Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LEVEL 0 - No.3 - Truss
Uploaded by
liayanajemainOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LEVEL 0 - No.3 - Truss
Uploaded by
liayanajemainCopyright:
Available Formats
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN AWAM
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
PAHANG LABORATORY MANUAL NO.3
COURSE BASIC STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS LABORATORY
COURSE CODE ECS258
LEVEL OF OPENNESS 0
CATEGORY TRADITIONAL
DEGREE OF OPEN-ENDED (%) 0
PERIOD OF ACTIVITY 1 WEEK (WEEK 4)
TITLE PIN JOINTED TRUSSES
1.1 Introduction
The traditional methods of conducting laboratory activities (assigned as Level 0) will
not be able to provide the avenue for students to enhance independent learning
activities and inculcate creativity and innovation. The traditional method is fully
prescriptive where the three elements namely problem, ways & means and answers
are provided/fully given to the students. However, it is still necessary to be
implemented as part of the whole laboratory course activity specially to first and
second year students.
In this laboratory activity students will be exposed to the apparatus and appropriate
methods to carry out tests to determine the reaction and internal forces in statically
determinate trusses.
1.2 Objective
To determine the reaction and internal forces in statically determinate trusses.
PREAMBLE
1.3 Learning Outcomes
At the end of the laboratory activity, students would be able to:
1. Identify and use the correct apparatus/tools to carry out experiment on pin
jointed truss.
2. Analyse the collected data correctly and present in the proper technical
format.
3. Work in a group to undertake the task and produce the technical report.
1.4 Theoretical Background
A truss is a structure constructed with straight members connected together at their
ends referred to as joints. Triangular configuration is usually used for the trusses
because of the structural stability of the shape and the joints are usually assumed to
be pin-jointed. External forces are considered to act only at the joints and result in
forces in the members which are either tension or compression force.
©FKA, UiTM, PAHANG MARCH 2018
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN AWAM
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
PAHANG LABORATORY MANUAL NO.3
Determination of the internal forces of each member of Warren Girder Truss is
important in structural analysis. As a group, you are required to record the strain at
PROBLEM
each member for each load increment using the appropriate apparatus available in
STATEMENT
the laboratory. Using suitable equation calculates the reaction and internal member
forces.
3.1 Apparatus
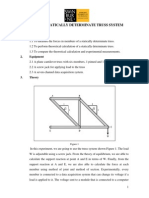
Figure 3.1: Warren Girder set up
B D
WAYS &
MEANS
60○
A E
C
W
Figure 3.2: Idealised Warren Girder set up
3.2 Procedures
1. Adjust the position of the load cell until the hole in the fork reaches the hole of the
loading position. Make sure it is also in the correct angular position. Tighten the
load cell using the 6 mm A/F Allen key. Secure the fork using a pin.
2. Make sure the Digital Force Display is ‘on’. Connect the mini DIN lead from ‘Force
Input 1’ on the digital force display to the socket marked ‘Force Output’ on the left
hand side of the load cell. Connect the strain gauges to the strain display
matching the number on the lead to the number on the socket. Leave the gauges
for 5 minutes to warm up and reach a steady state.
3. Measure the diameter of the rod and its length.
4. With no load on the load cell (the pin should turn) roughly zero the reading using
the control on the front of the load cell. Record the initial strain reading.
©FKA, UiTM, PAHANG MARCH 2018
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN AWAM
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
PAHANG LABORATORY MANUAL NO.3
4. Apply a load of ____ N (in the direction of loading) and record the strain readings
for each member.
5. Apply loads in the increments as in Table 3.1 recording the strain readings.
3.3 Data Acquisition
Equivalent member forces at ___ N
Rod diameter = ___ mm and Esteel = 210 GNm-2
Young’s Modulus is the ratio of stress to strain, that is;
E=σ where E = Young’s Modulus
ε σ = Stress in the member
ε = Displayed strain
and σ=F where F = Forces in member
A A = Cross-sectional area of member
Table 3.1: Strain reading
Strain
Load (N)
AB AC BC BD CD CE DE
0 (initial)
Table 3.2: Comparison of experiment and theoretical force
a) _____ N
Member Experimental Force (N) Theoretical Force (N)
AB
AC
BC
BD
CD
CE
DE
4.0 Results, Analysis and Conclusion
The group is required to submit the technical report of the laboratory results
highlighting the data acquisition process, analysis carried out and the relevancy of the
set-out output to achieve the objective. The report must incorporate the followings:
RESULTS 1. Using a suitable method calculate the theoretical member forces for the pin
jointed truss.
2. Compare the experiment and theoretical results.
3. Plot a graph of experiment and theoretical results.
The report must be submitted 7 days after the completion of the test.
©FKA, UiTM, PAHANG MARCH 2018
You might also like
- Lab REPORTTTDocument9 pagesLab REPORTTTepiXtremeNo ratings yet
- Experiment-1 Equation of Motion-Normal and TangentialDocument7 pagesExperiment-1 Equation of Motion-Normal and TangentialfazeenNo ratings yet
- LAB 4 - Forces in Trusses 1 v1Document11 pagesLAB 4 - Forces in Trusses 1 v1fauzaniNo ratings yet
- The Principle of The Moment of A ForceDocument6 pagesThe Principle of The Moment of A Forcedanny matangwayNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Experiment Polygon of ForcesDocument18 pagesLab 2 Experiment Polygon of ForcesalexNo ratings yet
- Procedure BONDDocument1 pageProcedure BONDMorapedi D. KealebogaNo ratings yet
- EE102 Lab 1Document12 pagesEE102 Lab 1Romulo TuiqalauNo ratings yet
- Beam Reaction Experiment Group 2Document22 pagesBeam Reaction Experiment Group 2AnushaBheenuck100% (1)
- Bending Moment in A BeamDocument8 pagesBending Moment in A BeamLim Ksoon100% (1)
- Lab ReportDocument16 pagesLab Reportabe97No ratings yet
- Lab 6 Pressure VesselDocument5 pagesLab 6 Pressure Vesselapi-3730129No ratings yet
- Alien Legacy-Manual PDFDocument93 pagesAlien Legacy-Manual PDFMark BallingerNo ratings yet
- TrussDocument12 pagesTrussAmirullah Adnan100% (1)
- Bending MomentDocument30 pagesBending MomentMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Truss Lab ActivityDocument15 pagesTruss Lab Activitysaifudin.itsNo ratings yet
- 3) Pin Jointed Truss (With Data)Document13 pages3) Pin Jointed Truss (With Data)Ainur NasuhaNo ratings yet
- Shear Force Experiment - 2Document6 pagesShear Force Experiment - 2Mohamad Afiq Afandi100% (1)
- PHY10L - Resolution of ForcesDocument14 pagesPHY10L - Resolution of Forcesdenzel94No ratings yet
- Laboratory 1aDocument7 pagesLaboratory 1aH2 MgZNo ratings yet
- Som 4Document11 pagesSom 4Ronaldo Ulisi100% (1)
- Engineering Mechanics Practical 02 It Deals With The Verification of Law of Triangle of ForcesDocument3 pagesEngineering Mechanics Practical 02 It Deals With The Verification of Law of Triangle of ForcesAbdur Rasheed NiazyNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 G5Document24 pagesExp 1 G5Abdullah Helmi100% (1)
- Equilibrium of Non-Concurrent ForcesDocument3 pagesEquilibrium of Non-Concurrent ForcesTamilManiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Trusses PDFDocument8 pagesTutorial 2 Trusses PDFBharat Sai100% (1)
- Principle of MomentsDocument4 pagesPrinciple of MomentsBruno D'almeidaNo ratings yet
- Shear ForceDocument22 pagesShear ForceGregory MillerNo ratings yet
- FrictionDocument14 pagesFrictionReincarnation Anukriti Nandan50% (6)
- Physics 110 Lab Report - Forces and EquilibriumDocument13 pagesPhysics 110 Lab Report - Forces and Equilibriumapi-375517913No ratings yet
- Experimental Lab Principles of Superposition ObjectiveDocument6 pagesExperimental Lab Principles of Superposition ObjectiveAizat HermanNo ratings yet
- Full Report Solid MechDocument19 pagesFull Report Solid MechMUHAMMAD ARIFF DYAMIMNo ratings yet
- Lab2 Forces in TrussDocument14 pagesLab2 Forces in TrussAlif EmirNo ratings yet
- E103 - Lab ReportDocument7 pagesE103 - Lab ReportJamiel CatapangNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Friction: Experiment #13Document8 pagesKinetic Friction: Experiment #13kate anne del castroNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 and Experiment 7Document5 pagesExperiment 6 and Experiment 7Gebre TensayNo ratings yet
- Verification of Lami's Theorem: Experiment # 3Document6 pagesVerification of Lami's Theorem: Experiment # 3Vedansh GargNo ratings yet
- EM ReportDocument22 pagesEM ReportAhmad Fakhrie ShahNo ratings yet
- L4 The Simple PendulumDocument13 pagesL4 The Simple PendulumNur Syamiza ZamriNo ratings yet
- SEV320 - Theory of Structures Assignment 1, 2020 Influence Lines & Deflection of Determinate Structures General InformationDocument3 pagesSEV320 - Theory of Structures Assignment 1, 2020 Influence Lines & Deflection of Determinate Structures General Informationhamza awanNo ratings yet
- Fixed End MomentDocument2 pagesFixed End MomentmuhammadalhafizNo ratings yet
- Lab-2 TrussDocument4 pagesLab-2 TrussBrian WongNo ratings yet
- Hookes Law ExperimentDocument3 pagesHookes Law ExperimentKhairul Razmin AbdurakmanNo ratings yet
- Fakulti Teknologi Kejuruteraan Universiti Teknikal Malaysia MelakaDocument15 pagesFakulti Teknologi Kejuruteraan Universiti Teknikal Malaysia MelakaToew Zhao MiaoNo ratings yet
- Fakulti Teknologi Kejuruteraan Universiti Teknikal Malaysia MelakaDocument15 pagesFakulti Teknologi Kejuruteraan Universiti Teknikal Malaysia MelakaToew Zhao MiaoNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering Department of Structure and Material Engineering Lab MaterialDocument19 pagesFaculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering Department of Structure and Material Engineering Lab Materialalnz100% (1)
- Lab 2 - Maxwell-Betti Reciprocal Theorem FinalDocument2 pagesLab 2 - Maxwell-Betti Reciprocal Theorem FinalCarlo Santos50% (2)
- Bending Test On WoodDocument8 pagesBending Test On WoodShekharappa MallurNo ratings yet
- s2 Bending MomentDocument22 pagess2 Bending MomentismailNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 (Bending Moments in Beam)Document13 pagesExperiment 3 (Bending Moments in Beam)Shafiq MahadiNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic JumpDocument5 pagesHydraulic JumpKafeel Bichu0% (1)
- Lab Newtons 2ndDocument3 pagesLab Newtons 2ndUgur ASİT50% (2)
- Mechatronics Engineering 1Document98 pagesMechatronics Engineering 1Sharma BharatNo ratings yet
- Tensile Test Lab Report: Strength of MaterialDocument5 pagesTensile Test Lab Report: Strength of Materialirfan bashirNo ratings yet
- MEC424 Content TorsionDocument12 pagesMEC424 Content TorsionHaFiy HaZimNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials Torsion TestDocument18 pagesMechanics of Materials Torsion Testjrkling100% (1)
- Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLab Reportdeanellis100% (1)
- EXP 5 TorsionDocument18 pagesEXP 5 TorsionYagami KirigayaNo ratings yet
- Torsion TestDocument7 pagesTorsion Testilya danisyahNo ratings yet
- Lab2 Principle of Moment PDFDocument7 pagesLab2 Principle of Moment PDFAnwaar SafdarNo ratings yet
- LAB REPORT BUCKLING OF STRUTS (Reference)Document13 pagesLAB REPORT BUCKLING OF STRUTS (Reference)jajenNo ratings yet
- Fakulti Kejuruteraan Awam Universiti Teknologi Mara Shah Alam Laboratory ManualDocument5 pagesFakulti Kejuruteraan Awam Universiti Teknologi Mara Shah Alam Laboratory ManualAinur NasuhaNo ratings yet
- Conclusion Fire AlarmDocument1 pageConclusion Fire Alarmliayanajemain0% (1)
- Lab 4 - Identification of Metamorphic Rocks (Level 0)Document2 pagesLab 4 - Identification of Metamorphic Rocks (Level 0)liayanajemainNo ratings yet
- Outflow MeterDocument5 pagesOutflow MeterliayanajemainNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Standard Consistency, Setting Time & Fineness of CementDocument3 pagesWeek 1 Standard Consistency, Setting Time & Fineness of CementliayanajemainNo ratings yet
- LEVEL 1 - No.5 - Suspension Cable Bridge System PDFDocument4 pagesLEVEL 1 - No.5 - Suspension Cable Bridge System PDFliayanajemainNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 - Geological Map 3 (Level 1)Document5 pagesLab 7 - Geological Map 3 (Level 1)liayanajemain0% (1)
- HAWE - FormulasDocument6 pagesHAWE - FormulasDeeDee BossNo ratings yet
- Casting: Definition, Types, Steps Involved in Casting, Advantages, Disadvantages, Importance (PDF)Document7 pagesCasting: Definition, Types, Steps Involved in Casting, Advantages, Disadvantages, Importance (PDF)Munem ShahriarNo ratings yet
- Hercules Engines c2 90d Engine Service ManualDocument7 pagesHercules Engines c2 90d Engine Service ManualRicardoNo ratings yet
- Transformer Design and Optimization A Literature Survey PDFDocument26 pagesTransformer Design and Optimization A Literature Survey PDFRushikesh MaliNo ratings yet
- 2015 - Fatigue Behavior and Modeling of Short Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites - A Literature ReviewDocument25 pages2015 - Fatigue Behavior and Modeling of Short Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites - A Literature ReviewSubramani PichandiNo ratings yet
- Senthil Kumaran ResumeDocument3 pagesSenthil Kumaran ResumeRamkumar SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Quadrosense - ManualDocument22 pagesQuadrosense - ManualdannraduNo ratings yet
- 20a-Esp8266 Rtos SDK Programming Guide enDocument41 pages20a-Esp8266 Rtos SDK Programming Guide enkellisgfNo ratings yet
- Int. J. Miner. Process.: Emin Cafer CilekDocument10 pagesInt. J. Miner. Process.: Emin Cafer CilekJose Patricio VelardeNo ratings yet
- LiliaGutnik Resume 2013Document2 pagesLiliaGutnik Resume 2013Lilia GutnikNo ratings yet
- Dana dsh40 3 25 Parts ManualDocument36 pagesDana dsh40 3 25 Parts ManualOswaldo PalaciosNo ratings yet
- GERMAN Embassy ContractDocument79 pagesGERMAN Embassy ContractVE.03 QELNo ratings yet
- PipeDocument30 pagesPipepudumai100% (1)
- Business Plan: Syeda Zurriat & Aimen RabbaniDocument11 pagesBusiness Plan: Syeda Zurriat & Aimen RabbanizaraaNo ratings yet
- Astm D 3241 - 02 - RdmyndetmdjbDocument13 pagesAstm D 3241 - 02 - RdmyndetmdjbSamuel EduardoNo ratings yet
- CS4411 Operating Systems Exam 2 Solutions Spring 2019Document7 pagesCS4411 Operating Systems Exam 2 Solutions Spring 2019DoremonNo ratings yet
- TSC 247 PrinterDocument2 pagesTSC 247 Printerr4zorxNo ratings yet
- List of Accredited Service Center - ProtechDocument1 pageList of Accredited Service Center - ProtechLarryMatiasNo ratings yet
- Cooling Coil SizingDocument4 pagesCooling Coil SizingRanu JanuarNo ratings yet
- Project Management Resume ExampleDocument2 pagesProject Management Resume ExampleGuino VargasNo ratings yet
- MZP10000000-30010-MTS-TC - 000007 - T&C Ahu & Fahu - FinalDocument59 pagesMZP10000000-30010-MTS-TC - 000007 - T&C Ahu & Fahu - FinalFaiyazsulthanNo ratings yet
- 327101-BJ81-C-RCC-0007 Rev.00 - Client MarkupDocument1 page327101-BJ81-C-RCC-0007 Rev.00 - Client MarkupGokulprabhuNo ratings yet
- Electric Power TransmissionDocument16 pagesElectric Power Transmissionsattar28No ratings yet
- Grain Diameter (MM) Strength (Mpa) : 0.015 170 Mpa 0.025 158 Mpa 0.035 151 Mpa 0.050 145 MpaDocument1 pageGrain Diameter (MM) Strength (Mpa) : 0.015 170 Mpa 0.025 158 Mpa 0.035 151 Mpa 0.050 145 MpaTEBATSONo ratings yet
- d1 - Evaluation - Justify Content Designs and Formats - FinalDocument5 pagesd1 - Evaluation - Justify Content Designs and Formats - Finalapi-466034593No ratings yet
- Ansi Asabe S261.7 Feb1989 (R2011)Document5 pagesAnsi Asabe S261.7 Feb1989 (R2011)StephanNo ratings yet
- Building Applied Natural Language GenerationDocument32 pagesBuilding Applied Natural Language Generationrat86No ratings yet
- Durag Dust MonitorDocument13 pagesDurag Dust MonitorVivek KumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document5 pagesExperiment 1Cheng BauzonNo ratings yet