Professional Documents
Culture Documents
04 Jan Unit 4 Ms - CWK WP
Uploaded by
dashapuskarjovaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
04 Jan Unit 4 Ms - CWK WP
Uploaded by
dashapuskarjovaCopyright:
Available Formats
A2 Economics Industrial Economics 04 Jan Mark Scheme
Question 1 If explanation ignores the flat AC condition award a maximum of (2
(1) C marks) for explanation/diagram.
Definition of concentration ratio (1 mark) Calculation of ratio for 2, 3
or 4 firms (1 mark). Understanding of 'high': a small number of firms (6) A
dominate the industry (1 mark). Definition of price discrimination (1 mark). Impossibility of separation
Also award observations about market structure: here oligopolistic. of markets with milk on the shelves (1 mark) impossibility of policing
second-hand transactions which undercut the discrimination (1 mark)
(2) B competition from other supermarkets (1 mark). Consideration of the
Explanation of components of formula: RPI inflation (1 mark), X for 'least likely' aspect ofthe question relative to airlines, rail etc (1 mark)
efficiency improvements i.e. expected cuts in costs (1 mark) therefore
within the cap firms will strive to make additional efficiency gains (7) C
because they can keep the resulting profits (1 mark). Definition of average cost and marginal cost - this may be implicit in a
Also award reference to consumer benefits as a result of efficiency gains correct calculation (1 mark). Appropriate calculation to show that
(1 mark). marginal cost is rising but average cost falling over the given range of
output (2 marks) diagram of MC, AC (1 mark) indication on diagram of
(3) E relevant output range (1 mark).
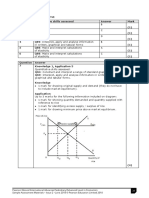
Relevant diagram (1 mark). Explanation or indication on diagram of
resulting productive inefficiency (1 mark). Explanation of only normal (8) ERecognition of collusion or cartel (1 mark). Identification (1) and
profit, or statement that AR=AC (1 mark). explanation (1) of the public interest consequences ofthis, e.g. in terms of
Also award definition of monopolistic competition (1 mark) higher prices, reduced output, loss of consumer surplus. Also award
diagrammatic illustrations of the welfare loss from price fixing.
(4) B
Statement of an assumption of perfect competition (1 mark). Related to
characteristic (flat AR) of diagram, or reference to "price taker" (1 (9) B
marks). Indication on diagram (1) or explanation of supernormal profit Definition or indication on diagram of MR=O for revenue max (1 mark),
(1 mark). definition or indication on diagram of profit max (1 mark). Indication on
Also award recognition that the firm is in the short run (1 mark) diagram or explanation that output is falling and price is rising (1 mark).
Also accept TR/TC diagrams (3 marks).
(5) D
Identification of profit maximizing condition (1 mark), explanation that (10) A
this will result in higher output because MR has shifted to the right (1' Contestable markets are those with low sunk costs or low exit barriers (1
mark), explanation illustration that this will result in higher supernormal mark), explanation that branding would require heavy advertising by new
profit (1 mark). Or appropriate diagram indicating results (3 marks). entrant (1 mark), some application to chocolate confectionery (1 mark).
Also award combinations of diagram and explanation. Also award (1 mark) for definition of sunk costs.
A2 Economics Industrial Economics 04 Jan Mark Scheme
Question 11 Reserve up to (4) marks for anyone evaluative point e.g. evaluating the
(a) (i) Identification of horizontal (1 mark) definition (1 mark). specific likelihood of price competition in the ice-cream industry, the
Reference to the passage as evidence that they both produced ice cream: great uncertainty of behaviour of firms in this situation, the illegality of
Richmond Foods is an "ice-cream company" (line 2) buying Nestle's ice- price fixing. Or for critical awareness of the analysis produced - e.g.
cream brands (2 marks) 4 marks weaknesses of the kinked demand curve. 10 marks
Also award marks if the candidate focuses on the (statutory) monopoly
(ii) Accept any reasonable suggestion - e.g. potentially faster than aspect of the industry. Identification of monopoly market power (1
organic growth, potentially cheaper in tenus of acquiring established mark) and thus the possibility of price setting behaviour by Birds Eye
brands and equipment, influx of new ideas and personnel, access to Wall's (1 mark). Analysis of the market power. The analysis may be
immediately greater market share. Anyone issue (4 marks) or two issues supported by a monopoly diagram. (4) Evaluation may refer to the
less well developed (2 marks) each. Award 'economies of scale' only if likelihood in this industry, e.g. to lower averages costs of the dominant
specific to an acquisition e.g. rationalisation of management. supplier making price competition less likely. (4)
Award (2 marks) for evaluation of the issues discussed. 6 marks Identifying (1) and explaining (1) two relevant barriers e.g. branding, high
levels of investment leading to potentially high sunk costs, other
(b) Identification of concept of economies of scale (1 mark) definition contestability issues such freezer exclusivity agreements. (4 marks).
in tenus falling average costs (1 mark).
For each of two potential economies of scale e.g. volume, overcoming (d) Definition of barriers to entry - may well be implicit (1 mark).
indivisibilities, marketing, bulk buying etc (1 mark) for identification, (1 Evaluation: prioritizing the barriers discussed, some costs in this industry
mark) for application to ice cream making. 6 marks are not sunk, other firms managed to enter this industry, emergence of
Also award cost diagram illustrating economies of scale (1 mark). international competition e.g. Ben and Jerry's, coming to a formal
conclusion (5 marks). Two evaluative points up to (3 marks) each to
(c) (i) Identifying oligopoly (1 mark) definition of oligopoly (1 mark). maximum of(5 marks).
Use of data, e.g. to point out the very high three firm concentration 10 marks
ratio (1 mark) the actual figure (1 mark).
Also allow monopoly (1) if candidate has also referred to dominance,
market power or the 25% statutory definition
(1). Birds Eye has> 60% market share (2). 4 marks
(ii) Identification of non-price competition (1 mark) and likelihood of
collusion or price wars (1 mark)
Analysis of the kinds of price competition likely under oligopoly in
tenus of a few large interdependent firms second-guessing each other.
This analysis may be supported by theory diagrams, e.g. the kinked
demand curve or game theory (4 marks)
A2 Economics Industrial Economics 04 Jan Mark Scheme
Question 12 Application to the railway catering industry or any other case study (4
(a)(i) The acquisition involved more than 25% market share (2 marks), marks).
identification of relevant data - combined market share of 83% (2 Also accept answers based on the 2003 Competition Act. 8 marks
marks). 4 marks
(ii) For each ofthe two motives: identification (1 mark) explanation (1 (d) Definition of two kinds of economic efficiency (allocative,
mark) application to food on trains (1 mark). e.g. economies of scope productive, dynamic, or absence of X) - this may be indicated on a
(e.g. management span reduced), diversification, bulk buying diagram (2 marks). .
opportunities, elimination of competition, attraction of potential Diagram illustrating that these may not be achieved in 'local monopoly'
market power over confined customers. situation (1 mark). Written explanation of likely inefficiency (2 marks).
Anyone evaluative point - which is the most significant motive?, Candidates may also argue that an increase in efficiency will result from
uncertainty of decision making, information failure, costs, opportunity economies of scale.
costs (2 marks) 8 marks Evaluation of anyone point - e.g. unlikely to be allocatively efficient
given the very high monopoly power once the train has departed,
(b) Identification of concept of barriers to entry or contestability, or however contracts have to be re-tendered for, or relating inefficient to
changing market conditions (1 mark) specific discussion of railway food efficient outcomes on the diagram (5 marks). 10 marks
services (1 mark).
Barriers to restaurant car entry might include: set-up costs, know-how
about logistics, advertisinglbranding of restaurant services, reputation
required for success in tendering for the contract etc. 2 marks for each of
two reasons (4). Also award changing consumer demand.
Reserve evaluation marks for an explicit comparison with trolley
services (low capital costs, little training required for workers etc). 10
marks (4 marks)
(c) Explanation of the public interest criterion (4 marks). Public interest
criteria may include (but accept more general explanations):
.
"Maintaining and promoting competition in the UK Promoting the
interests of consumers Promoting new products and reducing costs
Maintaining and promoting the balanced distribution of industry and
employment Maintaining and promoting competitive activity in
overseas markets by companies in the UK"
You might also like
- Answers To Chapter 8 Exercises Luis Cabral PDFDocument18 pagesAnswers To Chapter 8 Exercises Luis Cabral PDFMehdi Ben Slimane100% (2)
- Economics Edexcel As Unit 1 Workbook AnswersDocument73 pagesEconomics Edexcel As Unit 1 Workbook AnswersSam catlin100% (3)
- Quantitative Value: A Practitioner's Guide to Automating Intelligent Investment and Eliminating Behavioral ErrorsFrom EverandQuantitative Value: A Practitioner's Guide to Automating Intelligent Investment and Eliminating Behavioral ErrorsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- Applied Economics Module 2Document57 pagesApplied Economics Module 2Billy Joe93% (44)
- Net BookDocument17 pagesNet BookMaina SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Answers To Questions and Problems: Managerial Economics and Business Strategy, 5eDocument5 pagesChapter 8: Answers To Questions and Problems: Managerial Economics and Business Strategy, 5eadityaintouch100% (1)
- Practice ECF1100 Final Exam Sem 2 2019 SolutionsDocument7 pagesPractice ECF1100 Final Exam Sem 2 2019 SolutionsFarah PatelNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Exam 4q Applied Economics Last 1Document3 pagesGrade 12 Exam 4q Applied Economics Last 1Paul Paguia100% (1)
- Economics - Edexcel Theme1 Workbook AnswersDocument61 pagesEconomics - Edexcel Theme1 Workbook AnswersMoshe BenaimNo ratings yet
- 03 June Ecs 4 Ms - CWK WPDocument3 pages03 June Ecs 4 Ms - CWK WPIsaac WongNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2012: GCE Economics (6EC03) Paper 01Document19 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2012: GCE Economics (6EC03) Paper 01pojpijadNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) Winter 2010: GCE Economics (6EC03/01)Document13 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Winter 2010: GCE Economics (6EC03/01)Syed Salman AliNo ratings yet
- 6EC03 January 2010 MSDocument12 pages6EC03 January 2010 MSJennifer HoangNo ratings yet
- 6ec03 Econ Jan 2010 MsDocument10 pages6ec03 Econ Jan 2010 MsHannah Naomi RoseNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Final) January 2009: GCE Economics (6354/01)Document15 pagesMark Scheme (Final) January 2009: GCE Economics (6354/01)caramelcandyNo ratings yet
- Economics U1 MSDocument13 pagesEconomics U1 MSxidingNo ratings yet
- 6354 01 Ms 20060616Document13 pages6354 01 Ms 20060616golddust2012No ratings yet
- Memo Exam Jun 2017Document11 pagesMemo Exam Jun 2017Nathan VieningsNo ratings yet
- ECO101 - PS7 - Market StructureDocument13 pagesECO101 - PS7 - Market Structureislamrony8122000No ratings yet
- 2281 Economics: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2006 Question PaperDocument3 pages2281 Economics: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2006 Question Papermstudy123456100% (1)
- Eco 1 2002 JunDocument5 pagesEco 1 2002 JunTL LeNo ratings yet
- 6354 01 Rms 20080306Document18 pages6354 01 Rms 20080306Ismail MerajNo ratings yet
- Advanced Business EconomicsDocument4 pagesAdvanced Business EconomicsMuhammadSajidAbbasiNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document2 pagesProblem Set 1gorski29No ratings yet
- 1) Seller ConcentrationDocument5 pages1) Seller Concentration92_883755689No ratings yet
- BB 107 - BBB1023 - BBS1083 Janl '24 Group Assignment QDocument3 pagesBB 107 - BBB1023 - BBS1083 Janl '24 Group Assignment QJean珈祯No ratings yet
- 8 June 2007 AnswersDocument9 pages8 June 2007 AnswersAY6061No ratings yet
- Edexcel Economics Unit 3 June 2010 Mark SchemeDocument16 pagesEdexcel Economics Unit 3 June 2010 Mark SchemeEkaterina MozloevaNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad Warning: (Department of Economics)Document2 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad Warning: (Department of Economics)Kareem Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- WJEC Economics A Level Unit 3 MS S19Document18 pagesWJEC Economics A Level Unit 3 MS S19angeleschang99No ratings yet
- Eco 1A NewDocument3 pagesEco 1A NewTracy-lee JacobsNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 Managerial Economics - Farrukh Wazir Khan - Fall22Document5 pagesAssignment2 Managerial Economics - Farrukh Wazir Khan - Fall22IFRA AFZALNo ratings yet
- Ans. EC202 Take HomeDocument18 pagesAns. EC202 Take HomeHashimRaza100% (2)
- Mark Scheme June 2005 Unit-1Document10 pagesMark Scheme June 2005 Unit-1Tatyana LeeNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Sample Questions Econ 405 s09Document6 pagesExam 1 Sample Questions Econ 405 s09Petah LiuNo ratings yet
- School of Business and EconomicsDocument19 pagesSchool of Business and EconomicsIshtiaq Ahmed MugdhaNo ratings yet
- 2013 ZBDocument4 pages2013 ZBShershah KakakhelNo ratings yet
- Economics Paper 22-23-3Document4 pagesEconomics Paper 22-23-3george booksNo ratings yet
- Economics Test - 5.6.22 - Rodrigo MartinezDocument7 pagesEconomics Test - 5.6.22 - Rodrigo MartinezRodrigo MartínezNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Business Studies For Examination From 2020Document10 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Business Studies For Examination From 2020frederickNo ratings yet
- Assignment For 2024 Semester 1Document2 pagesAssignment For 2024 Semester 1nchimunyaclement5No ratings yet
- 2013 ZaDocument4 pages2013 ZaShershah KakakhelNo ratings yet
- Mba50 Wa1 202122Document6 pagesMba50 Wa1 202122serepasfNo ratings yet
- Business Economics ICFAIDocument20 pagesBusiness Economics ICFAIDaniel VincentNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 5Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet 5YvonneNo ratings yet
- Economics 100: AnswersDocument7 pagesEconomics 100: AnswersexamkillerNo ratings yet
- Economics Paper 3 HL MarkschemeDocument21 pagesEconomics Paper 3 HL Markschemekashnitiwary23No ratings yet
- Unit 11Document16 pagesUnit 11Mais OmerNo ratings yet
- Exam Practice-2Document10 pagesExam Practice-2dianoetikosNo ratings yet
- June 2008 Mark SchemeDocument38 pagesJune 2008 Mark SchemeDal MakhaniNo ratings yet
- BECO575-Worksheet 3 (CH 7, 8 And10 - Market Structures)Document11 pagesBECO575-Worksheet 3 (CH 7, 8 And10 - Market Structures)Sara HalabiNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics - Assessment BriefDocument8 pagesManagerial Economics - Assessment BriefSaim KhanNo ratings yet
- PYQs - On - Theories - of - Market - StructureDocument3 pagesPYQs - On - Theories - of - Market - StructureTusharNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (RESULTS) : January 2019Document24 pagesMark Scheme (RESULTS) : January 2019유리No ratings yet
- 2012 ZaDocument4 pages2012 ZaShershah KakakhelNo ratings yet
- 2010 Chpt9answersDocument6 pages2010 Chpt9answersmballas2012No ratings yet
- 9708 s09 Ms 2Document9 pages9708 s09 Ms 2roukaiya_peerkhanNo ratings yet
- Workshop 4 Perfect Competition 1Document4 pagesWorkshop 4 Perfect Competition 1GiovanniNico33No ratings yet
- Economics 100: Term Test 2 - December 4, 2009 Length: 1 Hour, 5 MinutesDocument6 pagesEconomics 100: Term Test 2 - December 4, 2009 Length: 1 Hour, 5 MinutesexamkillerNo ratings yet
- An Option Greeks Primer: Building Intuition with Delta Hedging and Monte Carlo Simulation using ExcelFrom EverandAn Option Greeks Primer: Building Intuition with Delta Hedging and Monte Carlo Simulation using ExcelNo ratings yet
- Markets from Networks: Socioeconomic Models of ProductionFrom EverandMarkets from Networks: Socioeconomic Models of ProductionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- 2015 AmDocument56 pages2015 AmdashapuskarjovaNo ratings yet
- 2014 VB PDFDocument58 pages2014 VB PDFdashapuskarjovaNo ratings yet
- ReturnsLabel PDFDocument1 pageReturnsLabel PDFdashapuskarjovaNo ratings yet
- 2014 PM P2Document62 pages2014 PM P2dashapuskarjovaNo ratings yet
- Returns LabelDocument1 pageReturns LabeldashapuskarjovaNo ratings yet
- MenuDocument1 pageMenudashapuskarjovaNo ratings yet
- ReturnsLabel PDFDocument1 pageReturnsLabel PDFdashapuskarjovaNo ratings yet
- Schengen Visa Application Form 1 23.01.13Document3 pagesSchengen Visa Application Form 1 23.01.13Anonymous jAqqXyPxXPNo ratings yet
- LSE100 Final Exam 2012Document5 pagesLSE100 Final Exam 2012dashapuskarjovaNo ratings yet
- Midterm SolutionDocument4 pagesMidterm SolutiondashapuskarjovaNo ratings yet
- Monetary ShocksDocument216 pagesMonetary ShocksdashapuskarjovaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam 2011Document5 pagesFinal Exam 2011dashapuskarjovaNo ratings yet
- Micro Revision SPS PDFDocument5 pagesMicro Revision SPS PDFdashapuskarjovaNo ratings yet
- Mid AnswerDocument10 pagesMid AnswerdashapuskarjovaNo ratings yet
- Ec325 Syllabus 2013 - v4Document12 pagesEc325 Syllabus 2013 - v4dashapuskarjovaNo ratings yet
- Micro Revision PSDocument1 pageMicro Revision PSdashapuskarjovaNo ratings yet
- WUP2011 F02 Proportion UrbanDocument14 pagesWUP2011 F02 Proportion UrbandashapuskarjovaNo ratings yet
- EC315 International Economics LSE Past PaperDocument9 pagesEC315 International Economics LSE Past PaperdashapuskarjovaNo ratings yet
- FM300 2000 Past PaperDocument15 pagesFM300 2000 Past PaperdashapuskarjovaNo ratings yet
- Is-Lm CurveDocument7 pagesIs-Lm Curvejmatsanura1No ratings yet
- FM300 Syllabus Section A 2012-13Document5 pagesFM300 Syllabus Section A 2012-13dashapuskarjovaNo ratings yet
- DES Lec 3 4Document103 pagesDES Lec 3 4Zhenyi ZhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Economies of Scale, Imperfect Competition, and International TradeDocument64 pagesChapter 6 - Economies of Scale, Imperfect Competition, and International Tradevintosh_pNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 MonopolyDocument24 pagesUnit 8 MonopolyRanjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- P1 AL Econs West Regional Mock CameroonDocument7 pagesP1 AL Econs West Regional Mock CameroonJohnson NjasotehNo ratings yet
- Uhu081 PDFDocument2 pagesUhu081 PDFsahibjotNo ratings yet
- Eng'g Eco - 1. Basic Economic Environment and ConceptDocument4 pagesEng'g Eco - 1. Basic Economic Environment and ConceptReuven SioseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Market StructureDocument14 pagesChapter 7 Market Structureapi-234789837No ratings yet
- Price Comparison and Pricing Strategies A Case Study: The Italian Motorway Refuelling MarketDocument39 pagesPrice Comparison and Pricing Strategies A Case Study: The Italian Motorway Refuelling MarketZehra KHanNo ratings yet
- Pure CompetitionDocument7 pagesPure CompetitionEricka TorresNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Principles of Economics 7Th Asia Pacific Edition by Joshua Gans PDFDocument41 pagesDwnload Full Principles of Economics 7Th Asia Pacific Edition by Joshua Gans PDFfrancisco.landa492100% (21)
- Bonus QuizDocument13 pagesBonus QuizAshley Ann StocktonNo ratings yet
- Economics Sem - 1Document229 pagesEconomics Sem - 1PRASANJIT MISHRANo ratings yet
- Imp Questions To Be Referred - Module 2 & 3Document2 pagesImp Questions To Be Referred - Module 2 & 3Akash NathwaniNo ratings yet
- Examen Ener 2016 (Ing) ADocument4 pagesExamen Ener 2016 (Ing) AManuel GranadosNo ratings yet
- EBEBE4Document6 pagesEBEBE4Porus GhurdeNo ratings yet
- Study of Foreign Trade in InidaDocument11 pagesStudy of Foreign Trade in InidaAYUSHI PATELNo ratings yet
- Monopolistic Comeptition: M. Shivarama Krishna 10HM28Document19 pagesMonopolistic Comeptition: M. Shivarama Krishna 10HM28Powli HarshavardhanNo ratings yet
- Joshua Greene - Public Finance - An International Perspective-World Scientific Publishing (2020)Document538 pagesJoshua Greene - Public Finance - An International Perspective-World Scientific Publishing (2020)Hazel Ann EtiongNo ratings yet
- MBA SyllabusDocument12 pagesMBA SyllabussushmanallapatiNo ratings yet
- Pre & Post EPIRA Implementation Impact To TheDocument8 pagesPre & Post EPIRA Implementation Impact To TheLeo Marcelo Villalba100% (1)
- 8 Management Accounting Practices in ManufacturingDocument69 pages8 Management Accounting Practices in ManufacturingAngel Rose CoralesNo ratings yet
- 4th Semester SyllabusDocument14 pages4th Semester Syllabus507 20L SK DarainNo ratings yet
- Mcomsem Imangerialeconomicpaper101compressedDocument250 pagesMcomsem Imangerialeconomicpaper101compressedGAGAN BHULLARNo ratings yet
- MC 103Document466 pagesMC 103saymtrNo ratings yet
- Abm 506 All NotesDocument207 pagesAbm 506 All Notesch meghanaNo ratings yet
- Unfair Trade PracticesDocument29 pagesUnfair Trade PracticesVasudha FulzeleNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics ECO 502 Sbs - Mba / MSC: Submission Date: 12 March, 2020Document27 pagesManagerial Economics ECO 502 Sbs - Mba / MSC: Submission Date: 12 March, 2020SZANo ratings yet