Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anthology
Uploaded by
api-332379661Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anthology
Uploaded by
api-332379661Copyright:
Available Formats
Page |1
Anthology:
Bradbury, R. (2004). The Pedestrian. Read, 54(6), 24.
Chith, M. (2017). Deterrence via Knowledge. In Tempest. Sydney, Australia: Xlibris.
Eplidakalota3idi. (Youtube Video). 2+2=5, Two plus two equals five. Posted by Youtube, 26 Feb
2013: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HTjM6S-kOmg.
Pulphus, D. (n.d.). Untitled #1. Congressional Art Competition Winner (Year unknown), Missouri.
Retrieved February 25, 2017, from
http://www.stlamerican.com/entertainment/living_it/david-pulphus-honored-by-u-s-
congress-for-protest-painting/article_736171a4-286e-11e6-94dc-1f8772a8ad56.html
Williams, W. C. (1938). The Use of Force. Retrieved from Classic Short Stories:
http://www.classicshorts.com/stories/force.html
Authority Rationale:
Authority can be the enforcer of obedience. Authority belongs to the powerful, and can be
wielded to oppress the powerless. In this unit, the concept of Authority will be explored by
questioning power imbalances visible within all aspects of society. Inequality within society can be
discussed using the binaries such as; gender, race, class, age, faith and academia; each has a sequential
rank in perceived superiority. Authority is present in all power structures; it is the individual, or
ideology, at the top of a hierarchy. Within this Area of Study, students will learn how to identify and
decode meaning in power structures, and question how Authority is perceived through foreign
perspectives.
High school student, David Pulphus’s Untitled #1, is a painting protesting the fatal shooting,
by police, of Michael Brown in Missouri, USA in 2014. Authority is portrayed using metaphoric
imagery to show that the police force are in fact animals; and the shooting of a black man in the street,
is as de-personalised for police as shooting a dog. The scales of Justice weigh the Ying and Yang –
Jessica Hayter ID: 18139336 English Curriculum 2A Anthology
Page |2
just one of the signifiers for racial divide. In this Area of Study, Untitled #1 highlights how Authority
is not always unprejudiced.
The Use of Force, by William Carlos Williams, is a short story about a Doctor who is called
to a home to treat a young girl that will not cooperate. There is a sickness around that could kill her
quickly, which explains the Doctor’s urgency in finding the problem. There is a revolving door of
who has authority and power within the text. The parents, who called the Doctor and discipline the
girl; the Doctor, as a leader in medicine; and finally, the girl, who fights to keep her secret. Eventually,
the girl loses the battle, and the Doctor has the power to let the child keep her tonsils, or take them
out. The nature of authority can be studied in this text, as something fluid; within this context.
The Youtube clip titled Two + Two violently explores oppression and control through a
Teacher’s position of power. There must be a regime outside of the classroom which condones this
oppression of freedom. Within the classroom, the audience sees from the child’s point of view, as the
classroom is quickly set up as a place where there is absolutely no leniency. The unembodied
Principal, Teacher, and three senior students are established as the enforcers of Authority. The child
that speaks out in order to correct the math problem is quickly and severely silenced, providing the
lesson for the day – Do not question Authority.
The Pedestrian, by Ray Bradbury, is a short story set in the dystopian future. All humans are
implied to be controlled by their addiction to television. The protagonist, Leonard Mead, is walking
at night, just to think, when he is stopped by a personified police car. The unmanned police car
‘speaks’ and orders Leonard to answer questions about why he is acting outside the norm. The police
car judges him to be crazy, and so orders him to get into the car and be taken to a psychiatric ward
for analysis on his ‘regressive tendencies’. The Authority in this story is technology. However, the
curious thing is, humanity has chosen to give technology this power over them.
Deterrence via Knowledge by Mehdi Chith is a poem written for a poetry slam event. Chith,
a university student, is commenting on social injustices based on prejudice and political perspectives,
Jessica Hayter ID: 18139336 English Curriculum 2A Anthology
Page |3
and how instead of listening to a perceived authority, society should step back and stick up for the
little guys. This text also gives students another avenue to view the concept of authority.
These texts will give students the analysis capabilities to discuss how Authority is viewed in
society. The teacher will be able to gauge student proficiency through the assessment of responding
and composing to the selected anthology (BOSTES, p20). Critical thinking is a key area of this area
of study, as the topic of Authority is related to student’s own social perspectives. The use of different
binaries allows students to broaden their understanding and utilise their skills in critical thinking.
Jessica Hayter ID: 18139336 English Curriculum 2A Anthology
Page |4
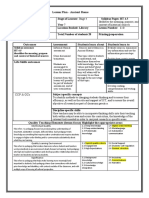
Lesson Plan #1
Who has Authority?
Topic area: Stage of Learner: Syllabus Pages:
Area of Study (Authority) Preliminary Stage 6 - Standard 20- 27
Date: Location Booked: Lesson Number:
20th April 2017 D.23 2 / 36
Time: Total Number of students Printing/preparation
60 minutes 25 students Room with smartboard
Print 25 copies of poem
See Resources listed
Outcomes Assessment Students learn about Students learn to
2.1 identifying similarities in Formative The contexts, Respond to texts
and differences between texts assessment will be purpose and Have skills in
4.1 identifying and describing a done as students audiences of texts investigation,
variety of language forms and articulate the The forms and imaginative and
features, and structures of techniques, and features of language, critical thinking,
particular texts language forms and the structures of and synthesis of
7.1 identifying and describing they recognise in texts ideas
the effects of language forms the texts. Use reflection as a
and features and structures of way to review,
particular texts Pre-existing reconsider and
knowledge is refine meaning and
gauged as teacher learning.
asks the students to
document examples
of authority.
Informal
summative
assessment is at the
end of the lesson,
the teacher asks if
there is anything
else they need to
add to their lists of
Authority forms.
This list will later
help students
identify forms of
Authority in texts.
Cross Curriculum themes & General capabilities Explicit subject specific concepts and skills
Literacy & critical thinking Connections and links within texts, contextual
understanding & uses of language to portray
meaning.
Jessica Hayter ID: 18139336 English Curriculum 2A Anthology
Page |5
Quality Teaching Elements (lesson focus) Highlight the appropriate areas
Intellectual Quality 1.1 Deep knowledge
This refers to pedagogy focused on producing deep understanding of important, 1.2 Deep understanding
substantive concepts, skills and ideas. Such pedagogy treats knowledge as something that 1.3 Problematic knowledge
requires active construction and requires students to engage in higher-order thinking 1.4 Higher-order thinking
and to communicate substantively about what they are learning. 1.5 Metalanguage
1.6 Substantive communication
Quality Learning Environment 2.1 Explicit quality criteria
This refers to pedagogy that creates classrooms where students and teachers work 2.2 Engagement
productively in an environment clearly focused on learning. Such pedagogy sets high and 2.3 High Expectations
explicit expectations and develops positive relationships between teacher and students 2.4 Social Support
and among students. 2.5 Students’ self regulation
2.6 Student direction
Significance 3.1 Background knowledge
This refers to pedagogy that helps make learning more meaningful and important to 3.2 Cultural knowledge
students. Such pedagogy draws clear connections with students’ prior knowledge and 3.3 Knowledge integration
identities, with contexts outside of the classroom, and with multiple ways of knowing all 3.4 Inclusivity
cultural perspective. 3.5 Connectedness
3.6 Narrative
How the quality teaching elements you have identified are achieved within the lesson
Teaching element Indicators of presence in the lesson
Metalanguage Metalanguage is the key component of the lesson, as students are required to read
through the provided Short Stories and articulate how Authority is represented in
the text.
High Expectations Students will be doing a lot of group work, to answer questions. This involves
good behaviour, as there is not much room for behavioural issues within the time
frame. The High Expectations of the work is having students use their knowledge
to answer questions independently and then share their information with the class.
Knowledge integration English is a subject that requires great memory, of all techniques and examples
from years prior. This activity is 100% utilising prior knowledge of these
techniques and critical thinking skills.
Jessica Hayter ID: 18139336 English Curriculum 2A Anthology
Page |6
Time Teaching and learning actions Organisation T/S
11:00 - Mark the roll Teacher: Short stories printed and
5min - Students to settle into seats and skim the handouts. already put on tables. Marking roll.
- Get notebooks/laptops out and ready for work
Student: Come into classroom and sit
and get organised, as expected. Look
over handouts on desk. Teacher
centred
Resources: The roll, a computer,
Printed copies of both The Pedestrian
by Ray Bradbury & The Use of Force
by William Carlos Williams.
11:05 - Ask students to note all forms of Authority that first come Teacher: Surveying classroom so
5min to mind in their notebooks/or on their laptops. students are on task. Make sure
- Group students by Jigsaw - 1,2,3,4 etc. students are grouped into effective
groups.
Student
Student: Write down ideas of
centred
Authority. Find fellow group members.
Resources: Student notation devices –
whether it is laptops, notebooks etc.
11:10 - Read The Use of Force by William Carlos Williams. Teacher: Surveying classroom so
15min - Group 1 & 2: Make notes of techniques while reading. students are on task, walking around to
Question 1: What does the lack of punctuation answer questions. Give hard copy
accomplish? questions to each group to answer.
Question 2: Name 2 techniques used to give the Doctor the Answers are on the teachers copy of
authority within the text? short story.
Student
- Group 3 & 4: Note where you find an example of authority Student: Reading through the Short centred
Question 3: Pick one example of Authority within the text, Story. Noting where and how the
who is in charge in that instance? Why? author represents Authority.
Question 4: What makes Authority stand out?
Resources: Student notebook/laptop.
The printed copies of The Use of Force.
11:25 - Group discussion – what is it about? Teacher: Facilitating discussion.
5min - Answer this: How does William Carlos Williams show Guiding students to see how Authority
Authority? is constructed in the text.
- What techniques does he use to do this? Collaboration
Student: Engage with class discussion.
- Re-Group: New Jigsaw – 1,2,3,4 etc.
Resources: Notebooks/laptops.
11:30 - Read The Pedestrian by Ray Bradbury. Teacher: Surveying classroom so
15min - Group 1&2: Make notes on how authority appears students are on task. Give hard copy
Question 1: Pick one example of Authority within the text, questions to each group to answer.
what does it mean? Answers are on the teachers copy of
Question 2: What makes Authority stand out? short story.
Student
- Group 3&4: Notate techniques. Student: Reading through the Short
centred
Question 3: What effect does personification have? Story. Noting where and how the
Question 4: What does the apocalyptic imagery achieve? author represents Authority.
Resources: Student notebooks/laptops.
The printed copies of The Pedestrian.
11:45 - Group discussion – what is it about? Teacher: Facilitating discussion.
10min - How does authority appear in The Pedestrian? Guiding students to see how Authority
- How does Ray Bradbury represent Authority? is constructed in the text.
Collaboration
Student: Engage with class discussion.
Resources: Student notebooks/laptops.
The printed copies of The Pedestrian.
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
Page |7
11:55 - Compare & contrast the two authors versions of Authority. Teacher: Facilitating discussion.
5min - Discuss the techniques that show this Guiding students to see how Authority
- Are there now any new ideas of authority to add to the list is constructed in the text.
you began at the beginning of the lesson.
Student: Contribute to class discussion
Collaboration
Resources: Write the final thoughts of
the lesson in notebooks/laptops for next
week’s class.
What have I learned about the teaching and learning process when preparing this lesson?
In preparing this lesson, it became apparent that 60 minutes is not long enough to cover two texts
comprehensively. Realistically, there is not enough time for slow readers to read through both short
stories, and answer the questions in one hour. This is why group discussions was included; what
students cannot do alone, they can share in groups.
How am I measuring the outcomes of this lesson?
Learning Outcome Method of measurement and recording
2.1 identifying similarities in Informal formative assessment completed at the end of the class, once they
and differences between texts have read the two short stories and can discuss similarities and differences.
4.1 identifying and describing Formative assessment completed while students are having group
a variety of language forms discussions. The teacher is walking around the classroom and engaging
and features, and structures of with students’ skill at identifying language forms within the texts.
particular texts
7.1 identifying and describing Formative assessment completed while students are having group
the effects of language forms discussions. The teacher is walking around the classroom and engaging
and features and structures of with students’ skill at deconstructing the texts and discussing what the
particular texts author intended, and how it effects the stories’ meaning.
Complete the table blow by inserting the AISTL graduate standards that you are demonstrating
and indicates the evidence from this lesson that should comply with the standard.
Graduate Standards Evidence within this lesson
1.2 Teacher has had these students since last semester. Is aware that students work
Understand how best when guided by a teacher as facilitator. The group work and student centred
students learn learning is the best framework for these students.
2.3 Teacher is new and has only been in front of a classroom for 6 months. The
Curriculum, amount of assessment utilised in this lesson plan, is to judge herself and how the
assessment & students internalise the lesson.
reporting
3.4 This schools policy on ICT is very inclusive. They have provided laptops for all
Select & use resources students, and recommended they get used in every lesson. Teacher uses ICT for
note-taking only. If students need to, they are able to use the online dictionary or
thesaurus.
4.2 This lesson revolves around the groups, grouped using the Jigsaw strategy, to
Manage classroom work successfully. The teacher must be flexible to any changes made, in order to
activities further the lesson in this configuration.
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
Page |8
Work Health & Safety: What are the key risk issues that may appear for and need to be reduced/
eliminated in this lesson? Using your syllabus and support documents as well as other WHS policy.
Outline the key WHS considerations that are to be applied in this lesson?
Students moving around the room, while using school-provided laptops, must be careful not to
drop, or run power cables across pathways.
Students must be seated safely in their chairs, to avoid falling or breaking the chairs.
All students must behave in agreeance with the schools policy/code of conduct.
Lesson-Plan References:
Bradbury, R. (2004). The Pedestrian. Read, 54(6), 24.
Williams, W. C. (1938). The Use of Force. Retrieved from Classic Short Stories:
http://www.classicshorts.com/stories/force.html
Lesson-Plan Resources Attached:
Group question cards for activity:
GROUP 1: GROUP 1:
What does the lack of punctuation accomplish? Pick one example of Authority within the text,
what does it mean?
GROUP 2:
GROUP 2:
Pick one example of Authority within the text,
What effect does personification have?
who is in charge in that instance & why?
GROUP 3:
GROUP 3:
Name 2 techniques used to give the Doctor the
What makes Authority stand out?
authority within the text?
GROUP 4: GROUP 4:
What makes Authority stand out? What does the apocalyptic imagery achieve?
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
Page |9
The Use of Force by William Carlos Williams
Student copy of
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 10
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 11
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 12
The Use of Force by William Carlos Williams
Teachers copy of
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 13
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 14
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 15
The Pedestrian by Ray Bradbury
Student copy of
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 16
Teachers copy of
The Pedestrian by Ray Bradbury
ANSWERS for groupwork:
Question 1: Pick one example of Authority within the text, what
does it mean?
Answer: The unmanned police car telling Mead to get in. It means
technology has that power.
Question 2: What effect does personification have?
Answer: Personification gives the police car the power of the law
– it is the symbolism.
Question 3: What makes Authority stand out?
Answer: The only interaction Mead has with another ‘person’ is
being talked down to.
Question 4: What does the apocalyptic imagery achieve?
Answer: In a world where you are different, you are thought to be
suspicious.
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 17
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 18
Lesson Plan #2
Authority through the lens of protest art.
Topic area: Stage of Learner: Syllabus Pages:
Area of Study (Authority) Preliminary Stage 6 20-27
Date: Location Booked: Lesson Number:
21st April 2017 D.23 3 / 36
Time: Total Number of students Printing/preparation
60 minutes 25 students Powerpoint
Homework sheets printed
Outcomes Assessment Students learn about Students learn to
2.2 identifying and describing Formal formative The contexts, Respond to texts
the connections between texts. assessment of purpose and Have skills in
(homework) audiences of texts investigation,
6.2 relating responses to aspects writing tasks to be The forms and imaginative and
of human experience. given to the features of language, critical thinking,
teacher to be and the structures of and synthesis of
6.4 discussing and reflecting on marked. texts ideas
the wider issues arising from Use reflection as a
their engagement with the texts. way to review,
reconsider and
13.4 writing refine meaning and
learning.
Cross Curriculum themes & General capabilities Explicit subject specific concepts and skills
Literacy & Critical Thinking Writing, Questioning, Reading.
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 19
Quality Teaching Elements (lesson focus) Highlight the appropriate areas
Intellectual Quality 1.1 Deep knowledge
This refers to pedagogy focused on producing deep understanding of important, 1.2 Deep understanding
substantive concepts, skills and ideas. Such pedagogy treats knowledge as something that 1.3 Problematic knowledge
requires active construction and requires students to engage in higher-order thinking 1.4 Higher-order thinking
and to communicate substantively about what they are learning. 1.5 Metalanguage
1.6 Substantive communication
Quality Learning Environment 2.1 Explicit quality criteria
This refers to pedagogy that creates classrooms where students and teachers work 2.2 Engagement
productively in an environment clearly focused on learning. Such pedagogy sets high and 2.3 High Expectations
explicit expectations and develops positive relationships between teacher and students 2.4 Social Support
and among students. 2.5 Students’ self regulation
2.6 Student direction
Significance 3.1 Background knowledge
This refers to pedagogy that helps make learning more meaningful and important to 3.2 Cultural knowledge
students. Such pedagogy draws clear connections with students’ prior knowledge and 3.3 Knowledge integration
identities, with contexts outside of the classroom, and with multiple ways of knowing all 3.4 Inclusivity
cultural perspective. 3.5 Connectedness
3.6 Narrative
How the quality teaching elements you have identified are achieved within the lesson.
Teaching element Indicators of presence in the lesson
Deep Understanding From prior class looking into forms and language, this class deepens the
knowledge with symbolism and representation. Students are now asked to
demonstrate what they have learned about deconstructing texts in a piece of
writing for homework.
Explicit Quality Criteria Teacher always provides clear expectations in lessons, through facilitating the
discussion and leading the class to higher-order thinking through questions
they should know the answers to. In the homework, students are required to
meet criteria so teacher can see development.
Student Self-Regulation Since the teacher has spent a lot of time with these students, and developed a
good relationship with them, there is a quality learning environment which
provides the space for students to respect each other and the teacher. There is
always work completed to a high standard when students are working
independently or in groups.
Background Knowledge Prior classes recapped certain aspects of deconstructing texts, this class looked
at more forms of textual analysing so the students are equipped to complete the
homework which is a low level task, bringing knowledge to the forefront of
their minds for Preliminary HSC type questions – but through the lense of the
concept of Authority,
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 20
Time Teaching and learning actions Organisation Centred
T/S
10:00 - Mark Roll Teacher: Mark roll, ready computer for
5min - Students take seats and get organised. lesson
Student: Come inside respectfully,
take a seat, and get organised for the Teacher
lesson. centred
Resources: roll, student
notebooks/laptops
10:05 - On Smartboard, bring up the David Pulphus painting, Teacher: Bring up Pulphus painting on
5min instruct students to look quickly. smartboard, then take away. Provide
- Take the artwork away and have the students write a instruction and monitor classroom so
sentence on what they think the artwork is about. on task. Lead discussion.
- Discuss
Student
Student: Look quickly at artwork,
centred
write down what they think it means.
Resources: Untitled #1 by David
Pulphus, smartboard, notebooks/laptops
10:10 - Bring the artwork back up and have the students look Teacher: Bring up Pulphus painting
10min deeply. Write down as many symbols as you can. again. Provide instruction. Monitor
- Explain the symbols and what they represent in dot point class.
format.
Student: Look closely at the artwork,
Student
note all symbolism. Expand on what
centred
the symbolism represents.
Resources: Untitled #1 by Pulphus,
smartboard, notebooks/laptops
10:20 - Teacher explain that what they have just done is similar to Teacher: Describe how that exercise
15min writing an essay, using critical analysis skills of a text. aids students in thinking about critical
- Write a short essay answering this question? essay writing. Pick symbols/patterns or
What does Untitled #1 say about the African American techniques, and expand. Facilitate
perspective of Authority? writing exercise. Monitor for on task.
Student &
Student: Write a short essay, make teacher
sure you answer the question.
Resources: Untitled #1 by Pulphus,
smartboard, notebooks/laptops
10:35 - Display question up on the board. Teacher: Facilitating discussion.
5min - Share ideas that arose from the artwork. Was there a key Coaxing students to share what they
feature that stood out for everybody? discovered in the text in answering the
- Did everybody take the same stance? question.
Collaboration
Student: Engage in discussion.
Resources: Smartboard,
notebooks/laptops
10:45 - Read the second text displayed on smartboard. Deterrence Teacher: Display text. Direct
5min via Knowledge, by Mehdi Chith. classroom. Monitor activity.
Student: Read.
Student
Resources: Smartboard, Deterrence via centred
Knowledge by Mehdi Chith.
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 21
10:50 - On smartboard Deterrence via Knowledge by Mehdi Chith. Teacher: Display text. Direct
10min - Think, Pair, Share what the possible meaning could be, classroom. Monitor activity. Hand out
keeping in mind; homework worksheets to class.
1. Language
2. Form Student: In pairs, discuss.
3. Punctuation
Resources: Homework worksheet, Student
HOMEWORK: containing explicit quality criteria. centred
Students are required to utilise the skills used in
deconstructing Untitled #1 by David Pulphus, in analysing
Deterrence via Knowledge by Mehdi Chith. Write a short
essay examining who the authority is within the text?
What is the author’s intention with this poem?
What have I learned about the teaching and learning process when preparing this lesson?
Teaching the subject of deconstructing texts is a bit daunting. A lot relies on prior learning. Since I have had
this class for awhile, I know what they have done in the past. Last lesson was a recap on techniques and how
they contribute to meaning. This lesson needed to provide a deeper analysis of texts so students could provide
the teacher with a formal formative assessment, so they can be measured with what still needs to be done
before the Preliminary HSC.
How am I measuring the outcomes of this lesson?
Learning Outcome Method of measurement and recording
2.2 identifying and describing Formative assessment completed by the teacher to gauge if the prior lesson
the connections between texts. was understood by the students. Connection between texts is the concept
of Authority and the undercurrent recap into deconstructing texts to
discover meaning.
6.2 relating responses to Students should have an empathetic understanding of the texts in this
aspects of human experience. class. Teacher can gauge responses formatively, to see if the students
understand the context of subjects.
6.4 discussing and reflecting The teacher completes an informal formative assessment on students
on the wider issues arising during the collaborative learning midway through the lesson. Students are
from their engagement with able to say what they think about the text and how it influences them in
the texts. society.
13.4 writing Teacher will complete a formal formative assessment of student writing
when collected homework from students in the next class. Teacher will
look for students’ skill at critical analysis.
Other Considerations:
Complete the table blow by inserting the AISTL graduate standards that you are demonstrating and
indicates the evidence from this lesson that should comply with the standard.
Graduate Standards Evidence within this lesson
1.1 Students are still in the stages of adolescent development where they
Physical, social and cannot understand abstract thoughts as well as adults. Lessons are
intellectual development and formulated to give more concrete evidence in studying an idea which is
characteristics of students very abstract.
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 22
2.2 In the sequence, this lesson makes sense as it is a recap of earlier
Content selection and knowledge, where students need to know how to use the skills of critical
organisation analysis in the future texts within the unit.
3.1 Students are given the opportunity to write a critical analysis at home.
Establish challenging This analysis must address the specific items we have studied in class over
learning goals the past two days. The content is hard, as it is an amateur poem, that will
not have a Sparknotes webpage for students to gain direction from. The
teacher needs this assessment for future lesson planning.
Work Health & Safety: What are the key risk issues that may appear for and need to be reduced/
eliminated in this lesson? Using your syllabus and support documents as well as other WHS policy.
Outline the key WHS considerations that are to be applied in this lesson?
Quality learning environment gives students a safe space to share opinions and perspectives,
especially when the texts touch on political views and concepts of racial divide.
Power cords for laptops need to be clear of walkways
Chairs must be sat on in the correct manner for student safety.
Lesson-Plan References:
Chith, M. (2017). Deterrence via Knowledge. In Tempest. Sydney, Australia: Xlibris.
Pulphus, D. (n.d.). Untitled #1. Congressional Art Competition Winner (Year unknown), Missouri.
Retrieved February 25, 2017, from
http://www.stlamerican.com/entertainment/living_it/david-pulphus-honored-by-u-s-
congress-for-protest-painting/article_736171a4-286e-11e6-94dc-1f8772a8ad56.html
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 23
Lesson-Plan Resources Attached:
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 24
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 25
Deterrence via Knowledge by Mehdi Chith
We empower the powerful by empowering the powerless. Let us change this mindset
that we all fall under categorical boxes which apparently define us, Instead it divides
us, emancipated by the shackles of self-denial, prejudice and questions never sought,
it started out as a whisper and soon intensified into a thought. Deterrence via
knowledge rather than the cold imprisonment of iron bars would elicit the better side
of humanity much more efficiently than the father who spends his life behind bars.
See, we are constantly being shattered and reconstructed, adaptable yet held
accountable for the actions of our previous selves. Knowledge will break you then
make you; self reflection will mediate the grounds for sincere regret, a far worse
imprisonment than iron bars. Your sentence was already given before your innocence
was proven, unbalanced judicial sentences yet cannot structure itself into proper
sentences... 8 months for a paedophile rapist yet years upon years for robbing that store
out of desperation to feed your children. See, we have it all wrong, the soldier fires a
missile that is worth more than he will make in an entire year on people who will not
make that amount in an entire lifetime. Tell me what is wrong here... If you were to
arm that soldier with the most priceless of armaments, knowledge, the barrel in which
once fired lead would fire philosophical rounds into each other's mind. Yet in that
moment, the soldier becomes a teacher.
Chith, M,. (2017). Deterrence via knowledge. Tempest. Xlibris Publishing. Australia
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 26
Lesson Plan #3
When Authority is wrong…
Topic area: Stage of Learner: Syllabus Pages:
Area of Study (Authority) Preliminary Stage 6 20-27
Date: Location Booked: Lesson Number:
23rd April 2017 D.23 4 / 36
Time: Total Number of students Printing/preparation
60 minutes 25 students Make sure can access youtube
Single page powerpoint
Outcomes Assessment Students learn about Students learn to
1.2 identifying and describing Formative The contexts, Respond to texts
the effects of those elements of assessment is purpose and Have skills in
a text which reflects context completed during audiences of texts investigation,
3.2 language for making class discussion. The forms and imaginative and
connections, questioning, features of language, critical thinking,
affirming, challenging, and the structures of and synthesis of
speculating about and texts ideas
generalising about texts. Use reflection as a
7.1 identifying and describing way to review,
the effects of language forms reconsider and
and features and structures of refine meaning and
particular texts. learning.
Cross Curriculum themes & General capabilities Explicit subject specific concepts and skills
Connections and links within texts, contextual
Literacy, ICT, Critical Thinking understanding & uses of language to portray
meaning.
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 27
Quality Teaching Elements (lesson focus) Highlight the appropriate areas
Intellectual Quality 1.1 Deep knowledge
This refers to pedagogy focused on producing deep understanding of important, 1.2 Deep understanding
substantive concepts, skills and ideas. Such pedagogy treats knowledge as something that 1.3 Problematic knowledge
requires active construction and requires students to engage in higher-order thinking 1.4 Higher-order thinking
and to communicate substantively about what they are learning. 1.5 Metalanguage
1.6 Substantive communication
Quality Learning Environment 2.1 Explicit quality criteria
This refers to pedagogy that creates classrooms where students and teachers work 2.2 Engagement
productively in an environment clearly focused on learning. Such pedagogy sets high and 2.3 High Expectations
explicit expectations and develops positive relationships between teacher and students 2.4 Social Support
and among students. 2.5 Students’ self regulation
2.6 Student direction
Significance 3.1 Background knowledge
This refers to pedagogy that helps make learning more meaningful and important to 3.2 Cultural knowledge
students. Such pedagogy draws clear connections with students’ prior knowledge and 3.3 Knowledge integration
identities, with contexts outside of the classroom, and with multiple ways of knowing all 3.4 Inclusivity
cultural perspective. 3.5 Connectedness
3.6 Narrative
How the quality teaching elements you have identified are achieved within the lesson.
Teaching element Indicators of presence in the lesson
Higher order thinking Taking the ability established previously and employing it to deconstruct a
different media text will call upon higher-order thinking.
Explicit quality criteria Lots of group work means the students can discuss any avenue they need to in
order to reach the lesson goals. The lesson goals are scaffolded by the teacher
during the facilitation of the group discussions.
Knowledge integration Prior knowledge of textual deconstruction is needed to attempt the video clip.
The integration of this knowledge aids in the students’ understanding of the
text.
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 28
Time Teaching and learning actions Organisation Centred
T/S
11:00 - Mark roll Teacher: Mark roll. & ready computer.
5min - Students enter and unpack notebooks/laptops
Student: Enter in an orderly fashion
Teacher
and unpack ready for lesson.
centred
Resources: Smartboard, roll
11:10 - Students split up into groups using the Jigsaw method. Teacher: Group students into effective
10min - Teacher to outline what class has learnt so far on Authority groups. Recap & Insight into the days
as a recap. lesson.
- Teacher to outline what todays lesson will cover.
1. Youtube clip Student: In correct groups, attentive Teacher
2. Writing and ready to take notes centred
3. Hand in homework from Fridays class.
Resources: Smartboard, youtube,
notebooks/laptops.
11:20 - Assign points to concentrate on to each group. Teacher: Assign groups. Play youtube
10min 1. Symbols video, monitor the classroom to ensure
2. Structure on task.
3. Context
Teacher
4. Language Student: Attentive and taking notes
centred
5. Camera angles
- Play 2+2=5 youtube clip Resources: Youtube,
notebooks/laptops
11:30 - Group discussion to share ideas about the dot points above. Teacher: Motivating students, make
5min sure on task. Walking around in case
students need help.
Student
Student: Engaging in the group
centred
conversation.
Resources: Notebooks/laptops
11:35 - Teacher re-jigsaws students to create new groups Teacher: Group into effective groups.
10min [systematically from existing table groups. ie. From group Assign points to groups. Play youtube
1, give out 1-5. etc.] video, monitor the classroom to ensure
- Assign the dot point to each new group on task.
- Re-watch clip
Teacher
Student: In correct groups, attentive
centred
and ready to take notes
Resources: Youtube,
notebooks/laptops
11:45 - Experts contribute to class discussion. What are the key Teacher: Facilitate the discussion,
10min things that stand out in the video: encourage students to share.
1. Symbols
2. Structure Student: Now experts in each point, Student
3. Context engage in discussion. centred
4. Language
5. Camera angles Resources: notebooks/laptops
11:55 - Teacher to sum up what students have learnt this lesson: Teacher: Summing up lesson. Collect
5 min textual analysis can be applied to cinema too. homework.
- Make sure homework handed in.
Student: Listening and slowly, quietly Teacher
packing up centred
Resources: N/A
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 29
Extension:
Students can go home and watch a 20 minute youtube video on the Myth of Authority. It goes with the criticial
stance we have taken on the approach to studying Authority.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0k4pXwmis7A&t=196s
What have I learned about the teaching and learning process when preparing this lesson?
There is not always enough time to get as in depth in a text as you would like to. The results from homework
handed in during this lesson will notify the teacher whether there needs to be further lessons dedicated to critical
textual analysis before moving on to the next skill base.
How am I measuring the outcomes of this lesson?
Learning Outcome Method of measurement and recording
1.2 identifying and describing Once the students have established the effects of language within the
the effects of those elements video, the teacher will use informal formative assessment to see how well
of a text which reflects context they use this information to judge the context.
3.2 language for making The whole exercise judges the use of language in the video. Students
connections, questioning, utilise what they have learnt in summing up the information they have,
affirming, challenging, with what they surmise to make speculations about the text’s purpose.
speculating about and Also, formative assessment.
generalising about texts.
7.1 identifying and describing Similar to above, the students will be able to identify the key uses of
the effects of language forms language in the video to puzzle together what the artist’s intentions are.
and features and structures of They will be able to describe each technique in detail, and how it
particular texts. contributes to their understanding. Teacher will be using informal
formative assessment to judge how well the students perform.
Other considerations:
Complete the table blow by inserting the AISTL graduate standards that you are demonstrating
and indicates the evidence from this lesson that should comply with the standard.
Graduate Standards Evidence within this lesson
1.1 Students in this class are at all different levels of ability. The constant use
Physical, social and of group work means there are no boundaries in my classroom. The
intellectual development and flexibility in the students has grown as they have let go of their friendship
characteristics of students groups and embraced the differing opinions of others. There is greater
respect for the teacher because there is greater respect amongst peers.
2.1 As a recap segment of critical analysis, the teacher has included many
Content and teaching different media types so students can get the most out of the Area of
strategies of the teaching Study. The teaching strategies include homework, and class assessment in
area order to document progress.
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 30
3.6 In these 3 lesson plans, the teacher has continuously taken formative
Evaluate and improve assessment. Since this teacher is new to the industry, she needs to do this
teaching programs to check on her effectiveness. Now that she has enough material to judge
whether her students are performing to the benchmark, she can surmise
whether she can move on to the next area of study, or create more lesson
plans based on critical analysis. This is for the student’s best chance at
understanding all material.
4.5 The content of this lesson’s text is quite confronting. Students are judged
Use ICT safely, responsibly by the teacher to be mature enough to handle to content. The teacher also
and ethically. warns students of the violent and graphic nature of the film at the
beginning of the lesson, so students can make informed decisions on
whether to participate or not.
Work Health & Safety:
What are the key risk issues that may appear for and need to be reduced/
eliminated in this lesson? Using your syllabus and support documents as well as other WHS policy.
Outline the key WHS considerations that are to be applied in this lesson?
Moving around for group work, students need to be careful with laptops. Unplug from wall if charging.
Power cords must not be across pathways.
When seated, students must sit correctly to prevent risk.
All students must behave in agreeance with the schools’ policy/code of conduct.
Lesson-Plan References:
Eplidakalota3idi. (Youtube Video). 2+2=5, Two plus two equals five. Posted by Youtube, 26 Feb 2013:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HTjM6S-kOmg.
Rose, L. (Youtube Video). The Myth of Authority (Video Contest Winner). Posted by Youtube, 5 May
2016: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0k4pXwmis7A&t=196s.
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 31
Lesson-Plan Resources Attached:
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
P a g e | 32
References
Australian Institute for Teaching and School Leadership. (2016). Graduate Teacher Standards.
Retrieved from Australian Professional Standards for Teachers:
http://www.aitsl.edu.au/australian-professional-standards-for-
teachers/standards/list?c=graduate
Bradbury, R. (2004). The Pedestrian. Read, 54(6), 24.
Chith, M. (2017). Deterrence via Knowledge. In Tempest. Sydney, Australia: Xlibris.
Eplidakalota3idi. (Youtube Video). 2+2=5, Two plus two equals five. Posted by Youtube, 26 Feb 2013:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HTjM6S-kOmg.
NSW Board of Studies. (2009). English Syllabus Stage 6. NSW, Australia.
Pulphus, D. (n.d.). Untitled #1. Congressional Art Competition Winner (Year unknown), Missouri.
Retrieved February 25, 2017, from http://www.stlamerican.com/entertainment/living_it/david-
pulphus-honored-by-u-s-congress-for-protest-painting/article_736171a4-286e-11e6-94dc-
1f8772a8ad56.html
Quality Teaching Guide. (2003). Retrieved from NSW Department of Education and Training.
Rose, L. (Youtube Video). The Myth of Authority (Video Contest Winner). Posted by Youtube, 5 May
2016: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0k4pXwmis7A&t=196s.
Williams, W. C. (1938). The Use of Force. Retrieved from Classic Short Stories:
http://www.classicshorts.com/stories/force.html
Jessica Hayter English Curriculum 2A
18139336 Anthology
You might also like
- Supervisor Observation 1 - PerspectiveDocument10 pagesSupervisor Observation 1 - Perspectiveapi-726483986No ratings yet
- Day 4Document6 pagesDay 4api-509542028No ratings yet
- Dramatic Role Play Hand OutDocument2 pagesDramatic Role Play Hand Outapi-263426795100% (1)
- Rasin in The Sun UbdDocument6 pagesRasin in The Sun Ubdapi-458171328No ratings yet
- Drama Unit PlanDocument19 pagesDrama Unit Planapi-349579702No ratings yet
- Sample-Unit-Standard-Year-12-Common-Module-Past-The-Shallows 2Document13 pagesSample-Unit-Standard-Year-12-Common-Module-Past-The-Shallows 2mahla fzpoorNo ratings yet
- UbD Level 3 - 8th GradeDocument40 pagesUbD Level 3 - 8th Graderasha zeinNo ratings yet
- Edma Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesEdma Lesson Planapi-662165409No ratings yet
- Standard 2 - sc2b Stage 6 Extension 1 Year 11Document13 pagesStandard 2 - sc2b Stage 6 Extension 1 Year 11api-459491146No ratings yet
- Ed615 Lesson He Lion Bruh Bear and Bruh RabbitDocument10 pagesEd615 Lesson He Lion Bruh Bear and Bruh Rabbitapi-394394249No ratings yet
- Intertextual Study Unit Plan Tkam Jasper JonesDocument12 pagesIntertextual Study Unit Plan Tkam Jasper Jonesapi-474141182100% (2)
- Attitudes of Doctor of Philosophy in Education Major in English Students Toward Teaching FictionDocument8 pagesAttitudes of Doctor of Philosophy in Education Major in English Students Toward Teaching FictionPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Teacher Perceptions of Critical Thinking Among Students and Its Influence On Higher EducationDocument9 pagesTeacher Perceptions of Critical Thinking Among Students and Its Influence On Higher EducationMonica PnzNo ratings yet
- Ej 1001528Document4 pagesEj 1001528JnjkkoNo ratings yet
- DLL04GDocument3 pagesDLL04GJojit VelascoNo ratings yet
- MYP Unit Planner: Stage 1: Integrate Significant Concept, Area of Interaction and Unit QuestionDocument5 pagesMYP Unit Planner: Stage 1: Integrate Significant Concept, Area of Interaction and Unit QuestionAndrea Hernandez-VilaNo ratings yet
- AT3 Literacy Mini-LessonDocument16 pagesAT3 Literacy Mini-LessonKairi EllisNo ratings yet
- LESSON - PLAN - Grade 8Document5 pagesLESSON - PLAN - Grade 8Reynard BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Cep Lesson Plan and Reflection - Brooklyn ReyesDocument10 pagesCep Lesson Plan and Reflection - Brooklyn Reyesapi-549599661No ratings yet
- Ubd Intro To ElaDocument11 pagesUbd Intro To Elaapi-349579702No ratings yet
- Ict Topic 2 TableDocument3 pagesIct Topic 2 Tableapi-351212860No ratings yet
- Labeling Theory Was Developed by Howard BeckerDocument2 pagesLabeling Theory Was Developed by Howard BeckerRoeina Abdul100% (1)
- Edsc 304 Dup TemplateDocument4 pagesEdsc 304 Dup TemplateDarrin ChingNo ratings yet
- Role PlayDocument61 pagesRole PlayGeraldine PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Us Formal 2Document7 pagesUs Formal 2api-576899685No ratings yet
- Wk3AssgnNatarajR - EDUC 4030 WK03 UnitTemplateDT+ (1) + (1)Document9 pagesWk3AssgnNatarajR - EDUC 4030 WK03 UnitTemplateDT+ (1) + (1)Roopa NatarajNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 4 InquiryDocument13 pagesLesson Plan 4 Inquiryapi-374439853100% (2)
- Module 4 Talits Reviewer Finals 1Document3 pagesModule 4 Talits Reviewer Finals 1Eari FujiyamaNo ratings yet
- Stage 6 English Advanced Year 12 Common Module Sample UnitDocument21 pagesStage 6 English Advanced Year 12 Common Module Sample UnithelenNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log APPLIED SUBJECT - GAS - Discipline and Ideas in The Social ScienceDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Log APPLIED SUBJECT - GAS - Discipline and Ideas in The Social ScienceHannae pascuaNo ratings yet
- Utopias and Dystopias ProgramDocument9 pagesUtopias and Dystopias ProgramOrmo@NormoNo ratings yet
- Eng10 q4 w1 Studentsversion v2Document11 pagesEng10 q4 w1 Studentsversion v2Potato100% (1)
- MAJ 17 Lesson 1Document12 pagesMAJ 17 Lesson 1March MarchNo ratings yet
- TitaaaaaDocument3 pagesTitaaaaaJerymy Dareen Alamares SantosNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log APPLIED SUBJECT - GAS - Discipline and Ideas in The Social ScienceDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Log APPLIED SUBJECT - GAS - Discipline and Ideas in The Social ScienceHannae pascuaNo ratings yet
- English Communication Arts and Skills Through Anglo-American and Philippine Literatures Ecas 10Document8 pagesEnglish Communication Arts and Skills Through Anglo-American and Philippine Literatures Ecas 10Jonathan M. AbelleraNo ratings yet
- 5E Lesson Plan Template: HS.2SS.C4.PO1 - The Highly Proficient Student Can Connect Ideas of TheDocument4 pages5E Lesson Plan Template: HS.2SS.C4.PO1 - The Highly Proficient Student Can Connect Ideas of Theapi-324796495No ratings yet
- Englishlp Biasandprejudicegrade9 220504115813Document4 pagesEnglishlp Biasandprejudicegrade9 220504115813Gilda TangposNo ratings yet
- Activity #4Document2 pagesActivity #4Alna Gamulo LosaNo ratings yet
- Final Reflection 2Document6 pagesFinal Reflection 2api-709711108No ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Time & Dates QuarterDocument3 pagesDaily Lesson Plan: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Time & Dates Quarterrodriguezmarkanthony653No ratings yet
- Ecur 379 Unit Plan - Macpherson Lerman OlsonDocument37 pagesEcur 379 Unit Plan - Macpherson Lerman Olsonapi-400754898No ratings yet
- Strategy Focus Questions When Have I Experienced This in The Past? How Have I Used This Strategy As A Teacher?Document4 pagesStrategy Focus Questions When Have I Experienced This in The Past? How Have I Used This Strategy As A Teacher?api-350824511No ratings yet
- Critical Literacies: NegotiatingDocument6 pagesCritical Literacies: NegotiatingyuNo ratings yet
- Mini Lesson Plan Template: Date: Class: English Iv Grade: Senior Period (S) : 2Document4 pagesMini Lesson Plan Template: Date: Class: English Iv Grade: Senior Period (S) : 2api-509364229No ratings yet
- Tfa Lesson Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesTfa Lesson Plan Templateapi-549568789No ratings yet
- 3 2 Lecture-TaxanomyDocument9 pages3 2 Lecture-Taxanomyk.i.n.g.ston.dra.ke.31No ratings yet
- Learning Styles, Psychological Types and Adult Learning TheoriesDocument31 pagesLearning Styles, Psychological Types and Adult Learning TheoriesSafiyaPiroNo ratings yet
- Edu 276 Technology Lesson Plan TemplateDocument4 pagesEdu 276 Technology Lesson Plan Templateapi-451753230No ratings yet
- FLCT Activity 1-2Document2 pagesFLCT Activity 1-2Ramon Pamero TasiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Learner Development TheoriesDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Learner Development TheoriesCharlyn CaraballaNo ratings yet
- Assessment 2 Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesAssessment 2 Lesson Planralph ghazziNo ratings yet
- Text Analysis PRDocument7 pagesText Analysis PRRean Riddick GuintoNo ratings yet
- Novel Study Unit PlanDocument7 pagesNovel Study Unit Planapi-548058713No ratings yet
- Myp Unit Planner: Stage 1: Integrate Significant Concept, Area of Interaction and Unit QuestionDocument5 pagesMyp Unit Planner: Stage 1: Integrate Significant Concept, Area of Interaction and Unit Questionkhush1802No ratings yet
- Elementary Lesson Plan CT ObservationDocument12 pagesElementary Lesson Plan CT Observationapi-695959570No ratings yet
- DLL-May-8-12 (1) PTDocument9 pagesDLL-May-8-12 (1) PTArnold ArceoNo ratings yet
- English s6 Billy Elliot Unit of WorkDocument29 pagesEnglish s6 Billy Elliot Unit of WorkMairead KellyNo ratings yet
- Sample Lesson Plan 1Document4 pagesSample Lesson Plan 1api-405933103No ratings yet
- Creative Writing for Critical Thinking: Creating a Discoursal IdentityFrom EverandCreative Writing for Critical Thinking: Creating a Discoursal IdentityNo ratings yet
- CTL - Critical ReflectionDocument4 pagesCTL - Critical Reflectionapi-3323796610% (1)
- 8 Lesson 13 Viking FranceDocument2 pages8 Lesson 13 Viking Franceapi-332379661No ratings yet
- Pple Assessment 1Document10 pagesPple Assessment 1api-332379661No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Coloured Markers Blank A4 Paper Viking Law Scenarios - Cut OutDocument2 pagesLesson Plan: Coloured Markers Blank A4 Paper Viking Law Scenarios - Cut Outapi-332379661No ratings yet
- History Curriculum - Assessment 2Document49 pagesHistory Curriculum - Assessment 2api-332379661No ratings yet
- English - Assessment 1Document20 pagesEnglish - Assessment 1api-332379661No ratings yet
- Poster For Aboriginal and Culturally Responsive Pedagogies UnitDocument1 pagePoster For Aboriginal and Culturally Responsive Pedagogies Unitapi-332379661No ratings yet
- Inclusive Education Assessment 2Document9 pagesInclusive Education Assessment 2api-332379661No ratings yet
- History Curriculum - Assessment 2Document49 pagesHistory Curriculum - Assessment 2api-332379661No ratings yet
- History - Unit Outline - Assessment 2Document14 pagesHistory - Unit Outline - Assessment 2api-332379661No ratings yet
- Summer 2017-2018 Assessment1Document10 pagesSummer 2017-2018 Assessment1api-332379661100% (1)
- Diversity Social Justice and Learning - Essay 1Document9 pagesDiversity Social Justice and Learning - Essay 1api-332379661No ratings yet
- Group ScriptDocument5 pagesGroup Scriptapi-332379661No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Analysis: Jessica HayterDocument24 pagesLesson Plan Analysis: Jessica Hayterapi-332379661No ratings yet
- Inclusive - Essay 1 FinalDocument10 pagesInclusive - Essay 1 Finalapi-332379661No ratings yet
- Selection: Suzaine Polancos Zaira Mae RafalDocument6 pagesSelection: Suzaine Polancos Zaira Mae RafalMarlene AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Tapak RPH Kelas Bercantum (P. Islam)Document1 pageTapak RPH Kelas Bercantum (P. Islam)AyieHfiyNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Project ProposalDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Project ProposalBoboy BerlsoNo ratings yet
- Bow - Community, Engagement, Solidarity, and Citizenship - 2nd QuarterDocument11 pagesBow - Community, Engagement, Solidarity, and Citizenship - 2nd QuarterCeeDyeyNo ratings yet
- S-DLP Direct VariationDocument4 pagesS-DLP Direct VariationChessa Mae PelongcoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Exam Dates 2019Document1 pageCambridge Exam Dates 2019Lesly NovalNo ratings yet
- Program of Studies and Instructional Procedures ANDREDocument13 pagesProgram of Studies and Instructional Procedures ANDREMichael CalesajrNo ratings yet
- IS574 01 Syllabus Fall 2016 0905Document6 pagesIS574 01 Syllabus Fall 2016 0905PUSHPU SINGHNo ratings yet
- Reading AssessmentDocument40 pagesReading AssessmentMay Tagalogon Villacora IINo ratings yet
- Smart and Active Students English Modul For SMP Students Grade Viii AdvertisementDocument19 pagesSmart and Active Students English Modul For SMP Students Grade Viii Advertisementptsp ptspNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Jepter Yolanderson LordeDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Jepter Yolanderson LordeJepter LordeNo ratings yet
- Timeline of Philippine Educational SystemDocument40 pagesTimeline of Philippine Educational Systemchat gazaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Reinforcement SkillDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Reinforcement SkillKadek RiskaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan TemplateDocument39 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan TemplateNicole Padilla100% (1)
- SESSION 1 GSC, My SEAL Class, and ME Student Ebook Guide 1Document6 pagesSESSION 1 GSC, My SEAL Class, and ME Student Ebook Guide 1Ika PinkNo ratings yet
- Pendidikan KesusateraanDocument15 pagesPendidikan KesusateraanramoneseNo ratings yet
- English Club Project ProposalDocument2 pagesEnglish Club Project ProposalJenan Escobedo50% (2)
- Advanced Stagecraft III IV SyllabusDocument2 pagesAdvanced Stagecraft III IV Syllabusapi-263186761100% (1)
- 786-Article Text-1601-1-10-20170722Document19 pages786-Article Text-1601-1-10-20170722EL MEHDI EL HAMDOUCHINo ratings yet
- The Dunn and Dunn Learning Style Model On InstructionDocument30 pagesThe Dunn and Dunn Learning Style Model On InstructionJulia Guan67% (3)
- Wawa National High School Grade Level G8 Rejoy O. Panganiban Learning Area EnglishDocument2 pagesWawa National High School Grade Level G8 Rejoy O. Panganiban Learning Area EnglishRej PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Shs Applied Research 2 Curriculum GuideDocument7 pagesShs Applied Research 2 Curriculum GuideMAUREEN BRILLANTES ENCABO (Lunduyan 4)No ratings yet
- IELTS General Reading SyllabusDocument2 pagesIELTS General Reading SyllabusRozitah Abu SamahNo ratings yet
- ESD Source BookDocument51 pagesESD Source BookchazunguzaNo ratings yet
- "Module Making": June 26, 2020 SLCB HallDocument29 pages"Module Making": June 26, 2020 SLCB HallJess ArceoNo ratings yet
- MAIN Building Earthquake Drill 1Document1 pageMAIN Building Earthquake Drill 1RechelNo ratings yet
- Homework 21st CenturyDocument7 pagesHomework 21st Centuryafmtjaifb100% (1)
- Duke, R. a., Simmons, A. L., & Cash, C. D. (2009). It's Not How Much; It's How Characteristics of Practice Behavior and Retention of Performance Skills. Journal of Research in Music Education, 56(4), 310-321.Document12 pagesDuke, R. a., Simmons, A. L., & Cash, C. D. (2009). It's Not How Much; It's How Characteristics of Practice Behavior and Retention of Performance Skills. Journal of Research in Music Education, 56(4), 310-321.goni56509No ratings yet
- Theories of First Language AcquisitionDocument2 pagesTheories of First Language AcquisitionYanina RojasNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis Worksheet For PDPDocument3 pagesSWOT Analysis Worksheet For PDPMin MinNo ratings yet