Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2010 Adolescent Immunization Schedule Final 121709
Uploaded by
Dustin Van WilkesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2010 Adolescent Immunization Schedule Final 121709
Uploaded by
Dustin Van WilkesCopyright:
Available Formats
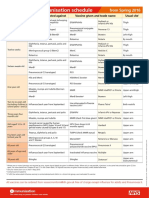
Recommended Immunization Schedule for Persons Aged 7 Through 18 Years— United States • 2010
For those who fall behind or start late, see the schedule below and the catch-up schedule
Vaccine ▼ Age ► 7–10 years 11–12 years 13–18 years
Tetanus, Diphtheria, Pertussis1 Tdap Tdap
Range of
Human Papillomavirus2 see footnote 2 HPV (3 doses) HPV series recommended
ages for all
children except
Meningococcal3 MCV MCV MCV
certain high-risk
groups
Influenza4 Influenza (Yearly)
5 PPSV
Pneumococcal
Range of
recommended
Hepatitis A6 HepA Series
ages for
catch-up
Hepatitis B7 Hep B Series immunization
Inactivated Poliovirus8 IPV Series
9 Range of
Measles, Mumps, Rubella MMR Series
recommended
ages for certain
Varicella10 Varicella Series high-risk groups
This schedule includes recommendations in effect as of December 15, 2009. Committee on Immunization Practices statement for detailed recommendations:
Any dose not administered at the recommended age should be administered at a http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/acip-list.htm. Clinically significant adverse
subsequent visit, when indicated and feasible. The use of a combination vaccine events that follow immunization should be reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event
generally is preferred over separate injections of its equivalent component vaccines. Reporting System (VAERS) at http://www.vaers.hhs.gov or by telephone,
Considerations should include provider assessment, patient preference, and 800-822-7967.
the potential for adverse events. Providers should consult the relevant Advisory
1. Tetanus and diphtheria toxoids and acellular pertussis vaccine (Tdap). 4. Influenza vaccine (seasonal).
(Minimum age: 10 years for Boostrix and 11 years for Adacel) • Administer annually to children aged 6 months through 18 years.
• Administer at age 11 or 12 years for those who have completed the recom- • For healthy nonpregnant persons aged 7 through 18 years (i.e., those who
mended childhood DTP/DTaP vaccination series and have not received a do not have underlying medical conditions that predispose them to influenza
tetanus and diphtheria toxoid (Td) booster dose. complications), either LAIV or TIV may be used.
• Persons aged 13 through 18 years who have not received Tdap should receive • Administer 2 doses (separated by at least 4 weeks) to children aged younger
a dose. than 9 years who are receiving influenza vaccine for the first time or who were
• A 5-year interval from the last Td dose is encouraged when Tdap is used as vaccinated for the first time during the previous influenza season but only
a booster dose; however, a shorter interval may be used if pertussis immunity received 1 dose.
is needed. • For recommendations for use of influenza A (H1N1) 2009 monovalent vaccine.
2. Human papillomavirus vaccine (HPV). (Minimum age: 9 years) See MMWR 2009;58(No. RR-10).
• Two HPV vaccines are licensed: a quadrivalent vaccine (HPV4) for the pre- 5. Pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV).
vention of cervical, vaginal and vulvar cancers (in females) and genital warts • Administer to children with certain underlying medical conditions, including a
(in females and males), and a bivalent vaccine (HPV2) for the prevention of cochlear implant. A single revaccination should be administered after 5 years
cervical cancers in females. to children with functional or anatomic asplenia or an immunocompromising
• HPV vaccines are most effective for both males and females when given condition. See MMWR 1997;46(No. RR-8).
before exposure to HPV through sexual contact. 6. Hepatitis A vaccine (HepA).
• HPV4 or HPV2 is recommended for the prevention of cervical precancers and • Administer 2 doses at least 6 months apart.
cancers in females. • HepA is recommended for children aged older than 23 months who live in
• HPV4 is recommended for the prevention of cervical, vaginal and vulvar areas where vaccination programs target older children or who are at increased
precancers and cancers and genital warts in females. risk for infection or for whom immunity against hepatitis A is desired.
• Administer the first dose to females at age 11 or 12 years. 7. Hepatitis B vaccine (HepB).
• Administer the second dose 1 to 2 months after the first dose and the third • Administer the 3-dose series to those not previously vaccinated.
dose 6 months after the first dose (at least 24 weeks after the first dose). • A 2-dose series (separated by at least 4 months) of adult formulation
• Administer the series to females at age 13 through 18 years if not previously Recombivax HB is licensed for children aged 11 through 15 years.
vaccinated. 8. Inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV).
• HPV4 may be administered in a 3-dose series to males aged 9 through 18 • The final dose in the series should be administered on or after the fourth
years to reduce their likelihood of acquiring genital warts. birthday and at least 6 months following the previous dose.
3. Meningococcal conjugate vaccine (MCV4). • If both OPV and IPV were administered as part of a series, a total of 4 doses
• Administer at age 11 or 12 years, or at age 13 through 18 years if not previ- should be administered, regardless of the child’s current age.
ously vaccinated. 9. Measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine (MMR).
• Administer to previously unvaccinated college freshmen living in a • If not previously vaccinated, administer 2 doses or the second dose for those
dormitory. who have received only 1 dose, with at least 28 days between doses.
• Administer MCV4 to children aged 2 through 10 years with persistent comple- 10. Varicella vaccine.
ment component deficiency, anatomic or functional asplenia, or certain other • For persons aged 7 through 18 years without evidence of immunity (see
conditions placing them at high risk. MMWR 2007;56[No. RR-4]), administer 2 doses if not previously vaccinated
• Administer to children previously vaccinated with MCV4 or MPSV4 who or the second dose if only 1 dose has been administered.
remain at increased risk after 3 years (if first dose administered at age 2 • For persons aged 7 through 12 years, the minimum interval between doses
through 6 years) or after 5 years (if first dose administered at age 7 years or is 3 months. However, if the second dose was administered at least 28 days
older). Persons whose only risk factor is living in on-campus housing are not after the first dose, it can be accepted as valid.
recommended to receive an additional dose. See MMWR 2009;58:1042–3. • For persons aged 13 years and older, the minimum interval between doses
is 28 days.
CS207330-A
The Recommended Immunization Schedules for Persons Aged 0 through 18 Years are approved by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices
(http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/recs/acip), the American Academy of Pediatrics (http://www.aap.org), and the American Academy of Family Physicians (http://www.aafp.org).
Department of Health and Human Services • Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
You might also like
- Multisystem & Genetic - BoardsDocument10 pagesMultisystem & Genetic - BoardsSoojung NamNo ratings yet
- Trifold Vaccine Card ENGLISHDocument2 pagesTrifold Vaccine Card ENGLISHGarrett GoldwaiteNo ratings yet
- Massachusetts immunization certificate guideDocument1 pageMassachusetts immunization certificate guidePrecilla Janet RosarioNo ratings yet
- Persistent Diarrhoea: IAP UG Teaching Slides 2015 16Document31 pagesPersistent Diarrhoea: IAP UG Teaching Slides 2015 16Srujana MohanNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasma Pneumocystis Microsporidia BabesiaDocument40 pagesToxoplasma Pneumocystis Microsporidia BabesiadhaineyNo ratings yet
- FelineCalicivirus FactSheet PDFDocument5 pagesFelineCalicivirus FactSheet PDFJuniClaudia13No ratings yet
- Ace ClassificationDocument15 pagesAce ClassificationKarla Margine Pérez100% (1)
- APhA Immunization Participant - Case - WorksheetsDocument11 pagesAPhA Immunization Participant - Case - WorksheetsGerald Gamboa100% (2)
- For Those Who Fall Behind or Start Late, See The Catch-Up ScheduleDocument4 pagesFor Those Who Fall Behind or Start Late, See The Catch-Up ScheduleTony MichelNo ratings yet
- Recommended Immunization Schedule For Persons Aged 0 Through 6 YearsDocument1 pageRecommended Immunization Schedule For Persons Aged 0 Through 6 YearshendergmNo ratings yet
- 7-18yr Schedule For Immunizations, CDC 2008Document1 page7-18yr Schedule For Immunizations, CDC 2008Tracy100% (1)
- 0 6 Yrs Immunization ScheduleDocument1 page0 6 Yrs Immunization ScheduleAira ReyesNo ratings yet
- Haemophilus Influenzae Type: RD ND STDocument4 pagesHaemophilus Influenzae Type: RD ND STnickyboreNo ratings yet
- 0 18yrs ScheduleDocument4 pages0 18yrs Schedulekar_ind4u5636No ratings yet
- Immunization Child2005 EnglDocument4 pagesImmunization Child2005 EnglGanesh BabuNo ratings yet
- 0 18yrs ScheduleDocument4 pages0 18yrs ScheduleprashantNo ratings yet
- 0 - 18yrs Schedule of VaccineDocument4 pages0 - 18yrs Schedule of VaccineEmanGamalAlbazNo ratings yet
- Vaccination of HIV Infected Children 2018Document4 pagesVaccination of HIV Infected Children 2018alpha.blocker11No ratings yet
- 0 18yrs Child Combined ScheduleDocument14 pages0 18yrs Child Combined ScheduleEphrem LemmaNo ratings yet
- CHS Recommended VaccinesDocument1 pageCHS Recommended Vaccineslonzell.brantleyNo ratings yet
- Peds Vaccination ScheduleDocument4 pagesPeds Vaccination Schedulekman0722No ratings yet
- Adult Schedule Easy ReadDocument2 pagesAdult Schedule Easy Read12345zolyNo ratings yet
- Recommended Childhood Vaccine Schedule 2018Document2 pagesRecommended Childhood Vaccine Schedule 2018Saddam HussainNo ratings yet
- Immunization-Lean-Lecture-Aug-2022 4in1Document14 pagesImmunization-Lean-Lecture-Aug-2022 4in1RawanNo ratings yet
- Cis 2018 PDFDocument3 pagesCis 2018 PDFTara Oliveros Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Adult Immunization ScheduleDocument5 pagesAdult Immunization Schedulejack01236No ratings yet
- Adult VaccinesDocument3 pagesAdult VaccinesJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- mu_06Document5 pagesmu_06aravindNo ratings yet
- Immunizations What Is Immunization?Document5 pagesImmunizations What Is Immunization?Bethrice MelegritoNo ratings yet
- Parent Ver SCH 0 6yrsDocument2 pagesParent Ver SCH 0 6yrsMatri SearchNo ratings yet
- Recommended Child and Adolescent Immunization ScheduleDocument24 pagesRecommended Child and Adolescent Immunization ScheduleNitesh GandhiNo ratings yet
- Immunizations Preg ChartDocument2 pagesImmunizations Preg ChartPutri MahacakriNo ratings yet
- Calendario Vacunacion Adultos 2010Document4 pagesCalendario Vacunacion Adultos 2010JOSERUPOLONo ratings yet
- ImmunizationDocument39 pagesImmunizationhhh11599No ratings yet
- Commonly Administered Pediatric Vaccines Coding TableDocument3 pagesCommonly Administered Pediatric Vaccines Coding TableEunice Mari San Diego0% (1)
- Antimicrobial Therapy and Its Modification After Diagnostic Test InterpretationDocument29 pagesAntimicrobial Therapy and Its Modification After Diagnostic Test Interpretationeka kemala sariNo ratings yet
- Megavac 6Document2 pagesMegavac 6Abhijith S. P100% (1)
- Hav ShieldDocument37 pagesHav ShielddragondostNo ratings yet
- Parent Ver SCH 0 6yrsDocument2 pagesParent Ver SCH 0 6yrsunmundoextranopodcastNo ratings yet
- ACIP Approves 2020 Adult and Childhood Adolescent Immunization SchedulesDocument2 pagesACIP Approves 2020 Adult and Childhood Adolescent Immunization Scheduleshossein kasiriNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis Distemper LeptospirosisDocument1 pageHepatitis Distemper LeptospirosisBhupamani DasNo ratings yet
- PHE Complete Immunisation Schedule Jun2020 05Document2 pagesPHE Complete Immunisation Schedule Jun2020 05GAnnNo ratings yet
- Infants & Toddlers (Age in Months) : Diphtheria and Tetanus Toxoids, Acellular Pertussis (Dtap)Document22 pagesInfants & Toddlers (Age in Months) : Diphtheria and Tetanus Toxoids, Acellular Pertussis (Dtap)Muhammad AdilNo ratings yet
- Baby Shots EngDocument2 pagesBaby Shots Engsunmo8217No ratings yet
- Immunisation 2013 PDFDocument1 pageImmunisation 2013 PDFjuniorebindaNo ratings yet
- PHE Complete Immunisation Schedule Jan2020 PDFDocument2 pagesPHE Complete Immunisation Schedule Jan2020 PDFJyotirmaya RajaNo ratings yet
- PHE Complete Immunisation ScheduDocument2 pagesPHE Complete Immunisation ScheduJasminewai927No ratings yet
- Dialysis Guide 2012Document12 pagesDialysis Guide 2012nadhifNo ratings yet
- Jama Sha 2019 It 190019Document2 pagesJama Sha 2019 It 190019xtineNo ratings yet
- Green Book Chapter 11Document9 pagesGreen Book Chapter 11VergaaBellanyNo ratings yet
- The Routine Immunisation ScheduleDocument10 pagesThe Routine Immunisation ScheduleJamesWaitonNo ratings yet
- Infant ImmunisationDocument1 pageInfant ImmunisationPaul GallagherNo ratings yet
- UNC Childrens Diagnosis and Management HAP VAP Nov 2021Document7 pagesUNC Childrens Diagnosis and Management HAP VAP Nov 2021adhitiaNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Project - FinalDocument2 pagesVaccine Project - Finalchelsea garzaNo ratings yet
- 0 To 18yrs Combined Immunization ScheduleDocument8 pages0 To 18yrs Combined Immunization ScheduleNurses CommunityNo ratings yet
- A&P Assignment ActivitiesDocument4 pagesA&P Assignment ActivitiesGURPARABJOT KAURNo ratings yet
- JabsDocument1 pageJabsgvswainNo ratings yet
- ImmunizationDocument29 pagesImmunizationTuliNo ratings yet
- ACT Immunisation ScheduleDocument2 pagesACT Immunisation ScheduleAlana TindaleNo ratings yet
- The Routine Immunisation Schedule: From Autumn 2018Document2 pagesThe Routine Immunisation Schedule: From Autumn 2018Adityo AriwibowoNo ratings yet
- Adult Combined ScheduleDocument6 pagesAdult Combined SchedulesharvaniNo ratings yet
- Health Advice and Immunizations for TravelersFrom EverandHealth Advice and Immunizations for TravelersNo ratings yet
- Good Health in the Tropics: Advice to Travellers and SettlersFrom EverandGood Health in the Tropics: Advice to Travellers and SettlersNo ratings yet
- Long Test 10Document2 pagesLong Test 10Jerome ManabatNo ratings yet
- Gay LinggoDocument16 pagesGay LinggoManel Seraspe Domingo100% (1)
- Acute AbdomenDocument16 pagesAcute AbdomenOnkar SinghNo ratings yet
- Conspiracy Theories About CoronavirusDocument1 pageConspiracy Theories About CoronavirusUmama TahirNo ratings yet
- Hand Washing Basics To Help Your Family Stay SafeDocument4 pagesHand Washing Basics To Help Your Family Stay Safechandy Rendaje100% (1)
- COVAX Facility Final Resolution Focuses on Equitable Vaccine AccessDocument7 pagesCOVAX Facility Final Resolution Focuses on Equitable Vaccine AccessDaniellaNo ratings yet
- Bronchiolitis Rs V Current Concepts 2009Document75 pagesBronchiolitis Rs V Current Concepts 2009adnan.engineer17049No ratings yet
- IMNCI Chart Booklet (New) OrignalDocument36 pagesIMNCI Chart Booklet (New) OrignaleresdNo ratings yet
- EntDocument11 pagesEntkhuzaima9No ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument25 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisGandung PrakosoNo ratings yet
- Kursk State Medical University Department of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology Exam Questions On Infectious Diseases Faculty: Medical Course: 6Document4 pagesKursk State Medical University Department of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology Exam Questions On Infectious Diseases Faculty: Medical Course: 6Elephant ksmileNo ratings yet
- Leprosy (Morbus Hansen) : Dr. Uun Khusnul Khotimah, SPKKDocument38 pagesLeprosy (Morbus Hansen) : Dr. Uun Khusnul Khotimah, SPKKagilNo ratings yet
- Human AlbuminDocument4 pagesHuman Albumingoya100% (2)
- Veterinary Leptospirosis Client BrochureDocument15 pagesVeterinary Leptospirosis Client BrochureatikNo ratings yet
- A Dental Home For PWAs 131027Document74 pagesA Dental Home For PWAs 131027Autism Society PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Navel DisplacementDocument4 pagesNavel Displacementdinesh100% (1)
- Perspective: New England Journal MedicineDocument3 pagesPerspective: New England Journal MedicineEmanuel LayonNo ratings yet
- Hand Hygiene When and How LeafletDocument2 pagesHand Hygiene When and How Leaflet13eNo ratings yet
- ErgotDocument40 pagesErgotAna Luca100% (1)
- She Borrowed The Book From Him Many Years Ago and Hasn't Yet Returned It - An AdmissionDocument15 pagesShe Borrowed The Book From Him Many Years Ago and Hasn't Yet Returned It - An AdmissionrealinspectorhoundNo ratings yet
- TocoshDocument8 pagesTocoshHansNo ratings yet
- Role of The Circulatory System in The Body's Defence MechanismsDocument15 pagesRole of The Circulatory System in The Body's Defence MechanismsArash Halim67% (3)
- OUTBREAKDocument66 pagesOUTBREAKAurian TormesNo ratings yet
- Inv A Sion Pha Se: Bill Julius Samuel G. Alferez BSN IiiDocument1 pageInv A Sion Pha Se: Bill Julius Samuel G. Alferez BSN IiiRudelsa Agcolicol LangamanNo ratings yet
- MSU-Iligan Institute of Technology: Nursing Health Assessment IDocument1 pageMSU-Iligan Institute of Technology: Nursing Health Assessment IJhon Jade PalagtiwNo ratings yet
- Chinese Remedy of Herbal Medicine To Treat H1N1 FluDocument2 pagesChinese Remedy of Herbal Medicine To Treat H1N1 FluCheng Bei HoneybeeNo ratings yet
- Hepatolithiasis: Alireza Sadeghi, MDDocument62 pagesHepatolithiasis: Alireza Sadeghi, MDSahirNo ratings yet