Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electronic Load Controller Poster
Uploaded by
Sharad PatelCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electronic Load Controller Poster
Uploaded by
Sharad PatelCopyright:
Available Formats
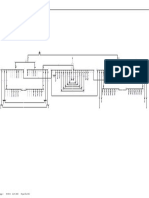
THE ELECTRONIC LOAD CONTROLLER (ELC) MODEL
Implemented by: YONAH Muwonge, DAVID Maganda
Supervised by: Assoc. Prof. Richard Okou, Mr. Maximus Byamukama.
(Makerere University)
Author : YONAH Muwonge
INTRODUCTION METHODOLOGY ACTIVITIES Principle of action Frequency and Voltage variation with ELC connected
55 300
• In all power generating schemes, voltage and frequency Objective Activities
control and regulation systems/means perform a vital 50
280
Freq / Hz
V/V
role. Without control, all the power generated goes to the
Desk research 260
user load. Uncontrolled flow of power can damage both 45
the load and the generators. Analysis of an operational installed
240
ELC at Suam MHP scheme (Eastern 40
• This is due to the unpredictable variations in the user Research on:
Uganda) , its several key components 220
Existing ELC designs
load, which consequently lead to variations in key and how it 35
Frequency
parameters such as the voltage, frequency and rotation System analysis of MHP power 200
Review of several programming Voltage
speed of the generator. Programming microcontrollers 30 180
tutorials and books about the Fig. 1: Analysing the ELC installed at SUAM MHP scheme.
04-May-15 3:44:38 PM
04-May-15 3:45:22 PM
04-May-15 3:46:05 PM
04-May-15 3:46:48 PM
04-May-15 3:47:31 PM
04-May-15 3:48:14 PM
04-May-15 3:48:58 PM
04-May-15 3:49:41 PM
microcontrollers
• In Pico and Micro hydro power plants, the user load and
the generation unit are connected directly with no Writing code for the microcontroller
transmission system, therefore, in both systems, the
parameters such as voltage and frequency are directly
reliant on each other.
PCB design of the ELC circuit
Simulation of the several circuit
• The Electronic Load Controller (ELC) is therefore installed components of the ELC;
to regulate the voltage and frequency of the system. RESULTS
Design and Simulation of the 1. Voltage Sensing circuit
Fig. 2: Design and simulation of electronic circuits.
controller circuit 2. Triac – dump load circuit
Frequency and Voltage variation without ELC
OBJECTIVES of the Project 3. Power circuit for the microcontroller
56.5 295
Using Multism and Proteus software
290
• To carry out background research and system analysis on 56
Freq / Hz
V / V
285
Micro-Hydro power. 55.5
• To carry out research on existing controller designs and 280
their disadvantages. Building up the electronic load 55 275
• To carry out research on programming microcontrollers.
Frequency
controller circuit based on the design 270
54.5 Voltage
• To develop with a system model and circuit design for an Setting up the control panel and 265 CONCLUSION
electronic load controller. Building and testing the prototype connecting the loads, dump loads, meters
54
260
• To carry out a simulation of the circuit design. In Pico and Micro hydro-power plants, a simplified
and switches 53.5 255
• Building and testing the prototype for illustrative microprocessor based ELC can be installed to achieve
04-May-15 3:37:26 PM
04-May-15 3:38:10 PM
04-May-15 3:38:53 PM
04-May-15 3:39:36 PM
04-May-15 3:40:19 PM
04-May-15 3:41:02 PM
04-May-15 3:41:46 PM
04-May-15 3:42:29 PM
04-May-15 3:43:12 PM
purposes. Testing the circuit with the test bench Fig. 3: Testing the ELC prototype.
optimal voltage and frequency regulation. The ELC model is
to visualise the control mechanism a robust and relatively cheaper to make compared to
already existing designs therefore reducing the cost of
setting up such small power plants.
You might also like
- Final Network DesignDocument1 pageFinal Network DesignAdam ThursbyNo ratings yet
- GRE - eec.D.99.CL.P.07576.12.014.01 Tracker Controller Cable ConnectionsDocument1 pageGRE - eec.D.99.CL.P.07576.12.014.01 Tracker Controller Cable ConnectionsJason DaNny FloResNo ratings yet
- MDRRF 855 RKDocument2 pagesMDRRF 855 RKToma GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Documentation PHENIX LIBERTY Anglais V05.00Document2 pagesDocumentation PHENIX LIBERTY Anglais V05.00klemionka2No ratings yet
- Batteries: Color Code For Schematic LinesDocument2 pagesBatteries: Color Code For Schematic LinesIsaac NewtonNo ratings yet
- In Edit State:save Key: 0.4mV/V 6mV/VDocument5 pagesIn Edit State:save Key: 0.4mV/V 6mV/VJulian HortaNo ratings yet
- (Exemplo) Matriz de Treinamento GEDocument1 page(Exemplo) Matriz de Treinamento GEpauloNo ratings yet
- Instruction on paralleling ET systemsDocument2 pagesInstruction on paralleling ET systemsPetr DvořákNo ratings yet
- Triaxial Test CoggleDocument1 pageTriaxial Test CoggleAndika PerbawaNo ratings yet
- DMM 1 e 007Document1 pageDMM 1 e 007mahesh reddy mNo ratings yet
- 01 Thermodynamics PrefaceDocument10 pages01 Thermodynamics PrefaceZahrani MuktiNo ratings yet
- PA6 MateuoDocument1 pagePA6 MateuoPhan Tuấn AnhNo ratings yet
- Instrument Hookup 10Document1 pageInstrument Hookup 10Wael ZakariaNo ratings yet
- 1007-ZN01-BM-103 - Small Power LayoutDocument1 page1007-ZN01-BM-103 - Small Power LayoutMHD MKNo ratings yet
- Load Schedule PB1 Load Schedule PB2,3,4,5 Unit 01 UNIT 02-03-04-05Document1 pageLoad Schedule PB1 Load Schedule PB2,3,4,5 Unit 01 UNIT 02-03-04-05domin domNo ratings yet
- BC-6200 Liquid MapDocument1 pageBC-6200 Liquid Mapacarrillo84No ratings yet
- 2010 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP (INDEX) : Choctaw County, AL: MILFORD 47500 Davis 18100Document1 page2010 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP (INDEX) : Choctaw County, AL: MILFORD 47500 Davis 18100Igor SemenovNo ratings yet
- AmpworksBass EFG1Document5 pagesAmpworksBass EFG1Jaasiel AcenderStudioNo ratings yet
- Tan-Delta and Capacitance Test Set For HT Generator/Motor TestingDocument3 pagesTan-Delta and Capacitance Test Set For HT Generator/Motor Testingmustafa180567% (3)
- Vectorworks Architect Essentials HandoutDocument4 pagesVectorworks Architect Essentials HandoutJoe Jones ForsythNo ratings yet
- Tokyo International Airport Chart with Runway 23 DetailsDocument108 pagesTokyo International Airport Chart with Runway 23 Details張允執No ratings yet
- D11-Architectural and Electrical PDFDocument13 pagesD11-Architectural and Electrical PDFSuppenguinNo ratings yet
- Planos 9978Document34 pagesPlanos 9978Omar50% (2)
- AMTED107013EN (Print)Document2 pagesAMTED107013EN (Print)Luis EduardoNo ratings yet
- Chaoshan Electrical PlanDocument4 pagesChaoshan Electrical PlanMilbert CandelarioNo ratings yet
- 1994 Lexus SC300 Overall WiringDocument43 pages1994 Lexus SC300 Overall WiringphilNo ratings yet
- Note ASG-MT-1196 - 27/8/2018 1BC, 2BC, 3BC, 4BC, 5BC PH-2Document1 pageNote ASG-MT-1196 - 27/8/2018 1BC, 2BC, 3BC, 4BC, 5BC PH-2Anonymous dH3DIEtzNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection System: Submitted in The Partial Fulfilment of The Requirements For The Award of The Degree ofDocument35 pagesIntrusion Detection System: Submitted in The Partial Fulfilment of The Requirements For The Award of The Degree ofMythreya BattulaNo ratings yet
- Instrument Hookup 9Document1 pageInstrument Hookup 9Wael ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Quickstart: Audio/Video Inputs/Outputs/Reference Power Cabling Control CablingDocument2 pagesQuickstart: Audio/Video Inputs/Outputs/Reference Power Cabling Control CablingINTERGUEST GuestNo ratings yet
- 5kv Insulation Resistance Tester Hioki 3455Document4 pages5kv Insulation Resistance Tester Hioki 3455industrialindiaNo ratings yet
- Automation Mind MapDocument1 pageAutomation Mind MapDanieleNo ratings yet
- 9 10 enDocument2 pages9 10 enparth kananiNo ratings yet
- Alim Knit (BD) LTD.: Recommended Process & Hydraulic Flow DiagramDocument1 pageAlim Knit (BD) LTD.: Recommended Process & Hydraulic Flow DiagramKamrul HasanNo ratings yet
- Manual de Instruccion 5kvaDocument1 pageManual de Instruccion 5kvaJuanca PiaNo ratings yet
- Spectrum WhiteDocument1 pageSpectrum WhitethebigfishxNo ratings yet
- Ac 1664434154655Document8 pagesAc 1664434154655Alaa Abo ShamaaNo ratings yet
- Plakat FESTO CPX MPA VTSADocument2 pagesPlakat FESTO CPX MPA VTSAtadNo ratings yet
- One-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Load Flow Analysis) : Page 1 09:45:54 Jul 19, 2020 Project File: EXCDocument1 pageOne-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Load Flow Analysis) : Page 1 09:45:54 Jul 19, 2020 Project File: EXCaraaf aji setiyawanNo ratings yet
- Al924a GB 019221900 1123 23062014Document1 pageAl924a GB 019221900 1123 23062014mahaNo ratings yet
- 3408E Industrial Engine Electrical System: Top ViewDocument2 pages3408E Industrial Engine Electrical System: Top ViewxuanNo ratings yet
- Wiring: Digital Controller Instruction ManualDocument1 pageWiring: Digital Controller Instruction ManualEdy WijayaNo ratings yet
- ELTR 343 Industrial Electronics PDFDocument148 pagesELTR 343 Industrial Electronics PDFEngr Shehzad HaneefNo ratings yet
- R33Y2014N04A0383Document11 pagesR33Y2014N04A0383Yadareli DothéNo ratings yet
- Essential LEDtube 8W & 16W T8Document9 pagesEssential LEDtube 8W & 16W T8Jinus JieNo ratings yet
- IM05D01C03-01E 06E 003.usDocument12 pagesIM05D01C03-01E 06E 003.usTeteNo ratings yet
- DUO For Wall and Column Formwork Poster US1 enDocument3 pagesDUO For Wall and Column Formwork Poster US1 enJc KrkmoNo ratings yet
- 120000032038_ESA100_SMPDocument1 page120000032038_ESA100_SMPmahmoud morsyNo ratings yet
- HH45, HH55, HH65, and HH75 Harvester Heads Electrical SystemDocument2 pagesHH45, HH55, HH65, and HH75 Harvester Heads Electrical SystemGilvan JuniorNo ratings yet
- 3412E-3408E Engine Electrical Schematics: Compartir Este DocumentoDocument1 page3412E-3408E Engine Electrical Schematics: Compartir Este DocumentoAxel ValenciaNo ratings yet
- ABB UNO DM 1.2 5.0 TL PLUS Quick Installation GuideDocument2 pagesABB UNO DM 1.2 5.0 TL PLUS Quick Installation GuideFlorin FlorinNo ratings yet
- Brochure SP Option Plus UK HDDocument2 pagesBrochure SP Option Plus UK HDkentNo ratings yet
- EDG LCP Wiring MARINEDocument14 pagesEDG LCP Wiring MARINEHeni HasanahNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits Basic CourseDocument9 pagesElectric Circuits Basic CourseJOSE AUGUSTO MODESTO HUAYLINOS GUERRERONo ratings yet
- 0MAF Un 13.8KV, in 2000A, FN 60HZ, SC 40KA/1SEC: Relay Function TableDocument1 page0MAF Un 13.8KV, in 2000A, FN 60HZ, SC 40KA/1SEC: Relay Function TableAnonymous dH3DIEtzNo ratings yet
- Poster Ecoc Rimini 030921Document1 pagePoster Ecoc Rimini 030921Jaya Kumar KbNo ratings yet
- Multilevel Six-Phase Machine Drive System Composed of Three-Level and Two-Level InvertersDocument5 pagesMultilevel Six-Phase Machine Drive System Composed of Three-Level and Two-Level InvertersPhelipe LealNo ratings yet
- 101.a 1 001 01 102Document1 page101.a 1 001 01 102Lady Johanna Quintero OsorioNo ratings yet
- Wlan Ez1100 DownloadDocument1 pageWlan Ez1100 Downloadc85320d9ddb90c13f4a215f1f0a87b531ab33310No ratings yet
- SPRING 2018 Book List ReturningDocument1 pageSPRING 2018 Book List ReturningSharad PatelNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: 02: Title: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesLab Report: 02: Title: ObjectiveSharad PatelNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument3 pagesResearch PaperSharad PatelNo ratings yet
- HNDBK TCHNG PT PDFDocument439 pagesHNDBK TCHNG PT PDFShahid Ahmed Heera100% (2)
- Lab Report: 03 - Management of Routing Table and Configure Dynamic Routing with OSPFDocument7 pagesLab Report: 03 - Management of Routing Table and Configure Dynamic Routing with OSPFSharad PatelNo ratings yet
- JFN Hport 26 JFN Hport 26: PLTJH PLTJH Onkhgtlvh OnkhgtlvhDocument8 pagesJFN Hport 26 JFN Hport 26: PLTJH PLTJH Onkhgtlvh OnkhgtlvhSharad PatelNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: 03 - Management of Routing Table and Configure Dynamic Routing with OSPFDocument7 pagesLab Report: 03 - Management of Routing Table and Configure Dynamic Routing with OSPFSharad PatelNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: 02: Title: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesLab Report: 02: Title: ObjectiveSharad PatelNo ratings yet
- CCNA LabDocument129 pagesCCNA LabNandan Bisht100% (4)
- Lab Report: 03 - Management of Routing Table and Configure Dynamic Routing with OSPFDocument7 pagesLab Report: 03 - Management of Routing Table and Configure Dynamic Routing with OSPFSharad PatelNo ratings yet
- JFN Hport 26 JFN Hport 26: PLTJH PLTJH Onkhgtlvh OnkhgtlvhDocument8 pagesJFN Hport 26 JFN Hport 26: PLTJH PLTJH Onkhgtlvh OnkhgtlvhSharad PatelNo ratings yet
- Automated Fault Location System For Primary Distribution NetworksDocument9 pagesAutomated Fault Location System For Primary Distribution NetworksSharad PatelNo ratings yet
- SPRING 2018 Book List ReturningDocument1 pageSPRING 2018 Book List ReturningSharad PatelNo ratings yet
- Implementation of The Numerical Laplace Transform: A ReviewDocument11 pagesImplementation of The Numerical Laplace Transform: A ReviewSharad PatelNo ratings yet
- NCVT Inquiry Form 2017Document1 pageNCVT Inquiry Form 2017Sharad PatelNo ratings yet
- plugin-9-6-7-2011-10-37-38-MM JournalDocument13 pagesplugin-9-6-7-2011-10-37-38-MM Journalnainesh goteNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Unit 1: Electrical DepartmentDocument1 pageQuestion Bank: Unit 1: Electrical DepartmentSharad PatelNo ratings yet
- GTU Course on Testing and Commissioning of Electrical EquipmentDocument4 pagesGTU Course on Testing and Commissioning of Electrical EquipmentMitesh Gandhi100% (2)
- Coordination of Overcurrent Relays Protection Systems For Wind Power PlantsDocument6 pagesCoordination of Overcurrent Relays Protection Systems For Wind Power PlantsSharad PatelNo ratings yet
- Stability Analysis of Power Transmission of Offshore Wind Farms Fed To Onshore Power Grids Using A Multi-Terminal VSC-HVDC SystemDocument4 pagesStability Analysis of Power Transmission of Offshore Wind Farms Fed To Onshore Power Grids Using A Multi-Terminal VSC-HVDC SystemSharad PatelNo ratings yet
- Enhancement of Power System StabilityDocument6 pagesEnhancement of Power System StabilitySharad PatelNo ratings yet
- Stability Analysis of Power Transmission of Offshore Wind Farms Fed To Onshore Power Grids Using A Multi-Terminal VSC-HVDC SystemDocument4 pagesStability Analysis of Power Transmission of Offshore Wind Farms Fed To Onshore Power Grids Using A Multi-Terminal VSC-HVDC SystemSharad PatelNo ratings yet
- Enhancement of Power System StabilityDocument6 pagesEnhancement of Power System StabilitySharad PatelNo ratings yet
- Capicitor PlacementDocument5 pagesCapicitor PlacementSharad PatelNo ratings yet
- Charotar University MTech Time Table 2014-15Document1 pageCharotar University MTech Time Table 2014-15Sharad PatelNo ratings yet
- Islanding Protection SystemDocument4 pagesIslanding Protection SystemSharad PatelNo ratings yet
- All Test Bus SystemsDocument37 pagesAll Test Bus SystemsMiguel Acb100% (2)
- FortranDocument35 pagesFortranVinay Gupta67% (3)
- Intel® Desktop Compatibility Tool: 3Rd Generation Intel® Core™ I7-3770S - Frequency: 3.10 GHZDocument38 pagesIntel® Desktop Compatibility Tool: 3Rd Generation Intel® Core™ I7-3770S - Frequency: 3.10 GHZWilmer CedronNo ratings yet
- Gym WebsiteDocument83 pagesGym WebsiteFreeProjectz.com73% (11)
- PY084Document7 pagesPY084Faizatul BorshaNo ratings yet
- How To Install DOS 6.22Document5 pagesHow To Install DOS 6.22Sujit KempraiNo ratings yet
- BD-SP309 Firmware Update WebDocument7 pagesBD-SP309 Firmware Update WebBinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Kubernetes SetupDocument6 pagesKubernetes SetupDebendraNathSahuNo ratings yet
- R6FG Introduction20210927Document3 pagesR6FG Introduction20210927Mike HadenNo ratings yet
- High-Level Programming Languages: FocusDocument3 pagesHigh-Level Programming Languages: FocusHassanRanaNo ratings yet
- Ta020819 1 Benefitsspec Fin-Epic950Document2 pagesTa020819 1 Benefitsspec Fin-Epic950STEVEN WUNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Introduction To Java: Write True or FalseDocument5 pagesUnit 2: Introduction To Java: Write True or FalseGopi SelvarajNo ratings yet
- LAVOCE Sistema F153.10N SuggDes RevB.ADocument23 pagesLAVOCE Sistema F153.10N SuggDes RevB.ARoshanNo ratings yet
- Cambium Networks Data Sheet WiFi-6 XE3-4TN APDocument7 pagesCambium Networks Data Sheet WiFi-6 XE3-4TN APrf.waveguideNo ratings yet
- SDIO SDmode ControllerDocument4 pagesSDIO SDmode ControllerDinh Hoang TungNo ratings yet
- E 10108Document314 pagesE 10108Sairam BalaNo ratings yet
- NTMP2014 1Document1 pageNTMP2014 1HannOtto StoreNo ratings yet
- AWSCertifiedBigDataSlides PDFDocument414 pagesAWSCertifiedBigDataSlides PDFUtsav PatelNo ratings yet
- RISc 2007 RAMBUS Paper QuestionsDocument4 pagesRISc 2007 RAMBUS Paper Questionsraghu dNo ratings yet
- KV8000 AbcdDocument38 pagesKV8000 AbcdKimberly Joy San JuanNo ratings yet
- Lola Download Tool: Technical Bulletin Oxo ConnectDocument6 pagesLola Download Tool: Technical Bulletin Oxo ConnectMarcelo Ratto CampiNo ratings yet
- E Health Care Management SystemDocument18 pagesE Health Care Management SystemKumara SNo ratings yet
- SDA Lab 4Document17 pagesSDA Lab 4Ali razaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 - Configuring DHCP and DNS: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesExperiment 6 - Configuring DHCP and DNS: ObjectiveM ZahidNo ratings yet
- Prasad - Double Block Zero Padding Acquisition Algorithm For GPS Software ReceiverDocument6 pagesPrasad - Double Block Zero Padding Acquisition Algorithm For GPS Software ReceiverMuhammadAbdullah59No ratings yet
- WRITTEN ASSIGNMENT - Latest Open Source Software Available and The Latest Development in ICTDocument12 pagesWRITTEN ASSIGNMENT - Latest Open Source Software Available and The Latest Development in ICTSYarafina SYed91% (11)
- Circuit Diagram 43''Document12 pagesCircuit Diagram 43''Jorge Humberto DuqueNo ratings yet
- Label - Text Textbox - Name: Server Txtserver Port Txtport Username Txtmysqluser Password Txtmysqlpw Database TXTDBDocument85 pagesLabel - Text Textbox - Name: Server Txtserver Port Txtport Username Txtmysqluser Password Txtmysqlpw Database TXTDBIyengar PrasadNo ratings yet
- Mini Project For Student Details FormDocument6 pagesMini Project For Student Details FormSrilakshmi NarayananNo ratings yet
- Sample MCQ For LinuxDocument15 pagesSample MCQ For Linuxy.alNo ratings yet
- CSE 303 - Final - AssignmentDocument2 pagesCSE 303 - Final - Assignmentমোহাম্মাদ নাজমুল হাসান আরিফNo ratings yet