphate buffer with swirling every 35 second film prepared with the HPMC E5 (15%
10 seconds. concentration) had shown fast disintegration as
compared to other concentration. Drug content was
Stability study evaluated and it varied in the range of 95.04±1.96 to
Accelerated (40ºc / 75% RH) and real time (30ºc / 99.01±1.15. drug content was found to be low for F1
65% RH) stability study was carried out as per ICH formulation i.e.93.15±1.05 and more for F5
guidelines at time intervals 0,7,14,28,42,60 days. formulation i.e. 99.01±1.15. as per the USP the drug
Film were evaluated for change in physical content was found to be in the range of 85-115%.
parameter, drug release and drug content. From the Three film strips of 4cm2 was cut from each film and
two months stability data it can be concluded that in estimated for uniformity of drug content using UV
F5 formulation there is no any significant change in spectrophotometric method. It is observed that all the
the physical appearance, disintegration time, drug selected formulation was found to be content almost
release, drug content compared with the initial data uniform quantity of drug as per content uniformity
for 25mg strength. Stability profiles of formulation at studies. The surface pH of all the selected
different temperature are shown in table number 7. formulation was ranging between 6.7 to 6.9, since
surface pH of the film was found to be around neutral
RESULT AND DISCUSSION: pH, there will not be any kind of irritation to the
The prepared films of all formulation were evaluated mucosal oral cavity. The moisture loss of all the
and results shown in table number 4,5,6. weight of selected formulation was measured. Out of all the
three films from all the formulation were determined selected formulation the film with HPMC E5 (15%
individually. As the concentration of polymer concentration) polymer showed the lowest %
increases, the weight of film also increases. All the moisture loss than other formulation and hence it is
batches were evaluated for thickness using digital more stable than other. Accelerated stability also
vernier caliper. As the formulations contain different shows that F5 formulation there is no any significant
concentration of polymer, hence the thickness of the change in the physical appearance, disintegration
films was found in the range of 0.40 to 0.56 mm. the time, drug release, drug content compared with the
thickness increases with the increase in the initial data from the two month stability data.
Table 4: Evaluation of oral fast dissolving film of cinnarizine of all batches
Formulation Film thickness (mm)* Folding endurance Drug content (%)* Dispersion test
code
F1 0.45 ± 0.004 105 ± 5 95.04 ± 1.96 Passed
F2 0.52 ± 0.006 102 ± 5 96.12 ± 1.12 Passed
F3 0.55 ± 0.008 99 ± 5 96.20 ± 0.94 Passed
F4 0.51 ± 0.004 104 ± 5 95.15 ± 1.05 Passed
F5 0.40 ± 0.004 100 ± 5 99.01 ± 1.15 Passed
F6 0.56 ± 0.008 96 ± 5 97.05 ± 0.60 Passed
F7 0.52 ± 0.014 103 ± 5 96.25 ± 0.85 Passed
F8 0.55 ± 0.006 99 ± 5 97.10 ± 0.91 Passed
F9 0.56 ± 0.004 93 ± 5 96.23 ± 1.01 Passed
*All value are mean of three reading ± standard deviation
www.iajps.com Page 2321
IAJPS 2018, 05 (04), 2316-2325 Mahesh Shinde et al ISSN 2349-7750
Table 5: Evaluation of oral fast dissolving film of cinnarizine of all batches
Formulation Uniformity weight (mg)* Surface pH % moisture loss* Disintegration time
code measurement* (sec.)*
F1 61.11 ± 0.05 6.72 ± 0.050 2.18 ± 0.071 35 ±2.08
F2 60.31 ± 0.09 6.70 ± 0.045 2.63 ± 0.022 32 ±2.51
F3 63.33 ± 0.12 6.85 ± 0.078 3.01 ± 0.032 30 ±2.66
F4 62.26 ± 0.09 6.72 ± 0.035 2.75 ± 0.041 31 ±1.55
F5 65.30 ± 0.15 6.80 ± 0.024 1.15 ± 0.012 25 ±1.21
F6 64.41 ± 0.16 6.85 ± 0.030 1.90 ± 0.032 28 ±1.91
F7 61.10 ± 0.11 6.90 ± 0.027 2.01 ± 0.015 33 ±1.88
F8 60.20 ± 0.10 6.79 ± 0.045 2.25 ± 0.019 29 ±2.21
F9 63.31 ± 0.13 6.75 ± 0.041 3.12 ± 0.042 27 ±2.11
*All value are mean of three reading ± standard deviation
In vitro drug release data 98.17%. formulation F5 showed better release. The
The result indicate that the best release among result are shown in table number 6.
formulations containing HPMC E5 (15%) i.e.
Table 6: In vitro cumulative % drug release in phosphate buffer pH 6.8
Time F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9
(sec.)
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
10 18.862 19.391 21.086 19.608 22.203 21.869 18.055 20.121 21.250
20 24.869 23.230 24.631 22.560 30.320 28.450 25.050 24.051 26.203
30 30.251 29.300 31.720 29.161 35.710 31.660 32.460 31.424 30.121
40 35.151 36.210 36.271 34.330 40.631 37.721 36.505 38.545 37.567
50 41.576 42.710 43.121 42.203 50.302 43.032 45.157 46.931 46.802
60 48.731 49.216 49.410 48.321 58.424 52.450 51.610 53.710 52.210
70 56.203 57.215 56.299 55.801 68.310 61.211 60.450 62.171 60.236
80 65.161 67.312 68.140 65.199 79.315 71.161 61.500 69.642 70.750
90 72.330 74.411 76.512 73.213 86.110 80.550 78.620 79.893 80.564
100 80.141 81.412 83.130 82.031 92.130 88.230 85.660 86.792 87.632
110 86.310 88.130 90.213 85.413 98.171 94.840 93.105 95.801 96.123
Fig. 10: % cumulative drug release from formulation F1 to F9
www.iajps.com Page 2322
IAJPS 2018, 05 (04), 2316-2325 Mahesh Shinde et al ISSN 2349-7750
Stability profile of formulation F5 at different temperature
Table 7: Stability profile of formulation F5 at different temprature
Time in Real time (30ºc / 65% RH) Accelerated (40ºc / 75% RH)
days
% drug release Drug content (mg) % drug release Drug content (mg)
0 96.13 25 96.13 25
7 96.06 24.95 96.04 24.94
14 95.97 24.87 95.96 24.84
28 95.89 24.80 95.85 24.72
42 95.73 24.72 95.74 24.48
60 95.66 24.63 95.62 24.25
Fig. 11: Showing % drug release at Real and Accelerated time.
www.iajps.com Page 2323
IAJPS 2018, 05 (04), 2316-2325 Mahesh Shinde et al ISSN 2349-7750
%
dr
ug
rel
ea
se
Fig. 12: Showing drug content in Real and Accelerated condition.
CONCLUSION: providing all the support and encouragements to do
Oral fast dissolving film of cinnarizine were prepared this work.
by solvent casting method using HPMC E5 as
polymer that rapidly dissolves film in the oral cavity REFERENCES:
and delivering the drug to the systemic circulation. 1. Kiran Goutam, Rajeev Garg, Ajay Sharma, Ajay
Plasticiser PEG 400 used to enhance the flexibility of Singh, Pooja Sharma, Shriya Kaushal:
the strip and reduces the brittleness of the strip. The Formulation and Evaluation of Oral Fast
formulation F5 which contain HPMC E5 (15%) and Dissolving Films of Promethazine Theoclate.
plasticiser PEG 400 (6%) which satisfied all Indo American Journal of Pharmaceutical
parameters of fast dissolving films as compare to Research, 2015; 2536-2544.
other films and appears to be promising would be 2. T. Balakrishna, S. Vidyadhara, T.E.G.K. Murthy,
able to offer benefits such as rapid drug release, good R.L.C. Sasidhar, S. Vikas: Formulation and
disintegration time and acceptable physicochemical Evaluation of Fast Dissolving Buccal Films of
characters and thereby may help to improve Sumitriptan Succinate. International Journal of
bioavailability of the drug. ChemTech Research, 2017; Vol.10: 545-552.
3. Dasharath M. Patel, Dharmendra Sinh, V. Dabhi:
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: Devolopment and Characterization of Oral
The authors thanks to Dr. J. G. Avari HOD of Dissolving Film for Promethazine HCL.
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, R.T.M. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences
Nagpur University,Nagpur, Dr. P. K. Puranik, and Research, 2014; Vol 5 (11):4728-4740.
Dr.(Mrs.)V. S. Belgamwar, Prashant Salunke, 4. Jui Trivedi, Janki Patel, Dr. Upendra Patel:
Sudarshan Jagtap,Vishal Mardhekar etc. for Formulation Development and Evaluation of
Fast Dissolving Film of Cinnarizine.
www.iajps.com Page 2324
IAJPS 2018, 05 (04), 2316-2325 Mahesh Shinde et al ISSN 2349-7750
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research Dispersible Tablets of Cinnarizine Using
and Bio-sciences, 2014; Vol. 3(2): 639-652. Sublimation technique. International Journal of
5. Bhupinder Bhyan, Sarita Jangra Bhyan, Vivek Pharmaceutical Sciences Review and Research,
Chopra, Ravi Berwal: Formulation and 2011, 6 (2), 178-184.
Evaluation of Novel Orodispersible Drug 14. Biswajit Basu, Abhishek Bagadiya, Sagar
Delivery System for the Administration of Makwana, Vora Vipul, Devraj Batt, Abhay
Bromhexine Hydrochloride. World Journal of Dharamasi: Formulation and Evaluation of Fast
Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences,2016; Disintegrating Tablet of Cinnarizine Using
vol. 5 (6);1452-1460. Superdisintigrant Blends and Subliming
6. Komaragiri Sasi Deepthi, Shaik Firoz, Yerram Muterial. Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutical
Chandramouli, R. Vishnu Vardhan, Amaravathi Technology and Research, 2011; 2(4):266-273.
Vikram, Uttaradi Aruna: Formulation and 15. Craig S: Motion Sickness: Review of Causes and
Characterization of Atenolol Fast Dissolving Preventive Strategies. Journal of Travel
Films. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Medicine,2002;9:251-256.
and Research, 2012; Vol. 2 (2):58-62. 16. Shubham Rai, Mohd Yasir: Cinnarizine Loaded
7. K. D. Tripathi: Essential of Medical Lipid Based System: Preparation, Optimization
Pharmacology. Jaypee Publication, Seventh and in vitro Evaluation. IOSR Journal of
Edition,2013. Pharmacy, 2012; 2 (5):47-56.
8. Patel A, Prajapati DS, and Raval JA: Fast 17. Iman Sabah Jaafar: Formulation and In Vitro
Dissolving Film as a Newer Venture in Fast Evaluation of Fast Dissolving Film of
Dissolving Dosage Form. International Journal Metoclopramide Hydrochloride. International
of Drug Development and Research, 2010; vol. 2 Journal of ChemTech Research, 2017; Vol.
(2): 232-246. 10(4):26-38.
9. Vishwkarma DK, Tripathi AK, Yogesh P and 18. Anjuman Pathan, Mahesh Kumar Gupta, Neetesh
Maddheshiya B: Review article on Mouth Kumar Jain, Ankita Dubey, Ankit Agrawal:
Dissolving Film. Journal of Global Pharma Formulation and Evaluation of Fast Dissolving
Technology, 2011;3(1):1-8. Oral Film of Promethazine HCL Using Different
10. Thakur N, Bansal M, Sharma N, Yadav G, Khare Surfactant. Journal of Innovations in
P: Overview ‘’A Novel Approach of Fast Pharmaceuticals and Biological Sciences, 2016;
Dissolving Films and their Patent’’. Advances in Vol. 3(1):78-84.
Biological Research, 2013;7(2),:0-58. 19. Deepak Heer, Geeta Agrawal, Hari Kumar:
11. Kumar Ravi K, Sulochna Mercy M, Fast Development of Fast Dissolving Oral Films and
Dissolving Films: A Unique Stratergy for Drug Tablets of Cinnarizine: Effect of
Delivery. Asian Journal Pharma Research, 2014; Superdisintegrants. International Journal of
Vol.4(1):47-55. Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical
12. N. Damodharan, M. Mothilal, G. Vasundhara: Sciences,2014;Vol. 6(2):186-191.
Formulation and Optimization of Fast Dissolving 20. Dr. M.M. Gupta, Vishal Patel: Formulation and
Cinnarizine Tablets. International Journal of Evaluation Oral Dispersible Tablet of
PharmaTech Research, 2100; Vol. 2(2):1095- Cinnarizine. Journal of Drug Delivery and
1100. Therapeutic,2013; Vol. 3(2):12-17.
13. Lakshmi C.S. R, Patel Nitesh J, Patel Hitesh P,
Akul Sagar: Formulation and Evaluation of oral
www.iajps.com Page 2325
You might also like
- 1, WS Clinical Pathway PERSIDocument29 pages1, WS Clinical Pathway PERSIkodokNo ratings yet
- GE Site Downtime Report SummaryDocument14 pagesGE Site Downtime Report SummaryHaseeb HassanNo ratings yet
- Program Kerja, Laporan Bulanan, Dan Evaluasi Kerja Manajemen Penggunaan Obat (Mpo) 2017Document11 pagesProgram Kerja, Laporan Bulanan, Dan Evaluasi Kerja Manajemen Penggunaan Obat (Mpo) 2017elisaNo ratings yet
- Down Time Record SheetDocument7 pagesDown Time Record SheetJorge LandryNo ratings yet
- Rekomendasi Antibiotik Pada Profilaksis BedahDocument4 pagesRekomendasi Antibiotik Pada Profilaksis BedahRya At ChinnamorariaNo ratings yet
- Kamar Bedah InventoryDocument2 pagesKamar Bedah InventoryAnonymous ntDYikdyNo ratings yet
- Form Perawatan Pasca OperasiDocument1 pageForm Perawatan Pasca OperasiFirman IsmailNo ratings yet
- Lembar Observasi NEWSS PDFDocument2 pagesLembar Observasi NEWSS PDFAnonymous 9U98YNNo ratings yet
- S富AⅳDar 富種調製1咄髄:績 08使呼血s2018宝 1D諾寵sま車重: Prosedur OperasioⅳAl u8購脚、Document1 pageS富AⅳDar 富種調製1咄髄:績 08使呼血s2018宝 1D諾寵sま車重: Prosedur OperasioⅳAl u8購脚、Dini MarianiNo ratings yet
- Daftar Harga e Catalog Electromedic Onemed Groups 2021Document21 pagesDaftar Harga e Catalog Electromedic Onemed Groups 2021PRABANTORO AHMAD AFIANNo ratings yet
- Peralatan Tim Code BlueDocument1 pagePeralatan Tim Code BlueAnonymous iglaw7J0rNo ratings yet
- Sop LogiqDocument7 pagesSop LogiqACHMAD REZANo ratings yet
- Presentasi SNARS1Document16 pagesPresentasi SNARS1Annisa Aisyha Malik50% (2)
- Kode Etik & Kompetensi RmikDocument42 pagesKode Etik & Kompetensi RmikZahara DarisNo ratings yet
- Kode Icd-10Document18 pagesKode Icd-10lazakiyahNo ratings yet
- FORM A MPP/case ManagerDocument1 pageFORM A MPP/case ManagerEvan SastriaNo ratings yet
- 5.21 Form Isian Indikasi Masuk Perinatologi Edit 11 NovDocument5 pages5.21 Form Isian Indikasi Masuk Perinatologi Edit 11 Novjohnporta8No ratings yet
- Form KLPCM Review 1 1AutoRecoveredFIXXXXXXXXXXXX AutosavedDocument43 pagesForm KLPCM Review 1 1AutoRecoveredFIXXXXXXXXXXXX AutosavedRiska YantiNo ratings yet
- Berita Acara Pasien KaburDocument2 pagesBerita Acara Pasien KaburtikaNo ratings yet
- Monitoring Suhu KulkasDocument3 pagesMonitoring Suhu KulkasMirna Melly Olivia100% (1)
- Hitachi Inspire the Next with Pocket DosemetersDocument4 pagesHitachi Inspire the Next with Pocket DosemetersStark Ko AsyariNo ratings yet
- RMC Provides Integrated Medical ServicesDocument13 pagesRMC Provides Integrated Medical ServicesAlen RendakNo ratings yet
- LAPORAN MONITORING DAN EVALUASI HPKDocument17 pagesLAPORAN MONITORING DAN EVALUASI HPKrahmajumilaNo ratings yet
- Standing Order Indonesia Dan Luar Negeri (Moh. Afif)Document3 pagesStanding Order Indonesia Dan Luar Negeri (Moh. Afif)Apip JaKariaNo ratings yet
- PDF Program Kerja Poliklinik 2020 DDDocument7 pagesPDF Program Kerja Poliklinik 2020 DDAulia AbdurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Per Tanya AnDocument2 pagesPer Tanya AnMomoraNo ratings yet
- ID-Centrifuge 6S 6S AccuDocument78 pagesID-Centrifuge 6S 6S AccucsclzNo ratings yet
- Icd 9 Tindakan UmumDocument2 pagesIcd 9 Tindakan UmumAlbarokah CrewNo ratings yet
- Suhu KulkasDocument114 pagesSuhu KulkasROYANANo ratings yet
- Of The Prostate: (Studi Dilakukan Di Ruang Bima RSUD Sanjiwani Gianyar)Document119 pagesOf The Prostate: (Studi Dilakukan Di Ruang Bima RSUD Sanjiwani Gianyar)Febriyana Casia PutraNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Dinas Tim Code Blue Area IDocument10 pagesJadwal Dinas Tim Code Blue Area IKiki Reski MustikaNo ratings yet
- A.2. PRESENTASE KEPATUHAN/KESESUAIAN DOKTER MENULISKAN RESEP BERDASARKAN FORMULARIUM RSDocument14 pagesA.2. PRESENTASE KEPATUHAN/KESESUAIAN DOKTER MENULISKAN RESEP BERDASARKAN FORMULARIUM RSRida NurulNo ratings yet
- Tugas Mors Kelompok 5 Analisis ABC Indeks KritisDocument11 pagesTugas Mors Kelompok 5 Analisis ABC Indeks Kritishastomo prabowoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathway for Inguinal Hernia RepairDocument6 pagesClinical Pathway for Inguinal Hernia RepairTina HerreraNo ratings yet
- Surveilans Hais Ppi Lanjut Persi 2015Document36 pagesSurveilans Hais Ppi Lanjut Persi 2015dianNo ratings yet
- Hak Pasien Dan KeluargaDocument3 pagesHak Pasien Dan KeluargaAlavezNo ratings yet
- Urology Procedure and Diagnosis RatesDocument10 pagesUrology Procedure and Diagnosis RatesNandarNo ratings yet
- PROGRAM KERJA Pemulasaran JenazahDocument3 pagesPROGRAM KERJA Pemulasaran JenazahAndika RizkiNo ratings yet
- ICD9CMDocument470 pagesICD9CMBayyinah ArdianNo ratings yet
- Implementasi Prinsip Keselamatan Pasien dalam Pelayanan KefarmasianDocument60 pagesImplementasi Prinsip Keselamatan Pasien dalam Pelayanan KefarmasianNicky NurfajriNo ratings yet
- Formulir Pelaporan Nilai KritisDocument1 pageFormulir Pelaporan Nilai Kritisnovi mulyani putriNo ratings yet
- Poster Caesarean HTDocument1 pagePoster Caesarean HTBoimAmachiNo ratings yet
- SPO AssemblingDocument4 pagesSPO AssemblingNana TwinsNo ratings yet
- Elemen Penilaian KksDocument36 pagesElemen Penilaian KkssektimagineNo ratings yet
- ABFC Evaluasi Reagen HIV 2016 - 2Document1 pageABFC Evaluasi Reagen HIV 2016 - 2Rocmatullah AshariNo ratings yet
- BeneHeart D6 SpecificationsDocument2 pagesBeneHeart D6 SpecificationsΒαγγέλης ΛυράκηςNo ratings yet
- KERANGKA ACUAN KERJA PENGADAAN Chemical Laundry 21Document6 pagesKERANGKA ACUAN KERJA PENGADAAN Chemical Laundry 21GG MultimediaNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat Anestesi Di Kamar BedahDocument1 pageDaftar Obat Anestesi Di Kamar BedahYayah MulyatiNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Design of Taste Masked Quetiapine Fumarate Orally Fast Disintegrating Tablets by Sublimation MethodDocument16 pagesFormulation and Design of Taste Masked Quetiapine Fumarate Orally Fast Disintegrating Tablets by Sublimation MethodJuan IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Ganti 2018Document31 pagesGanti 2018WentySafitriNo ratings yet
- Preparation, Evaluation and Optimization of Film Forming GelDocument14 pagesPreparation, Evaluation and Optimization of Film Forming Gelphú nguyễnNo ratings yet
- Pune University First Year B Pharmacy SyllabusDocument17 pagesPune University First Year B Pharmacy SyllabusSidhharrth S KumaarNo ratings yet
- Nystatinniosomes PDFDocument7 pagesNystatinniosomes PDFEufrasia Willis PakadangNo ratings yet
- CAPTOPRIL COMPLEXDocument13 pagesCAPTOPRIL COMPLEXMareta Ovy YuliaNo ratings yet
- Solubility Enhancement of Nitazoxanide Using SolidDocument15 pagesSolubility Enhancement of Nitazoxanide Using SolidErick SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Evaluation of Taste-Masked Ciprofloxacin Oral Reconstitutable Dry SyrupDocument10 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Taste-Masked Ciprofloxacin Oral Reconstitutable Dry SyrupdhilahNo ratings yet
- Minutes For 271st Registration Board MeetingDocument540 pagesMinutes For 271st Registration Board MeetingUsama SayedNo ratings yet
- Analytical Method Development For Simultanious Quantification of Ternary Mixture Containing Anticonvulsant Drugs by RP-HPLC MDocument8 pagesAnalytical Method Development For Simultanious Quantification of Ternary Mixture Containing Anticonvulsant Drugs by RP-HPLC MInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- General Considerations of Design and Development of Dosage Forms: Pre-Formulation ReviewDocument11 pagesGeneral Considerations of Design and Development of Dosage Forms: Pre-Formulation ReviewFilipNo ratings yet
- Design and Evaluation of An Extended Release Tablet Dosage Form of Class-Ii Drug, Quetiapine FumarateDocument5 pagesDesign and Evaluation of An Extended Release Tablet Dosage Form of Class-Ii Drug, Quetiapine FumarateErlita Nur ArifanaNo ratings yet
- Formulation, Optimization and Evaluation Colon Targated Drug Delivery System For OrniadazoleDocument9 pagesFormulation, Optimization and Evaluation Colon Targated Drug Delivery System For OrniadazoleBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Development and Validation of Stability Indicating Assay Method For Estimation of Teriflunomide in Tablet Dosage FormDocument11 pagesDevelopment and Validation of Stability Indicating Assay Method For Estimation of Teriflunomide in Tablet Dosage FormBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Gastroprotective Activity of Methanolic Extract of Phyllanthus Acidus Fruit Against Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Ulcers in RatsDocument7 pagesGastroprotective Activity of Methanolic Extract of Phyllanthus Acidus Fruit Against Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Ulcers in RatsBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Non-Adherence in Hyppertensive Patients of Peshawar, PakistanDocument13 pagesNon-Adherence in Hyppertensive Patients of Peshawar, PakistanBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Simultaneous Estimation of Rosuvastatin Calcium and Ezetimibe As Bulk Drug and in Tablet Dosage Form by RP-HPLC MethodDocument6 pagesSimultaneous Estimation of Rosuvastatin Calcium and Ezetimibe As Bulk Drug and in Tablet Dosage Form by RP-HPLC MethodBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Nephroprotective Activityof Acorus Calamus Leaves Extract Against Lithium Induced Nephrotoxicity in Wistar RatsDocument12 pagesNephroprotective Activityof Acorus Calamus Leaves Extract Against Lithium Induced Nephrotoxicity in Wistar RatsBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Analytical Method Development and Validation of Stability Indicating RP-HPLC Method For Estimation of Lercanidipine Hydrochloride and Enalapril Maleate in CombinationDocument8 pagesAnalytical Method Development and Validation of Stability Indicating RP-HPLC Method For Estimation of Lercanidipine Hydrochloride and Enalapril Maleate in CombinationBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Development of Cell Culture System From Selected Tissues of Pangaius HypopthalmusDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Cell Culture System From Selected Tissues of Pangaius HypopthalmusBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Genetic Enhancment of Groundnut (Arachis Hypogaea L.) Through Induced Muiation.Document5 pagesGenetic Enhancment of Groundnut (Arachis Hypogaea L.) Through Induced Muiation.Baru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Knowledge On Antibiotics Use and Its Storage Among Saudi Arabia Residents: A Cross Sectional StudyDocument8 pagesKnowledge On Antibiotics Use and Its Storage Among Saudi Arabia Residents: A Cross Sectional StudyBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- A Brief Review On YawsDocument7 pagesA Brief Review On YawsBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles From Herbal PlantDocument9 pagesPreparation of Silver Nanoparticles From Herbal PlantBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Review On: Inventory ManagementDocument8 pagesReview On: Inventory ManagementBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- The Bordering Areas (Nine Areas of Panjgur District) Issue of Pakistan About Human Malaria Prevalence: A Cross-Sectional Research of Malaria Parasites Identification in Blood SlidesDocument8 pagesThe Bordering Areas (Nine Areas of Panjgur District) Issue of Pakistan About Human Malaria Prevalence: A Cross-Sectional Research of Malaria Parasites Identification in Blood SlidesBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Relationship of Testosterone With Body Mass Index in Infertile Males in Local CommunityDocument4 pagesRelationship of Testosterone With Body Mass Index in Infertile Males in Local CommunityBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- An Incidence of Hypertension Among People and Its Association To Consumption of Hard Water: A Cross-Sectional ResearchDocument6 pagesAn Incidence of Hypertension Among People and Its Association To Consumption of Hard Water: A Cross-Sectional ResearchBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Correlation Between Physical Activity and Academic Performance Among The Students of Gujranwala Medical College, GujranwalaDocument7 pagesAssessment of Correlation Between Physical Activity and Academic Performance Among The Students of Gujranwala Medical College, GujranwalaBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Role of Simvastatin in Addition To Metformin in Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome Patients, A Randomized Controlled Trial On Pakistani WomenDocument4 pagesRole of Simvastatin in Addition To Metformin in Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome Patients, A Randomized Controlled Trial On Pakistani WomenBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Sciences: IAJPS 2018, 05 (04), 3075-3081 Aneeqa Ali RaoDocument7 pagesPharmaceutical Sciences: IAJPS 2018, 05 (04), 3075-3081 Aneeqa Ali RaoBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Study Knowing The Patients Load in The Neonatal Icu at The Tertiary Care Hospital LahoreDocument4 pagesDescriptive Study Knowing The Patients Load in The Neonatal Icu at The Tertiary Care Hospital LahoreBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Identification of Clostridium Perfringens Causing Enterotoxaemia in Bovine of Kacchi District Balochistan.Document8 pagesIsolation and Identification of Clostridium Perfringens Causing Enterotoxaemia in Bovine of Kacchi District Balochistan.Baru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Association of Socioeconomic Status, Hypertension and Treatment Modality With Diabetic Amputation - A Case Control StudyDocument4 pagesAssociation of Socioeconomic Status, Hypertension and Treatment Modality With Diabetic Amputation - A Case Control StudyBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- After Acute Myocardial Infarction End Result of Cardiogenic Shock in Hospitalized PatientsDocument4 pagesAfter Acute Myocardial Infarction End Result of Cardiogenic Shock in Hospitalized PatientsBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- C-Reactive Protein Levels Preoperatively and Postoperatively Effect On Cardiovascular Surgery ComplicationsDocument5 pagesC-Reactive Protein Levels Preoperatively and Postoperatively Effect On Cardiovascular Surgery ComplicationsBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Study of Clinical Profile of Transfused Thalassemic Childrens With Special Reference To Hepatitis B Profile and Liver Function.Document6 pagesStudy of Clinical Profile of Transfused Thalassemic Childrens With Special Reference To Hepatitis B Profile and Liver Function.Baru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Oppertunistic Hypertension Screening in Rural Health Population of Umar Abad Tehsil Kharezat Disrtrict Pishin Balochistan. A Cross Sectional StudyDocument10 pagesOppertunistic Hypertension Screening in Rural Health Population of Umar Abad Tehsil Kharezat Disrtrict Pishin Balochistan. A Cross Sectional StudyBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- An Exploratory Review of The Myths and Common Beliefs About Acne and Its TreatmentDocument6 pagesAn Exploratory Review of The Myths and Common Beliefs About Acne and Its TreatmentBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- An Epidemiological Survey About The Infections Caused by Dengue in The Perspective of Hematological, Clinical and Demographic Risk FactorsDocument6 pagesAn Epidemiological Survey About The Infections Caused by Dengue in The Perspective of Hematological, Clinical and Demographic Risk FactorsBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- The Role of Clinical Pharmacist in Pharmacovigilance and Drug Safety in Teritiary Care Teaching HospitalDocument11 pagesThe Role of Clinical Pharmacist in Pharmacovigilance and Drug Safety in Teritiary Care Teaching HospitalBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- A Cross Sectional Survey Information About Weaning Process Among Mothers of Infants Above 6 Months of Age in Opd Pediatrics at Kishwer Fazal Teaching Hospital LahoreDocument8 pagesA Cross Sectional Survey Information About Weaning Process Among Mothers of Infants Above 6 Months of Age in Opd Pediatrics at Kishwer Fazal Teaching Hospital LahoreBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
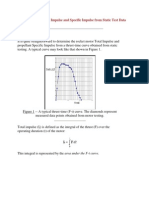
- Determining Total Impulse and Specific Impulse From Static Test DataDocument4 pagesDetermining Total Impulse and Specific Impulse From Static Test Datajai_selvaNo ratings yet
- PB Engine Kappa EngDocument20 pagesPB Engine Kappa EngOscar AraqueNo ratings yet
- BC Specialty Foods DirectoryDocument249 pagesBC Specialty Foods Directoryjcl_da_costa6894No ratings yet
- Statement of PurposeDocument2 pagesStatement of Purposearmaan kaurNo ratings yet
- Structures Module 3 Notes FullDocument273 pagesStructures Module 3 Notes Fulljohnmunjuga50No ratings yet
- High Uric CidDocument3 pagesHigh Uric Cidsarup007No ratings yet
- Recommended lubricants and refill capacitiesDocument2 pagesRecommended lubricants and refill capacitiestele123No ratings yet
- UPGRADEDocument2 pagesUPGRADEVedansh OswalNo ratings yet
- Vallance - Sistema Do VolvoDocument15 pagesVallance - Sistema Do VolvoNuno PachecoNo ratings yet
- High Frequency Voltage Probe Non-Availability on GeMDocument2 pagesHigh Frequency Voltage Probe Non-Availability on GeMjudeNo ratings yet
- Concept, Types, Characteristics and ClassificationsDocument6 pagesConcept, Types, Characteristics and ClassificationsCJ FaNo ratings yet
- 2011 Mid America - WebDocument156 pages2011 Mid America - WebFaronNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Materials That Undergo DecayDocument14 pagesLesson 3 - Materials That Undergo DecayFUMIKO SOPHIA67% (6)
- Kuliah Statistik Inferensial Ke4: Simple Linear RegressionDocument74 pagesKuliah Statistik Inferensial Ke4: Simple Linear Regressionvivian indrioktaNo ratings yet
- Company's Profile Presentation (Mauritius Commercial Bank)Document23 pagesCompany's Profile Presentation (Mauritius Commercial Bank)ashairways100% (2)
- SABIC Ethanolamines RDS Global enDocument10 pagesSABIC Ethanolamines RDS Global enmohamedmaher4ever2No ratings yet
- 272 Concept Class Mansoura University DR Rev 2Document8 pages272 Concept Class Mansoura University DR Rev 2Gazzara WorldNo ratings yet
- Lea 201 Coverage Topics in Midterm ExamDocument40 pagesLea 201 Coverage Topics in Midterm Examshielladelarosa26No ratings yet
- Cycles in Nature: Understanding Biogeochemical CyclesDocument17 pagesCycles in Nature: Understanding Biogeochemical CyclesRatay EvelynNo ratings yet
- STS Chapter 5Document2 pagesSTS Chapter 5Cristine Laluna92% (38)
- Research Grants Final/Terminal/Exit Progress Report: Instructions and Reporting FormDocument13 pagesResearch Grants Final/Terminal/Exit Progress Report: Instructions and Reporting FormBikaZee100% (1)
- Exam Venue For Monday Sep 25, 2023 - 12-00 To 01-00Document7 pagesExam Venue For Monday Sep 25, 2023 - 12-00 To 01-00naveed hassanNo ratings yet
- 【4DI+4DO】MA01+-AXCX4040 UserManual EN v1.1Document36 pages【4DI+4DO】MA01+-AXCX4040 UserManual EN v1.1RioNorte LojaNo ratings yet
- VB 2Document11 pagesVB 2Sudhir IkkeNo ratings yet
- Safety interlock switches principlesDocument11 pagesSafety interlock switches principlesChristopher L. AlldrittNo ratings yet
- Managing operations service problemsDocument2 pagesManaging operations service problemsJoel Christian Mascariña0% (1)
- DAP FullTextIntroductionByStuartLichtman PDFDocument21 pagesDAP FullTextIntroductionByStuartLichtman PDFAlejandro CordobaNo ratings yet
- Instruction/Special Maintenance Instruction (IN/SMI)Document2 pagesInstruction/Special Maintenance Instruction (IN/SMI)ANURAJM44No ratings yet
- Lab - Activity CCNA 2 Exp: 7.5.3Document13 pagesLab - Activity CCNA 2 Exp: 7.5.3Rico Agung FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Denys Vuika - Electron Projects - Build Over 9 Cross-Platform Desktop Applications From Scratch-Packt Publishing (2019)Document429 pagesDenys Vuika - Electron Projects - Build Over 9 Cross-Platform Desktop Applications From Scratch-Packt Publishing (2019)Sarthak PrakashNo ratings yet