Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Face Recognition Technology: Abstract-Face Is An Important Part of Who
Uploaded by
Vinod Arumugam0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views5 pagesA screensaver equipped with face recognition technology can automatically unlock the screen whenever the authorized user approaches the computer. Face recognition is probably one of the most non-intrusive and user-friendly biometric authentication methods currently available. A facial recognition software can pick someone's face out of a crowd, extract that face from the rest of the scene and compare it to a database full of stored images.
Original Description:
Original Title
face tech
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA screensaver equipped with face recognition technology can automatically unlock the screen whenever the authorized user approaches the computer. Face recognition is probably one of the most non-intrusive and user-friendly biometric authentication methods currently available. A facial recognition software can pick someone's face out of a crowd, extract that face from the rest of the scene and compare it to a database full of stored images.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views5 pagesFace Recognition Technology: Abstract-Face Is An Important Part of Who
Uploaded by
Vinod ArumugamA screensaver equipped with face recognition technology can automatically unlock the screen whenever the authorized user approaches the computer. Face recognition is probably one of the most non-intrusive and user-friendly biometric authentication methods currently available. A facial recognition software can pick someone's face out of a crowd, extract that face from the rest of the scene and compare it to a database full of stored images.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
FACE RECOGNITION TECHNOLOGY
Abstract—Face is an important part of who I INTODUCTION
we are and how people identify us. It is
arguably a person's most unique physical Face is an important part of who we are and how
characteristic. While humans have had the people identify us. It is arguably a person's most
innate ability to recognize and distinguish unique physical characteristic. While humans
different faces for millions of years, have had the innate ability to recognize and
computers are just now catching up Machine distinguish different faces for millions of years,
recognition of human faces from still or video computers are just now catching up. Machine
images has attracted a great deal of attention recognition of human faces from still or video
in the psychology, image processing, pattern images has attracted a great deal of attention in
recognition, neural science, computer the psychology, image processing, pattern
security, and computer vision communities. recognition, neural science, computer security,
Face recognition is probably one of the most and computer vision communities. Face
non-intrusive and user-friendly biometric recognition is probably one of the most non-
authentication methods currently available; a intrusive and user-friendly biometric
screensaver equipped with face recognition authentication methods currently available. The
technology can automatically unlock the detail of how it works and why it is used is
screen whenever the authorized user discussed in this paper.
approaches the computer. A facial recognition
software can pick someone's face out of a II WORKING PRINCIPLE OF FACE
crowd, extract that face from the rest of the RECOGNITION TECHNOLOGY:
scene and compare it to a database full of
stored images. In order for this software to A company based in Minnesota, is one of many
work, it has to know what a basic face looks developers of facial recognition technology. Its
like. Facial recognition software is designed to software, Face can pick someone's face out of a
pinpoint a face and measure its features. Each crowd, extract the face from the rest of the scene
face has certain distinguishable landmarks, and compare it to a database of stored images.
which make up the different facial features.
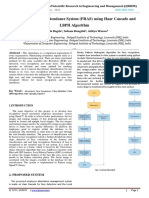
These landmarks are referred to as nodal III WORKING PRINCIPLE-FLOWCHART:
points. There are about 80 nodal points on a
human face. These nodal points are measured Input Face
to create a numerical code, a string of Image.
numbers that represents the face in a
database. This code is called a face print. Only
14 to 22 nodal points are needed for the Face feature
software to complete the recognition process. extraction
Facial recognition methods generally involve
a series of steps that serve to capture, analyze
and compare a face to a database of stored Face
images. The basic processes used by the Databas Feature Decision
software system to capture and compare e. matching. maker.
images are: Detection, Alignment,
Normalization, Representation and Matching.
The technology is now creating waves in Output
image processing, pattern recognition, neural result.
science, computer security, and computer
vision communities.
IV WORKING OF FACE RECOGNITION
SOFTWARE:
The software involves two working components:
the preprocessing component and
The actual procedure.
These nodal points are measured to create a
Preprocessing involves: numerical code, a string of numbers that
Segmentation-where in the background of the represents the face in a database. This code is
subject is eliminated. called a face print. Only 14 to 22 nodal points
Scaling-The image of the subject extracted from are needed for the Facet software to complete the
the surroundings is scaled in order to mark and recognition process.
process. The performance decreases if the scale
is misjudged. Facial recognition methods generally involve a
Rotation-The symmetry operator is used to series of steps that serve to capture, analyze and
estimate head orientation. Thus the tilt position compare a face to a database of stored images.
of the head is altered to obtain a rather straight The basic processes used by the Face It system
image. to capture and compare images are:
Procedure:
Detection - When the system is attached to a
video surveillance system, the recognition
software searches the field of view of a video
camera for faces. If there is a face in the view, it
is detected within a fraction of a second. A
multi-scale algorithm is used to search for faces
in low resolution. The system switches to a high-
resolution search only after a head-like shape is
detected.
Alignment- Once a face is detected, the system
determines the head's position, size and pose. A
face needs to be turned at least 35 degrees
toward the camera for the system to register it.
Normalization -The image of the head is scaled
and rotated so that it can be registered and
A face recognition system can pick someone's mapped into an appropriate size and pose.
face out of a crowd, extract that face from the Normalization is performed regardless of the
rest of the scene and compare it to a database full head's location and distance from the camera.
of stored images. In order for this software to Light does not impact the normalization process.
work, it has to know what a basic face looks like.
Facial recognition software is designed to
pinpoint a face and measure its features. Each Representation - The system translates the facial
face has certain distinguishable landmarks, data into a unique code. This coding process
which make up the different facial features. allows for easier comparison of the newly
These landmarks are referred to as nodal points. acquired facial data to stored facial data.
There are about 80 nodal points on a human face.
Here are a few of the nodal points that are
measured by the software:
Matching - The newly acquired facial data is
compared to the stored data and (ideally) linked
Distance between eyes to at least one stored facial representation.
“Width of nose
“Depth of eye sockets
In most instances the images were not taken in a
" Cheekbones
controlled environment. Even the smallest
" Jaw line
changes in light or orientation could reduce the
" Chin
effectiveness of the system, so they couldn't be
matched to any face in the database, leading to a � Construction: computationally intense, but
high rate of failure. need to be done infrequently
� Fair robustness to facial distortions, pose and
V THE RECOGNITION TECH INVOLVES lighting conditions
THREE MATCHING METHODS: � Need to rebuild the eigenspace if adding a
new person
Feature based matching: Interesting feature � Start to break down when there are too many
points in the face image are located by Gabon classes
filters, which gives us an automatic system that � Retains unwanted variations due to lighting
is notdependent on accurate detection of facial and facial expression
features. The feature points are typically located
at positions with high information content (such Hybrid: A hybrid face recognition method
as facial features), and at each of these positions combines both holistic and feature analysis based
we extract a feature vector consisting of Gabor approaches using a Markov random field (MRF)
coefficients. We report some initial results on the model. The face images are divided into small
ORL dataset. This system belongs to a category patches, and the MRF model is used to represent
that uses the same approach for feature the relationship between the image patches and
description as most other “local features” system the patch ID's. The MRF model is first learned
do, namely Gabor coefficients.The main from the training image patches, given a test
advantage with our approach is that it is image. The most probable patch ID's are then
automatic. Since we find all local features inferred using the belief propagation (BP)
automatically, and make no demand on the algorithm. Finally, the ID of the test image is
features extracted to be pre determined facial determined by a voting scheme from the
features (such as eyes/nose/mouth), we also estimated patch ID's. Experimental results on
claim to have a robust strategy. By this we mean several face datasets indicate the significant
that we do not base our system on locating potential of this method
specific facial features, we base our system on
locating feature points in the face images which VI WHY FACE RECOGNITION IS USED?
contain interesting information. These are
usually located around facial features. Our In addition to being used for security systems,
approach is also easily extendible to face authorities have found a number of other
recognition in video sequences and situation applications for facial recognition systems. At
where the training data is of varying quality and Super Bowl XXXV in January 2001, police in
quantity. Tampa Bay, Florida, used Dentin’s facial
recognition software, FaceIt, to search for
Holistic: This is one of the most successful and potential criminals and terrorists in attendance at
well studied techniques. The technique involves the event. (it found 19 people with pending arrest
representing an image of N pixels by a vector warrants) In the 2000 presidential election, the
N*1 in an N-dimensional space. Dimensionality Mexican government employed facial
reduction techniques are then used to scale down recognition software to prevent voter fraud.
the image. A set of transformation vectors Some individuals had been registering to vote
(displayed as feature images), put them into W under several different names, in an attempt to
of size N*d which is the defining the face place multiple votes. By comparing new facial
subspace images to those already in the voter database,
The face images are projected onto the “face authorities were able to reduce duplicate
subspace” The central idea is to find a weighted registrations. Similar technologies are being used
combination of a small number of in the United States to prevent people from
transformations vectors that can approximate any obtaining fake identification cards and driver’s
face in the face database called Eigenfaces. A licenses. There are also a number of potential
new image is recognized using a nearest uses for facial recognition that are currently
neighbor classifier in an Eigenface subspace. being developed. For example, the technology
Classify a new face as the person with the closest could be used as a security measure at ATM’s;
distance. The advantages of this system are: instead of using a bank card or personal
�Recognition accuracy increases identification number, the ATM would capture
� Run-time performance is very good an image of your face, and compare it to your
photo in the bank database to confirm your
identity. This same concept could also be applied
to computers; by using a webcam to capture a IX PRESENT DEVELOPMENTS:
digital image of yourself, your face could replace
your password as a means to log-in.
Face Recognition Technology is now
considered for use in retails and stores
VII SHORTCOMINGS: in order to facilitate a secure and
independent shopping system.
Face recognition is not perfect and struggles to It is being widely incorporated in
perform under certain conditions. Conditions computer systems, mobile phones and
where face recognition does not work well other communication devices in order to
include poor lighting, sunglasses, long hair, or allow the user alone to access using
other objects partially covering the subject’s unique face recognition.
face, and low resolution images. The algorithms for the three systems are
being revised and alterations are done in
Another serious drawback is that many systems order to better the working of this
are less effective if facial expressions vary. Even technology.
a big smile can render in the system less The three methods are being combined
effectively. in order to provide more accurate
results.
Despite the potential benefits of this technology,
many citizens are concerned that their privacy IX COMPARITIVE STUDY
will be invaded. Some fear that it could lead to a
“total surveillance society,” with the government Among the different biometric techniques, facial
and other authorities having the ability to know recognition may not be the most reliable and
where you are, and what you are doing, at all efficient. However, one key advantage is that it
times. does not require aid (or consent) from the test
subject. Properly designed systems installed in
airports, multiplexes, and other public places can
identify individuals among the crowd. Other
VIII OVERCOMING PROBLEMS: biometrics like fingerprints, iris scans, and
speech recognition cannot perform this kind of
In 2006, the performance of the ‘latest face mass identification. However, questions have
recognition algorithms’ were evaluated in the been raised on the effectiveness of facial
Face Recognition Grand Challenge. High- recognition software in cases of railway and
resolution face images, 3-D face scans, and iris airport security the performance of the latest face
images were used in the tests. The results recognition algorithms were evaluated in
indicated that the new algorithms are 10 times the Face Recognition Grand Challenge (FRGC).
more accurate than the face recognition High-resolution face images, 3-D face scans, and
algorithms of 2002 and 100 times more accurate iris images were used in the tests. The results
than those of 1995. Some of the algorithms were indicated that the new algorithms are 10 times
able to outperform human participants in more accurate than the face recognition
recognizing faces and could uniquely identify algorithms of 2002 and 100 times more accurate
identical twins. than those of 1995. Some of the algorithms were
able to outperform human participants in
recognizing faces and could uniquely identify
Another emerging trend uses the visual details of
identical twins.[6]
the skin, as captured in standard digital or
scanned images. This technique, called skin
texture analysis, turns the unique lines, patterns, Low-resolution images of faces can be enhanced
and spots apparent in a person’s skin into a using face hallucination. Further improvements
mathematical space. Tests have shown that with in high resolution, mega pixel cameras in the last
the addition of skin texture analysis, few years have helped to resolve the issue of
performance in recognizing faces can increase 20 insufficient resolution.
to 25 percent.
X CONCLUSION
We present a novel approach for face recognition
based on the physiological information extracted
from thermal facial images. First, we delineate
the human face from the background using a
Bayesian method. Then, we extract the blood
vessels present on the segmented facial tissue
using image morphology. The extracted vascular
network produces contour shapes that are unique
for each individual. The branching points of the
skeleton zed vascular network are referred to as
thermal minutia points (TMPs). These are
reminiscent of the minutia points produced in
fingerprint recognition techniques. During the
classification stage, local and global structures of
TMPs extracted from test images are matched
with those of database images. We have
conducted experiments on a large database of
thermal facial images collected in our lab. The
good experimental results show that our
proposed approach has merit and promise.
X I REFERENCE:
• http://www.seminarsonly.com/computer
%20science/Face%20Recognition
%20Technology.php
• http://www.vlsi.uwindsor.ca/presentatio
ns/xu1v_seminar_1.pdf
• http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/fa
cial-recognition.htm
• http://www.ansatt.hig.no/erikh/papers/n
obim2000.pdf
• http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Facial_reco
gnition_system#Skin_texture_analysis
You might also like
- Facial Recognition: U Bio-M (I)Document13 pagesFacial Recognition: U Bio-M (I)kiran_ballamudiNo ratings yet
- Face RecognitionDocument8 pagesFace RecognitionRishikaa RamNo ratings yet
- Face Ditection Avishek ProjectDocument32 pagesFace Ditection Avishek Projectmd shahanwaz siddiqueNo ratings yet
- Face RecognitionDocument16 pagesFace RecognitionManu MathewNo ratings yet
- Face Recognition TechnologyDocument2 pagesFace Recognition TechnologyRashmi SureshNo ratings yet
- Face RecognitionDocument42 pagesFace RecognitionG.J. ShivRajNo ratings yet
- Face Recognition Using Pca and Neural Network Model: Submitted by Aadarsh Kumar (15MIS0374Document11 pagesFace Recognition Using Pca and Neural Network Model: Submitted by Aadarsh Kumar (15MIS0374KrajadarshNo ratings yet
- Face RecognitionDocument27 pagesFace RecognitionManendra PatwaNo ratings yet
- Pattern RecognitionDocument12 pagesPattern RecognitionHarvinraj MohanapiragashNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Smart Doorbell Facial Recognition (Ayman Ben Thabet, 2015)Document5 pagesEnhanced Smart Doorbell Facial Recognition (Ayman Ben Thabet, 2015)guianÜNo ratings yet
- Face Recognigion-SystemDocument30 pagesFace Recognigion-SystemOliifan BaayyooNo ratings yet
- 011-Digital Image ProcessingDocument11 pages011-Digital Image ProcessingRaja sekhar polisettiNo ratings yet
- Face RecognitionDocument29 pagesFace RecognitiongevijahokNo ratings yet
- Project DesignDocument20 pagesProject DesignAshishKumarNo ratings yet
- Auromatic AttendanceDocument4 pagesAuromatic AttendanceAli AslamNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Smart Attendance On FPGADocument5 pagesImplementation of Smart Attendance On FPGAMebin P M 19MVD0044No ratings yet
- Face Recognition in Non-Uniform Motion Using Raspberry Pi: 15 IJRE - Vol. 03 No. 05 - May 2016Document3 pagesFace Recognition in Non-Uniform Motion Using Raspberry Pi: 15 IJRE - Vol. 03 No. 05 - May 2016Abraham CandelariaNo ratings yet
- Automatic AttendanceDocument4 pagesAutomatic AttendanceAli AslamNo ratings yet
- Facial Recognition Using Machine LearningDocument21 pagesFacial Recognition Using Machine LearningNithishNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Real Time Product Recommendation Using Facial Sentiment Analysis PDFDocument6 pagesAn Efficient Real Time Product Recommendation Using Facial Sentiment Analysis PDFManju Ancy John ImmanuelNo ratings yet
- B2Document44 pagesB2orsangobirukNo ratings yet
- Face Mask Detection With Fine AllocationDocument5 pagesFace Mask Detection With Fine Allocationsachin achariNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Face Recognition Security SystemDocument21 pagesPresentation On Face Recognition Security Systemvivekanand kumarNo ratings yet
- Project Report For Face TrackingDocument13 pagesProject Report For Face Trackingjohnbri100% (1)
- Face Recognition TechnologyDocument30 pagesFace Recognition TechnologyRsyedNo ratings yet
- Internal Guide: Mr. Gaurav Bhardwaj External Guide: Mr. Shakti PatelDocument23 pagesInternal Guide: Mr. Gaurav Bhardwaj External Guide: Mr. Shakti Patelshital shermaleNo ratings yet
- For Image Processing in Signals &systems A Real-Time Face Recognition System Using Custom VLSI HardwareDocument10 pagesFor Image Processing in Signals &systems A Real-Time Face Recognition System Using Custom VLSI Hardwareameerunnisa123No ratings yet
- RealTimeFacialDetectionandRecognitionUsingHaarCascadeandSupportVectorMachines PDFDocument21 pagesRealTimeFacialDetectionandRecognitionUsingHaarCascadeandSupportVectorMachines PDFNguyễn Hoàng ÂnNo ratings yet
- Face Detection by Using OpenCVDocument4 pagesFace Detection by Using OpenCVvickey rajputNo ratings yet
- Facial Login SystemDocument15 pagesFacial Login Systemrajeevs54785No ratings yet
- Deepak Result PaperDocument7 pagesDeepak Result Papervikas chawlaNo ratings yet
- Atm Security Using Face Recognition: Rahul. K, Arvind.S, B.Prashanth, N.Balaji AbhishekDocument3 pagesAtm Security Using Face Recognition: Rahul. K, Arvind.S, B.Prashanth, N.Balaji AbhishekPrashant MaliNo ratings yet
- Face Recognition Seminar Presentation Day1Document23 pagesFace Recognition Seminar Presentation Day1abdi geremewNo ratings yet
- Face DetectionDocument6 pagesFace DetectionMaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Face Detection in Python Using OpenCVDocument17 pagesFace Detection in Python Using OpenCVKaruna SriNo ratings yet
- Abstract:: Case Study of Real Time Based Facial Recognition System For Criminal IdentificationDocument5 pagesAbstract:: Case Study of Real Time Based Facial Recognition System For Criminal IdentificationSachinNo ratings yet
- Pca For Image RecognitionDocument5 pagesPca For Image Recognitionnedal altitiNo ratings yet
- AF and Face RecogDocument9 pagesAF and Face RecogKALAI SELVAM .MNo ratings yet
- Face RecognitionDocument20 pagesFace Recognitionpixels mmmutNo ratings yet
- Emotion Based Music PlayerDocument3 pagesEmotion Based Music Playerpratiksha jadhavNo ratings yet
- Face Recognition Using Haar Cascade Classifier: Varun Garg Kritika GargDocument3 pagesFace Recognition Using Haar Cascade Classifier: Varun Garg Kritika GargVarunNo ratings yet
- IEEE PaperDocument5 pagesIEEE Paperமகேஸ்கண்ணன் அண்ணாத்துரைNo ratings yet
- VA Lecture 23Document42 pagesVA Lecture 23akshittayal24No ratings yet
- Face Recognition TechnologyDocument9 pagesFace Recognition TechnologySireesha TekuruNo ratings yet
- Image-Based Face Detection and Recognition Using MATLABDocument4 pagesImage-Based Face Detection and Recognition Using MATLABIjcemJournal100% (1)
- Morpho Face RecognitionDocument20 pagesMorpho Face Recognitionn3rmaNo ratings yet
- Face Recognigion-SystemDocument30 pagesFace Recognigion-SystemNikhil VarmaNo ratings yet
- Face Attendance: Project No: 90Document22 pagesFace Attendance: Project No: 90Anshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- EP494 PowerpointFaDocument30 pagesEP494 PowerpointFaBharath KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 BM Learning Material With ActDocument17 pagesUnit 3 BM Learning Material With ActveeravalliyogeshsaivenkatNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Applying Artificial Neural Networks For Face RecognitionDocument17 pagesResearch Article: Applying Artificial Neural Networks For Face Recognitionsalman1992No ratings yet
- Smart Class Room Attendance System Using Group Face Recognition ObjectiveDocument11 pagesSmart Class Room Attendance System Using Group Face Recognition ObjectiveTaj SNo ratings yet
- Correlation Method Based PCA Subspace Using Accelerated Binary Particle Swarm Optimization For Enhanced Face RecognitionDocument4 pagesCorrelation Method Based PCA Subspace Using Accelerated Binary Particle Swarm Optimization For Enhanced Face RecognitionEditor IJRITCCNo ratings yet
- Aimlab-Group Assignment - Group 1: XP21036 XP21009 XP21021 XP21025 XP21006 XP21010Document25 pagesAimlab-Group Assignment - Group 1: XP21036 XP21009 XP21021 XP21025 XP21006 XP21010Kumar SandeepNo ratings yet
- Face Recognition TechnologyDocument15 pagesFace Recognition Technologycharysahith528No ratings yet
- Face Detection AppDocument15 pagesFace Detection Apprithikashivani06No ratings yet
- Welcome: Computer EngineeringDocument13 pagesWelcome: Computer EngineeringParikshit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Facial Recognition Attendance System (FRAS) Using Haar Cascade and LBPH AlgorithmDocument4 pagesFacial Recognition Attendance System (FRAS) Using Haar Cascade and LBPH AlgorithmSaroj RimalNo ratings yet
- Share Face Recognition TechnologyDocument15 pagesShare Face Recognition TechnologyBikram RockNo ratings yet
- Strategi Pencegahan Kecelakaan Di PT VALE Indonesia Presentation To FPP Workshop - APKPI - 12102019Document35 pagesStrategi Pencegahan Kecelakaan Di PT VALE Indonesia Presentation To FPP Workshop - APKPI - 12102019Eko Maulia MahardikaNo ratings yet
- Eugène Burnouf: Legends of Indian Buddhism (1911)Document136 pagesEugène Burnouf: Legends of Indian Buddhism (1911)Levente Bakos100% (1)
- STEM BeesDocument36 pagesSTEM BeesHitesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Arsu and AzizoDocument123 pagesArsu and AzizoZebu BlackNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Task Harry PotterDocument3 pagesVocabulary Task Harry PotterBest FriendsNo ratings yet
- Second Grading EappDocument2 pagesSecond Grading EappConnieRoseRamos100% (2)
- Donor S Tax Exam AnswersDocument6 pagesDonor S Tax Exam AnswersAngela Miles DizonNo ratings yet
- 1929 Davos DisputationDocument20 pages1929 Davos DisputationEstevao Cruz100% (1)
- Collocations and IdiomsDocument6 pagesCollocations and IdiomsNguyen HuyenNo ratings yet
- Individual Psychology (Adler)Document7 pagesIndividual Psychology (Adler)manilyn dacoNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument341 pagesThermodynamicsjonathan2788100% (4)
- Epic Story of IbalonDocument30 pagesEpic Story of IbalonKi Ko100% (3)
- Drug Distribution MethodsDocument40 pagesDrug Distribution MethodsMuhammad Masoom Akhtar100% (1)
- Module6 (Margie Ybanez)Document3 pagesModule6 (Margie Ybanez)Margie Ybañez82% (17)
- Parwati DeviDocument25 pagesParwati DevikvntpcsktprNo ratings yet
- AIDA Deconstruction of Surf Excel AdDocument6 pagesAIDA Deconstruction of Surf Excel AdRoop50% (2)
- CURRICULUM VITAE Kham Khan Suan Hausing, PHDDocument8 pagesCURRICULUM VITAE Kham Khan Suan Hausing, PHDCinpu ZomiNo ratings yet
- Baltimore Catechism No. 2 (Of 4)Document64 pagesBaltimore Catechism No. 2 (Of 4)gogelNo ratings yet
- Habanera Botolena & Carinosa (Gas-A)Document8 pagesHabanera Botolena & Carinosa (Gas-A)christian100% (4)
- Entrepreneur: Job/Career InvolvementDocument5 pagesEntrepreneur: Job/Career InvolvementYlaissa GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Linking and Relocation - Stacks - Procedures - MacrosDocument11 pagesLinking and Relocation - Stacks - Procedures - MacrosJeevanantham GovindarajNo ratings yet
- Entity-Level Controls Fraud QuestionnaireDocument8 pagesEntity-Level Controls Fraud QuestionnaireKirby C. LoberizaNo ratings yet
- Acidity (As Acetic Acid) On Undenatured and Denatured EthanolDocument10 pagesAcidity (As Acetic Acid) On Undenatured and Denatured EthanolVinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- PED100 Mod2Document3 pagesPED100 Mod2Risa BarritaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To E-Business SystemsDocument19 pagesIntroduction To E-Business SystemsArtur97% (79)
- BSCHMCTT 101Document308 pagesBSCHMCTT 101JITTUNo ratings yet
- Role of Courts in Granting Bails and Bail Reforms: TH THDocument1 pageRole of Courts in Granting Bails and Bail Reforms: TH THSamarth VikramNo ratings yet
- Filipino HousesDocument4 pagesFilipino HousesjackNo ratings yet
- A Global StudyDocument57 pagesA Global StudyRoynal PasaribuNo ratings yet
- Asian Journal of ForestryDocument3 pagesAsian Journal of ForestryTeguh MuslimNo ratings yet