Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vestibular Handout Final
Uploaded by
api-414170492Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vestibular Handout Final
Uploaded by
api-414170492Copyright:
Available Formats
Astronaut Training- Spinning Program
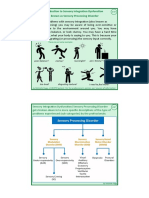
Sensory Integration What is the
Therapy Vestibular System?
Training the brain to process and
regulate sensory information Gives our body a
effectively to organize sense of balance, tells
us if we are moving,
movements of the body
what direction we are
Disorientation of the vestibular moving, and how fast
we are moving
system can help the brain Works together with
regulate new information and visual system and
how to learn to process it auditory system to
help engage learning
about the
environment and
Rotary Vestibular Input world around us
(Spinning) Balance, posture,
head control, and
gross & fine motor
Most powerful form of function, all develop
sensory input for the and continue to
brain to process function based on the
vestibular system
Helps the body self- Has an effect on fine
regulate and resets the motor skills, eye hand
coordination, visual
vestibular system motor skills, poor
15 minutes of spinning attention, balance,
can have a 6 hour core strength and
organizational skills
effect on the brain
A child who is constantly in
movement is likely to have Eye Movements (Nystagmus)
an under-responsive Side to side movements of the eyes after spinning in upright sitting & up and
vestibular system, causing down movements after side lying
them to seek more intense
stimulation (flipping,
Normal response: Eye movement will occur for ½ the amount of time that
crashing, hanging upside
spinning occurred (8 seconds of spinning= 4 seconds of eye movement)
down)
A child who is avoidant of If no nystagmus- vestibular system is under-responsive
intense movements is likely
to have an over-responsive Excessive nystagmus- vestibular system is over-responsive
vestibular system
Lorem Ipsum Issue | Date
Benefits of Spinning:
Use the spinning
protocol as prep work in
therapy, at school, or at
home to provide a
calming or alerting
sensation
Helps the brain learn to
regulate information and
generalize new learning
to other opportunities
Image: http://www.thinkingfountain.org/gallery/spinartgallery/spinartgallery.html
Astronaut Training Program
A child is spun on a swing or large “lazy susan” board in various directions (right side lying, left side lying,
and upright sitting), both clockwise and counterclockwise “Movement is key to all
The therapist spins the board at a certain number of revolutions per minute (average of 7x) with controlled,
rhythmic movements aspects of life and learning”
When the body is spinning, the eyes attempt to focus on objects to help orient the body
After the spins, the therapist stops and observes the eye movement of the child to see if there is a typical or
abnormal response
o See above. Typical movement= continuous eye movement side to side or up and down
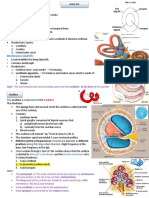
The fluid that is in our ear canal (part of our vestibular system) is responsible for telling us where our body
is in space. After spinning, the fluid is still in motion and trying to orient back to a still position.
Examples of Vestibular Avoiding Examples of Vestibular Seeking
Behaviors Behaviors
• Afraid of activities that involve movement
• Inability to sit still, always in constant
• Scared of playground equipment (i.e. stairs,
motion
merry go rounds)
• Can never seem to get enough movement
• Fearful of elevators
• Very impulsive, leading to unsafe risks
• Does not like being turned upside down or
and behaviors
being lifted off the ground
• Prefers to be upside down or hang off a
• Avoids stairs and may hold on to railing tightly
couch or chair
• May appear clumsy or have poor coordination
Dolor Sit Amet 2
You might also like
- Sensory Processing Presentation February 2014Document58 pagesSensory Processing Presentation February 2014Geovanny NuñezNo ratings yet
- Low Muscle Tone, Muscle Weakness or Poor Learning Strategies?Document5 pagesLow Muscle Tone, Muscle Weakness or Poor Learning Strategies?Ruztiqa Kasih Pramudya VardaniNo ratings yet
- Concept Evolution in Sensory Integration-A Proposed Nosology For DiagnosisDocument7 pagesConcept Evolution in Sensory Integration-A Proposed Nosology For Diagnosisapi-368273177No ratings yet
- Estrategias Conductuales ASDDocument66 pagesEstrategias Conductuales ASDSuperfixenNo ratings yet
- OT For AutismDocument2 pagesOT For AutismArianna Apreutesei3152eri8oawiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document30 pagesChapter 8Karla CarazoNo ratings yet
- Goal Attainment Scaling As A Measure of MeaningfulDocument7 pagesGoal Attainment Scaling As A Measure of MeaningfulCarlhos Waliithoo Muñoz JimenezNo ratings yet
- Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and The Somatic Nervous System PDFDocument4 pagesNeural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and The Somatic Nervous System PDFAmandaNo ratings yet
- Praktikum PX Sensoris: Dr. Nisa Karima, M.SCDocument18 pagesPraktikum PX Sensoris: Dr. Nisa Karima, M.SCCaesarioNo ratings yet
- 2.operational Guidelines DEIC RBSKDocument100 pages2.operational Guidelines DEIC RBSKChristopher Mala100% (1)
- Oral Motor ExaminationDocument2 pagesOral Motor ExaminationJershon YongNo ratings yet
- International Physical Activity Questionnaire - Short Form: Evaluation MeasuresDocument8 pagesInternational Physical Activity Questionnaire - Short Form: Evaluation MeasuresAyyNo ratings yet
- Guide To Functional Assessment ScreeningDocument2 pagesGuide To Functional Assessment ScreeningStudent StudentNo ratings yet
- Speech and Motor Speech Disorders and Intelligibility in Adolescents With Down SyndromeDocument26 pagesSpeech and Motor Speech Disorders and Intelligibility in Adolescents With Down SyndromeMaria Fernanda BahamondezNo ratings yet
- FxwsensorychildDocument31 pagesFxwsensorychildapi-534627445No ratings yet
- Down Syndrome Sensory Integration Vestibular Stimulation and Neurodevelopmental Therapy Approaches For ChildrenDocument23 pagesDown Syndrome Sensory Integration Vestibular Stimulation and Neurodevelopmental Therapy Approaches For Childrenshaima nasimNo ratings yet
- Process of Motor DevelopmentDocument33 pagesProcess of Motor Developmentmohitnet1327No ratings yet
- Perkins Activity and Resource Guide Chapter 2 - Foundations of Learning Language, Cognition, and Social Relationships: Second Edition: Revised and UpdatedFrom EverandPerkins Activity and Resource Guide Chapter 2 - Foundations of Learning Language, Cognition, and Social Relationships: Second Edition: Revised and UpdatedNo ratings yet
- Masgutova Neurosensorimotor Integration MethodDocument14 pagesMasgutova Neurosensorimotor Integration MethodristeacristiNo ratings yet
- Binocular Saccadic Dysfunction - a Precursor to Dyslexia?: N/AFrom EverandBinocular Saccadic Dysfunction - a Precursor to Dyslexia?: N/ANo ratings yet
- Ants and Syns Sentence Maze 2Document1 pageAnts and Syns Sentence Maze 2Ann KarapNo ratings yet
- Paper - Sensory Processing in AutismDocument15 pagesPaper - Sensory Processing in Autismapi-258682603100% (1)
- Evaluation of MealSense A Sensory Integration-Based Feeding Support Program For ParentsDocument7 pagesEvaluation of MealSense A Sensory Integration-Based Feeding Support Program For ParentsLauraNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Tactile Defensiveness and Tactile Discrimination On In-Hand ManipulationDocument8 pagesThe Effects of Tactile Defensiveness and Tactile Discrimination On In-Hand ManipulationNuriaNo ratings yet
- Supporting Children To Participate Successfully in Everyday Life Using Sensory Processing KnowledgeDocument19 pagesSupporting Children To Participate Successfully in Everyday Life Using Sensory Processing Knowledgeapi-26018051100% (1)
- Sensory Processing Disorder ChecklistDocument12 pagesSensory Processing Disorder ChecklistMadison CurleyNo ratings yet
- Cap 1 Sensory Integration Theory and PracticeDocument33 pagesCap 1 Sensory Integration Theory and PracticeLuz Dianeth ZapataNo ratings yet
- Supporting Therapy in The Classroom Strategies For OccupationalDocument70 pagesSupporting Therapy in The Classroom Strategies For Occupationalapi-451269263No ratings yet
- Evidence Based in Practise - CPLOLDocument41 pagesEvidence Based in Practise - CPLOLInês SofiaNo ratings yet
- AUT - Unit3.4 Sensory Self-RegulationDocument31 pagesAUT - Unit3.4 Sensory Self-RegulationMai Mahmoud100% (1)
- Observations Based On SI TheoryDocument10 pagesObservations Based On SI Theoryhelenzhang888No ratings yet
- Introduction To Sensory Integration Dysfunction / Sensory Processing DisorderDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Sensory Integration Dysfunction / Sensory Processing DisorderMichelle FNo ratings yet
- Occupational Therapists Prefer Combining PDFDocument12 pagesOccupational Therapists Prefer Combining PDFSuperfixenNo ratings yet
- NATURE Is The ULTIMATE SENSORY EXPERIENCE: A Pediatric Occupational Therapist Makes The Case For Nature Therapy: The New Nature MovementDocument5 pagesNATURE Is The ULTIMATE SENSORY EXPERIENCE: A Pediatric Occupational Therapist Makes The Case For Nature Therapy: The New Nature MovementSimonetta MangioneNo ratings yet
- Reflex DR Arpana HazarikaDocument126 pagesReflex DR Arpana HazarikaDorin Pathak100% (1)
- Finger To NoseDocument1 pageFinger To NoseAridhotulHaqiyahNo ratings yet
- The Efficacy of Sensory Integration Therapy On Children With Asperger's Syndrome and Pdd-NosDocument278 pagesThe Efficacy of Sensory Integration Therapy On Children With Asperger's Syndrome and Pdd-NosAbu FayyadhNo ratings yet
- Sensory Integration Theory - InserviceDocument10 pagesSensory Integration Theory - Inserviceapi-238703581No ratings yet
- Oral Motor Development in DS Baldwin and Rosebush October 2015Document55 pagesOral Motor Development in DS Baldwin and Rosebush October 2015Tânia DiasNo ratings yet
- Psychological Aspects of Dysphagia PresentationDocument28 pagesPsychological Aspects of Dysphagia Presentationjenmae2028No ratings yet
- Chapter 16: Application of Motor Control and Motor LearningDocument8 pagesChapter 16: Application of Motor Control and Motor LearningJireh Chambers100% (1)
- Working With Children With Atypical Tone 07Document37 pagesWorking With Children With Atypical Tone 07Martha FrankNo ratings yet
- Pre-Post OT InterventionDocument16 pagesPre-Post OT InterventionIdanerlisNo ratings yet
- 14.understanding Primitive Reflexes and Their Role in Growth and DevelopmentDocument6 pages14.understanding Primitive Reflexes and Their Role in Growth and DevelopmentGeotamNo ratings yet
- Sensory, Motor & Integrative SystemsDocument50 pagesSensory, Motor & Integrative SystemsDerón Asbery HolmesNo ratings yet
- A Field Guide to Sensory Motor Integration: The Foundation for LearningFrom EverandA Field Guide to Sensory Motor Integration: The Foundation for LearningNo ratings yet
- Sensory DevelopmentDocument1 pageSensory DevelopmentShiella Mae TeañoNo ratings yet
- 11 17 17 Treatment PlanDocument7 pages11 17 17 Treatment Planapi-435469413No ratings yet
- 275-Higher Cortical Functions Bedside Examination - Yuttachai LikitjaroenDocument46 pages275-Higher Cortical Functions Bedside Examination - Yuttachai LikitjaroennavneetNo ratings yet
- Sensory DefensivenessDocument4 pagesSensory DefensivenessKarla CarazoNo ratings yet
- Ot Pre-Referral Form: Intervention Strategies: Poor Posture/ Falls Out of Chair/ Slumps Significantly (All Ages)Document15 pagesOt Pre-Referral Form: Intervention Strategies: Poor Posture/ Falls Out of Chair/ Slumps Significantly (All Ages)maria vasquezNo ratings yet
- Ota Watertown Si Clinical Assessment WorksheetDocument4 pagesOta Watertown Si Clinical Assessment WorksheetPaulinaNo ratings yet
- Case Report of AbdullahDocument7 pagesCase Report of AbdullahNosheen RamzanNo ratings yet
- Issue 4 Sensory WORDDocument19 pagesIssue 4 Sensory WORDRabe AllahNo ratings yet
- Fidgets Are ToolsDocument4 pagesFidgets Are Toolsapi-660820048No ratings yet
- Adhd Dan Reflex PrimitifDocument5 pagesAdhd Dan Reflex PrimitifBangkit KunNo ratings yet
- Left or Right Brain TestDocument5 pagesLeft or Right Brain TestHadi azfar channelNo ratings yet
- Neural Foundations of Ayres Sensory Integration®Document15 pagesNeural Foundations of Ayres Sensory Integration®Muskaan KhannaNo ratings yet
- A Sensory-Motor IntegrationDocument389 pagesA Sensory-Motor IntegrationXlian Myzter YosaNo ratings yet
- MCQ 2Document12 pagesMCQ 2Zahid Mahmood RaahatNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Examination and Classification of NystagmusDocument7 pagesApproach To The Examination and Classification of NystagmusAlexandros GidarakosNo ratings yet
- Assessment: Vestibular Testing Techniques in Adults and ChildrenDocument13 pagesAssessment: Vestibular Testing Techniques in Adults and ChildrenpuputNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Sensory Activities On Correct Responding For Children With AutismDocument14 pagesThe Effect of Sensory Activities On Correct Responding For Children With Autismapi-26018051No ratings yet
- Case Report - VERTIGODocument71 pagesCase Report - VERTIGOjanetaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Part 3 - Work Environment Design - Vestibular SenseDocument42 pagesTopic 2 - Part 3 - Work Environment Design - Vestibular SenseCamille AmparoNo ratings yet
- Sensory Processing: 100 Facts AboutDocument8 pagesSensory Processing: 100 Facts AboutHusaini100% (2)
- The MedTrak ProgramDocument11 pagesThe MedTrak ProgramInBalanceNo ratings yet
- NystagmusDocument14 pagesNystagmusJefferson CaesarioNo ratings yet
- Referat NystagmusDocument44 pagesReferat NystagmusNadira Danata100% (1)
- Visual Perceptual SkillsDocument200 pagesVisual Perceptual Skillsriddajeen100% (1)
- Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) History, Pathophysiology, Office Treatment and Future DirectionsDocument13 pagesBenign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) History, Pathophysiology, Office Treatment and Future DirectionsAngelo DonihoNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Hearing and Balance: Departemen Fisiologi FK UsuDocument46 pagesPhysiology of Hearing and Balance: Departemen Fisiologi FK UsuSyarifah FauziahNo ratings yet
- Natures Instruments Catalogue - Digital Version-1Document110 pagesNatures Instruments Catalogue - Digital Version-1LeslieNo ratings yet
- Modelling Motion Sickness and Subjective Vertical Mismatch Detailed For Vertical MotionsDocument6 pagesModelling Motion Sickness and Subjective Vertical Mismatch Detailed For Vertical MotionsVu MinhNo ratings yet
- NIH Stroke Scale Neurological Assessment Flow SheetDocument16 pagesNIH Stroke Scale Neurological Assessment Flow SheetSarah AmbidaNo ratings yet
- Revised Vestibular System 1Document7 pagesRevised Vestibular System 1KevinYonathanNo ratings yet
- Si Gede Teguh Surya Negara 011.06.0043: 28/08/2017 1 FK Unizar Mataram 2017Document50 pagesSi Gede Teguh Surya Negara 011.06.0043: 28/08/2017 1 FK Unizar Mataram 2017'aac' JujuuNo ratings yet
- Vestibular Testing.5Document18 pagesVestibular Testing.5Luiz Gabriel Reis MattosoNo ratings yet
- Dizziness and VertigoDocument27 pagesDizziness and VertigoPutriAyuWidyastutiRNo ratings yet
- Vestibular Exercise Program To Overcome DizzinessDocument4 pagesVestibular Exercise Program To Overcome DizzinessAbidin ZeinNo ratings yet
- Human Balance SystemDocument6 pagesHuman Balance SystemPutri DianaNo ratings yet
- Vertigo: DR Bala Pradeep Boyidapu Post Graduate Resident Department of Neurology GMKMCH, SalemDocument42 pagesVertigo: DR Bala Pradeep Boyidapu Post Graduate Resident Department of Neurology GMKMCH, SalemBALA PRADEEP BOYIDAPUNo ratings yet
- Pusher Syndrome A Frequent But Little-Known Disturbance of Body Orientation PerceptionDocument11 pagesPusher Syndrome A Frequent But Little-Known Disturbance of Body Orientation PerceptionKlgo Alex AyalaNo ratings yet
- 24 Inner Ear Anatomy, Emberyology, Drugs Ototoxicity (Done)Document24 pages24 Inner Ear Anatomy, Emberyology, Drugs Ototoxicity (Done)osamaeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Vestibular Organ and NeuralDocument56 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Vestibular Organ and Neuralvineet_ent100% (1)
- The Evolutionary Basis of Strabismus and Nystagmus in ChildrenDocument244 pagesThe Evolutionary Basis of Strabismus and Nystagmus in ChildrenComan MihaelaNo ratings yet
- Verbo-Tonal Method For Rehabilitating People With Communication ProblemsDocument53 pagesVerbo-Tonal Method For Rehabilitating People With Communication ProblemsTom Fletcher100% (1)
- Furman 2013 Vestibular MigraineDocument10 pagesFurman 2013 Vestibular MigraineJuan Hernández GarcíaNo ratings yet
- AICA Vs SCA Vs PICADocument9 pagesAICA Vs SCA Vs PICAFadilla PermataNo ratings yet