Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grade 9: Unit B: Matter and Chemical Change
Uploaded by
api-253059746Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Grade 9: Unit B: Matter and Chemical Change
Uploaded by
api-253059746Copyright:
Available Formats
Grade 9 Unit B: Matter and Chemical Change
Examining Matter
Matter: Any substance that takes up space. Matter can be solid, liquid or gas.
Particle Theory of Matter
• Matter is made up of tiny particles.
• Every type of pure matter (not mixed with anything) is made of its own
unique particles.
• The particles in matter are attracted to one another and stick together.
• The particles in matter are always moving (even in solids).
• When matter is warm, the particles move faster and when matter is cold,
the particles move more slowly.
All matter is made of very tiny particles called atoms. When atoms of all the same type
are joined together, they are called elements. Sometimes atoms of different elements
are joined together to make molecules.
Atoms
Elements – examples: oxygen (O), carbon (C), nitrogen (N), hydrogen
(H)
Molecules – examples: CO2 (carbon dioxide)
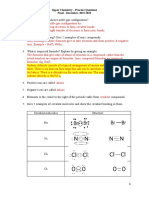
1. Work with a partner to write definitions in your own words for the terms atom,
element and molecule.
Knowledge and Employability Studio
Science Grade 9 Unit B: Matter and Chemical Change
©Alberta Education, Alberta, Canada, June 2007 (www.LearnAlberta.ca) Examining Matter 1/7
Compounds: Molecules that are made of different elements that are stuck
together.
2. With a partner or group, describe the differences between elements and
compounds. Summarize these differences in the chart below.
ELEMENTS COMPOUNDS
Knowledge and Employability Studio
Science Grade 9 Unit B: Matter and Chemical Change
©Alberta Education, Alberta, Canada, June 2007 (www.LearnAlberta.ca) Examining Matter 2/7
Chemical Properties of Matter
The properties of a substance are the characteristics that make it unique.
Matter has chemical and physical properties.
Chemical properties of matter include:
• the atoms or molecules that make up a substance
• how a substance reacts to temperature with other
substances, such as water, oil, oxygen, acids and
bases.
Examples:
• copper (a metallic solid) exposed to air turns green over time
• sulphur (a solid) combined with pure oxygen (a gas) forms sulphur dioxide (S20)
(a colourless poisonous gas)
• hydrogen and sulphur combine to make hydrogen sulphide (H2S), a poisonous
gas in sour gas wells that smells like rotten eggs.
3. Use a variety of objects to illustrate the structure of atoms and molecules. Draw a
diagram of a molecule in the space below.
Knowledge and Employability Studio
Science Grade 9 Unit B: Matter and Chemical Change
©Alberta Education, Alberta, Canada, June 2007 (www.LearnAlberta.ca) Examining Matter 3/7
Physical Properties of Matter
The chart below lists qualitative and quantitative physical properties
of matter.
Examples of physical properties of matter
Qualitative Example Quantitative Example
Tin is silvery in Melting Ice melts at 0°C.
Colour
colour and has a temperature
(shade, lustre) shiny lustre.
Texture Chlorine Boiling temperature Water boils at
(household bleach) 100°C.
(how it feels)
is slippery.
Cocoa (raw Density Sand can be
Taste
chocolate) is bitter. packed tightly or
(salty, sweet, bitter) loosely in a bucket.
Smell Sulphur smells like Viscosity Oil gets thicker and
(sweet, bitter, sour) rotten eggs. flows more slowly
when it is cold.
Malleability Gold can be Heat conductivity An iron pan gets
hammered into thin hot when placed on
(how easily it can
sheets and a hot stove
be reshaped)
different shapes. element.
Knowledge and Employability Studio
Science Grade 9 Unit B: Matter and Chemical Change
©Alberta Education, Alberta, Canada, June 2007 (www.LearnAlberta.ca) Examining Matter 4/7
4. Review Safety in Science before you begin the following activity. Obtain a sample of
a safe, non-toxic solid or liquid substance used everyday at home, school or in the
workplace. Complete the chart for the substance. Compare charts with classmates.
Substance:
Physical properties
Qualitative Quantitative
Colour Melting point
Texture Boiling point
Taste Density
Smell Viscosity
Malleability Heat conductivity
List other information about the substance that you know or observed.
Knowledge and Employability Studio
Science Grade 9 Unit B: Matter and Chemical Change
©Alberta Education, Alberta, Canada, June 2007 (www.LearnAlberta.ca) Examining Matter 5/7
5. With a group, examine and investigate the following materials
and complete the chart below.
Material Is it a pure substance, How do you know this?
solution or
mechanical mixture?
carbon
table salt
salt water
fertilizer
motor oil
plastic
fruit-flavoured
drink
iron
Knowledge and Employability Studio
Science Grade 9 Unit B: Matter and Chemical Change
©Alberta Education, Alberta, Canada, June 2007 (www.LearnAlberta.ca) Examining Matter 6/7
6. With a group, examine and investigate the following
materials and fill out the chart below.
Material Is it a metal or How do you know this?
non-metal?
soda can
table salt
pencil
gold chain
frying pan
plastic cup
carrot
magnet
Knowledge and Employability Studio
Science Grade 9 Unit B: Matter and Chemical Change
©Alberta Education, Alberta, Canada, June 2007 (www.LearnAlberta.ca) Examining Matter 7/7
You might also like
- Chem. Lesson 1Document31 pagesChem. Lesson 1Ashlee Talento100% (1)
- Lesson 1.2 Properties of MatterDocument48 pagesLesson 1.2 Properties of MatterRacelle KayeNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Describing MatterDocument16 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Describing MatterJohn Paul Recopuerto ParachaNo ratings yet
- Observing Matter (WWW - Irlanguage.com)Document10 pagesObserving Matter (WWW - Irlanguage.com)aminNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter: An In-Depth Look at Physical and Chemical TraitsDocument36 pagesProperties of Matter: An In-Depth Look at Physical and Chemical TraitsMcubedd StemNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter RevisedDocument36 pagesProperties of Matter RevisedPierre Joseph HareNo ratings yet
- Junior High Science ClassDocument10 pagesJunior High Science ClassCherry May DurezaNo ratings yet
- Gen - Chem 1-Week 1 and 2Document13 pagesGen - Chem 1-Week 1 and 2Mishal NoroñaNo ratings yet
- Matter and its PropertiesDocument31 pagesMatter and its PropertiesKate IgtosNo ratings yet
- Cot 1Document57 pagesCot 1Richard TalameraNo ratings yet
- Diversity of Materials in The EnvironmentDocument19 pagesDiversity of Materials in The EnvironmentMarjorie TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter and Changes in MatterDocument55 pagesProperties of Matter and Changes in MatterPrinces April ArrezaNo ratings yet
- TEMPLATE - AS - PROPERTIES of MATTERDocument4 pagesTEMPLATE - AS - PROPERTIES of MATTERJana BantasNo ratings yet
- Prep For Quiz 2: ChemistryDocument13 pagesPrep For Quiz 2: ChemistryAndreLiengNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Chemistry Notes BDocument31 pagesScience 9 Chemistry Notes BJoe HarringtonNo ratings yet
- Understanding States of MatterDocument6 pagesUnderstanding States of MatterJenjen GammadNo ratings yet
- Revision Final Bio ChemDocument21 pagesRevision Final Bio ChemWormaggedonNo ratings yet
- GeneralChemistry1 - Quarter1 - Week 1-4Document81 pagesGeneralChemistry1 - Quarter1 - Week 1-4Aze Mamalayan100% (1)
- Module 1 Lesson 1Document60 pagesModule 1 Lesson 107 JAVIER LLYOD GENELSON B.No ratings yet
- Properties of Matter and its Various FormsDocument77 pagesProperties of Matter and its Various FormsMika CossidNo ratings yet
- Science8 Q3 W1-8Document30 pagesScience8 Q3 W1-8Maricar agawa GuntanNo ratings yet
- The Properties of MatterDocument22 pagesThe Properties of MatterLENON ANSANONo ratings yet
- 04 Unit 2. Matter and EnergyDocument29 pages04 Unit 2. Matter and EnergyKevin Mark IlaganNo ratings yet
- Competency 10Document20 pagesCompetency 10Charis RebanalNo ratings yet
- Water Displacement MatterDocument20 pagesWater Displacement MatterJeannie Rose M. Sarabia IIINo ratings yet
- Properties of MatterDocument34 pagesProperties of MatterMirza Adnan100% (2)
- Chemistry 2nd Topic BridgingDocument24 pagesChemistry 2nd Topic BridgingRhean ParbaNo ratings yet
- Upper Final 1 Practice Questions - December 2022 - Ans KeyDocument10 pagesUpper Final 1 Practice Questions - December 2022 - Ans KeyNgô Thúy ViNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Module-1Document13 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Module-1CO, Kathleen - STEM-11 ANo ratings yet
- Elizabeth Seton School: Third Term General Chemistry 2 Mini-Laboratory Activity No. 1Document4 pagesElizabeth Seton School: Third Term General Chemistry 2 Mini-Laboratory Activity No. 1Elisa Medina AlbinoNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Chapt.1Document45 pagesGen Chem Chapt.1Dave Cercado BugadorNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter RevisedDocument36 pagesProperties of Matter RevisedSachi EmiNo ratings yet
- 040 Physical & Chemical Properties 13sDocument13 pages040 Physical & Chemical Properties 13sMSKCNo ratings yet
- (CHEM) UNIT 1. Lesson 2. Properties & Characteristics of MatterDocument7 pages(CHEM) UNIT 1. Lesson 2. Properties & Characteristics of MatterTrishia Mae Gregorio BelenNo ratings yet
- TEMPLATE - AS - PROPERTIES of MATTERDocument4 pagesTEMPLATE - AS - PROPERTIES of MATTERJana BantasNo ratings yet
- Chem & Physical Properties & ChangesDocument20 pagesChem & Physical Properties & Changesjulio ahleNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Matter and EnergyDocument8 pagesUnit 2 Matter and EnergyAngelika Barte MulletaNo ratings yet
- Module in Properties, Changes, and Classification of MatterDocument5 pagesModule in Properties, Changes, and Classification of MatterRaymart MesugaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Physical and Chemical Change PowerpointDocument7 pagesGrade 9 Physical and Chemical Change Powerpointapi-19727066No ratings yet
- MATTER AND ITS PROPERTIESDocument57 pagesMATTER AND ITS PROPERTIESArvin Corpuz DiamanteNo ratings yet
- Separating Mixtures and Pure SubstancesDocument9 pagesSeparating Mixtures and Pure SubstancesMaria BachilleratoNo ratings yet
- Interactive Textbook1 2 Pproperties of MatterDocument7 pagesInteractive Textbook1 2 Pproperties of Matterapi-240094705No ratings yet
- Unit 3: Classifying Matter and Energy ChangesDocument77 pagesUnit 3: Classifying Matter and Energy ChangeskironmosNo ratings yet
- Types and Properties of SolidsDocument12 pagesTypes and Properties of SolidsJayzl Lastrella CastanedaNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its Properties: A Chemistry GuideDocument15 pagesMatter and Its Properties: A Chemistry GuideAnele CatayasNo ratings yet
- Matter Around Me: SC1 - Teaching Science in ElementaryDocument27 pagesMatter Around Me: SC1 - Teaching Science in ElementaryYanna Marie Porlucas Macaraeg50% (2)
- Sorting Materials Into Groups Class 6 Extra Questions Short Answer Typ1 2Document7 pagesSorting Materials Into Groups Class 6 Extra Questions Short Answer Typ1 2Giridhar RagavasimhanNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 3Document12 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 3shareeandradaNo ratings yet
- St. Francis School, Indirapuram Science Ch. 4 Sorting Materials Into Groups Worksheet I SolutionsDocument5 pagesSt. Francis School, Indirapuram Science Ch. 4 Sorting Materials Into Groups Worksheet I Solutionssakshi singhNo ratings yet
- Building Blocks of MatterDocument20 pagesBuilding Blocks of MatterTi NeNo ratings yet
- 01 - Matter in Our SurroundingDocument20 pages01 - Matter in Our SurroundingSudha SinghNo ratings yet
- Communicate The DataDocument4 pagesCommunicate The DataMary Grace LlorenteNo ratings yet
- Chem HandoutDocument11 pagesChem HandoutEllen Mae PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Week 11 Properties of Matter NotesDocument70 pagesGrade 8 Week 11 Properties of Matter NotesmkraemerNo ratings yet
- Sept 13, 2023 - Mint & Olive - DLPDocument3 pagesSept 13, 2023 - Mint & Olive - DLPdaffodil joy eresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MatterDocument8 pagesChapter 2 MatterShirly Mae GumaruNo ratings yet
- Free Science Education ResourcesDocument18 pagesFree Science Education ResourcesNestor Langit GaladoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 16: Crystal Art: - Description - MaterialsDocument13 pagesLESSON 16: Crystal Art: - Description - Materialsrose belle garciaNo ratings yet
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Power CalculationsDocument1 pagePower Calculationsapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Sleep Infographic EngDocument1 pageSleep Infographic Engapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Cool-Down CardsDocument10 pagesCool-Down Cardsapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Alphabet-Activity-Cards EasDocument26 pagesAlphabet-Activity-Cards Easapi-253059746No ratings yet
- gr7 HealthDocument55 pagesgr7 Healthapi-253059746No ratings yet
- ADocument1 pageAapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Cool-Down CardsDocument10 pagesCool-Down Cardsapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Grade 6 - Specific Outcomes: Can Affect Human Development From Conception Through BirthDocument49 pagesGrade 6 - Specific Outcomes: Can Affect Human Development From Conception Through Birthapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Alphabet-Activity-Cards EasDocument26 pagesAlphabet-Activity-Cards Easapi-253059746No ratings yet
- A - Z Spelling WorkoutDocument3 pagesA - Z Spelling Workoutapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Charades Relay and Fundamental Movement Skills PosterDocument7 pagesCharades Relay and Fundamental Movement Skills Posterapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Brain Breaks 1Document15 pagesBrain Breaks 1api-253059746No ratings yet
- Hawksbill BlueprintsDocument5 pagesHawksbill Blueprintsapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Grade 9: Unit E: Space ExplorationDocument4 pagesGrade 9: Unit E: Space Explorationapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Or CF Sci gr09 Ue 02 SpacetechDocument2 pagesOr CF Sci gr09 Ue 02 Spacetechapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Or CF Sci gr09 Ub 06 AssessDocument3 pagesOr CF Sci gr09 Ub 06 Assessapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Or CF Sci gr09 Ue 03 SpaceissuesDocument2 pagesOr CF Sci gr09 Ue 03 Spaceissuesapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Or CF Sci gr09 Ub 05 EquationsDocument3 pagesOr CF Sci gr09 Ub 05 Equationsapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Or CF Sci gr09 Ub 04 NatureDocument3 pagesOr CF Sci gr09 Ub 04 Natureapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Or CF Sci gr09 Ua 04 HumanDocument2 pagesOr CF Sci gr09 Ua 04 Humanapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Grade 9: Unit B: Matter and Chemical ChangeDocument4 pagesGrade 9: Unit B: Matter and Chemical Changeapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Or CF Sci gr09 Ua 02 ReprodDocument4 pagesOr CF Sci gr09 Ua 02 Reprodapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Or CF Sci gr09 Ub 01 WhmisDocument1 pageOr CF Sci gr09 Ub 01 Whmisapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Or CF Sci gr09 Ua 03 NaturalDocument3 pagesOr CF Sci gr09 Ua 03 Naturalapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Or CF Sci gr09 Ud 04 ImpactDocument5 pagesOr CF Sci gr09 Ud 04 Impactapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Or CF Sci gr09 Ua 05 AssessDocument3 pagesOr CF Sci gr09 Ua 05 Assessapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Or CF Sci gr09 Ua 01 ExaminDocument5 pagesOr CF Sci gr09 Ua 01 Examinapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Or CF Sci gr09 Ud 05 AssessDocument3 pagesOr CF Sci gr09 Ud 05 Assessapi-253059746No ratings yet
- Safari - 6 Sep 2022 at 2:40 PMDocument1 pageSafari - 6 Sep 2022 at 2:40 PMTerrence AzariaNo ratings yet
- SEM 1, 2 Syllabus KJSCEDocument53 pagesSEM 1, 2 Syllabus KJSCEKeyur KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 9 Mechanical Properties of SolidsDocument19 pagesChapter - 9 Mechanical Properties of SolidsTilahun ArfichoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of The Elements (2nd Edition)Document14 pagesChemistry of The Elements (2nd Edition)mycomiccityNo ratings yet
- Granta EduPack ReleaseingDocument8 pagesGranta EduPack ReleaseingAshwary Sheel Wali Research Scholar, Dept of Mech Engg., IIT (BHU)No ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Compounding CalculationsDocument6 pagesPharmaceutical Compounding Calculationsklr mnsdNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument1 pageAssignmentKen LaguiabNo ratings yet
- KIDDE PQS 2020 - PRE - E - IND - IG - PresentationDocument281 pagesKIDDE PQS 2020 - PRE - E - IND - IG - PresentationfranciscoNo ratings yet
- Astm d86Document28 pagesAstm d86Brenda Garcia AcostaNo ratings yet
- US Crete HF - 2020Document2 pagesUS Crete HF - 2020kemdoNo ratings yet
- 05 S and P Block Elements Que. Final E 1Document15 pages05 S and P Block Elements Que. Final E 1gnkstarNo ratings yet
- Recommendations for Lubricating Oil SelectionDocument7 pagesRecommendations for Lubricating Oil SelectionSergei KurpishNo ratings yet
- 08ch1013 Anik Roy Iit KGP Mckinsey ResumeDocument2 pages08ch1013 Anik Roy Iit KGP Mckinsey ResumeAnik RoyNo ratings yet
- Síntesis de Alcohol VainillílicoDocument6 pagesSíntesis de Alcohol VainillílicoYago L100% (1)
- Free Damped VibrationsDocument7 pagesFree Damped VibrationsYob YnnosNo ratings yet
- LubesDocument2 pagesLubesPeyman SazandehchiNo ratings yet
- Cables: Compensating and ExtensionDocument32 pagesCables: Compensating and ExtensionAyadi_AymanNo ratings yet
- Determination of Reducing SugarsDocument5 pagesDetermination of Reducing SugarsrheamaeNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Dr. Syed Sibte Asghar AbidiDocument5 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Dr. Syed Sibte Asghar AbidiDesh BhaktNo ratings yet
- 1mrk507004-Uen B en Radhl User S GuideDocument40 pages1mrk507004-Uen B en Radhl User S Guideali surfNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity ChartDocument2 pagesElectronegativity ChartDana FransenNo ratings yet
- Produced Water OverviewDocument86 pagesProduced Water Overviewsigit cahyonoNo ratings yet
- Absolute Dating Methods ExplainedDocument20 pagesAbsolute Dating Methods ExplainedJorilyn LlandaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes .Document6 pagesEnzymes .Nathan SsekamatteNo ratings yet
- B Som and FM Lab ManualDocument101 pagesB Som and FM Lab ManualGANESH GOMATHINo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1: Dynamic Physics Problems/TITLEDocument3 pagesProblem Set 1: Dynamic Physics Problems/TITLEpeneNo ratings yet
- Resins For Battery ManufactureDocument4 pagesResins For Battery ManufacturecmscostaNo ratings yet
- EMPC2015 - Wire Bonding of Au-Coated Ag Wire Bondwire Properties, Bondability andDocument4 pagesEMPC2015 - Wire Bonding of Au-Coated Ag Wire Bondwire Properties, Bondability andChong Leong GanNo ratings yet
- Concrete Aggregates: Standard Specification ForDocument15 pagesConcrete Aggregates: Standard Specification ForHasanalmahmudNo ratings yet