Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brochure Math
Uploaded by
api-4296875660 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
117 views2 pagesOriginal Title
brochure math
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
117 views2 pagesBrochure Math
Uploaded by
api-429687566Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
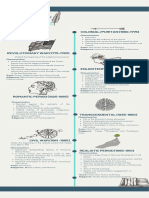
Mathematics as a Language Culturally and
Mathematics usually known as the Universal Lingustically Diverse
Language yet it is not the case. The students.
procedures and symbols used in math are not
universal but rather culturally determine. Our country is composed of people all around
the world. In the USA the percentage of
How would you as a teacher
Culturally and Diverse students keeps
approach a student using a different
increasing. From 2012-2013 9.2 % or about
method to solve a mathematic
4.4 million students were in ELL programs in
problem?
public school and about almost 18 million are
Latinos. As teachers we have to be responsive
Will you require the students to show their
to students’ backgrounds, experiences,
steps (disregarding the way they learned it)?
cultural perspectives, traditions and
Will you ask students to elaborate on how they knowledge.
did it?
Will you have students show other students
their way of thinking?
Aspect of Culturally Responsive Instruction
Communicate high expectations.
Make content relevant.
Attend to students’ mathematical
identities.
Ensure shared power.
Make Content Relevent
Think about the Mathematics: is it
presented meaningfully and conected
to the other content?
Select Contexts: mathematics
presented connects to
Teaching Culturally
relevant/authentic situations in
students’ lives?
and Linguistically
Diverse Students
Melissa Gallegos
Mathematical Identity
`
The students’ state of mind towards math
and sense of competence as a learner and
the contribution the student will have in
the mathematics classrooms.
Build Background
Ensure Shared Power Knowledge
The teacher plays a major role in
establishing and distributing power,
whether intentional or not. The way the
groups are assign, seat students, and call
on students sends clear messages about
who has power in the classroom.
Strategies Academic Vocabulary
Reflective Questions for Teaching It make take ELL students as many as seven
years to learn academic language. Teachers
1. Introduce the task (the Before phase). should value a student’s native language it is
one of the ways you value his or her cultural
2. Work on the task (the During phase). heritage
Content and Language Objectives
3. Debrief and discuss the task and the
mathematics (the After phase). Students will analyze properties and
attributes of three-dimensional
Formative Assessmen solids.(mathematics)
Throughout lesson and unit
Students will describe in writing and
speaking a similarity and a difference
Provide Accommodation between two different solids. (language
and mathematics)
Select Tasks with Multiple Entry and
Exit Points Limit Linguistic Load
You might also like
- Convert Between Fractions, Decimals, and PercentDocument3 pagesConvert Between Fractions, Decimals, and PercentAmy LiNo ratings yet
- DEWA Electrical Installation Regulations Section 1 OverviewDocument123 pagesDEWA Electrical Installation Regulations Section 1 Overviewsiva_nagesh_280% (5)
- GooglepreviewDocument69 pagesGooglepreviewtarunchatNo ratings yet
- American Literature TimelineDocument2 pagesAmerican Literature TimelineJoanna Dandasan100% (1)
- VV016042 Service Manual OS4 PDFDocument141 pagesVV016042 Service Manual OS4 PDFCamilo Andres Uribe Lopez100% (1)
- Lesson Plan - PolynomialsDocument10 pagesLesson Plan - PolynomialsgrvchikNo ratings yet
- HOW To Use Jmeter To Load Test T24Document27 pagesHOW To Use Jmeter To Load Test T24Hiếu KoolNo ratings yet
- Peptan - All About Collagen Booklet-1Document10 pagesPeptan - All About Collagen Booklet-1Danu AhmadNo ratings yet
- Probability Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesProbability Lesson Planhix8073No ratings yet
- Relations and Functions Lesson Plan-2Document4 pagesRelations and Functions Lesson Plan-2api-524919792No ratings yet
- CHECK LIST FOR HIGH RISE BUILDING NOCDocument15 pagesCHECK LIST FOR HIGH RISE BUILDING NOCNedunuri.Madhav Murthy100% (2)
- Lesson 3. Lesson Plan Solving Quadratic Equations by FactoringDocument2 pagesLesson 3. Lesson Plan Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoringcarla mae navarroNo ratings yet
- Strategicmanagement Finalpaper 2ndtrisem 1819Document25 pagesStrategicmanagement Finalpaper 2ndtrisem 1819Alyanna Parafina Uy100% (1)
- Surface Area - LessonDocument3 pagesSurface Area - Lessonapi-257911767No ratings yet
- Shaping the College Curriculum: Academic Plans in ContextFrom EverandShaping the College Curriculum: Academic Plans in ContextRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- 1detailed Lesson Plan - Solving ProblemsDocument5 pages1detailed Lesson Plan - Solving ProblemsKhim ChavezNo ratings yet
- SLM Math9 L4 Q2Document19 pagesSLM Math9 L4 Q2Roxas Marry GraceNo ratings yet
- Blank Lesson Plan Template 2021Document3 pagesBlank Lesson Plan Template 2021api-598461723No ratings yet
- Tandaay National High School Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 9 January 21, 2016 I. Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesTandaay National High School Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 9 January 21, 2016 I. Learning ObjectivesOmixam OdagrebNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Mathematics Lesson Plan (March 2022)Document7 pagesGrade 3 Mathematics Lesson Plan (March 2022)Trudy SmithNo ratings yet
- Activity PlanDocument13 pagesActivity Planapi-208363067No ratings yet
- High School Sets LessonDocument13 pagesHigh School Sets Lessonapi-273147283100% (2)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsRenderizzah FloraldeNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts and Terms in GeometryDocument17 pagesBasic Concepts and Terms in GeometryEderlyn LeuterioNo ratings yet
- Evaluate Algebraic ExpressionsDocument5 pagesEvaluate Algebraic ExpressionsDonna Joyce MagdaongNo ratings yet
- Quadrilaterals Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesQuadrilaterals Lesson Planapi-194359519No ratings yet
- Lesson Plans Ed Tpa Task 1Document6 pagesLesson Plans Ed Tpa Task 1api-218854185No ratings yet
- Kothari International School Math Lesson Plan for OctoberDocument1 pageKothari International School Math Lesson Plan for OctoberPooja SharmaNo ratings yet
- LP Parallel Lines Feb 2018Document9 pagesLP Parallel Lines Feb 2018Thess MiraflorNo ratings yet
- Sample Lesson Plan 1Document3 pagesSample Lesson Plan 1siargao_english2918100% (7)
- Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesLesson PlanCher JhetsNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Grade 10Document20 pagesUnit Plan Grade 10api-381868432No ratings yet
- Exponents Lesson Plan 3Document4 pagesExponents Lesson Plan 3api-317906729No ratings yet
- Maths - Lesson Plan 3Document1 pageMaths - Lesson Plan 3api-427319867100% (1)
- Sat Lesson Plan BiconditionalDocument6 pagesSat Lesson Plan Biconditionalapi-526889056No ratings yet
- Math Lesson on Direct VariationDocument2 pagesMath Lesson on Direct VariationCaren Pogoy ManiquezNo ratings yet
- Math 7 quarterly specsDocument5 pagesMath 7 quarterly specsArianne Joy Villamor MallariNo ratings yet
- EE 333 Third Grade Introduction To Multiplication Unit Lesson PlanDocument27 pagesEE 333 Third Grade Introduction To Multiplication Unit Lesson Plancdavila2100% (1)
- 9.lesson Plan Application of Special RightDocument6 pages9.lesson Plan Application of Special RightAeron TamaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Applications of Right TrianglesDocument2 pagesLesson Plan - Applications of Right Trianglesapi-448318028No ratings yet
- 16.illustrate Systems of Linear EquationsDocument3 pages16.illustrate Systems of Linear EquationsMiriam Galicia100% (1)
- Solving One-Step InequalitiesDocument7 pagesSolving One-Step Inequalitiesapi-534102323No ratings yet
- RATIONAL NUMBERS Lesson Plan PDFDocument3 pagesRATIONAL NUMBERS Lesson Plan PDFHaribabu SunkaraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8.6Document3 pagesLesson 8.6Lewis Miranda100% (1)
- Ubd Final MathDocument6 pagesUbd Final Mathapi-296454132No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (Hubby)Document5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (Hubby)Joem'z Burlasa-Amoto Esler-DionaldoNo ratings yet
- Bar Graph Lesson Plan - Sig AssignDocument2 pagesBar Graph Lesson Plan - Sig Assignapi-383456990No ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics Grade8 Quarter4-IVc (Palawan Division)Document5 pagesDLL Mathematics Grade8 Quarter4-IVc (Palawan Division)Mark Kiven MartinezNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Rat DenomDocument1 pageLesson Plan Rat DenomJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Sharing To A RatioDocument1 pageLesson Plan Sharing To A RatioJonathan Robinson100% (1)
- LESSON PLAN IN Probability of Simple Events: March 2019Document9 pagesLESSON PLAN IN Probability of Simple Events: March 2019Tintin SaintsNo ratings yet
- Dance Dance Transversal LPDocument4 pagesDance Dance Transversal LPapi-340226547No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Lesson PlanDocument17 pagesGrade 9 Lesson PlanSamuel BaunNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Fundamental TheoremDocument2 pagesLesson Plan - Fundamental Theoremapi-296220127No ratings yet
- Common Core State StandardsDocument7 pagesCommon Core State Standardsapi-343459926No ratings yet
- 7 - Slope-Intercept Formal Lesson PlanDocument2 pages7 - Slope-Intercept Formal Lesson Planapi-304704633No ratings yet
- m201 Math Lesson Plan 4 1Document4 pagesm201 Math Lesson Plan 4 1api-384966224No ratings yet
- Congruent and Similar Figures PlanDocument3 pagesCongruent and Similar Figures Planapi-235840787No ratings yet
- 7es DLP For Math8Document7 pages7es DLP For Math8Trisha Mae BanalnalNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 4 MathematicsDocument8 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 4 MathematicsDiane joy ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Final Demonstration LPDocument8 pagesFinal Demonstration LPEdmond BajadoNo ratings yet
- QuestionnairesDocument3 pagesQuestionnairesPatricia TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Genesis Limoico Lesson ExemplarDocument2 pagesGenesis Limoico Lesson ExemplarNoci Nusa OciomilNo ratings yet
- IV-Day 9Document4 pagesIV-Day 9Nicole TanyagNo ratings yet
- Similarity in The Real World - Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesSimilarity in The Real World - Lesson Planapi-215449942No ratings yet
- WK7 Largado G7 DLLDocument7 pagesWK7 Largado G7 DLLMark A. SolivaNo ratings yet
- Ratios and Rates Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesRatios and Rates Lesson Planapi-284522310No ratings yet
- Schedule FinalDocument6 pagesSchedule FinalJamora ManilynNo ratings yet
- MUM202001007 - 300 TR Price BOQ ChillerDocument4 pagesMUM202001007 - 300 TR Price BOQ ChillerB DASNo ratings yet
- (Salim Ross) PUA 524 - Introduction To Law and The Legal System (Mid Term)Document4 pages(Salim Ross) PUA 524 - Introduction To Law and The Legal System (Mid Term)Salim RossNo ratings yet
- Food 8 - Part 2Document7 pagesFood 8 - Part 2Mónica MaiaNo ratings yet
- Class 9 - Half Yearly Examination - 2023 - Portions and BlueprintDocument16 pagesClass 9 - Half Yearly Examination - 2023 - Portions and BlueprintSUBRAMANI MANOHARANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-The Indian Contract Act, 1872, Unit 1-Nature of ContractsDocument10 pagesChapter 1-The Indian Contract Act, 1872, Unit 1-Nature of ContractsALANKRIT TRIPATHINo ratings yet
- Specification: F.V/Tim e 3min 5min 8min 10MIN 15MIN 20MIN 30MIN 60MIN 90MIN 1.60V 1.67V 1.70V 1.75V 1.80V 1.85VDocument2 pagesSpecification: F.V/Tim e 3min 5min 8min 10MIN 15MIN 20MIN 30MIN 60MIN 90MIN 1.60V 1.67V 1.70V 1.75V 1.80V 1.85VJavierNo ratings yet
- Provisional List of Institutes1652433727Document27 pagesProvisional List of Institutes1652433727qwerty qwertyNo ratings yet
- French Ox Cheek Stew with MushroomsDocument2 pagesFrench Ox Cheek Stew with MushroomsMihai LeancăNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences in NT Greek Ruben VideiraDocument62 pagesConditional Sentences in NT Greek Ruben Videiraruviso100% (1)
- School readiness assessmentDocument10 pagesSchool readiness assessmentJave Gene De AquinoNo ratings yet
- Format For Handout - Comparative Models of EducationDocument5 pagesFormat For Handout - Comparative Models of EducationAdrian AsiNo ratings yet
- Nurses Week Program InvitationDocument2 pagesNurses Week Program InvitationBenilda TuanoNo ratings yet
- UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DE COLOMBIA PALMIRA ENGLISH PROGRAMDocument1 pageUNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DE COLOMBIA PALMIRA ENGLISH PROGRAMAlejandro PortoNo ratings yet
- Good Evil EssayDocument2 pagesGood Evil EssayuniquebythemillionsNo ratings yet
- Gizmotchy 3 Element Complete Assembly InstructionsDocument5 pagesGizmotchy 3 Element Complete Assembly InstructionsEuropaNo ratings yet
- ExportDocument18 pagesExportDolon MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- 1ST Periodical Test ReviewDocument16 pages1ST Periodical Test Reviewkaren rose maximoNo ratings yet
- Oposa vs. Factoran 224 Scra 792Document28 pagesOposa vs. Factoran 224 Scra 792albemartNo ratings yet
- Demo TeachingDocument22 pagesDemo TeachingCrissy Alison NonNo ratings yet
- Mobile-Friendly Cooperative WebDocument7 pagesMobile-Friendly Cooperative WebWahyu PNo ratings yet
- Camp ApplianceDocument1 pageCamp ApplianceflyzalNo ratings yet