Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cvs (Diuretics)
Uploaded by
CatOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cvs (Diuretics)
Uploaded by
CatCopyright:
Available Formats
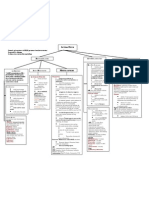
CVS: Diuretics
Segments 3. L O O P D I U R E T I C S ( h i g h _ - c e i l i n g
diuretics)
SEGMENT FUNCTION TRANSPORTER DRUGS
‣ Furosemide
Proximal Reabsorpti
Convoluted on of Na+ /
Na/H (NHE3), Carbonic ‣ Torsemide
carbonic anhydrase
tubule K+/ Ca2+/ & ‣ Ethacrynic acid
anhydrase inhibitors
(PCT) Mg2+
4. K+-SPARING DIURETICS
Active
reabsorption ‣ Amiloride
Thick
of Na+ /
ascending ‣ Triamterene
K+/ Cl+; Na/ K/ 2Cl Loop
limb of
henge
Secondary (NKCC2) diuretics ‣ Spironolactone
absorption
(TAL)
of Ca2+ &
5. OSMOTIC DIURETICS
Mg2+ ‣ Mannitol IV
Distal Active 6. VASOPRESSIN ANTAGONITS
Convoluted reabsorption Na/Cl
tubule of Na+ / (NCC)
Thiazides ‣ Conivaptan
(DCT) Ca2+/ Cl+; ‣ Tolvaptan
Na+ Na channels
Cortical
reabsorption (ENaC), K K+
collecting
tubule
coupled to channel, H+ sparing USES
K+ & H+ transporter, diuretics
(CCT) 1. HYPERTENSION
secretion Aquaporins
Water 2. GLAUCOMA
Medullary
reabsorption
collecting Vasopressin ‣ Acetazolamide
under Aquaporins
duct antagonists
(MCT)
vasopressin ‣ Mannitol IV
control
3. REDUCE INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE
‣ Mannitol IV
CLASS 4. TREATMENT OF SYNDROME OF
1. CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS INAPPROPRIATE ADH SECRETION
‣ Acetazolamide (SIADH)
‣ Brinzolamide ‣ Demeclocycline
‣ Dorzolamide 5. T R E A T M E N T O F P O T A S S I U M
2. THIAZIDE DIURETICS W A S T I N G A S S O C I AT E D W I T H
‣ Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) THIAZIDE/LOOP
‣ Chlorthalidone ‣ K+- sparing diuretics
6. T R E A T M E N T OF Osmotic Remains in
Hypo/hyper
HYPERALDOSTERONISM diuretics the lumen
natremia
Aldosterone antagonists (Mannitol) “holds” water
‣
✴ ALL DIURETICS may cause
ADVERSE EFFECTS hyponatremia, hypotension, &
dehydration
ADVERSE
DRUG CLASS MOA ✴ In MANNITOL, hyponatremia occurs
EFFECTS
when water is withdrawn from the cells,
METABOLIC
Carbonic Hypernatremia occurs when water is
Inhibits ACIDOSIS,
anhydrase excreted out the urine
carbonic alkalinazation
inhibitors
anhydrase of urine, low
(acetazolamide)
potassium
DRUG INTERACTION
Low K+, Ca2+,
1. Furosemide + Aminoglycosides =
Mg2+,
elevated INCREASE ototoxicity
blood sugar, 2. Furosemide + NSAIDS = reduce diuretic
Loop
Inhibits Hyperlipidemia
Diuretics effect
(furosemide)
NAKCC2 , ototoxicity, Loop
Sulfonamide 3. K-sparing diuretics + ACE inhibitors =
allergy, hyperkalemia
METABOLIC
ALKALOSIS
Low K+,
Mg2+, High
Ca2+,
Elevated
Thiazide blood sugar
Diuretics Inhibits NCC and uric acid,
(HCTZ) Hyperlipidemia
, Sulfonamide
allergy,
METABOLIC
ALKALOSIS
a.Inhibits Na+
Hyperkalemia,
influx
METABOLIC
• Triamterene
• Amiloride ACIDOSIS,
K+-sparing
Gynecomastia
diuretics
b. Antagonizes ,
aldosterone Antiandrogenic
• Spironolactone
effects
• Eplerenone
You might also like
- 1 - Immuno Tables1Document4 pages1 - Immuno Tables1Urugonda VenumadhavNo ratings yet
- Drugs For AsthmaDocument3 pagesDrugs For AsthmaMelissa Deso MillerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of PlacentaDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of PlacentaAmuNo ratings yet
- Family Medicine OSCE Dr. Rebeca HoilettDocument20 pagesFamily Medicine OSCE Dr. Rebeca HoilettFatma El FaresNo ratings yet
- FMS 1 - Week 7 Tutorial 1 LO PDFDocument17 pagesFMS 1 - Week 7 Tutorial 1 LO PDFAprillia AlmaasNo ratings yet
- Mental Status Examination Medical StudentsDocument23 pagesMental Status Examination Medical StudentseurocoupeNo ratings yet
- Week-2 Mental Status ExaminationDocument23 pagesWeek-2 Mental Status ExaminationSaud TariqNo ratings yet
- 3-Major Veins of The BodyDocument26 pages3-Major Veins of The BodyTJPlayz100% (1)
- 2a Haematology Saq QuestionsDocument12 pages2a Haematology Saq QuestionskamaluNo ratings yet
- ECG Demographics Rate: 300/# Large Box in RR IntervalDocument11 pagesECG Demographics Rate: 300/# Large Box in RR IntervalJonathan DavisNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine VivasDocument9 pagesInternal Medicine Vivasponcus payNo ratings yet
- Hem-Onc: AnswerDocument3 pagesHem-Onc: AnswerAman Raj KNo ratings yet
- Transfusion For ChildrenDocument5 pagesTransfusion For ChildrenKristine Mae AbrasaldoNo ratings yet
- Diuretic DrugsDocument2 pagesDiuretic DrugsEngku ElisaNo ratings yet
- Asthma DrugsDocument1 pageAsthma DrugskakuNo ratings yet
- 4 Blood ProductsDocument11 pages4 Blood ProductsGampa VijaykumarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Ospe PDFDocument25 pagesAnatomy Ospe PDFrizki ardiansyahNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid ChartDocument2 pagesIV Fluid Chartbenny christantoNo ratings yet
- Medical Boards Step 2 Made Ridiculously Simple (Medicalstudyzone - Com)Document377 pagesMedical Boards Step 2 Made Ridiculously Simple (Medicalstudyzone - Com)Benyamin KhalevNo ratings yet
- Medicine OSCE - Common Diseases Ver2Document4 pagesMedicine OSCE - Common Diseases Ver2TrisNo ratings yet
- Asthma Drugs Clinical PharmacologyDocument3 pagesAsthma Drugs Clinical PharmacologycrystalsheNo ratings yet
- Description of The Patient & Instructions To SimulatorDocument7 pagesDescription of The Patient & Instructions To SimulatorCindy WongNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain Investigation Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument4 pagesChest Pain Investigation Diagnosis and TreatmentHadsabsaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory AssessmentDocument43 pagesRespiratory AssessmentLui Andrei AnilaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Heart Failure: Drugs Catego Ry Drug Function Adverse Effect NoteDocument2 pagesDrugs For Heart Failure: Drugs Catego Ry Drug Function Adverse Effect NoteyukariNo ratings yet
- Immune System Docs 2019Document13 pagesImmune System Docs 2019David DavidNo ratings yet
- Disease & Def Patho/Mech Clinical S/S DX/ Tests/Labs TX NotesDocument11 pagesDisease & Def Patho/Mech Clinical S/S DX/ Tests/Labs TX NotesSara AshurstNo ratings yet
- Cell Inclusions: John SantangeloDocument45 pagesCell Inclusions: John Santangelosaint5470No ratings yet
- Case History M.SCDocument10 pagesCase History M.SCRaksha RNNo ratings yet
- 03 The Cardiorespiratory SystemDocument24 pages03 The Cardiorespiratory SystemDuane N Lin WertNo ratings yet
- 1 6 Regulation of Blood Glucose PDFDocument3 pages1 6 Regulation of Blood Glucose PDFtiaraNo ratings yet
- Anti Viral DrugsDocument6 pagesAnti Viral DrugskakuNo ratings yet
- Cross Match TechniqueDocument5 pagesCross Match TechniqueANDREW MWITI100% (3)
- Community OSCE.Document26 pagesCommunity OSCE.aaaskgamerNo ratings yet
- A) Vision B) Hearing C) Equilibrium D) Smell E) Taste 2. General SensesDocument6 pagesA) Vision B) Hearing C) Equilibrium D) Smell E) Taste 2. General SensesWilliam TongNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart DseDocument8 pagesValvular Heart DseJane Pineda CuraNo ratings yet
- Nsaids: Non Steroidal Anti Inflammatory DrugsDocument20 pagesNsaids: Non Steroidal Anti Inflammatory DrugsEvan Permana PutraNo ratings yet
- Pain 2. Pallor Poikylothermia Parasthesia Pulselessness Factor V Leiden (Activated Protein C Resistance)Document3 pagesPain 2. Pallor Poikylothermia Parasthesia Pulselessness Factor V Leiden (Activated Protein C Resistance)Ryan TurnerNo ratings yet
- Anti Arrhythmic Anti Arrhythmic: Class IDocument1 pageAnti Arrhythmic Anti Arrhythmic: Class Inizam_ghaniNo ratings yet
- Acute Post Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis: DiseaseDocument3 pagesAcute Post Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis: DiseaseHades Luciferos PallonesNo ratings yet
- St. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: AnatomyDocument3 pagesSt. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: AnatomyMavic VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic DrugsDocument65 pagesAntiepileptic DrugsZarish IftikharNo ratings yet
- Overview of AnaemiaDocument2 pagesOverview of AnaemiaGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Immune System Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesImmune System Review Questionsapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Subject: Physiology Topic: Vision Physiology 1 Lecturer: Dr. Vic Mendoza DATE: MARCH, 2011Document7 pagesSubject: Physiology Topic: Vision Physiology 1 Lecturer: Dr. Vic Mendoza DATE: MARCH, 2011Std DlshsiNo ratings yet
- Disoreder of PerceptionDocument36 pagesDisoreder of PerceptionUmar Khan100% (1)
- Immunopharmacology: Dr. Hamad AlshabiDocument8 pagesImmunopharmacology: Dr. Hamad AlshabiHamad Alshabi100% (1)
- Immune System Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesImmune System Review Questionsapi-524061079No ratings yet
- Cancer ChemotherapyDocument19 pagesCancer ChemotherapySamatha Mohan100% (1)
- 7 - Hand ExaminationDocument18 pages7 - Hand Examinationdaacad muuminNo ratings yet
- Pap SmearDocument34 pagesPap Smearevi_ermaNo ratings yet
- RBC MorphologyDocument9 pagesRBC MorphologybiancsNo ratings yet
- Table Summary For Gross Anatomy of Upper LimbDocument20 pagesTable Summary For Gross Anatomy of Upper Limbafifah zabidiNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience - 4.3 - Examination of Cerebellar Systems and Meninges (KSD)Document4 pagesNeuroscience - 4.3 - Examination of Cerebellar Systems and Meninges (KSD)Kevin C. AguilarNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Fever-Tropmed2013Document24 pagesPathophysiology of Fever-Tropmed2013Yessy Dwi Oktavia100% (1)
- 1.MSE Part 1Document9 pages1.MSE Part 1sisqaNo ratings yet
- Anaemia: What Is Anemia?Document21 pagesAnaemia: What Is Anemia?Rashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Halo On Bright Objects) ArrhythmiaDocument9 pagesHalo On Bright Objects) ArrhythmiaNoriko MatsumotoNo ratings yet
- I Na's C Upcakes I Na's C Upcakes I Na's C UpcakesDocument1 pageI Na's C Upcakes I Na's C Upcakes I Na's C UpcakesCatNo ratings yet
- Task 3 CoachingDocument1 pageTask 3 CoachingCatNo ratings yet
- Badminton Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesBadminton Lesson PlanCatNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic PharmacologyDocument17 pagesAdrenergic PharmacologyCatNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal: State Your Primary Reasons of Organizing This ActivityDocument6 pagesProject Proposal: State Your Primary Reasons of Organizing This ActivityCatNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal: State Your Primary Reasons of Organizing This ActivityDocument7 pagesProject Proposal: State Your Primary Reasons of Organizing This ActivityCatNo ratings yet
- Delerio, Janel O. Resistance Training ActivityDocument2 pagesDelerio, Janel O. Resistance Training ActivityCatNo ratings yet
- Must To Know Formulas (NMAT)Document2 pagesMust To Know Formulas (NMAT)CatNo ratings yet
- Pedagology ApproachesDocument1 pagePedagology ApproachesCatNo ratings yet
- Pedigree Analysis Hand-OutDocument4 pagesPedigree Analysis Hand-OutCatNo ratings yet
- Bay Leaves Group 2 Plant Material Data SheetDocument7 pagesBay Leaves Group 2 Plant Material Data SheetCat100% (1)
- Certificate For Catrina Dimayacyac For "Evaluation For KKK-COVID19 Mahirap Maging Mahirap - How Are The Poor Coping With COVID-19?"Document1 pageCertificate For Catrina Dimayacyac For "Evaluation For KKK-COVID19 Mahirap Maging Mahirap - How Are The Poor Coping With COVID-19?"CatNo ratings yet
- ExercisesDocument3 pagesExercisesCatNo ratings yet
- SPC Crude Drugs CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesSPC Crude Drugs CarbohydratesCatNo ratings yet
- August 6 September 30docxDocument2 pagesAugust 6 September 30docxCatNo ratings yet
- Tablets: Tablets Characteristics of Ideal TabletDocument4 pagesTablets: Tablets Characteristics of Ideal TabletCatNo ratings yet
- Topics For Reporting and ReportersDocument1 pageTopics For Reporting and ReportersCatNo ratings yet
- Statistical Assistance Certification Form: This Is To Certify That The Statistical Data For This Manuscript EntitledDocument1 pageStatistical Assistance Certification Form: This Is To Certify That The Statistical Data For This Manuscript EntitledCatNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 RecrystallizationDocument17 pagesExperiment 4 RecrystallizationCatNo ratings yet
- TUM CoursesDocument3 pagesTUM CoursesJoao N Da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet Idfilm 220 X: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and The CompanyDocument4 pagesSafety Data Sheet Idfilm 220 X: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and The CompanyHunterNo ratings yet
- GOVERNMENT Leave - Form - Complete2Document2 pagesGOVERNMENT Leave - Form - Complete2Marc CaurelNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka: PenyakitDocument9 pagesDaftar Pustaka: Penyakitmagdalena kristantiNo ratings yet
- Mobil™ Dexron-VI ATF: Product DescriptionDocument2 pagesMobil™ Dexron-VI ATF: Product DescriptionOscar GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Fatimah Kti FixDocument71 pagesFatimah Kti FixOktaviani MuhaddistNo ratings yet
- 19-CPS Student Induction Presentation-RAZAK FinalDocument18 pages19-CPS Student Induction Presentation-RAZAK FinalbaderNo ratings yet
- Star Health ProjectDocument52 pagesStar Health ProjectParvat Patil83% (6)
- Team Ubasan Brgy. Pasong Camachile 1: Certificate of RecognitionDocument4 pagesTeam Ubasan Brgy. Pasong Camachile 1: Certificate of RecognitionReienel FerrerNo ratings yet
- Body Parts Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesBody Parts Lesson Planapi-372758719No ratings yet
- OptoPrep Part1 StudyCalendar 3-MonthDocument4 pagesOptoPrep Part1 StudyCalendar 3-MonthmelanieNo ratings yet
- Clasp BDJDocument11 pagesClasp BDJAtiq RehmanNo ratings yet
- Edicted PG, StanDocument69 pagesEdicted PG, StanNwakpa Stanley OgbonnayaNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment: Severity (1, 2 or 3)Document1 pageRisk Assessment: Severity (1, 2 or 3)Ulviyye ElesgerovaNo ratings yet
- Chap 4Document14 pagesChap 4Bambi AlaizaNo ratings yet
- Draft Resolution ExampleDocument8 pagesDraft Resolution ExampleAyutasariNo ratings yet
- Glucose KitDocument2 pagesGlucose KitJuan Enrique Ramón OrellanaNo ratings yet
- Migrants' Election ManifestoDocument2 pagesMigrants' Election ManifestoMimi Panes - CorosNo ratings yet
- Big Drugs!!Document2,145 pagesBig Drugs!!Solomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Analisis Keberhasilan Implementasi RME Mutu PelayananDocument8 pagesAnalisis Keberhasilan Implementasi RME Mutu PelayananWinda PurbaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Keme 1Document9 pagesCase Study Keme 1JhovelNo ratings yet
- Steven Franklin Greer 1 PDFDocument136 pagesSteven Franklin Greer 1 PDFWKYC.comNo ratings yet
- Px. Abdomen RadiologiDocument46 pagesPx. Abdomen RadiologiwagigtnNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahasa InggrisDocument2 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggrisana fauziahNo ratings yet
- VtM2nded1 Page PDFDocument1 pageVtM2nded1 Page PDFJoseph CortesNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Hemorrhage: Prevention and Treatment: Table 1Document10 pagesPostpartum Hemorrhage: Prevention and Treatment: Table 1erikafebriyanarNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat Generik Klinik Citalang Medika Golongan Nama Obat Komposisi Golongan Nama ObatDocument2 pagesDaftar Obat Generik Klinik Citalang Medika Golongan Nama Obat Komposisi Golongan Nama ObattomiNo ratings yet
- Mental and Emotional Health PowerpointDocument36 pagesMental and Emotional Health PowerpointYen Aduana86% (7)
- Discrimination in Different FormsDocument2 pagesDiscrimination in Different FormsPillow ChanNo ratings yet
- Health & Illness FinalDocument16 pagesHealth & Illness FinalAJNo ratings yet