Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Proteoglycans
Uploaded by
Jhoanna Rein DuzonOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Proteoglycans
Uploaded by
Jhoanna Rein DuzonCopyright:
Available Formats
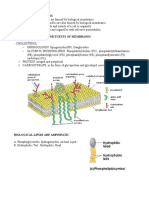
Proteoglycans
-ECM
-form the hydrated polysaccharide gel that acts as a ground substance and allows diffusion of
substances such as nutrients and hormones, from the blood to tissue and vice versa. It is consist of a
core protein molecule to which chains of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are covalently attached.
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
- are unbranched polysaccharide chains of repeating disaccharide units (A-B-A-B where A and
B represent two different sugars)
repeating disaccharide consists of: 1.Amino sugar - N-Acetylglucosamine or N-
Acetylgalactosamine 2. Acidic sugar- Hyaluronic acid or Glucoronic acid
- Highly acidic- due to the presence of both sulfate and carboxyl group attached to the sugar
rings
- Very hydrophilic
- Has an extended coil structure which takes up extensive pace
- Polyanions: have a lot of negative charges because of huge number of carboxylic and sulfate
groups which attract polycations (Na+, K) bringing water into the matrix giving turgor
pressure able to withstand forces of many hundreds of times atm pressure
Proteoglycans function to:
-provide hydrated space: It binds huge number of cations which in turn bind large number of water
molecules which results to form a porous, hydrated gel that fills the extracellular space like packing
material that resists crushing (compression forces)
-bind secreted signaling molecules: a number of growth factors have been found to bind to
proteoglycans including fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
-act as sieves to regulate molecular trafficking: polyanions interact with polycations which traps water;
they act as molecular sieves that trap small molecules and does not allow these molecules to move from
one place to another place
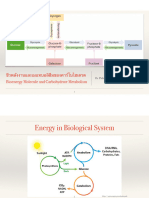
Proteoglycans are formed in the Golgi apparatus where:
the core protein is linked via a serine to a tetrasachharide
glycosyl transferases add sugar residues
ordered sulphation and epimerization reactions (conversion of some amino acids from their
natural L-isomer to the D-isomer) occur
Formed through:
1. O-type linkages
Ser- O- Xylose- gal-gal-repeating dissacharide (GAGs)
2. N-type linkages- synthesized in the Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic reticular membrane which has a lipid molecule, dolichal pyrophosphate with two
phosphates attached. To the dolichal pyrophosphate, olisaccharide unit will be attached and then
transferred to a protein molecule, asparagine. To its side chain nitrogen, the entire oligosachharide
chain are transferred. Further processing takes place in golgi complex.
Role of dolichal pyrophosphate: a lipid molecule with a phosphate attached to the RER and the
carbohydrate is built from it and added to nitrogen side of Asp
Main types of GAGs are:
1. Hyaluronic acid – has high negative charges and act as a lubricant in synovial fluid and shock absorber
in a joint; helps in cell migration during embryogenesis and morphogenesis and also in wound healing
process; Atherosclerosis
2. Chondroitin sulfate- found in ECM especially in cartilage which is involved in bone and cartilage
formation; hold tightly to ECM which make cartilage and bone
3. Dermatan sulfate- found in skin, heart, blood vessel and transparency of cornea
4. Heparin sulfate- found in the basement membrane; helps in the formation of stratified squamous
epthelium; important in glomerular filtration. Glomerulus has charge selectiveness and filters based on
the size and the charge because of the presence of heparin sulfate which are highly negative charge.
Heparin sulfate are present on basement membranes of kidney.
5. Heparin- only intracellular GAGs; acts as anticoagulant
6. Keratin sulfate- found in skin
Two types:
a) Keratin sulfate I- found in cornea; systematic arrangement resulting to the transparency of
cornea
b) Keratin sulfate II- found in loose connective tissue
Four leucine rich repeat proteoglycans are present in the extracellular matrix of corneal stroma:
1. decorin 2. lumican 3. mimecan and 4. keratocan
The first is a dermatan sulfate proteoglycan and the last three are keratan sulfate
proteoglycan
Dermatan sulfate proteoglycan- are involved in the regulation of collagen fibril diameter
You might also like
- Heteropolysaccharides Lecture For 1st Yr MBBS by DR Waseem KausarDocument20 pagesHeteropolysaccharides Lecture For 1st Yr MBBS by DR Waseem KausarIMDCBiochem67% (6)
- GAGsDocument53 pagesGAGsAlishba AzizNo ratings yet
- Glycosaminoglycan S and ProteoglycansDocument54 pagesGlycosaminoglycan S and ProteoglycansBharath wajNo ratings yet
- Glycoproteins and Proteoglycans TTVDocument34 pagesGlycoproteins and Proteoglycans TTVcraigNo ratings yet
- Glycosaminoglycans: DR Sadia HaroonDocument54 pagesGlycosaminoglycans: DR Sadia HaroonsubhamchampNo ratings yet
- Bio 310Document39 pagesBio 310flipside1o1No ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument74 pagesConnective TissueAffie SaikolNo ratings yet
- Extracellular Matrix: Mrs. Ofelia Solano SaludarDocument29 pagesExtracellular Matrix: Mrs. Ofelia Solano SaludarmskikiNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument39 pagesCarbohydratesWardah AliNo ratings yet
- Dr. Astha Goyal Dept. of Biochemistry MGMC&HDocument28 pagesDr. Astha Goyal Dept. of Biochemistry MGMC&HASTHA GOYALNo ratings yet
- Bio Unit 1 and Unit 2 Revision Posters - ComprehensiveDocument70 pagesBio Unit 1 and Unit 2 Revision Posters - Comprehensiveapi-247243068No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Chapter 7 (Part II)Document19 pagesCarbohydrates: Chapter 7 (Part II)Omer KareemNo ratings yet
- ProteoglycansDocument4 pagesProteoglycansRoxana FrincuNo ratings yet
- OutputDocument12 pagesOutputMarielle VentulaNo ratings yet
- Bio Chemistry AssignmentDocument8 pagesBio Chemistry AssignmentHKNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Part IDocument32 pagesCarbohydrate Part IHamza QaziNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Carbohydrates: MonosaccharidesDocument5 pagesChapter 8 - Carbohydrates: MonosaccharidesAlexis MunyentwaliNo ratings yet
- ECM NotesDocument27 pagesECM NotesTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Galactosemia 1B1G6Document13 pagesGalactosemia 1B1G6Karen Estavillo100% (1)
- NO.11 1. Golgi ApparatusDocument25 pagesNO.11 1. Golgi ApparatusEkaterina SurguladzeNo ratings yet
- Heteroglycans: Proteoglycans (Gags), Peptidoglycans and GlycoproteinsDocument13 pagesHeteroglycans: Proteoglycans (Gags), Peptidoglycans and GlycoproteinsSaeed AbdulhadiNo ratings yet
- NBDEDocument151 pagesNBDEfadi100% (1)
- ZOO302: CHAPTER 2 (Pages 24-46)Document3 pagesZOO302: CHAPTER 2 (Pages 24-46)Charlene ElioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Jnu Biomembranes-1 - 複本Document48 pagesChapter 4-Jnu Biomembranes-1 - 複本Wai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of MucopolysaccharidesDocument7 pagesBiosynthesis of MucopolysaccharidesadheenaNo ratings yet
- 01.5 Bio Lec TransDocument8 pages01.5 Bio Lec TransKyleNo ratings yet
- N-Linked Glycosylation, Is The Attachment of AnDocument18 pagesN-Linked Glycosylation, Is The Attachment of AnMick KieNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of CarbohydrateDocument30 pagesBiochemistry of Carbohydratesofianeha2012No ratings yet
- Metabolic Pathway of Carbohydrate and GlycolysisDocument22 pagesMetabolic Pathway of Carbohydrate and GlycolysisDarshansinh MahidaNo ratings yet
- Protein Modification and TraffickingDocument45 pagesProtein Modification and TraffickingKok MerngNo ratings yet
- The Plant Cell WallDocument56 pagesThe Plant Cell WallAngeline BayudanNo ratings yet
- Sheet 13 GhaithDocument15 pagesSheet 13 GhaithСаша ТищенкоNo ratings yet
- Lipid Movement BiochemDocument9 pagesLipid Movement BiochemCrowNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates (CHO)Document190 pagesCarbohydrates (CHO)Mustafa KhandgawiNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Cellulose and ChitinDocument6 pagesThe Difference Between Cellulose and Chitincindy khairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Sugar MetabolismDocument113 pagesSugar MetabolismmismaelNo ratings yet
- 9 ชีวพลังงานและเมแทบอลิซึมของคาร์โบไฮเดรตDocument41 pages9 ชีวพลังงานและเมแทบอลิซึมของคาร์โบไฮเดรต22vk6svnb4No ratings yet
- Study Exercise Biology 10-12 97.03Document7 pagesStudy Exercise Biology 10-12 97.03Fabiola Vania FeliciaNo ratings yet
- Cells and Genomes MacromoleculesDocument10 pagesCells and Genomes MacromoleculesAkmad SugodNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument10 pagesBiomoleculeststylizeNo ratings yet
- Golgi ApparatusDocument4 pagesGolgi ApparatusalecNo ratings yet
- 1 CytologyDocument86 pages1 CytologyRathana Nguon100% (1)
- ACFrOgB4ugyviBu1XK4Lh1UX8Pt64wVQwa2 Exi6l8nAFhE Uu1QLN5OIKowfbqMbZ48dVUAL2yq7eDi4HBBlOHGoCWigzrxxjl305MoZfTvJxd54XHQjc6yi-YzD8c PDFDocument12 pagesACFrOgB4ugyviBu1XK4Lh1UX8Pt64wVQwa2 Exi6l8nAFhE Uu1QLN5OIKowfbqMbZ48dVUAL2yq7eDi4HBBlOHGoCWigzrxxjl305MoZfTvJxd54XHQjc6yi-YzD8c PDFLpNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Hormone Action: DR Jehad Al-ShuneigatDocument47 pagesMechanism of Hormone Action: DR Jehad Al-Shuneigatyousef sarairehNo ratings yet
- Enzymatic Synthesis of Carbohydrate-Containing Biomolecules: Advanced ArticleDocument22 pagesEnzymatic Synthesis of Carbohydrate-Containing Biomolecules: Advanced Articleazzaass100% (1)
- Saliva PhysiologyDocument19 pagesSaliva Physiologyjatt_mu_phattNo ratings yet
- Collagen A. What Are The Primary Amino Acids Compositions?Document2 pagesCollagen A. What Are The Primary Amino Acids Compositions?mumen abusadahNo ratings yet
- Lipids - ReviewerDocument5 pagesLipids - ReviewerGabrielle FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Struktur Dan Fungsi Dinding SelDocument63 pagesStruktur Dan Fungsi Dinding SelAtika Rachmania LiloNo ratings yet
- Stryer Biochem10e Lectureslides Ch16Document155 pagesStryer Biochem10e Lectureslides Ch16will011225No ratings yet
- Chem 1223 - A8Document5 pagesChem 1223 - A8Ramil LucasNo ratings yet
- BIOL 215 - CWRU Final Exam Learning GoalsDocument32 pagesBIOL 215 - CWRU Final Exam Learning GoalsKesharaSSNo ratings yet
- 03lect Cell2 Summary2017Document4 pages03lect Cell2 Summary2017Dan ChoiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6-Carbohydrates Spring 24Document25 pagesLecture 6-Carbohydrates Spring 24ziadwageh74No ratings yet
- CYTOPLASM - : PlasmalemmaDocument9 pagesCYTOPLASM - : Plasmalemmaminhmap90_635122804No ratings yet
- CarbohidratosDocument8 pagesCarbohidratosElena OlmedoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates ReviewerDocument6 pagesCarbohydrates ReviewerNino D. AtilanoNo ratings yet
- Lactose Permease Scrambles PhospholipidsDocument13 pagesLactose Permease Scrambles PhospholipidsClaudia TorresNo ratings yet
- Lipids, Membranes and Transport OutlineDocument25 pagesLipids, Membranes and Transport Outlinefalcons22No ratings yet
- Tuna Kinilaw PDFDocument3 pagesTuna Kinilaw PDFJhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 6: Terrestrial Sampling Techniques: Ña, Manila PhilippinesDocument6 pagesEXERCISE 6: Terrestrial Sampling Techniques: Ña, Manila PhilippinesJhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- Tuna Kinilaw PDFDocument3 pagesTuna Kinilaw PDFJhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- Time vs. Temperature (Group 1: Solanum Tuberosum)Document22 pagesTime vs. Temperature (Group 1: Solanum Tuberosum)Jhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- ADDITIONALDocument4 pagesADDITIONALJhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- Long Distance Relationship Within Context of MarriageDocument8 pagesLong Distance Relationship Within Context of MarriageJhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- J BergerDocument4 pagesJ BergerJhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- Facilitated DiffusionDocument15 pagesFacilitated DiffusionJhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- Cuadrasal, Grei Duzon, Jhoanna Rein Salviejo, Jericho Topic: Myotonic Muscular Dystrophy ReferencesDocument3 pagesCuadrasal, Grei Duzon, Jhoanna Rein Salviejo, Jericho Topic: Myotonic Muscular Dystrophy ReferencesJhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6Document1 pageExercise 6Jhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of Saponifiable and NonDocument18 pagesIsolation and Characterization of Saponifiable and NonJhoanna Rein Duzon100% (2)
- Pacem in Terris (Peace On Earth)Document7 pagesPacem in Terris (Peace On Earth)Jhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- Results and DiscussionDocument2 pagesResults and DiscussionJhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- Jhoanna Rein S. Duzon 4B4Document8 pagesJhoanna Rein S. Duzon 4B4Jhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- Facilitated Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion (Also Known As Facilitated Transport or Passive-Mediated Transport) Is The Process ofDocument5 pagesFacilitated Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion (Also Known As Facilitated Transport or Passive-Mediated Transport) Is The Process ofJhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- A Divine Misconception - A New CriticalDocument5 pagesA Divine Misconception - A New CriticalJhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- Oia Rabbit PDFDocument13 pagesOia Rabbit PDFJhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- Work Power and EnergyDocument8 pagesWork Power and EnergyJhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- Development of Sociology and Anthropology in The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDevelopment of Sociology and Anthropology in The PhilippinesJhoanna Rein Duzon75% (8)
- Relection Action See Judge Act BookletDocument4 pagesRelection Action See Judge Act BookletJhoanna Rein Duzon100% (1)
- John Milton (1608-1674)Document3 pagesJohn Milton (1608-1674)Jhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- Hellen KellerDocument6 pagesHellen KellerJhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- Two Unique Systems: Dewey vs. LOC - Clash of Classification TitansDocument3 pagesTwo Unique Systems: Dewey vs. LOC - Clash of Classification TitansJhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- MB Lab ReportDocument7 pagesMB Lab ReportJhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- CarbohydrateDocument43 pagesCarbohydrateJhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- Dodatak MozzartDocument27 pagesDodatak MozzartMarko MilerovicNo ratings yet
- What Is An OligoDocument4 pagesWhat Is An OligokavyamotianisgNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Biology FA 4 Question and Answer - EnzymesDocument5 pagesGrade 8 Biology FA 4 Question and Answer - EnzymesdhuriprashantNo ratings yet
- Protein Structure PredictionDocument17 pagesProtein Structure PredictiongppbiinfoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - DNA Structure PDFDocument6 pagesLecture 3 - DNA Structure PDFАбу ДжудNo ratings yet
- Dieta 2 SemanasDocument2 pagesDieta 2 SemanasAndrey CaroNo ratings yet
- Inquiry Based LearningDocument3 pagesInquiry Based LearningJennifer De Guzman ReloxNo ratings yet
- Molbio HandoutDocument29 pagesMolbio HandoutHazel FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- MCQ Cytology 2012-2016Document10 pagesMCQ Cytology 2012-2016stuffNo ratings yet
- Biomolecule QuestionsDocument8 pagesBiomolecule QuestionsNayan Bhardwaz100% (2)
- BS 161 QuizletDocument25 pagesBS 161 QuizletKaushik SridasyamNo ratings yet
- L2 Amino Acids, Protein Structure Nursing 2021-3Document27 pagesL2 Amino Acids, Protein Structure Nursing 2021-3RNo ratings yet
- Solutions 25Document11 pagesSolutions 25abhilashlovesall100% (7)
- Biological Databases GenbankDocument31 pagesBiological Databases GenbankjaineemNo ratings yet
- Helicos TSMS Technology PrimerDocument2 pagesHelicos TSMS Technology PrimerNhu Phuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Form Hasil Pemeriksaan Laboratorium 2Document5 pagesForm Hasil Pemeriksaan Laboratorium 2puskesmas sarijadiNo ratings yet
- Spatial Imaging of Glycorna in Single Cells With Arpla: Nature BiotechnologyDocument26 pagesSpatial Imaging of Glycorna in Single Cells With Arpla: Nature Biotechnology郑子豪No ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument3 pagesDNA ReplicationApril Marie100% (3)
- Lab Report On Gene Cloning and Vector ExpressionDocument11 pagesLab Report On Gene Cloning and Vector Expressionselina_kolls100% (2)
- Protein Characterization/Purification: Dr. Kevin AhernDocument34 pagesProtein Characterization/Purification: Dr. Kevin AhernkelpachurpaNo ratings yet
- Structure of RnaDocument44 pagesStructure of RnaAditi CharakNo ratings yet
- 5e Plan-Central DogmaDocument2 pages5e Plan-Central Dogmaapi-307962259No ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Polymers - DTS 2 Main (Archive)Document2 pagesBiomolecules and Polymers - DTS 2 Main (Archive)Shreyas MuthaNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Enzyme and Its ClassificationDocument30 pagesLec 1 Enzyme and Its ClassificationSadia DinNo ratings yet
- Chap 011Document17 pagesChap 011alexa chalhoubNo ratings yet
- Cell SignalingDocument118 pagesCell SignalingHimakiran BabuNo ratings yet
- Cloning MethodsDocument24 pagesCloning MethodsRam Nivas Ahirwar100% (7)
- Pierce SM Chapter10Document10 pagesPierce SM Chapter10vaishali shuklaNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Fusion Protein Linkers: Property, Design and FunctionalityDocument32 pagesNIH Public Access: Fusion Protein Linkers: Property, Design and FunctionalityDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- MIMM 385 Experimental Plan Ver. 1 - He, Zhang, YousefDocument12 pagesMIMM 385 Experimental Plan Ver. 1 - He, Zhang, YousefMatthew HeNo ratings yet
- ICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideFrom EverandICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideAndrew TeasdaleNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingFrom EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeFrom EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsFrom EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- The Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesFrom EverandThe Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeFrom EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodFrom EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (20)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Billion-Dollar Molecule: The Quest for the Perfect DrugFrom EverandThe Billion-Dollar Molecule: The Quest for the Perfect DrugRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Essential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid DosagesFrom EverandEssential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid DosagesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)