Professional Documents
Culture Documents
15ECE286 Electronic Circuits Laboratory Week - 2 Expt. 1 Networks - Measurements and Limitations
Uploaded by
Slim ShadyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
15ECE286 Electronic Circuits Laboratory Week - 2 Expt. 1 Networks - Measurements and Limitations
Uploaded by
Slim ShadyCopyright:
Available Formats
Amrita
School of Engineering, Coimbatore Dec. 2017 – May 2018
15ECE286 Electronic Circuits Laboratory
Week -‐2
Expt. 1 Networks – Measurements and Limitations
Objective:
In this laboratory session, the student will get to know the principle behind making some of the simple
measurements in the laboratory and the limitations of the instruments that are commonly used for this purpose.
Instructions:
1. Before you start connecting up your circuit, ensure that all power supplies are switched off and that the control
knobs are in the minimum setting.
2. Before you start taking measurements, make sure that your Voltmeters, Ammeters, Oscilloscopes, etc are working
properly. The display on the power sources may not be reliable – use either the voltmeter or the Oscilloscope to
check.
3. Double check the values of the resistors that you are using – they may not have been in the right bin, when you
picked them up. Using the wrong value of the resistance might mean that you damage your circuit, board, other
equipment as well as the chances of your continued presence in the laboratory.
4. Follow any instructions given by the Laboratory Staff, Teaching Assistants or the Faculty-‐in-‐Charge.
Procedure:
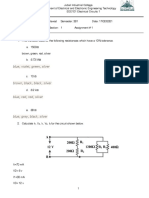
1. Consider the circuit given in Fig. 1. Answer the following questions before you come to the A 100 kΩ C 10 MΩ
lab:
a. What is the effective resistance across AB ? 10 MΩ
b. How would you measure the resistance across AB ? (Just a brief note will
B
suffice – no circuit diagrams or explanations are required) What equipment
1
Fig.
would you use ? What would be the specifications of the equipment ?
+
A -‐
P
+
A -‐
P
1
2
Network
-‐
1
Network
-‐
1
+
+
Vin
V1
Vin
V2
-‐
-‐
Q
Q
Fig. 2a Fig. 2b
2. Obtain the network, whose input impedance is to be determined, from the Lab Staff. (Do not attempt to open up
the network given to you). This network is shown as Network – 1 in Fig. 2a above. Connect up the voltage source
Vin, ammeter A and Voltmeter V1 to the network as shown in Fig. 2a. Take care to ensure that the meters are
connected with the correct polarity. Keep both the meters in the highest range.
3. Switch on the power supply. Vary the input voltage Vin from 0 to 20 V, in steps of 2 V. Use the power supply display
as Vin. Step down the ranges on both the voltmeter and the ammeter to the appropriate one.
4. Note V1 and A1, in a table as shown below. Calculate the effective resistance of the network as . Determine
the average value of R1.
Table 1 Effective Resistance with the circuit of Fig. 2b
Vin (V) V1 (V) A1 (mA) R1 (kΩ)
Dept. of Electronics and Communication Engineering Page 1 / 2
Amrita School of Engineering, Coimbatore Dec. 2017 – May 2018
5. Now, connect up your network as in Fig. 2b. Repeat Step 3.
6. Note down V2 and A2 in Table 2. Calculate the effective resistance of the network as . Determine the
average value of R2.
Table 2 Effective Resistance with the circuit of Fig. 2a
Vin (V) V2 (V) A2 (mA) R2 (kΩ)
Answer the following questions:
1. Are the average values of the effective resistance of the network as determined by the circuits of Figs. 2a and 2b,
the same ?
2. If the average values for the two circuits are different, why ?
3. Which is the correct way of measuring the effective resistance of the network ? Why ?
4. What is the input resistance of the voltmeter that you are using ?
Dept. of Electronics and Communication Engineering Page 2 / 2
You might also like
- Mipi Csi-2Document170 pagesMipi Csi-2back_to_battery100% (2)
- EEC 115 Electrical Engg Science 1 PracticalDocument29 pagesEEC 115 Electrical Engg Science 1 PracticalImokhai Abdullah50% (2)
- ST ND RD TH ND TH TH THDocument6 pagesST ND RD TH ND TH TH THprdpks2000No ratings yet
- Basic Lab Equipment and Circuit MeasurementsDocument14 pagesBasic Lab Equipment and Circuit MeasurementsAsma GulzarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Lab ExperimentsDocument75 pagesElectrical Engineering Lab ExperimentsUpender Rao SunkishalaNo ratings yet
- ST ND RD TH ND TH TH THDocument2 pagesST ND RD TH ND TH TH THprdpks2000No ratings yet
- Manual OfcDocument38 pagesManual OfcAnonymous eWMnRr70qNo ratings yet
- strain gage labDocument4 pagesstrain gage labGeniusNo ratings yet
- 1647 6044 1 PBDocument4 pages1647 6044 1 PBAria Nurul HaqNo ratings yet
- foanfis pptDocument23 pagesfoanfis pptSrinivasNo ratings yet
- FortiMail 4000A - QuickStart - Guide 06 30004 0346 20080909Document2 pagesFortiMail 4000A - QuickStart - Guide 06 30004 0346 20080909Kejal PatelNo ratings yet
- LW Le: Approved - BOS May 2018 (W.e.f A.Y 2018-19) 2017 BatchDocument24 pagesLW Le: Approved - BOS May 2018 (W.e.f A.Y 2018-19) 2017 BatchChatrola JeelNo ratings yet
- Chemical EngineeringDocument4 pagesChemical Engineeringprdpks2000No ratings yet
- NAMUR Resistor Network F-NR3-Ex1: FunctionDocument2 pagesNAMUR Resistor Network F-NR3-Ex1: FunctionLuis Ernesto Miranda BurgosNo ratings yet
- Simulation-Based Optimum Sensor Selection Design For An Uncertain EMS System Via Monte-Carlo Technique.Document6 pagesSimulation-Based Optimum Sensor Selection Design For An Uncertain EMS System Via Monte-Carlo Technique.sankaralingamNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument4 pagesManualIdk Maybe AwaisNo ratings yet
- FN PC10CB01 MT01 BTH CPB - EDocument1 pageFN PC10CB01 MT01 BTH CPB - EMahmoud AlsaeedNo ratings yet
- ILJIN HV Cable Catalog PDFDocument17 pagesILJIN HV Cable Catalog PDFRobert McAlisterNo ratings yet
- Elec 3404 Lab Note 2011Document15 pagesElec 3404 Lab Note 2011Mrinal MitraNo ratings yet
- Elements of Radio Servicing (First Edition 1947)Document474 pagesElements of Radio Servicing (First Edition 1947)jrodhNo ratings yet
- Lab Plan ED 2023-24Document3 pagesLab Plan ED 2023-24pulkit.dwivedi22No ratings yet
- Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College: Laboratory ManualDocument25 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Engineering College: Laboratory ManualanjuprasuNo ratings yet
- Op-Amp Errors, Another View: Derivations of Basic Circuit EquationsDocument7 pagesOp-Amp Errors, Another View: Derivations of Basic Circuit Equationsمحمد المحمديNo ratings yet
- SPH3000-6000 Quick InstallationDocument2 pagesSPH3000-6000 Quick InstallationPMV DeptNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits: Lab Manual Experiment No 8Document6 pagesElectric Circuits: Lab Manual Experiment No 8usamaNo ratings yet
- Loop-Antenna CalibrationDocument12 pagesLoop-Antenna CalibrationAton LuanNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 - Wireless Power Transfer PDFDocument2 pagesLab 5 - Wireless Power Transfer PDFRuben CollinsNo ratings yet
- 1995_NEURAL NETWORK APPROACH TO FAULT CLASSIFICATIONDocument10 pages1995_NEURAL NETWORK APPROACH TO FAULT CLASSIFICATIONParesh NayakNo ratings yet
- Be Lab ManualDocument42 pagesBe Lab ManualELECTRONICS COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING BRANCHNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report on Characteristics of BJT AmplifierDocument12 pagesLaboratory Report on Characteristics of BJT AmplifierBen EdwardNo ratings yet
- Shubham 15EE1075 C4 DBMS Experiment 5Document4 pagesShubham 15EE1075 C4 DBMS Experiment 5Shubham YelekarNo ratings yet
- EIS Application NoteDocument6 pagesEIS Application NoteNoor RaihanNo ratings yet
- Circuitos Lab 1Document22 pagesCircuitos Lab 1Alejandro RojasNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment EEP (CE00436-1)Document8 pagesIndividual Assignment EEP (CE00436-1)Ravi SinghNo ratings yet
- Proposal Minilecture FA15Document20 pagesProposal Minilecture FA15Semiu AdelekeNo ratings yet
- 905-0001 Sita Multipoint ASD Detector Base: Installation and Maintenance InstructionsDocument2 pages905-0001 Sita Multipoint ASD Detector Base: Installation and Maintenance Instructionsamartins1974No ratings yet
- 3-PS Lab FINAL Jan2024Document46 pages3-PS Lab FINAL Jan2024Akshat PradhanNo ratings yet
- .NG EEC115 Electrical Engineering Science 1Document29 pages.NG EEC115 Electrical Engineering Science 1archibong dominicNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document6 pagesLab 2dueshawn09No ratings yet
- Nobaz PE Lab 07Document10 pagesNobaz PE Lab 07Muhammad DanialNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Target Reliability SAIDI For Distribution LinesDocument5 pagesCalculation of Target Reliability SAIDI For Distribution LinesGheorghe HaziNo ratings yet
- ET301 Linear Integrated Circuits and ApplicationsDocument41 pagesET301 Linear Integrated Circuits and ApplicationsChaitanya P V KNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Electrical Engineering Syllabus 2015-16Document76 pagesB.Tech Electrical Engineering Syllabus 2015-16ବିଭୁତି ଭୁଷଣ ବେହେରାNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit Analysis of IEEE Test FeedersDocument9 pagesShort Circuit Analysis of IEEE Test FeedersMACARIO CRUZNo ratings yet
- LDICA Lecture Notes by A.Mounika PDFDocument143 pagesLDICA Lecture Notes by A.Mounika PDFTwinkle Ratna100% (1)
- EE201 CHP 3.1 W4L2 UpDocument14 pagesEE201 CHP 3.1 W4L2 Upzain khuramNo ratings yet
- EEE 101-Assignment 1.1Document3 pagesEEE 101-Assignment 1.1ali mohammedNo ratings yet
- ICA Lab Manual PDFDocument193 pagesICA Lab Manual PDFVijay MNo ratings yet
- Ee-Mock Test SampleDocument14 pagesEe-Mock Test SampleVivekanand KumarNo ratings yet
- State Council For Technical Education and Vocational Training, OdishaDocument25 pagesState Council For Technical Education and Vocational Training, Odishasantosh975No ratings yet
- PEE492C Electrical Machines and Measurement LabDocument12 pagesPEE492C Electrical Machines and Measurement LabRaqib ChohdharyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics Lab ManualDocument29 pagesEngineering Physics Lab ManualariyanshkadamNo ratings yet
- 22423-2019-Winter-Model-Answer-Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Document18 pages22423-2019-Winter-Model-Answer-Paper (Msbte Study Resources)OM BURADENo ratings yet
- Telecom - Module - 3 Assignment - Paper - Batch 3 PDFDocument2 pagesTelecom - Module - 3 Assignment - Paper - Batch 3 PDFMani Chandu PaboluNo ratings yet
- PM750 Install ManualDocument2 pagesPM750 Install ManualCarlos Andres RojasNo ratings yet
- R18 B.Tech Eee Iii YearDocument42 pagesR18 B.Tech Eee Iii YearNIMMANAGANTI RAMAKRISHNANo ratings yet
- GST-C-9202 Conventional Manual Call Point Issue1.06 PDFDocument2 pagesGST-C-9202 Conventional Manual Call Point Issue1.06 PDFwayeb andoremNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1434841117329758 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S1434841117329758 MainRAJANo ratings yet
- Intel Ethernet Connection I219 Reference Schematic Rev1 0Document1 pageIntel Ethernet Connection I219 Reference Schematic Rev1 0Смартфон СигмаNo ratings yet
- APPLIED ELECTRICITY AND ELECTRONICS - FDocument3 pagesAPPLIED ELECTRICITY AND ELECTRONICS - FMahmoud SaeedNo ratings yet
- BihavedcDocument1 pageBihavedcSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- Dmesg TutorialDocument2 pagesDmesg TutorialSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- Netplan TutorialDocument3 pagesNetplan TutorialSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- Uname TutorialDocument2 pagesUname TutorialSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- Linux Var LogDocument2 pagesLinux Var LogSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- TestjkfDocument1 pageTestjkfSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- AdrayewDocument1 pageAdrayewSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- ksz9477 Dsa BootlogDocument2 pagesksz9477 Dsa BootlogSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- TestqweDocument1 pageTestqweSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- Open Lab ReportDocument7 pagesOpen Lab ReportSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- AonanaDocument1 pageAonanaSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- CSE 230: Data Structures: Lecture 2: Complexity AnalysisDocument21 pagesCSE 230: Data Structures: Lecture 2: Complexity AnalysisSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Slim ShadyNo ratings yet
- Dac P2Document12 pagesDac P2Slim ShadyNo ratings yet
- Insertion Sort Bubble Sort Selection SortDocument31 pagesInsertion Sort Bubble Sort Selection SortSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- Finance NotesDocument6 pagesFinance NotesSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- Types of control valves: multi-turn, quarter-turn and linear motion valvesDocument19 pagesTypes of control valves: multi-turn, quarter-turn and linear motion valvesSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- Scott Guinn - Table-Hopping Cups and Balls PDFDocument11 pagesScott Guinn - Table-Hopping Cups and Balls PDFarnav0chakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Model For A Stirred Tank HeaterDocument14 pagesMathematical Model For A Stirred Tank HeaterMfon100% (3)
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- P&ID Diagrams: The Essential Process Control DrawingDocument15 pagesP&ID Diagrams: The Essential Process Control DrawingSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- 15EIE312+Process+Control Tutorial+1+questionsDocument1 page15EIE312+Process+Control Tutorial+1+questionsSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- Sevens Tournament by PG: Group 1Document2 pagesSevens Tournament by PG: Group 1Slim ShadyNo ratings yet
- Epm Manual FD910 FD950 FD960Document61 pagesEpm Manual FD910 FD950 FD960Slim ShadyNo ratings yet
- 15ECE202 Nov2016Document2 pages15ECE202 Nov2016Slim ShadyNo ratings yet
- 15EC303 - Ass I - Aug2017 PDFDocument2 pages15EC303 - Ass I - Aug2017 PDFSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- 15MAT204 Dec2016Document1 page15MAT204 Dec2016Slim ShadyNo ratings yet
- Hello 123Document1 pageHello 123Slim ShadyNo ratings yet
- TemplateDocument1 pageTemplateSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- Sn74als245a PDFDocument21 pagesSn74als245a PDFRodriguezJoseCarlosNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry ES 105Document1 pageBiochemistry ES 105Ko Phyo Wai100% (3)
- DISP TRUST 18 SEPTIEMBRE 2023 ClientesDocument100 pagesDISP TRUST 18 SEPTIEMBRE 2023 ClientesAlex David Dueñas QuinteroNo ratings yet
- PM Sensor Power Supply Fault DiagnosisDocument5 pagesPM Sensor Power Supply Fault DiagnosisJoanmanel Sola QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Mercury Series V16 PN 07008 00067Document280 pagesMercury Series V16 PN 07008 00067Hiep VoNo ratings yet
- UPS & Battery SizingDocument0 pagesUPS & Battery SizingShrikant Kajale100% (1)
- m500 Brushed DC Servo Motors DatasheetDocument2 pagesm500 Brushed DC Servo Motors Datasheethafidzfb100% (1)
- 8086 Address/Data Buses: WR RD M/Io Addr ControlDocument40 pages8086 Address/Data Buses: WR RD M/Io Addr ControlMike ThomsonNo ratings yet
- Networking Concepts ExplainedDocument3 pagesNetworking Concepts ExplainedDaniel TendeanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Syllabus - Optical CommunicationDocument3 pagesDetailed Syllabus - Optical Communicationiamitgarg7No ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Sequential Circuits: Examples: COSC3410Document36 pagesAnalysis and Design of Sequential Circuits: Examples: COSC3410markolzNo ratings yet
- CT's and PT's - Learn MeteringDocument3 pagesCT's and PT's - Learn MeteringDGGNo ratings yet
- 50mm Size Ring Type: Large Encoder With 31mm Inside Diameter Even Takes A Small LCDDocument3 pages50mm Size Ring Type: Large Encoder With 31mm Inside Diameter Even Takes A Small LCDshyhuNo ratings yet
- Ba 5826 FPDocument7 pagesBa 5826 FPdragon-red0816No ratings yet
- Frequency Mixer SYM-25DMHW+: Typical Performance DataDocument5 pagesFrequency Mixer SYM-25DMHW+: Typical Performance DataAparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- DC aDCghskjskksks FjsDocument4 pagesDC aDCghskjskksks FjsSaiteja GundapuNo ratings yet
- SBGR Ils-T-Rwy-28r Iac 20220908Document1 pageSBGR Ils-T-Rwy-28r Iac 20220908jcndrckz4qNo ratings yet
- s7300 PDFDocument238 pagess7300 PDFLong HuynhNo ratings yet
- J1000 basic inverter V/f control and specificationsDocument12 pagesJ1000 basic inverter V/f control and specificationsVarga LászlóNo ratings yet
- Analog Devices O-RAN Wireless White PaperDocument9 pagesAnalog Devices O-RAN Wireless White PaperAfrim BerişaNo ratings yet
- Zelda Welding Machine CatalogDocument72 pagesZelda Welding Machine CatalogJuan Manuel Suarez OreNo ratings yet
- The Miracle Whip: A Multiband QRP Antenna Made From Inexpensive PartsDocument4 pagesThe Miracle Whip: A Multiband QRP Antenna Made From Inexpensive PartsAnonymous vRX0OvwHNo ratings yet
- LM2901/ LM2901A/ LM2903/ LM2903A: Dual and Quad Differential ComparatorsDocument16 pagesLM2901/ LM2901A/ LM2903/ LM2903A: Dual and Quad Differential ComparatorsafonsomoutinhoNo ratings yet
- SSC Je Digital Electronics E6dad2ca PDFDocument3 pagesSSC Je Digital Electronics E6dad2ca PDFarpitrockNo ratings yet
- Vacon NX Products For Common DC Bus SystemsDocument20 pagesVacon NX Products For Common DC Bus SystemsSilvian IonescuNo ratings yet
- Smart Card Attendance SystemDocument81 pagesSmart Card Attendance Systemsunil100% (2)
- Mach3 To Run JK02-M5 Breakout BoardDocument7 pagesMach3 To Run JK02-M5 Breakout BoardAmr MohamedNo ratings yet
- RamDocument3 pagesRamJaveed AhamedNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 2: Voltage Divider and Current Divider Circuit DesignDocument5 pagesActivity No. 2: Voltage Divider and Current Divider Circuit DesignFe Shannen CincoNo ratings yet