Professional Documents
Culture Documents
I.-NCP John Richmond Lacaden
Uploaded by
Richmond Lacaden100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
128 views3 pagesncp about risk aspiration
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentncp about risk aspiration
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
128 views3 pagesI.-NCP John Richmond Lacaden
Uploaded by
Richmond Lacadenncp about risk aspiration
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
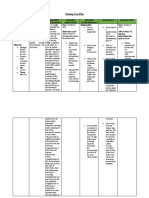
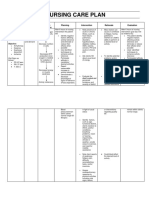
NURSING CARE PLAN
Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Explanation
Objective: Risk for Aspiration of stomach After 4 hours of Nursing Identify at risk To determine After 4 hour of nursing
DAT with Aspiration contents into the Intervention the client will: client according when intervention goal was met
SAP lungs is a serious Experience no to condition or observation as evidence by:
Cleft lip complication that can aspiration as disease process and/or Experienced no
Palate cause pneumonia evidence by as listed in risk interventions aspiration as
Cough and result in the noiseless factors. may be evidence by
following clinical respirations; clear required. noiseless
picture: tachycardia, breath sounds; Assess for age- respirations; clear
dyspnea, central clear, odorless related risk Aspiration breath sounds;
cyanosis,hypotension secretions. factors pneumonia is clear, odorless
, and finally death. It Identify causative potentiating risk more common secretions.
can occur when the risk factors. of aspiration (e.g. in extremely Identified
protective airway Demonstrate Premature infant, young or old causative risk
reflexes is absent or techniques to elderly infirm) patients and factors.
decreased due to prevent and/or commonly Demonstrated
medical conditions correct aspiration. occurs in techniques and
like cleft lip and Patient is free from individuals prevented and/or
palate and use of any signs of with showed correct
devices like aspiration and the chronically aspiration.
endotracheal risk of aspiration is impaired air The Patient has
intubation. In addition decreased. Note client’s level way defense no signs of
to this, oropharyngeal of mechanism. aspiration and the
secretions, or solids consciousness, risk of aspiration
or fluids could also awareness of As was decreased
enter surroundings and impairments in
tracheobronchial cognitive these disease
passages due to function. increase
decreased coughing client’s risk of
gag, and epiglottis aspiration
reflexes. Prevention owing to the
is the primary goal inability to
when caring for cough or
aspiration. Evidence swallow well
confirms that one of and/or the
the main preventive presence of an
measures for Determine the artificial
aspiration is placing presence of airway,
at risk patients in a neuromuscular mechanical
semi recumbent disorders, noting ventilation,
position. Other muscles groups and/or tube
measures are involved degree feeding.
compensating for of impairment
absent reflexes, and whether they Helps to
assessing feeding are of an acute or determine
tube placement, progressive effectiveness
identifying delayed nature. of protective
stomach emptying. mechanisms.
And managing effects Assess client’s
of prolonged ability to swallow
intubation. and strength of
gag reflex or
cough reflex.
Evaluate
amount/consisten
cy of secret Client with a
Observe for neck head/neck
and facial surgery or a
edema. tracheal/bronc
hial injury is at
Note particular risk
administration of for airway
enteral feeding obstruction
and an
inability to
handle
secretions.
You might also like
- Risk For AspirationDocument2 pagesRisk For AspirationGly Mtg100% (6)
- Risk For Aspiration:: Pathophysiolo GyDocument7 pagesRisk For Aspiration:: Pathophysiolo GySandra GabasNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance PediaDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance PediaFaith CalimlimNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Short TermDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Short TermChi SabbalucaNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For InfectionDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For InfectionRolan BulandosNo ratings yet
- University of The East: Assessmen T Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesUniversity of The East: Assessmen T Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationPATRICIA JEANNE JABIANNo ratings yet
- Coran - PS, 7th - Chapter 65 - Lesions of The Larynx, Trachea, and Upper AirwayDocument18 pagesCoran - PS, 7th - Chapter 65 - Lesions of The Larynx, Trachea, and Upper AirwayLuis AvalosNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationNichol John MalabananNo ratings yet
- NCP ManenDocument5 pagesNCP ManenArdiene Shallouvette GamosoNo ratings yet
- NCP, Drug StudyDocument9 pagesNCP, Drug StudyTresha CaliboNo ratings yet
- Risk For Infection Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageRisk For Infection Pneumonia Nursing Care PlantososNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Tract Infection URTI - PPTX GROUP 2 BSN 3CDocument22 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract Infection URTI - PPTX GROUP 2 BSN 3CIren RamosoNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - NCPDocument10 pagesGroup 1 - NCPArdiene Shallouvette GamosoNo ratings yet
- NCP Not FinishDocument3 pagesNCP Not FinishJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Risk For Infection - NCPDocument3 pagesRisk For Infection - NCPHamil BanagNo ratings yet
- NCP PotentialDocument2 pagesNCP PotentialKathleenJoyGalAlmasinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanJehan Lois QuinesNo ratings yet
- Checklist Using Nasopharengeal and Oropharengeal SuctioningDocument4 pagesChecklist Using Nasopharengeal and Oropharengeal SuctioningKristine Louise JavierNo ratings yet
- Iac RT ObstructionDocument7 pagesIac RT Obstructionia.sumbillaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjectivecammel ramos100% (1)
- Ob2 Sas 26Document9 pagesOb2 Sas 26????No ratings yet
- NCP-Combate-Risk For AspirationDocument2 pagesNCP-Combate-Risk For AspirationKayelyn-Rose CombateNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENTDocument6 pagesASSESSMENTZerimar Adawe DulnuanNo ratings yet
- Study of Illness Condition (Sic) : Assessment Anatomy Physiology Pathophysiolo GY AnalysisDocument5 pagesStudy of Illness Condition (Sic) : Assessment Anatomy Physiology Pathophysiolo GY AnalysisKurt Andrew CarpioNo ratings yet
- SIC (Carpio, Kurt Andrew)Document5 pagesSIC (Carpio, Kurt Andrew)Kurt Andrew CarpioNo ratings yet
- Risk For AspirationDocument11 pagesRisk For AspirationSanket TelangNo ratings yet
- 5 MED II 1 - PneumoniaDocument11 pages5 MED II 1 - PneumoniaDeann RoscomNo ratings yet
- Dino File 2Document6 pagesDino File 2Jhade Danes BalanlayNo ratings yet
- Risk For Aspiration: Risk For Aspiration: at Risk For Entry of Gastrointestinal Secretions, Oropharyngeal SecretionDocument6 pagesRisk For Aspiration: Risk For Aspiration: at Risk For Entry of Gastrointestinal Secretions, Oropharyngeal SecretionAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System: Basco, Kimberly BSN-2Document5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System: Basco, Kimberly BSN-2Cxazandra Kaith CasasNo ratings yet
- IPPA SampleDocument28 pagesIPPA Samplekimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (2)
- Performance Task # 9Document6 pagesPerformance Task # 9Aileen Reign MalonzoNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Activity (NCP, Drug)Document25 pagesGroup 2 - Activity (NCP, Drug)christelNo ratings yet
- Aspiration Pneumonitis and Aspiration Pneumonia in Neurologically Impaired ChildrenDocument5 pagesAspiration Pneumonitis and Aspiration Pneumonia in Neurologically Impaired ChildrenYuliaAntolisNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Nursing Care Plans - 10 Nursing Diagnosis - NurseslabsDocument34 pagesPneumonia Nursing Care Plans - 10 Nursing Diagnosis - NurseslabsMenard Velasco100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Mucus Production COPDDocument7 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Mucus Production COPDMa. Elaine Carla Tating67% (3)
- NCP Acute BronchitisDocument9 pagesNCP Acute BronchitisCarl Simon CalingacionNo ratings yet
- System Disorder - Cystic FibrosisDocument1 pageSystem Disorder - Cystic Fibrosisjorge herreraNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument20 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKen BaxNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Health: Laguna State Polytechnic UniversityDocument5 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Health: Laguna State Polytechnic UniversityEdelrose LapitanNo ratings yet
- New Update 35 Laryngospasm PDFDocument4 pagesNew Update 35 Laryngospasm PDFRobertaNo ratings yet
- University of The East: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesUniversity of The East: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationPATRICIA JEANNE JABIANNo ratings yet
- 5 NCP LaryngectomyDocument29 pages5 NCP LaryngectomyICa MarlinaNo ratings yet
- NCP For Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesNCP For Pleural EffusionLilian Linogao71% (7)
- Name and Classification of DrugDocument7 pagesName and Classification of DrugMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- ABADINGO-Pedia Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesABADINGO-Pedia Nursing Care PlanAndrea Abadingo100% (1)
- Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center Inc.: College of NursingDocument6 pagesRamon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center Inc.: College of NursingJona Joyce JunsayNo ratings yet
- 5 Bronchiolitis Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsDocument14 pages5 Bronchiolitis Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsAnnapoorna SHNo ratings yet
- Chona NCP 1Document5 pagesChona NCP 1Jan Mark SotoNo ratings yet
- Cebu Institute of Technology - University: Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesCebu Institute of Technology - University: Nursing Care PlanSergiNo ratings yet
- 118 ReviewerDocument6 pages118 ReviewerAna Rose Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Palileo NCPDocument5 pagesPalileo NCPAeron PalileoNo ratings yet
- Pulmo Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesPulmo Nursing Care PlanVincent RoyNo ratings yet
- NAME: Kristyn Joy D. Atangen DATE: Oct. 7, 2019: Subjective: DXDocument2 pagesNAME: Kristyn Joy D. Atangen DATE: Oct. 7, 2019: Subjective: DXTyn TynNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: Romero, Pamela Sanchez, DianeDocument13 pagesPneumonia: Romero, Pamela Sanchez, DianePam RomeroNo ratings yet
- NUR 103A RLE Learning Activity - PneumothoraxDocument8 pagesNUR 103A RLE Learning Activity - PneumothoraxLaica & AivanNo ratings yet
- School of Health Sciences Bayombong, Nueva Vizcaya 1 Semester S.Y 2015-2016 NCM 106-RLE Skills LaboratoryDocument1 pageSchool of Health Sciences Bayombong, Nueva Vizcaya 1 Semester S.Y 2015-2016 NCM 106-RLE Skills LaboratoryRichmond LacadenNo ratings yet
- RHD PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesRHD PathophysiologyRichmond LacadenNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 Final ExamDocument5 pagesNCM 103 Final ExamRichmond LacadenNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseXtiaR85% (13)
- Oxygenation NCM 103Document10 pagesOxygenation NCM 103Richmond LacadenNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 Final ExamDocument10 pagesNCM 103 Final ExamRichmond LacadenNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 Final ExamDocument5 pagesNCM 103 Final ExamRichmond LacadenNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationRichmond LacadenNo ratings yet
- Ineffective AirwayDocument2 pagesIneffective AirwayRichmond LacadenNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 Final ExamDocument10 pagesNCM 103 Final ExamRichmond LacadenNo ratings yet
- AMK DiseasesDocument384 pagesAMK Diseaseshanif ahmadNo ratings yet
- Impact Vap Bundle 2017Document6 pagesImpact Vap Bundle 2017Elisya KharuniawatiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Risk For Ineffective Breathing Pattern IndependentDocument5 pagesNursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Risk For Ineffective Breathing Pattern Independentjeff_scarlet26No ratings yet
- Dr. R V S N Sarma., MD., MSC., (Canada) Consultant Physician & Chest Specialist Visit Us At: WWW - Drsarma.InDocument76 pagesDr. R V S N Sarma., MD., MSC., (Canada) Consultant Physician & Chest Specialist Visit Us At: WWW - Drsarma.InAndry Wahyudi AgusNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Eval ExamDocument11 pagesNCM 112 Eval ExamMartin T Manuel100% (1)
- EDGE CEOMrngBrief 16septDocument27 pagesEDGE CEOMrngBrief 16septZulfah Nur RachmaniaNo ratings yet
- G9 Week 1-2 WorksheetDocument49 pagesG9 Week 1-2 WorksheetMarjorie Nebalasca GalongNo ratings yet
- Pre Test and Post TestDocument27 pagesPre Test and Post TestMATALANG GRACENo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Adult With Dyspnea in The Emergency DepartmentDocument16 pagesEvaluation of The Adult With Dyspnea in The Emergency DepartmentmericenteNo ratings yet
- Scale For Ranking Health Conditions and Problems in Family Nursing PracticeDocument3 pagesScale For Ranking Health Conditions and Problems in Family Nursing PracticeDjan Kurvie Valencerina100% (1)
- How To RecoverDocument3 pagesHow To RecoverSterr LiingNo ratings yet
- Short White CoatDocument228 pagesShort White Coategnicks100% (6)
- CHN 145 QuestionsDocument46 pagesCHN 145 QuestionsAlyssaGrandeMontimorNo ratings yet
- First Page PDFDocument1 pageFirst Page PDFBukola Christianah AkinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 RS12015 PDFDocument136 pagesLecture 3 RS12015 PDFDaniel AshooriNo ratings yet
- Childhood Pneumonia A Literature ReviewDocument20 pagesChildhood Pneumonia A Literature ReviewJeveraNo ratings yet
- Classification: Community-Acquired PneumoniaDocument15 pagesClassification: Community-Acquired PneumoniaHASLINDANo ratings yet
- BRONCHOPNEUMONIADocument18 pagesBRONCHOPNEUMONIAMANEESH MANINo ratings yet
- Zinnat PIDocument10 pagesZinnat PIfsdfNo ratings yet
- Ethics SDocument40 pagesEthics SDr. XNo ratings yet
- A. Retrospective Cohort Study B. Cross-Sectional Study C. D. Prospective Cohort StudyDocument19 pagesA. Retrospective Cohort Study B. Cross-Sectional Study C. D. Prospective Cohort StudyTiến MinhNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Case StudyDocument21 pagesPneumonia Case StudyEmel Brant Jallores0% (1)
- Recall 2022 Dec 14Document5 pagesRecall 2022 Dec 14Nimer Abdelhadi AliNo ratings yet
- Community Evaluation Exam 2022Document11 pagesCommunity Evaluation Exam 2022Ryan-Jay Abolencia100% (1)
- Pediatric Chest X-RayDocument61 pagesPediatric Chest X-Rayyi ngNo ratings yet
- Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionDocument21 pagesLower Respiratory Tract InfectionJohn Vincent Dy OcampoNo ratings yet
- Reo VirusesDocument17 pagesReo VirusesLaura Anghel-MocanuNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory InfectionDocument15 pagesAcute Respiratory InfectionmNo ratings yet
- ICDXDocument43 pagesICDXAris NurzamzamiNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Report: Patient Name: Ritesh Sharma RITSF30101992 0202UB003850Document2 pagesDiagnostic Report: Patient Name: Ritesh Sharma RITSF30101992 0202UB003850Dhyan VigyanNo ratings yet