Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Simultaneous Equation IGCSE 02-05
Uploaded by
EriqCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Simultaneous Equation IGCSE 02-05
Uploaded by
EriqCopyright:
Available Formats
Simultaneous Equation
IGCSE Past Papers (2002-2005)
0606/1/M/J/02
1. Find the coordinates of the points at which the straight line y +2 x =7 intersects
the curve y 2=xy – 1 .
[4]
0606/1/M/J/03
2. Find the values of k for which the line
2 2
y=kx−2 meets the curve y =4 x – x
[4]
4
3. Find the distance between the points of intersection of the curve y=3+ and
x
the line y=4 x+ 9 .
[6]
0606/1/O/N/03
4. Find the values of k for which the line x=3 y +k and the curve y 2=2 x+3 do
not intersect.
[4]
0606/2/O/N/03
2
5. The line 4 y – x +11 intersects the curve y =2 x+1 at points A and B. Find the
coordinates of the midpoint of line AB.
[4]
0606/1/M/J/04
3
6. Find the x-coordinates of the three points of intersection of the curve y=x with
the line y=5 x−2 expressing non-integer values in the form a ± √ b , where a
and b are integers.
[5]
0606/1/O/N/04
7. Without using a calculator, solve, for x and y, the simultaneous equations
y−1
1
82 ÷2 y =64 3 ×
4x
()
9
=81
[5]
0606/2/O/N/04
8. Find the values of k for which the line y=x +2 meets the curve y 2+ ( x+ k )2=2
[5]
0606/02/M/J/05
9. The diagram shows a square ABCD of area 60m2. The point P lies on A B
BC and the sum of the lengths of AP and BP is 12 m. Given that the P
lengths of AP and BP are x m and y m respectively, from two
equations in x and y and hence find the length of BP.
D C
[5]
10. Solve, for x and y, the simultaneous equations
x y
125 =25(5 ) ,
x y
7 ÷ 49 =1.
[6]
© UCLES 2002-2005 Compiled by eriq @ eric
2018
0606/02/M/J/08
11. The equation of a curve is given by y = x2 + ax + 3, where a is a constant. Given that
this equation can also be written as y = (x + 4)2 + b, find
(i) the value of a and of b,
[2]
(ii) the coordinates of the turning point of the curve.
[1]
You might also like
- ACSIAM1Document3 pagesACSIAM1JASON_INGHAMNo ratings yet
- Previous Year Boards Questions on PolynomialsDocument2 pagesPrevious Year Boards Questions on PolynomialsASgroup NasirabadNo ratings yet
- 03 0580 22 2024 3rp Afp m24 12022024Document12 pages03 0580 22 2024 3rp Afp m24 12022024nflbubba468No ratings yet
- F3 Maths Exam 2013Document25 pagesF3 Maths Exam 2013Andrew ArahaNo ratings yet
- Sec 1E - Chapter 2 - Real NumbersDocument15 pagesSec 1E - Chapter 2 - Real Numbersyusdi afandiNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Mathematics+Olympiad inDocument8 pagesGrade 8 Mathematics+Olympiad inJjnnhhhhhNo ratings yet
- 254.4 Quadratic Equations-Cie Igcse Maths 0580-Ext Theory-QpDocument7 pages254.4 Quadratic Equations-Cie Igcse Maths 0580-Ext Theory-QpFaithNo ratings yet
- 2018 Year 1 EOY Paper 1Document13 pages2018 Year 1 EOY Paper 1FN2022021 WONG ZHI YANG0% (1)
- 10 - Linear LawDocument4 pages10 - Linear LawJASON_INGHAMNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle Theory WorksheetDocument2 pagesKinetic Particle Theory WorksheetFandy ArdyNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Maths Questions PDFDocument3 pagesYear 7 Maths Questions PDFcmhewNo ratings yet
- Simultaneous Equations - Past-Year QuestionsDocument2 pagesSimultaneous Equations - Past-Year QuestionsCgzam ZamNo ratings yet
- Simplifying Expressions CSEC TOPICDocument2 pagesSimplifying Expressions CSEC TOPICLatoyaWatkinsNo ratings yet
- CHEM SPM Chapter 4 Periodic Table StudentDocument23 pagesCHEM SPM Chapter 4 Periodic Table Studentangie0812No ratings yet
- Pure Maths Work Sheet On Surds, Indices and LogarithmsDocument2 pagesPure Maths Work Sheet On Surds, Indices and Logarithmsanwar hossainNo ratings yet
- Secondary 1 AlgebraDocument55 pagesSecondary 1 AlgebraJoann NgNo ratings yet
- Sec 2 Math Changing The SubjectDocument1 pageSec 2 Math Changing The SubjectdreamydamselNo ratings yet
- Indices Rules - BasicsDocument3 pagesIndices Rules - Basicsrh 077No ratings yet
- Sec 2 MathDocument30 pagesSec 2 MathSpike BearingNo ratings yet
- H2 Math Topical Worksheet (Functions)Document3 pagesH2 Math Topical Worksheet (Functions)Tim Gan MathNo ratings yet
- Myp QuestionsDocument5 pagesMyp QuestionsnizNo ratings yet
- Sec 1E - Chapter 4 - Introduction To AlgebraDocument12 pagesSec 1E - Chapter 4 - Introduction To Algebrayusdi afandiNo ratings yet
- Basic Laws of Indices GREENDocument6 pagesBasic Laws of Indices GREENRedzuan SaidiNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Graphs & EquationsDocument2 pagesQuadratic Graphs & EquationsJamaliah DaudNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Maths Question PaperDocument4 pagesClass 8 Maths Question PaperErldc Control Room POSOCONo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 Mathematics Question Paper Set B - 0Document3 pagesCBSE Class 6 Mathematics Question Paper Set B - 0AnimeshNo ratings yet
- Significant Figures Bronze Silver GoldDocument1 pageSignificant Figures Bronze Silver GoldshuchitaNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Identities PracticeDocument3 pagesAlgebraic Identities PracticeCyril KiranNo ratings yet
- GCSE Revision - Straight Line Equations: Test Your Understanding: 1. Finding A GradientDocument8 pagesGCSE Revision - Straight Line Equations: Test Your Understanding: 1. Finding A GradientIvan Jerkovic0% (1)
- LCM & HCFDocument5 pagesLCM & HCFArockia RajNo ratings yet
- Sec 2 Term 1 - 1 NotesDocument35 pagesSec 2 Term 1 - 1 NotesWolfie Saraswathi Santhosham100% (1)
- Worksheet States of Matter ks3Document2 pagesWorksheet States of Matter ks3Edward edwardNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Squares, Square Roots, Cubes and Cube RootsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 - Squares, Square Roots, Cubes and Cube RootssmkpthoeNo ratings yet
- Express 1B (FWS)Document199 pagesExpress 1B (FWS)yusdi afandi100% (2)
- Add Maths F4 Topical Test 6 (E)Document4 pagesAdd Maths F4 Topical Test 6 (E)HANIFAHNo ratings yet
- Surds Practice QuestionsDocument1 pageSurds Practice QuestionsJustine PowellNo ratings yet
- 03 0580 42 2024 3RP Afp M24 20022024060643Document20 pages03 0580 42 2024 3RP Afp M24 20022024060643nflbubba468No ratings yet
- Math - Ratio & Proportion (Past Paper Q)Document4 pagesMath - Ratio & Proportion (Past Paper Q)GAURI GUPTANo ratings yet
- 4 Algebraic Representation & ManipulationDocument9 pages4 Algebraic Representation & Manipulationkishhannatth vickneshNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper Class 7 Maths Set 1 MergedDocument21 pagesCBSE Sample Paper Class 7 Maths Set 1 MergedNAMANNo ratings yet
- 0606 Indices and Surd2Document6 pages0606 Indices and Surd2Anonymous Kx8TAybnXQNo ratings yet
- Dunman High School 2009 Maths D Paper 1Document20 pagesDunman High School 2009 Maths D Paper 1ZeneonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions SAT Questions 3-6Document8 pagesChemical Reactions SAT Questions 3-6balalaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Math Test Preparation - Indices and Standard FormDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Math Test Preparation - Indices and Standard FormAntonius LukitoNo ratings yet
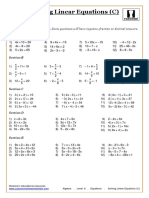
- Algebra. Equations. Solving Linear Equations C PDFDocument1 pageAlgebra. Equations. Solving Linear Equations C PDFRoberto CastroNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 Mathematics Worksheet - Squares and Square RootsDocument8 pagesCBSE Class 8 Mathematics Worksheet - Squares and Square RootsISHAAN GOYALNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 Math Exam 2013Document4 pagesCBSE Class 8 Math Exam 2013rthirupaNo ratings yet
- Solutions workbook exercises sections 1-5Document12 pagesSolutions workbook exercises sections 1-5Roqia AbulebbehNo ratings yet
- Add Maths F4 Topical Test 2 (E)Document3 pagesAdd Maths F4 Topical Test 2 (E)HANIFAHNo ratings yet
- Add Math IGCSE Topical Test - IntegrationDocument3 pagesAdd Math IGCSE Topical Test - IntegrationMelinda Tiong100% (1)
- Revision Sheet MYP 4Document10 pagesRevision Sheet MYP 4Manan SachdevaNo ratings yet
- AREA UNDER CURVEDocument13 pagesAREA UNDER CURVEAnita Yun Chu PengNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Additional Mathematics 0606/23Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Additional Mathematics 0606/23Richard FernandezNo ratings yet
- 11 Maths Impq 10 Straight Lines KvsDocument3 pages11 Maths Impq 10 Straight Lines KvsEzhilarasiPazhanivelNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Manipulation Worksheet 1Document3 pagesAlgebraic Manipulation Worksheet 1dreamydamselNo ratings yet
- Indices: Answers: (1) (A)Document3 pagesIndices: Answers: (1) (A)Halal BoiNo ratings yet
- D1 Diff With Normal & Tangents QPDocument19 pagesD1 Diff With Normal & Tangents QPvocalsfnNo ratings yet
- Ah Sam 1Document3 pagesAh Sam 1JASON_INGHAMNo ratings yet
- College Algebra TOPICAL TEST 5: Exponential Functions and Logarithmic Functions InstructionDocument4 pagesCollege Algebra TOPICAL TEST 5: Exponential Functions and Logarithmic Functions InstructionEriqNo ratings yet
- Algorithmic IndefiniteDocument1 pageAlgorithmic IndefiniteEriqNo ratings yet
- Prob. Dist. Past State PapersDocument5 pagesProb. Dist. Past State PapersEriqNo ratings yet
- College Algebra TOPICAL TEST 5: Exponential Functions and Logarithmic Functions InstructionDocument4 pagesCollege Algebra TOPICAL TEST 5: Exponential Functions and Logarithmic Functions InstructionEriqNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric FunctionDocument12 pagesTrigonometric FunctionEriqNo ratings yet
- "One Good Friend Is Better Than A Thousand Poor Ones" To What Extent Is This Statement True? DiscussDocument1 page"One Good Friend Is Better Than A Thousand Poor Ones" To What Extent Is This Statement True? DiscussEriqNo ratings yet
- Air PressureDocument2 pagesAir PressureEriqNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Progression Worksheet 1Document2 pagesArithmetic Progression Worksheet 1EriqNo ratings yet
- MetalDocument3 pagesMetalEriqNo ratings yet
- Migrant Workers and Xenophobia in The UK Labour Movement: Net ContributorsDocument13 pagesMigrant Workers and Xenophobia in The UK Labour Movement: Net ContributorsEriqNo ratings yet
- 6.10 History of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pages6.10 History of PhotosynthesisEriqNo ratings yet
- History of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesHistory of PhotosynthesisEriqNo ratings yet
- SC f3 DetailDocument1 pageSC f3 DetailEriqNo ratings yet
- 9 Key Questions About the Longest US Government Shutdown AnsweredDocument9 pages9 Key Questions About the Longest US Government Shutdown AnsweredEriqNo ratings yet
- TH Sacrifices Economic Growth For The Good of EnvironmentDocument6 pagesTH Sacrifices Economic Growth For The Good of EnvironmentEriqNo ratings yet
- NUNAMAS Highlighted SCDocument5 pagesNUNAMAS Highlighted SCEriqNo ratings yet
- What's Happening in Zimbabwe?: Important Elections Took Place in Zimbabwe in Southern Africa On 30 July 2018Document6 pagesWhat's Happening in Zimbabwe?: Important Elections Took Place in Zimbabwe in Southern Africa On 30 July 2018EriqNo ratings yet
- Brexit: All You Need To Know About The UK Leaving The EU: What Does Brexit Mean?Document30 pagesBrexit: All You Need To Know About The UK Leaving The EU: What Does Brexit Mean?EriqNo ratings yet
- BDS - The Boycott, Divestment, and Sanctions Movement Against Israel - ExplainedDocument6 pagesBDS - The Boycott, Divestment, and Sanctions Movement Against Israel - ExplainedEriqNo ratings yet
- 10 Things About ExtraditionDocument3 pages10 Things About ExtraditionEriqNo ratings yet
- SiliconDocument2 pagesSiliconHaslinda OthmanNo ratings yet
- Science Form 2 Notes on Water Solutions Acids and AlkalisDocument17 pagesScience Form 2 Notes on Water Solutions Acids and AlkalisDhiipagesan Muniandy100% (1)
- Science Form 2Document6 pagesScience Form 2EriqNo ratings yet
- PT3 Science Notes Part 1 PDFDocument40 pagesPT3 Science Notes Part 1 PDFAnonymous 6KSWc2JZy100% (9)
- f2 cp1 Express NotesDocument7 pagesf2 cp1 Express NotesEriqNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Progression Worksheet 1Document2 pagesArithmetic Progression Worksheet 1EriqNo ratings yet
- Brexit: All You Need To Know About The UK Leaving The EU: What Does Brexit Mean?Document30 pagesBrexit: All You Need To Know About The UK Leaving The EU: What Does Brexit Mean?EriqNo ratings yet
- 3 Mobile Crane ChecklistDocument5 pages3 Mobile Crane ChecklistEriq100% (1)
- Chemistry Chapter 6Document1 pageChemistry Chapter 6EriqNo ratings yet
- Solving PDEs Using Separation of VariablesDocument3 pagesSolving PDEs Using Separation of VariablesMîån ÅbdûllãhNo ratings yet
- Solving Rational Equations Step-by-Step GuideDocument17 pagesSolving Rational Equations Step-by-Step GuideCarl Joseph Baluarte SamsonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Engineering AnalysisDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Engineering AnalysisSuprioNo ratings yet
- 04 - Tangent LinesDocument2 pages04 - Tangent LinesCss PursuerNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument19 pagesFunctionsHitesh BhavnaniNo ratings yet
- Damped Oscillation: Topic 2Document41 pagesDamped Oscillation: Topic 2puppyarav2726No ratings yet
- Advances in Mechanical EngineeringDocument17 pagesAdvances in Mechanical EngineeringDr. NasreenNo ratings yet
- DFGDFGDocument7 pagesDFGDFGtempmail user 69No ratings yet
- DOLFIN For Solving PDE With FEDocument12 pagesDOLFIN For Solving PDE With FEJohn VardakisNo ratings yet
- Solve linear equations and word problems involving linear equationsDocument2 pagesSolve linear equations and word problems involving linear equationseddiechowNo ratings yet
- Boyce ODEch 2 S 4 P 28Document2 pagesBoyce ODEch 2 S 4 P 28...No ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Maths Unit 3 Study Material em 215283 PDFDocument32 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Maths Unit 3 Study Material em 215283 PDFAakaash C.K.No ratings yet
- Basics of Optimal Control TheoryDocument91 pagesBasics of Optimal Control TheoryAshutosh AnandNo ratings yet
- PT1 MCQDocument8 pagesPT1 MCQAlka MehraNo ratings yet
- P6, P7 Linear Systems of Differential EquationsDocument10 pagesP6, P7 Linear Systems of Differential EquationsYosua Petra HattuNo ratings yet
- Plotting Curves and Solving Differential EquationsDocument61 pagesPlotting Curves and Solving Differential EquationsPriya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Math 9Document5 pagesMath 9Rommiel ClanzaNo ratings yet
- MST326 202109Document8 pagesMST326 202109llynusNo ratings yet
- Ch. 2 Free Vibration AnalysisDocument32 pagesCh. 2 Free Vibration AnalysisHFNo ratings yet
- 3.3. Phase and Amplitude Errors of 1-D Advection EquationDocument52 pages3.3. Phase and Amplitude Errors of 1-D Advection EquationSamKtkNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.2 Graphing Linear Functions by The Point Plotting MethodDocument4 pagesLesson 2.2 Graphing Linear Functions by The Point Plotting MethodAliah GombioNo ratings yet
- 7760lecture 3 NotesDocument19 pages7760lecture 3 NotesSyed Osama GhaniNo ratings yet
- UG MTH2semDocument3 pagesUG MTH2semMuhammad YousufNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 Algebra WorksheetDocument1 pageCBSE Class 6 Algebra WorksheetAmrita Sen100% (1)
- Phas0009: Mathematical Methods Ii: University College London Department of Physics and AstronomyDocument3 pagesPhas0009: Mathematical Methods Ii: University College London Department of Physics and AstronomyRoy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Preliminary of Differential EquationsDocument6 pagesPreliminary of Differential EquationsSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- L1 PPTDocument13 pagesL1 PPTkimberlyNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: 1.7. Quadratic InequalityDocument10 pagesAnswer Key: 1.7. Quadratic InequalityPrincess BoloyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14 Effects of Changing The Values of A, H and KDocument4 pagesLesson 14 Effects of Changing The Values of A, H and KMarion Nico EspiloyNo ratings yet
- Y X X X X X X X X X X y X X X X X XX XX X X X: Solving Quadratics Equations SummaryDocument3 pagesY X X X X X X X X X X y X X X X X XX XX X X X: Solving Quadratics Equations SummaryWilson ZhangNo ratings yet