Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CT findings and complications of subdural and epidural haematomas
Uploaded by
Kay Bristol0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
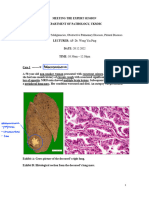
12 views3 pages1. Haematomas can be subdural or epidural based on their location and appearance on CT scans. Subdural haematomas follow the contour of the brain while epidural haematomas are lens shaped. Acute haematomas enhance on CT scans while chronic haematomas appear dark. They result from tears in bridging veins or middle meningeal artery ruptures. Presentation involves an initial brief loss of consciousness, followed by a lucid interval and then rapid deterioration within 6 hours.
2. The thyroid gland document discusses pre-surgical procedures like normalizing thyroid levels to avoid storms during surgery. It also describes potential steroid side effects and complications after thyroid surgery like haematoma,
Original Description:
surg
Original Title
Reading List
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Haematomas can be subdural or epidural based on their location and appearance on CT scans. Subdural haematomas follow the contour of the brain while epidural haematomas are lens shaped. Acute haematomas enhance on CT scans while chronic haematomas appear dark. They result from tears in bridging veins or middle meningeal artery ruptures. Presentation involves an initial brief loss of consciousness, followed by a lucid interval and then rapid deterioration within 6 hours.
2. The thyroid gland document discusses pre-surgical procedures like normalizing thyroid levels to avoid storms during surgery. It also describes potential steroid side effects and complications after thyroid surgery like haematoma,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesCT findings and complications of subdural and epidural haematomas
Uploaded by
Kay Bristol1. Haematomas can be subdural or epidural based on their location and appearance on CT scans. Subdural haematomas follow the contour of the brain while epidural haematomas are lens shaped. Acute haematomas enhance on CT scans while chronic haematomas appear dark. They result from tears in bridging veins or middle meningeal artery ruptures. Presentation involves an initial brief loss of consciousness, followed by a lucid interval and then rapid deterioration within 6 hours.
2. The thyroid gland document discusses pre-surgical procedures like normalizing thyroid levels to avoid storms during surgery. It also describes potential steroid side effects and complications after thyroid surgery like haematoma,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
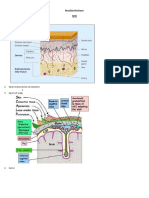
1.
Haematomas
Subdural Epidural
CT scan findings Follows brain contour Lens shaped
Doesn’t cross midline as its limited
by Falx cerebri
Crescent shaped
Acute Enhancing lesion – bright white
Chronic (>2weeks) Dark
Pathos Bridging veins torn Middle meningeal artery rupture
Presentation Brief LOC
Lucid interval (recovery)
Then rapid deterioration within 6hrs
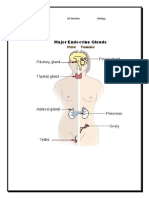
2. Thyroid gland
Pre-surgical procedures:
o Normalise thyroid levels (TSH) before surgery to avoid a thyroid storm - arrhythmias an
hyperthermia, exaggerated catecholamine response
o Direct laryngoscopy
To view vocal cords
Bilateral damage of both recurrent laryngeal nerves – stridor (both adducted)
Unilateral damage – hoarseness, mid abducted position
Steroids
o MOA
Anti- inflammatory agents
Prednisolone is a synthetic glucocorticoid and derivative of cortisol. It is the
active form of prednisone and used in patients with renal failure
Irreversibly bind with glucocorticoid receptors and modify gene transcriptions at
a nuclear level for inflammatory mediators including COX 2, cytokines
Regulation of gene suppression leads to systemic suppression of inflammation
and immune response.
o S.E.
Osteoporosis – can be irreversible
Immune system – suppression
Upper GI bleed
Cushings Syndrome – moon face (fluid retention in face), acne, constipation,
purple striae
Thinning of skin
Gluconeogenesis
Proteolysis
Lipolysis
Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal axis suppression
Sudden withdrawal causes Addison’s disease
Papillary – mostly <30years old; one O (Orphan Annie) and 2Ps (Psammoma bodies)
Scars – collar incision – previous thyroid surgeries
Posterior triangle – lymphadenopathy
Haematoma
o I believe patient should have the haematoma evacuated in theatre but
Calcium on ECG – hypo and hyper
Patient assessment post op
o Dyspnoea
o Get laryngoscope ready
o Intubation tray ready
o Call for help
o Assess airway – look listen feel
o Check evidence or signs of cyanosis
o Stridor
o Air entry
Complications
o Bilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve injury causing stridor – occurs only with total
thyroidectomy
o Haematoma – reactionary haemorrhage within 24hrs of operation
Remove all sutures: Layers to go through:
Skin
Subcutaneous tissue
Platsyma
Deep cervical fascia
o Hypocalcemia due to damage to parathyroid glands
Chovstek’s
Trousseau
o Tracheomalacia – tracheal rings collapse
Post-op management
o Radioiodine therapy
o Thyroxine – if total thyroidectomy was done
Multi-nodular goitre
o Signs of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism
o Investigations
o Diagnosis
You might also like
- Epidural Hematoma Diagnosis and ManagementDocument12 pagesEpidural Hematoma Diagnosis and ManagementNavid BabluNo ratings yet
- Presented by Andrew LamDocument20 pagesPresented by Andrew LamAndrew LamNo ratings yet
- AdrenalDocument9 pagesAdrenalNada MuchNo ratings yet
- Rheumatology SBIM Part 1 High Yield FactsDocument5 pagesRheumatology SBIM Part 1 High Yield FactsGousay AlkhazmariNo ratings yet
- Burn and Electrical Injury: Epidemiology, Prognosis, Pathophysiology, TreatmentDocument29 pagesBurn and Electrical Injury: Epidemiology, Prognosis, Pathophysiology, TreatmentDr_minskyNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint: Disorders of The Thyroid GlandDocument67 pagesPowerpoint: Disorders of The Thyroid Glandj.doe.hex_87100% (1)
- Adrenal Gland DisordersDocument24 pagesAdrenal Gland Disorderssimona mariana dutuNo ratings yet
- End of 4 Year OSCE - SurgeryDocument53 pagesEnd of 4 Year OSCE - SurgerySyed Irfan ArifNo ratings yet
- NCM 116: Neurologic Dysfunctions: Joyce Bernadette P. Andot - Anna Delle Nicole P. Aranding, BSN-IIIDocument46 pagesNCM 116: Neurologic Dysfunctions: Joyce Bernadette P. Andot - Anna Delle Nicole P. Aranding, BSN-IIIMercy Anne EcatNo ratings yet
- Mousab Kibreet Notes of Internal Medicine 2ed EditionDocument253 pagesMousab Kibreet Notes of Internal Medicine 2ed EditionAbdulltif AliNo ratings yet
- Postoperative Surgical Complications 2015Document26 pagesPostoperative Surgical Complications 2015AlaaGaballaNo ratings yet
- ROS, PE, PathoDocument8 pagesROS, PE, PathoMichelle Vera GabunNo ratings yet
- The pericardium is the sac surrounding the heart. In this CT scan, the breast cancer tumor has invaded and infiltrated the pericardiumDocument86 pagesThe pericardium is the sac surrounding the heart. In this CT scan, the breast cancer tumor has invaded and infiltrated the pericardiumNick Rajma100% (7)
- Messages in Surgical Approach To Endocrine Glands: Prof. Ayman Mismar 17/ 8/ 2019Document46 pagesMessages in Surgical Approach To Endocrine Glands: Prof. Ayman Mismar 17/ 8/ 2019AmyandNo ratings yet
- Tetanus-Dr. A.M IyagbaDocument32 pagesTetanus-Dr. A.M IyagbaDr. Amb. Monday ZaccheausNo ratings yet
- Lecture Thyroid GlandDocument54 pagesLecture Thyroid GlandMarinaNo ratings yet
- Patologi Endokrin 2016Document132 pagesPatologi Endokrin 2016agusNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Neck Swellings PDFDocument3 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Neck Swellings PDFSiddharth KatyalNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Fever SymposiumDocument52 pagesRheumatic Fever SymposiumNamratha MedaNo ratings yet
- Wilm's Tumor EtcDocument5 pagesWilm's Tumor EtcDanica BonNo ratings yet
- 8 P6 Respiratory Malignancies, Obstructive Pulmona_230219_231952Document10 pages8 P6 Respiratory Malignancies, Obstructive Pulmona_230219_231952a189192No ratings yet
- EOP AssessmentDocument13 pagesEOP AssessmentNuruliznie RosezaideeNo ratings yet
- PDF New NBME High-Yield Images CompleteDocument80 pagesPDF New NBME High-Yield Images CompleteHamid100% (2)
- Spinal TraumaDocument47 pagesSpinal TraumadeepaNo ratings yet
- Addison's Disease (Primary Adrenal Insufficiency)Document5 pagesAddison's Disease (Primary Adrenal Insufficiency)sunnnydayNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Carcinoma - DR - NishanthDocument88 pagesThyroid Carcinoma - DR - Nishanth57- Kalanidhi mNo ratings yet
- Gas Gangrene: DR Mohammed Akbar KhanDocument89 pagesGas Gangrene: DR Mohammed Akbar KhanAkbar KhanNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Glands Cushing's SyndromeDocument7 pagesAdrenal Glands Cushing's SyndromeSue SongNo ratings yet
- Q1.Flaccid Paresis: Diagnostical VariantsDocument47 pagesQ1.Flaccid Paresis: Diagnostical VariantsNelson OduorNo ratings yet
- Mock OSCE AnswersDocument7 pagesMock OSCE AnswersUsama SabeehNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Deseases: Na ShaoDocument38 pagesSpinal Cord Deseases: Na ShaoArvindhanNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Adrenal Glands.Document41 pagesPathology of Adrenal Glands.Sukma Eka PratiwiNo ratings yet
- L19 - Parasite and Fungal Infection of The BrainDocument16 pagesL19 - Parasite and Fungal Infection of The BrainGarry SoloanNo ratings yet
- UWorld Notes Step 2Document93 pagesUWorld Notes Step 2Vee Mend100% (1)
- rheumatic feverDocument36 pagesrheumatic fevertarakeeshbai1802No ratings yet
- Krok Key WordsDocument50 pagesKrok Key WordsKeller 0No ratings yet
- 0 Yazan Mini-OSCE Neck and ThyroidDocument37 pages0 Yazan Mini-OSCE Neck and Thyroidmoyasserayoub78No ratings yet
- Emergency Medicine: by DR Maimun ShikderDocument22 pagesEmergency Medicine: by DR Maimun ShikderFarwa RazaNo ratings yet
- Case 2Document41 pagesCase 2JUVIELY PREMACIONo ratings yet
- Title of Lecture: AY 2018-2019 1 Shifting Exam Instructor's Name (Name, MD, Other-Post-Nominals) Mm/Dd/YyyyDocument5 pagesTitle of Lecture: AY 2018-2019 1 Shifting Exam Instructor's Name (Name, MD, Other-Post-Nominals) Mm/Dd/YyyyMarielle MalabananNo ratings yet
- AdrenalpathologyDocument81 pagesAdrenalpathologyjoavchNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE DISORDERS (Autosaved)Document81 pagesENDOCRINE DISORDERS (Autosaved)Princewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- TUMORDocument13 pagesTUMORGabrielle Joyce TagalaNo ratings yet
- Infections of SpineDocument64 pagesInfections of Spineefancoolhand09100% (2)
- Pediatric Surgery: Burns - Lecture Monday 19/10Document10 pagesPediatric Surgery: Burns - Lecture Monday 19/10AmalNo ratings yet
- Revalida ReviewerDocument63 pagesRevalida ReviewerJam ChuaNo ratings yet
- Branchial Cleft Anomalies: Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument20 pagesBranchial Cleft Anomalies: Diagnosis and TreatmentMelita GanNo ratings yet
- K17. Parasit Yang Menyebabkan Infeksi OtakDocument71 pagesK17. Parasit Yang Menyebabkan Infeksi OtakSarahGustiaWoromboniNo ratings yet
- All Previous Essay SurgeryDocument170 pagesAll Previous Essay Surgeryalsfyabdullah2021No ratings yet
- MaternalDocument29 pagesMaternalJim XieNo ratings yet
- Neuroradiology: Dr. Dhanti Erma, SP - RadDocument64 pagesNeuroradiology: Dr. Dhanti Erma, SP - RadizzkibipNo ratings yet
- Pathoma Notes Part 1 - TPDocument50 pagesPathoma Notes Part 1 - TPluckyz89100% (1)
- Alpha-Fetoprotein & Acetylcholinesterase Can Be Measured As Surrogates of Neural TubeDocument23 pagesAlpha-Fetoprotein & Acetylcholinesterase Can Be Measured As Surrogates of Neural TubeAndresNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Stroke - 3B5Document77 pagesIschemic Stroke - 3B5Aireen Grace GilosNo ratings yet
- Kibreet With ImagesDocument260 pagesKibreet With Imagesعباس عبداللهNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland: Anatomy, Physiology, and DiseasesDocument21 pagesThyroid Gland: Anatomy, Physiology, and DiseasesMAH pedNo ratings yet
- Rheumatology SBIM Part 1Document5 pagesRheumatology SBIM Part 1Gousay AlkhazmariNo ratings yet
- Ortho VIVA TopicsDocument22 pagesOrtho VIVA TopicsSiti RaudahNo ratings yet
- Rheumatology MBBS ReviewDocument34 pagesRheumatology MBBS ReviewKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Disorder: Best Practices in Screening, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument51 pagesBipolar Disorder: Best Practices in Screening, Diagnosis and TreatmentKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Anatomical and Physiological Changes During PregnancyDocument25 pagesAnatomical and Physiological Changes During Pregnancyqaleeq100% (1)
- Religion Los Asesinos Del VaticanoDocument85 pagesReligion Los Asesinos Del VaticanoGerardoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Guidelines - Pocket Edition PDFDocument2 pagesDiabetes Guidelines - Pocket Edition PDFKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic/Nephritic Syndrome: AK. Soyibo Department of Medicine Review ClassDocument143 pagesNephrotic/Nephritic Syndrome: AK. Soyibo Department of Medicine Review ClassKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Management of Type 2 Diabetes and Its ChallengesDocument81 pagesManagement of Type 2 Diabetes and Its ChallengesKay BristolNo ratings yet
- OSCE Communication Skills ReviewDocument45 pagesOSCE Communication Skills ReviewKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Barton Review ClassDocument4 pagesBarton Review ClassKay BristolNo ratings yet
- OSCE Xray SummaryDocument3 pagesOSCE Xray SummaryKay BristolNo ratings yet
- HIV testing guide for GPsDocument1 pageHIV testing guide for GPsKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Thyroid Gland PDFDocument72 pagesDiseases of The Thyroid Gland PDFKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Thyroid Gland PDFDocument72 pagesDiseases of The Thyroid Gland PDFKay BristolNo ratings yet
- 80-87 2009Document4 pages80-87 2009Kay BristolNo ratings yet
- AV Fistula ExamDocument4 pagesAV Fistula ExamKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Haem Pres 2012 StefDocument12 pagesHaem Pres 2012 StefKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Describe How Nasopharyngeal Eradication Is Performed and Its Significance WRT To Meningococcal InfectionDocument2 pagesDescribe How Nasopharyngeal Eradication Is Performed and Its Significance WRT To Meningococcal InfectionKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Full Term Baby Is Noted To Have Cyanosis and ApneaDocument28 pagesFull Term Baby Is Noted To Have Cyanosis and ApneaKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet OtologyDocument3 pagesAnswer Sheet OtologyKay BristolNo ratings yet
- 2007 MAY JUNE 2007 CompleteDocument68 pages2007 MAY JUNE 2007 CompleteKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Full Term Baby Is Noted To Have Cyanosis and ApneaDocument28 pagesFull Term Baby Is Noted To Have Cyanosis and ApneaKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Anaes Clerkship StationsDocument1 pageAnaes Clerkship StationsKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Anaemia HXDocument2 pagesAnaemia HXKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Anaemia in PregnancyDocument5 pagesAnaemia in PregnancyKay BristolNo ratings yet
- 10 Reasons For Direct Reflex LossDocument1 page10 Reasons For Direct Reflex LossKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Anaes ReviewDocument2 pagesAnaes ReviewKay BristolNo ratings yet
- 2007 Nov 07 CompleteDocument62 pages2007 Nov 07 CompleteKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Drug PrescDocument1 pageDrug PrescKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Prepregnancy CounselDocument1 pagePrepregnancy CounselKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Janeway Lesions VsDocument4 pagesJaneway Lesions VsKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Surgical Treatment For BREAST CANCERDocument5 pagesSurgical Treatment For BREAST CANCERJericho James TopacioNo ratings yet
- EMS Drug DilutionDocument21 pagesEMS Drug Dilutionthompson godfreyNo ratings yet
- Acupuncture Has Been Used For Thousands of YearsDocument13 pagesAcupuncture Has Been Used For Thousands of Yearsoluwasegun DavidNo ratings yet
- All Models W ExplanationDocument63 pagesAll Models W Explanationpayal1407No ratings yet
- LevaquinDocument1 pageLevaquinKatie McPeek100% (1)
- Safety Data Sheet: Product Name: MOBILGEAR 600 XP 320Document11 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Product Name: MOBILGEAR 600 XP 320RupeshBabu SankariyaNo ratings yet
- Medication Error Reporting FormDocument2 pagesMedication Error Reporting Formahmad ganieNo ratings yet
- Firstaid ModuleDocument143 pagesFirstaid Moduleretni wulandariNo ratings yet
- Guide Sondes Logiq s8Document4 pagesGuide Sondes Logiq s8mahfoudNo ratings yet
- BLEEDING TIME AND CLOTTING TIME TESTSDocument30 pagesBLEEDING TIME AND CLOTTING TIME TESTScharutha gopalNo ratings yet
- You Can Grow Your IntelligenceDocument6 pagesYou Can Grow Your IntelligenceSoniaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Dental Anatomy: DR - Yad Raouf BDS, Efb, MrcsedDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Dental Anatomy: DR - Yad Raouf BDS, Efb, MrcsedRabarNo ratings yet
- AYR Patient Experience PresentationDocument29 pagesAYR Patient Experience Presentationaustin_tx6No ratings yet
- Range of Motion PresentationDocument27 pagesRange of Motion Presentationsathish100% (1)
- Anderson2008 Levofloxasin A ReviewDocument31 pagesAnderson2008 Levofloxasin A ReviewFazdrah AssyuaraNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat High AlertDocument2 pagesDaftar Obat High Alertayu aNo ratings yet
- Records of Patient Medical CheckupsDocument237 pagesRecords of Patient Medical CheckupsPanca WirawanNo ratings yet
- Cor Pulmonale PresentationDocument17 pagesCor Pulmonale Presentationandi reskifaisNo ratings yet
- Jan Marc Bulatao 10-Einstein BiologyDocument3 pagesJan Marc Bulatao 10-Einstein BiologyNomer SenadorNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Financing in IndiADocument86 pagesHealthcare Financing in IndiAGeet Sheil67% (3)
- CefepimeDocument2 pagesCefepimeMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- 11 16 16Document22 pages11 16 16WoodsNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic Agents: Conventional vs AtypicalDocument18 pagesAntipsychotic Agents: Conventional vs AtypicalmengakuNo ratings yet
- Aspirin: The widely used pain reliever and fever reducerDocument4 pagesAspirin: The widely used pain reliever and fever reducerEithel EithelNo ratings yet
- R - MN R - 1 Z: Mkg-Xixltechlib/1 T/06Document48 pagesR - MN R - 1 Z: Mkg-Xixltechlib/1 T/06Jhantu MazumderNo ratings yet
- Assessment Gestational AgeDocument61 pagesAssessment Gestational Ageleaslim100% (1)
- CaseDocument31 pagesCaseErnes PutraNo ratings yet
- Beximco Pharma FinalDocument14 pagesBeximco Pharma FinalAli Asgor Raton67% (3)
- 1 - General Indications and Contraindications - 2019 - Lumbar Interbody FusionsDocument12 pages1 - General Indications and Contraindications - 2019 - Lumbar Interbody FusionsSergiu MalinNo ratings yet
- Niyog-Niyogan - Quisqualis Indica Herbal Medicine-Health Benefits-Side Effects PDFDocument4 pagesNiyog-Niyogan - Quisqualis Indica Herbal Medicine-Health Benefits-Side Effects PDFJikka RodriguezNo ratings yet