Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Evidencia 2 - Workshop "Distribution Channels"
Uploaded by
ChechoVegaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Evidencia 2 - Workshop "Distribution Channels"
Uploaded by
ChechoVegaCopyright:
Available Formats
ACTIVIDAD DE APRENDIZAJE 4
EVIDENCIA 2: WORKSHOP “DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS”
PRESENTADO POR:
MARIA YOLANDA PEREZ GOMEZ
SERGIO AUGUSTO VEGA LEGUIZAMO
FASE PLANEACIÓN
SERVICIO NACIONAL DE APRENDIZAJE SENA
NEGOCIACIÓN INTERNACIONAL
2018
Tabla de contenido
1. Lectura primera ......................................................................................................................... 3
2. Responda T si es verdadero o F si es falso. ......................................................................... 4
3. Lectura segunda - Respuestas ................................................................................................ 4
4. Describa en inglés un producto de su preferencia, asígnele una marca y presente,
tanto las características como los costos de dicho producto, luego seleccione un canal y
tipo de estrategia de distribución según la clase de producto. ................................................. 6
Actividad de aprendizaje 4
Evidencia 2: Workshop “Distribution channels”
1. Lectura primera
Susan: Good morning Mr. White.
Mr. White: Good morning, Ms. Susan. Can we start the meeting?
Susan: Of course, Mr. White. I have the options on the board.
Mr. White: That‟s good. Remember, we need to choose the most suitable
distribution strategy for our products.
Susan: We have three strategies: Intensive, exclusive and selective. Intensive
strategy pretends to reach the largest possible number of POS (Point of Sale), but
unfortunately it‟s difficult to control. That‟s because we would have to deal with
many intermediaries.
Mr. White: What about the exclusive strategy?
Susan: It‟s different from the first one. Only it‟s necessary one POS by each
geographic area, no matter if it‟s retailer or wholesaler.
Mr. White: Sounds god to me. And the last one?
Susan: Well, it‟s the selective strategy. It‟s the intermediate strategy between the
other ones.
Mr. White: I don‟t know. I like the first one, but I don‟t know how profitable it is.
Hhhhmmm, well. What do you think?
Susan: Well, I consider that the selective strategy is the best.
Mr. White: You‟re right. Well done.
Susan: Thanks, Mr. White.
2. Responda T si es verdadero o F si es falso.
a. The Company product is a cake.
T ( ) F (x)
b. The meeting objective is to choose the product‟s price.
T ( ) F (x)
c. Susan proposes three distribution strategies.
T (x) F ( )
d. The selective strategy pretend to reach many POS.
T ( ) F (x)
e. The exclusive strategy is difficult to control.
T ( ) F (x)
f. Mr. White chooses the intensive strategy.
T ( ) F (x)
3. Lectura segunda - Respuestas
Economic aspects – understanding of cannel emergence
Economic reasons are the foremost determinant of channel structure. The
emergence of the wide variety of intermediaries can be explained in terms of four
logically related steps in an economic process:
• Intermediaries can increase the efficiency of the process of exchange,
• They align the quantities and assortments produced with the quantities and
assortments consumed,
• They make transactions routine, and
• They facilitate the searching process.
Dependence and cooperation
Each member of a distribution channel is dependent upon the behaviour of other
channel members. Four different approaches have been used to assess
dependence levels in channel relationships:
• The „sales and profit‟ approach, which postulates that the larger the
percentage of sales and profit contributed by the source firm, the greater the
target‟s dependence on the source.
• The „role performance‟ approach, which assesses the firm‟s role
performance in carrying out its role in relation to another company down or up the
channel.
• The „specific assets –offsetting investment‟ approach, which maintains that
offsetting investments help to safeguard the target company against opportunism
by the source.
• The „trust‟ approach, in which a long-term relationship is built on the extent
to which companies trust one another.
Preguntas:
1. The raise of such many intermediaries, are explained in Four steps.
a) Three.
b) Two.
c) Five.
d) Four.
2. Intermediaries make:
a) Process of exchange.
e) Transactions routine.
b) New members.
c) Assortments.
3. A member of a distribution channel depends on:
a) Other channel members.
b) The retailers.
c) The wholesalers.
d) Intermediaries.
4. The „trust‟ approach is based on:
a) The role of another company.
b) The percentage of sales.
c) How much companies trust each other.
d) Channel members.
5. The „role performance‟ approach assesses:
a. The firm‟s role performance.
b. other channel members‟ behavior.
c. Retailers.
d. Wholesalers.
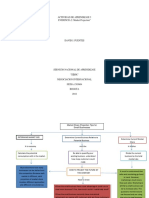
4. Describa en inglés un producto de su preferencia, asígnele una
marca y presente, tanto las características como los costos de
dicho producto, luego seleccione un canal y tipo de estrategia de
distribución según la clase de producto.
You might also like
- Evidencia 2 Workshop Distribution ChannelsDocument6 pagesEvidencia 2 Workshop Distribution ChannelsANDRES PERDOMONo ratings yet
- Actividad de Aprendizaje 4 Name: Juan Sebastian Lozano Guarnizo Evidencia 2: Workshop "Distribution Channels"Document5 pagesActividad de Aprendizaje 4 Name: Juan Sebastian Lozano Guarnizo Evidencia 2: Workshop "Distribution Channels"juan sebastian loano guarnizoNo ratings yet
- Evid 5 Iimportancia de 1 IdiomaDocument2 pagesEvid 5 Iimportancia de 1 IdiomaJuliana Beltran ramirezNo ratings yet
- 2 Market Projection (1) NuevoDocument3 pages2 Market Projection (1) NuevoLeonardo Fabio Franco Area0% (1)
- Evidencia 3 Ensayo Free Trade Agreement FTA Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument4 pagesEvidencia 3 Ensayo Free Trade Agreement FTA Advantages and Disadvantagesmiguel angel ruedaNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 5 Video Presenting Orally A Business Process Improvement PlanDocument9 pagesEvidencia 5 Video Presenting Orally A Business Process Improvement PlanDANIA MELISSA RAMIREZ LOANGONo ratings yet
- Evidencia 2 Market Projection 1Document1 pageEvidencia 2 Market Projection 1Anderson PaezNo ratings yet
- Market Share Projection TipsDocument9 pagesMarket Share Projection TipsDavid J Puentes0% (1)
- Evidencia 4: Sesión virtual sobre preposicionesDocument5 pagesEvidencia 4: Sesión virtual sobre preposicionesJorge NiñoNo ratings yet
- Workshop: Business Plan AnalysisDocument8 pagesWorkshop: Business Plan Analysisdaniel pinzonNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 1 Writing and Essay About Logistics CostsDocument3 pagesEvidencia 1 Writing and Essay About Logistics Costsana yepesNo ratings yet
- Evidence 4: Sesion Virtual "Debate About and Support Your Essay"Document7 pagesEvidence 4: Sesion Virtual "Debate About and Support Your Essay"NiiQoGuerreroNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 4 Sesión Virtual "Debate About and Support Your Essay"Document4 pagesEvidencia 4 Sesión Virtual "Debate About and Support Your Essay"Jheison DiazNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 1 Dialogue Evaluating Product and ServiceDocument7 pagesEvidencia 1 Dialogue Evaluating Product and ServiceJuanc MonsalveNo ratings yet
- Potential Clients SegmentationDocument3 pagesPotential Clients SegmentationOs AndradeNo ratings yet
- FTA Advantages and Disadvantages for Colombia-US TradeDocument4 pagesFTA Advantages and Disadvantages for Colombia-US TradeMARIANo ratings yet
- Evidencia 2 Market Projection 1Document1 pageEvidencia 2 Market Projection 1Alejandro Betancur Agudelo100% (4)
- Evidencia 2: Workshop on products and servicesDocument4 pagesEvidencia 2: Workshop on products and servicesvictor mayaNo ratings yet
- Evidence 9 Ingles Pt14Document7 pagesEvidence 9 Ingles Pt14Paola TorresNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 4 Workshop Assessing Your Supply ChainDocument3 pagesEvidencia 4 Workshop Assessing Your Supply ChainA CORALNo ratings yet
- English Evidence 2 Workshop Distribution ChannelsDocument2 pagesEnglish Evidence 2 Workshop Distribution ChannelsANGELA TOLOZANo ratings yet
- Evidencia 3 Workshop Customer Satisfaction ToolsDocument6 pagesEvidencia 3 Workshop Customer Satisfaction Toolsvaleria sierraNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 2.free Trade Agreement (FTA) Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument14 pagesEvidencia 2.free Trade Agreement (FTA) Advantages and DisadvantagesCarlos RodriguezNo ratings yet
- The Interoperable Economy: Blurring Lines Between Products and ServicesDocument9 pagesThe Interoperable Economy: Blurring Lines Between Products and Serviceszulma sanchezNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 1 Move It - Logistics CostsDocument4 pagesEvidencia 1 Move It - Logistics CostsDahiana ChavesNo ratings yet
- PDF Evidencia 5 Summary Export Import Theory v2 1Document8 pagesPDF Evidencia 5 Summary Export Import Theory v2 1Jesus PavaNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 3 Profit and LossDocument4 pagesEvidencia 3 Profit and LossFelipe CruzNo ratings yet
- ACTIVIDAD DE APRENDIZAJE 12 EVIDENCIA 1 Writing and Essay About Logistics CostsDocument3 pagesACTIVIDAD DE APRENDIZAJE 12 EVIDENCIA 1 Writing and Essay About Logistics CostsStefy QuinteroNo ratings yet
- STEPS TO SUCCESSFUL EXPORTINGDocument4 pagesSTEPS TO SUCCESSFUL EXPORTINGOMAR ANDRES SERNANo ratings yet
- Evidencia 4 Workshop. Assessing Your Supply ChainDocument7 pagesEvidencia 4 Workshop. Assessing Your Supply ChainDaniel Barrera NiñoNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 1Document2 pagesEvidencia 1Jerez DianitaNo ratings yet
- Evidence Safety Rules-1Document2 pagesEvidence Safety Rules-1Juan CrNo ratings yet
- How Incoterms Help Avoid Misunderstanding in International TradeDocument5 pagesHow Incoterms Help Avoid Misunderstanding in International TradeAngela Valeria Royero DelganNo ratings yet
- Export Steps Video: How to Export Goods and Services EffectivelyDocument6 pagesExport Steps Video: How to Export Goods and Services Effectivelyhelmer jerezNo ratings yet
- Taking the Single Market into the 21st Century: Integration of Products and ServicesDocument8 pagesTaking the Single Market into the 21st Century: Integration of Products and ServicesvivianaNo ratings yet
- International Physical Distribution Logistics and IpdDocument13 pagesInternational Physical Distribution Logistics and IpdVera Lucia Montejo SarangoNo ratings yet
- 8 Steps to Segment Markets by Customer CharacteristicsDocument3 pages8 Steps to Segment Markets by Customer Characteristicsvictor mayaNo ratings yet
- Optimize your international physical distribution costsDocument2 pagesOptimize your international physical distribution costsLeidy Pineda100% (1)
- Evidencia 5 Workshop Using Verbs To Build Customer Satisfaction ToolsDocument3 pagesEvidencia 5 Workshop Using Verbs To Build Customer Satisfaction Toolsyesid lopezNo ratings yet
- Actividad de Aprendizaje 1 Aproximación A Los Diagnósticos Del Complejo de Comercialización de La Empresa IndustrialDocument2 pagesActividad de Aprendizaje 1 Aproximación A Los Diagnósticos Del Complejo de Comercialización de La Empresa IndustrialLuis Carlos Aceros50% (2)
- Evidencia Profit and LossDocument8 pagesEvidencia Profit and LossGina GinaNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 1 Fase Analisis - Sena Neg Intern Cesar Ingles Markenting IndustrialDocument2 pagesEvidencia 1 Fase Analisis - Sena Neg Intern Cesar Ingles Markenting IndustrialRobinson RiveraNo ratings yet
- Learning Session on Distribution Channels PrepositionsDocument2 pagesLearning Session on Distribution Channels PrepositionsJOHANo ratings yet
- Actividad SenaDocument5 pagesActividad SenaPaola MarquezNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 5 Summary Export Import Theory V2Document6 pagesEvidencia 5 Summary Export Import Theory V2Alexis Montoya ObandoNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 2 Workshop Distribution ChannelsDocument6 pagesEvidencia 2 Workshop Distribution ChannelsmonicaNo ratings yet
- Actividad de Aprendizaje 14 Ramiro Roldan Evidencia 3:: Workshop "Customer Satisfaction Tools"Document4 pagesActividad de Aprendizaje 14 Ramiro Roldan Evidencia 3:: Workshop "Customer Satisfaction Tools"ramiro roldanNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 1. SummaryDocument1 pageEvidencia 1. SummaryLina González100% (1)
- Evidence 9 Workshop Cultural Awareness As A Key Element To NegotiateDocument8 pagesEvidence 9 Workshop Cultural Awareness As A Key Element To NegotiateMilton EscobarNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 6 Workshop "Telling Where Is It".Document11 pagesEvidencia 6 Workshop "Telling Where Is It".Milton EscobarNo ratings yet
- P16 7Document6 pagesP16 7heywinmenesesNo ratings yet
- Aa12 Evidencia 4 Sesión Virtual Debate About and Support Your EssayDocument3 pagesAa12 Evidencia 4 Sesión Virtual Debate About and Support Your EssayMARIA ELISANo ratings yet
- Evidencia 5 Summary Export Import Theory V2Document7 pagesEvidencia 5 Summary Export Import Theory V2Lilleyra RomeroNo ratings yet
- English 3 - EJE 1 - Week 2Document3 pagesEnglish 3 - EJE 1 - Week 2Daniel Ossa100% (1)
- Evidencia 6 Segmentation Describing Potential ClientsDocument5 pagesEvidencia 6 Segmentation Describing Potential ClientsSergio andres Espinosa alfordNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 5 - Summary Export Import TheoryDocument7 pagesEvidencia 5 - Summary Export Import Theoryjenny bernalNo ratings yet
- Rosa Liliana Gómez Guevara Ficha 1667915: Customer Satisfaction Is The Ultimate Goal. There's No HigherDocument5 pagesRosa Liliana Gómez Guevara Ficha 1667915: Customer Satisfaction Is The Ultimate Goal. There's No HigherLiliana GomezNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 2 Workshop Distribution ChannelsDocument8 pagesEvidencia 2 Workshop Distribution ChannelsJASBLEIDER SANTIAGO MIRANDANo ratings yet
- Actividad 4 Evidencia 2Document7 pagesActividad 4 Evidencia 2Lina Marcela Molina CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Distribution Channels and Strategies for Video Game ConsolesDocument6 pagesDistribution Channels and Strategies for Video Game ConsolesMiguel GamezNo ratings yet
- Colombian Exports Fell 1% in Q1 Due to Lower Coal Shipments AbroadDocument4 pagesColombian Exports Fell 1% in Q1 Due to Lower Coal Shipments AbroadChechoVegaNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 6 - Video "Steps To Exports"Document7 pagesEvidencia 6 - Video "Steps To Exports"ChechoVegaNo ratings yet
- Survey Shows Lemon Export PotentialDocument4 pagesSurvey Shows Lemon Export PotentialChechoVegaNo ratings yet
- Alternativas Brindadas para El Desarrollo de La Etapa Productiva Ofrecidas Por El SENADocument2 pagesAlternativas Brindadas para El Desarrollo de La Etapa Productiva Ofrecidas Por El SENAChechoVegaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae SummaryDocument5 pagesCurriculum Vitae SummaryChechoVegaNo ratings yet
- Actividad 8 Evidencia 11Document2 pagesActividad 8 Evidencia 11ChechoVega0% (2)
- Curriculum Vitae SummaryDocument5 pagesCurriculum Vitae SummaryChechoVegaNo ratings yet
- IFRS 17 Risk Adjustment For Non-Financial Risk For Life and Health Insurance ContractsDocument34 pagesIFRS 17 Risk Adjustment For Non-Financial Risk For Life and Health Insurance ContractsaljdummyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 MafinDocument36 pagesChapter 9 MafinReymilyn SanchezNo ratings yet
- Progress Test 5 (Units 13-15) : Complete All Seven Sections. There Are Seventy Marks in TotalDocument7 pagesProgress Test 5 (Units 13-15) : Complete All Seven Sections. There Are Seventy Marks in TotalIlia GviniashviliNo ratings yet
- Richard CuretonDocument24 pagesRichard CuretonHayk HambardzumyanNo ratings yet
- What Music Really Means To ChildrenDocument5 pagesWhat Music Really Means To ChildrenMara Sofia ValenteNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Content and Contextual Analysis of Selected Primary andDocument41 pagesModule 2 - Content and Contextual Analysis of Selected Primary andAngelica CaldeoNo ratings yet
- Carb-Based-Dll No. 2 - 4th Qtr.Document5 pagesCarb-Based-Dll No. 2 - 4th Qtr.Kathrene Santos RiveraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, 12 Curve Tracing and EnvelopeDocument37 pagesChapter 11, 12 Curve Tracing and EnvelopeNitish PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Life and Works of Jose RizalDocument5 pagesLife and Works of Jose Rizalnjdc1402No ratings yet
- To Sir With LoveDocument2 pagesTo Sir With LoveRamita Udayashankar100% (2)
- Adina CFD FsiDocument481 pagesAdina CFD FsiDaniel GasparinNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesLiterature Reviewapi-549241187No ratings yet
- Christian Storytelling EvaluationDocument3 pagesChristian Storytelling Evaluationerika paduaNo ratings yet
- BCOM 302 BookDocument179 pagesBCOM 302 BookHitanshi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- My Manifesto - Huma 1100Document2 pagesMy Manifesto - Huma 1100api-490833029No ratings yet
- Analysing Context CluesDocument2 pagesAnalysing Context CluesSwathiNo ratings yet
- 600 2 Sub-Zero Built-In Series Refrigerator Service ManualDocument188 pages600 2 Sub-Zero Built-In Series Refrigerator Service Manual911servicetechNo ratings yet
- Lung BiopsyDocument8 pagesLung BiopsySiya PatilNo ratings yet
- The Role of Christian Education in Socia Group 6Document6 pagesThe Role of Christian Education in Socia Group 6Ṭhanuama BiateNo ratings yet
- Adjustment DisordersDocument2 pagesAdjustment DisordersIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Why Narcissists Need You To Feel Bad About Yourself - Psychology TodayDocument51 pagesWhy Narcissists Need You To Feel Bad About Yourself - Psychology Todaytigerlo75No ratings yet
- Phantom Susan KayDocument379 pagesPhantom Susan Kaytheeyeofthemoon100% (9)
- Foundation of Special and Inclusive EducationDocument25 pagesFoundation of Special and Inclusive Educationmarjory empredoNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Philippine Arts From The RegionsDocument29 pagesContemporary Philippine Arts From The RegionsDina Ilagan50% (2)
- Sengoku WakthroughDocument139 pagesSengoku WakthroughferdinanadNo ratings yet
- Intro To Flight (Modelling) PDFDocument62 pagesIntro To Flight (Modelling) PDFVinoth NagarajNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION Quali Observation ReportDocument2 pagesINTRODUCTION Quali Observation Reportmira hamzahNo ratings yet
- ViscosityDocument7 pagesViscositykiran2381No ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 5090/61 October/November 2017Document6 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 5090/61 October/November 2017Zarish NoorNo ratings yet
- 2 NDDocument52 pages2 NDgal02lautNo ratings yet
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0From EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0No ratings yet
- Lean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation, 2nd EdFrom EverandLean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation, 2nd EdRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (17)
- Small Business For Dummies: 5th EditionFrom EverandSmall Business For Dummies: 5th EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- SYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsFrom EverandSYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (48)
- How to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffFrom EverandHow to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (61)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't (Rockefeller Habits 2.0 Revised Edition)From EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't (Rockefeller Habits 2.0 Revised Edition)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Impact Networks: Create Connection, Spark Collaboration, and Catalyze Systemic ChangeFrom EverandImpact Networks: Create Connection, Spark Collaboration, and Catalyze Systemic ChangeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Systems Thinking: A Guide to Strategic Planning, Problem Solving, and Creating Lasting Results for Your BusinessFrom EverandSystems Thinking: A Guide to Strategic Planning, Problem Solving, and Creating Lasting Results for Your BusinessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (80)
- Sales Pitch: How to Craft a Story to Stand Out and WinFrom EverandSales Pitch: How to Craft a Story to Stand Out and WinRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)From EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- The Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerFrom EverandThe Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (121)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (104)
- How to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffFrom EverandHow to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantFrom EverandBlue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (387)
- Amp It Up: Leading for Hypergrowth by Raising Expectations, Increasing Urgency, and Elevating IntensityFrom EverandAmp It Up: Leading for Hypergrowth by Raising Expectations, Increasing Urgency, and Elevating IntensityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (50)
- HBR Guide to Setting Your StrategyFrom EverandHBR Guide to Setting Your StrategyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Tax-Free Wealth: How to Build Massive Wealth by Permanently Lowering Your TaxesFrom EverandTax-Free Wealth: How to Build Massive Wealth by Permanently Lowering Your TaxesNo ratings yet
- The 10X Rule: The Only Difference Between Success and FailureFrom EverandThe 10X Rule: The Only Difference Between Success and FailureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (289)
- Elevate: The Three Disciplines of Advanced Strategic ThinkingFrom EverandElevate: The Three Disciplines of Advanced Strategic ThinkingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Strategic Roadmap: An Intentional, Memorable Approach to Achieving SuccessFrom EverandStrategic Roadmap: An Intentional, Memorable Approach to Achieving SuccessNo ratings yet
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Business Model InnovationFrom EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Business Model InnovationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Understanding Michael Porter: The Essential Guide to Competition and StrategyFrom EverandUnderstanding Michael Porter: The Essential Guide to Competition and StrategyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (24)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Managing Yourself, Vol. 2From EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Managing Yourself, Vol. 2Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- The One-Hour Strategy: Building a Company of Strategic ThinkersFrom EverandThe One-Hour Strategy: Building a Company of Strategic ThinkersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- New Sales. Simplified.: The Essential Handbook for Prospecting and New Business DevelopmentFrom EverandNew Sales. Simplified.: The Essential Handbook for Prospecting and New Business DevelopmentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Strategic Risk Management: New Tools for Competitive Advantage in an Uncertain AgeFrom EverandStrategic Risk Management: New Tools for Competitive Advantage in an Uncertain AgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)