Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Jozette Roberts Matrices Lesson Plan Two Inverse of Matricies 1
Uploaded by
api-403984108Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Jozette Roberts Matrices Lesson Plan Two Inverse of Matricies 1
Uploaded by
api-403984108Copyright:
Available Formats
SCHOOL OF EDUCATION, UNIVERSITY OF THE WEST INDIES, ST.
AUGUSTINE
MATHEMATICS LESSON PLAN
Teacher: Jozette Roberts
Date: Class: form 4 Time: 70mins
Unit: Matrices
Topic: Concept of the inverse of a (2×2) matrix
Pre-knowledge: addition, subtraction, multiplication of real numbers, concept of a matrix, addition,
subtraction and multiplication of matrices, scalar multiplication of matrices, determinant of a matrix, singular
matrices
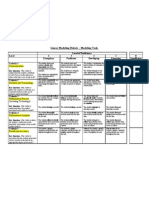
OBJECTIVES: Pupils will: Classification
1. Define inverse of a (2×2) matrix K
2. Identify why singular matrices have no inverse K
3. Define multiplicative identity of (2 ×2) matrices K
4. Apply inverse formula to determine the inverse of a (2 ×2) matrix AT
5. Show that a matrix multiplied by its inverse is the identity matrix AT
6. Develop time management skills through timed practice HFLE
7. Identify the usefulness of matrices in cryptography for spying AFF
SET INDUCTION: (Time: 2 minutes)
Students are all handed a small piece of paper with matrix (2 ×6) matrix on it. E=
The teacher explains to the students that is was a secrete message hidden within the matrix
The teacher explains that each number in the matrix has a letter equivalent
Teacher explains that spies use matrices to send secrete messages all over the world in wartime and after
learning enemies secretes.
Teacher explains that unless you know the encoding matrix it would be impossible to crack.
She explains that letters are given number codes then a matrix is formed using these numbers.
This matrix is then multiplied by an encoding matrix so that no undesirable person can read it.
Teacher asks students how would they discover what the secrete message is?
What will they need to do to find the matrix?
(Resources required: handout)
SECTION 1 (Time: 13 minutes)
Content: concept of the inverse of a (2×2) matrix
Associated Objective: 1, 2
Teaching Points:
1. It is the reverse or opposite operation to the multiplication of a (2×2) matrix
2. It is denoted by the matrix to the power of -1
3. it involves the adjoint and the determinant of a matrix
4. It is the reciprocal of the determinant multiplied by the adjoint of a (2×2) matrix
5. Inverse of a (2×2) matrix M= is M-1= =
6. It does not involve matrices with determinants of zero or singular matrices
7. the product of a matrix and its inverse is the identity matrix M× M-1= I=
Method:
Teaching Strategy: Student Activity Resources
Inductive method /Questioning Discussion/ observation Whiteboard marks,
Are there any similarities with the -Students will observe examples of on notebooks
fractions of the and known matrix the inverse of a matrix
formulae? -Students will use examples to derive
What are the similarities between the the general the formula for finding
matrix and the matrix in the inverse inverse
What are the differences between the -use it to pick the criterial attributes of
matrix and the matrix of the inverse? the inverse of (2 × 2) matrix
Sectional Review: (Time: 10 minutes)
students will find the single matrix representation for each example of the inverse.
If A= then the inverse of A= A-1=
If B= then the inverse of B= B-1=
If C= then the inverse of C= C-1=
If D= then the inverse of D= D-1=
SECTION 2 (Time: 15 minutes)
Content: Finding the inverse of a matrix
Associated Objective: 3, 4
Teaching Points:
1. Given A= is a (2 ×2) matrix its calculate the value of the determinant
-if the determinant is zero stop;
-if it is not equal to zero go on to step two
2. Find the adjoint of the (2 ×2) matrix A
3. Calculate the inverse by Multiplying the reciprocal of the determinant A by its adjoint
Or
2. substitute the values of a, b, c, d into the inverse matrix formula
3. Calculate the single matrix representation of the inverse
4. check if the inverse is correct by multiplying A ×A-1 or A-1×A
-if A ×A-1 or A-1×A= I= answer is correct
-if A ×A-1 or A-1×A≠I= inverse is not correct
Method:
Teaching Strategy: Student Activity Resources
Guided instruction Guided practice
Guided discovery -Students must determine the inverse Whiteboard, markers,
notebooks
of the A=
Students work in pairs to show that
A ×A-1= A-1×A = I=
One half of students solve A ×A-1
And the other half A-1×A
Sectional Review: (Time: 5 minutes)
Students will be given the matrix used to encode the secrete message to find the inverse S=
SECTION 3 (Time: 15 minutes)
Content: Cryptography and matrices
Associated Objective: 6,5
Teaching Points:
1. Cryptography is the art of encoding and decoding data
2. Messages are coded replacing letters with the number place in the English alphabet example A=1, T=20
and spaces between words=0
3. These numbers are then placed in matrix with even rows, labelled M
4. M is multiplied by the encrypting matrix, S, to give an encoded Matrix E
5. S is a square matrix characterized by the number of rows in the in M,
6. The message is decrypted by multiplying the inverse of S by E.
7. Replace each number by a letter
8. Read message
Method:
Teaching Strategy: Student Activity Resources
Discussion/Investigation Discussion/Small group work
-determine the encrypted message Notebook, handout,
Students will be given ten minutes to whiteboard and markers
decipher the secrete message
Sectional Review: (Time:5 minutes)
Write solution on the board
CLOSURE: (Time: 2 minutes)
Students state the key points of the lesson
- The multiplicative inverse can only be found for 2 x2 matrices
- The multiplicative inverse can only exist when matrices are non-singular
- The inverse a matrix is the reciprocal of the determinant by the adjoint of the square matrix
- A matrix multiplied by its inverse is the identity
- Matrices are used in cryptography when sending and decoding secrete messages
FINAL EVALUATION: (Time: 3 minutes)
Students will determine the inverse of
Reasonable level of Achievement: Objective
30/30 students will find the inverse of a 2×2 matrix correctly 2, 3
CONTINUOUS EVALUATION: A Complete Course in Mathematics Vol 2 pg 1147 Ex 24c
TEACHER EVALUATION OF THE LESSON:
TUTOR’S COMMENT:
SCHOOL OF EDUCATION, UNIVERSITY OF THE WEST INDIES, ST. AUGUSTINE
MATHEMATICS CONCEPT ANALYSIS FORM
Teacher Name: Ms. Jozette School Name: Fatima College Class: Form 4
Concept Name: Inverse of a (2×2) Matrix
Criterial attributes / Essential Characteristics: It is the reverse or opposite operation to the multiplication of a
matrix; it is denoted by the matrix to the power of -1. It involves the adjoint and the determinant of a matrix; It is
the reciprocal of the determinant multiplied by the adjoint of a matrix; It does not involve matrices with
determinants of zero or singular matrices; the product of a matrix and its inverse is the identity matrix
Non-criterial attributes / Non-Essential Characteristics: the name of the matrix; units that the matrix elements
represent.
Concept rule: The in inverse of a (2×2) matrix is the product of the reciprocal of the determinant and the adjoint
when the adjoint is not equal to zero; such that the matrix times its inverse is the identity matrix.
The inverse of a matrix M = M-1= = , where |M|≠0 such that M× M-1=
Teaching Points:
1. It is the reverse or opposite operation to the multiplication of a matrix;
2. It is denoted by the matrix to the power of -1
3. It involves the adjoint and the determinant of a matrix;
4. It is the reciprocal of the determinant multiplied by the adjoint of a matrix;
5. The inverse of a matrix M = M-1= =
6. It does not involve matrices with determinants of zero or singular matrices
7. the product of a matrix and its inverse is the identity matrix
8. M× M-1=
Concept examples:
If A= then the inverse of A= A-1=
If B= then the inverse of B= B-1=
If C= then the inverse of C= C-1=
Concept non-examples:
If D= then the inverse of D= D-1=
If E= then the inverse of E= E-1=
If F then the inverse of F= =
Relationship with another concept(s):
Consumer arithmetic, simultaneous equations, transformations
You might also like
- Factor by Grouping Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesFactor by Grouping Lesson Planapi-246371537No ratings yet
- Jozette Roberts Unit Plan On Matrices PortfolioDocument5 pagesJozette Roberts Unit Plan On Matrices Portfolioapi-403984108No ratings yet
- m201 Math Lesson Plan 4 1Document4 pagesm201 Math Lesson Plan 4 1api-384966224No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Template 20170831 Mathematical InductionDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Template 20170831 Mathematical Inductionapi-367457807100% (1)
- 5e Lesson Plan Perspectives Scientific NotationDocument5 pages5e Lesson Plan Perspectives Scientific Notationapi-509411193No ratings yet
- FOIL Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesFOIL Lesson Planahebe001100% (1)
- Lesson 3. Lesson Plan Solving Quadratic Equations by FactoringDocument2 pagesLesson 3. Lesson Plan Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoringcarla mae navarroNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Simultaneous Equations With Different CoefficientsDocument2 pagesLesson Plan - Simultaneous Equations With Different Coefficientsrobo00123100% (3)
- Program Plan Class 9 SA-I Mathematics SyllabusDocument5 pagesProgram Plan Class 9 SA-I Mathematics Syllabusgobeyondsky1No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Rat DenomDocument1 pageLesson Plan Rat DenomJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Linear Modelling Rubric - For ProjectDocument1 pageLinear Modelling Rubric - For ProjectmakunjapNo ratings yet
- 5e Lesson Plan - Measures of CenterDocument9 pages5e Lesson Plan - Measures of Centerapi-444187171No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2Document3 pagesLesson Plan 2api-281594404No ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesQuadratic Equations Lesson PlanJerson YhuwelNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesLesson PlanAli FaisalNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan VolumeDocument3 pagesDaily Lesson Plan VolumeFarah Anis Ismail100% (2)
- Solving Linear Systems (Substitution)Document10 pagesSolving Linear Systems (Substitution)Cathlyn Domingo Madamba100% (1)
- Finite Geometry of YoungDocument11 pagesFinite Geometry of YoungLEIZEL MANAGATNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Direct Linear VariatiionDocument6 pagesLesson Plan For Direct Linear VariatiionAllen Mae DaypuyartNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Parallel LinesDocument1 pageLesson Plan Parallel LinesJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Measure of Skewness ExplainedDocument16 pagesMeasure of Skewness ExplainedGemmavi DulnuanNo ratings yet
- C1 - L2A - Extracting Square RootsDocument2 pagesC1 - L2A - Extracting Square RootsJo-Amver Valera ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Group 5e Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesGroup 5e Lesson Planapi-474068432No ratings yet
- Different Forms of A Straight Line's EquationDocument6 pagesDifferent Forms of A Straight Line's EquationCharalampidis Dimitris100% (1)
- Basic Triangle Congruence Lesson PlanDocument1 pageBasic Triangle Congruence Lesson Planapi-219434647No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Inverse ProportionDocument1 pageLesson Plan Inverse ProportionJonathan Robinson100% (5)
- 5e Lesson Plan 1 Ed508Document6 pages5e Lesson Plan 1 Ed508api-458166115No ratings yet
- Standard Form Significant FiguresDocument7 pagesStandard Form Significant FiguresfayyzalNo ratings yet
- DAY 1 Illustrating Polynomial FunctionsDocument15 pagesDAY 1 Illustrating Polynomial FunctionsJennylou CanlasNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Sharing To A RatioDocument1 pageLesson Plan Sharing To A RatioJonathan Robinson100% (1)
- Week 2Document12 pagesWeek 2Ederzon IlustricimoNo ratings yet
- DLLmath PermutationDocument9 pagesDLLmath PermutationErwin DiosoNo ratings yet
- 8thLP Graphs A Linear Equation Given Two Points and Intercepts 7pgsDocument7 pages8thLP Graphs A Linear Equation Given Two Points and Intercepts 7pgsAna Arandia II100% (1)
- Combination and Permutation Lesson for Grade 10 StudentsDocument12 pagesCombination and Permutation Lesson for Grade 10 StudentsChello Ann Pelaez AsuncionNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 8Document6 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 8Roldan CaroNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocument19 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsCatherine PartidasNo ratings yet
- Table of SpecificationDocument1 pageTable of SpecificationAngelica Manalo PerezNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesTrigonometry Lesson Planapi-570462651No ratings yet
- Inverse VariationDocument4 pagesInverse VariationSiti Ida MadihaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsGeraldine RamosNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3Document3 pagesLesson Plan 3api-338888247No ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7 - Measures of Central Tendency of Ungrouped Data I. ObjectivesDocument9 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7 - Measures of Central Tendency of Ungrouped Data I. ObjectivesKayzeelyn MoritNo ratings yet
- Arc Length Lesson PlanDocument1 pageArc Length Lesson PlanJonathan Robinson100% (3)
- Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Mathematicsaspirinjr18No ratings yet
- Probability Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesProbability Lesson Planhix8073No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Two BracketsDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Two BracketsJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- 7e Lesson Plan For DepedDocument17 pages7e Lesson Plan For DepedRozelyn Rodil Leal-LayanteNo ratings yet
- Alg1 Jigsaw LessonDocument15 pagesAlg1 Jigsaw LessonCacait RojanieNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Algebra Jennifer CoballesDocument3 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in Algebra Jennifer CoballesCherry Arcilla CanapiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Solving Systems by GraphingDocument12 pagesLesson Plan Solving Systems by Graphingyusi rizaNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesLesson PlanCher JhetsNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN IN Probability of Simple Events: March 2019Document9 pagesLESSON PLAN IN Probability of Simple Events: March 2019Tintin SaintsNo ratings yet
- Evaluate Algebraic ExpressionsDocument5 pagesEvaluate Algebraic ExpressionsDonna Joyce MagdaongNo ratings yet
- Area of Sectors Lesson PlanDocument1 pageArea of Sectors Lesson PlanJonathan Robinson100% (2)
- Lesson Plan Omer Baktir 1Document10 pagesLesson Plan Omer Baktir 1api-501227468No ratings yet
- Quadratic Functions UbDDocument6 pagesQuadratic Functions UbDVia Terrado CañedaNo ratings yet
- Matrix Madness UnitDocument44 pagesMatrix Madness UnitKeri-ann MillarNo ratings yet
- Instructionppedu 202Document18 pagesInstructionppedu 202api-711925909No ratings yet
- Year 11 Mathematics Extension 1: ME-A1 Working With Combinatorics Unit DurationDocument18 pagesYear 11 Mathematics Extension 1: ME-A1 Working With Combinatorics Unit DurationMahmoud Abdel-SalamNo ratings yet
- Manual TelescopioDocument126 pagesManual Telescopioslanka279099No ratings yet
- FFFFDocument3 pagesFFFFMotlatso MaakeNo ratings yet
- CH 06Document21 pagesCH 06filippo0% (2)
- FPM Issue 040Document130 pagesFPM Issue 040Gábor Lipcsei50% (2)
- Jun Mars Reino A. Amante PDSDocument4 pagesJun Mars Reino A. Amante PDSJun Mars Reino Alpas AmanteNo ratings yet
- Timken Ball Bearings CatalogDocument126 pagesTimken Ball Bearings Catalogmohananc67No ratings yet
- Leadership PrinciplesDocument2 pagesLeadership PrinciplesPedro FonsecaNo ratings yet
- EPC Contractor Rep. Authority/Authority's EngineerDocument6 pagesEPC Contractor Rep. Authority/Authority's Engineersunil kuldeepNo ratings yet
- 4667 Mick̪�㺷鶉Abilities (Book PDFDocument19 pages4667 Mick̪�㺷鶉Abilities (Book PDFsusee98100% (2)
- Analysis of Bassoon StopDocument16 pagesAnalysis of Bassoon StopashockleyNo ratings yet
- Q1 Q21Document23 pagesQ1 Q21Harshil GuptaNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health NursingDocument7 pagesOccupational Health NursingCris Laurence PabustanNo ratings yet
- FRM Download FileDocument34 pagesFRM Download FilePrasant KumarNo ratings yet
- Oral Presentation TN3Document2 pagesOral Presentation TN3Jhon Jairo ObandoNo ratings yet
- ANN Mini Project on Artificial Neural Networks (40Document16 pagesANN Mini Project on Artificial Neural Networks (40amithbalu100% (1)
- Install Nagios Core 4.0.8 On Ubuntu 14.04 - Sysa..Document6 pagesInstall Nagios Core 4.0.8 On Ubuntu 14.04 - Sysa..Arthur MedeirosNo ratings yet
- Marilyn Monroe Research Paper TopicsDocument5 pagesMarilyn Monroe Research Paper Topicsfys1q18y100% (1)
- Human Relations & YouDocument27 pagesHuman Relations & YouDhea Rizky Amelia SatoNo ratings yet
- OXE Installation On VMware 8 - Complete - ProcedureDocument71 pagesOXE Installation On VMware 8 - Complete - ProcedureLuis100% (3)
- Martha Crampton Guided Imagery PDFDocument75 pagesMartha Crampton Guided Imagery PDFamimaimiuta100% (3)
- APA7 Briefing and Workshop SummaryDocument73 pagesAPA7 Briefing and Workshop Summaryryan angNo ratings yet
- MODBUS Connection C5 enDocument20 pagesMODBUS Connection C5 enLanderNo ratings yet
- Selecc Primitive-Culture-1 PDFDocument15 pagesSelecc Primitive-Culture-1 PDFguadalupe_51947962100% (1)
- Unit 4: Benefit EstimationDocument12 pagesUnit 4: Benefit EstimationRaj ChavanNo ratings yet
- B1+ (11) Vocabulary Transport and Travel AccommodationDocument2 pagesB1+ (11) Vocabulary Transport and Travel AccommodationMalik HamzaNo ratings yet
- Buddhist Foundation of EconomicsDocument21 pagesBuddhist Foundation of Economicsbyangchubsems100% (1)
- 10mm Ball Indenter impression diameter dataDocument2 pages10mm Ball Indenter impression diameter dataRajesh Sharma71% (7)
- ResumeDocument2 pagesResumeVincentNo ratings yet
- Corporate Innovations Drive M&AsDocument2 pagesCorporate Innovations Drive M&AsMarat SafarliNo ratings yet
- 1Document13 pages1ihpeterNo ratings yet