Professional Documents
Culture Documents
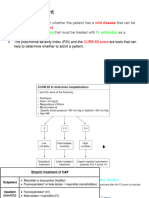
Treating Community-Acquired Pneumonia
Uploaded by
dwi-1485020 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageThis document provides treatment guidelines for community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in various patient populations and settings. It recommends using macrolides, doxycycline, amoxicillin, or cephalosporins for outpatient treatment of CAP without risk factors. For hospitalized patients, it suggests second- or third-generation cephalosporins with or without erythromycin. For severe CAP, ICU patients, or those at risk of drug-resistant bacteria, it recommends combinations of beta-lactams, macrolides, fluoroquinolones, or aminoglycosides. Treatment duration depends on resolution of symptoms and is typically 5 days or longer for severe cases.
Original Description:
Journal Pneumonia
Original Title
Journal 2 Pneumonia_3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides treatment guidelines for community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in various patient populations and settings. It recommends using macrolides, doxycycline, amoxicillin, or cephalosporins for outpatient treatment of CAP without risk factors. For hospitalized patients, it suggests second- or third-generation cephalosporins with or without erythromycin. For severe CAP, ICU patients, or those at risk of drug-resistant bacteria, it recommends combinations of beta-lactams, macrolides, fluoroquinolones, or aminoglycosides. Treatment duration depends on resolution of symptoms and is typically 5 days or longer for severe cases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageTreating Community-Acquired Pneumonia
Uploaded by
dwi-148502This document provides treatment guidelines for community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in various patient populations and settings. It recommends using macrolides, doxycycline, amoxicillin, or cephalosporins for outpatient treatment of CAP without risk factors. For hospitalized patients, it suggests second- or third-generation cephalosporins with or without erythromycin. For severe CAP, ICU patients, or those at risk of drug-resistant bacteria, it recommends combinations of beta-lactams, macrolides, fluoroquinolones, or aminoglycosides. Treatment duration depends on resolution of symptoms and is typically 5 days or longer for severe cases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
are more expensive than erythromycin but better tolerated and •
Doxycycline 100mg PO bid
more active against Haem. Influenzae [22]. About 30 percent of the
• If received prior antibiotic within 3 months:
strains of Haem. influenzae produce beta-lactamase and are resistant
to ampicillin; most are susceptible to cephalosporins, doxycycline, • Azithromycin or clarithromycin plus amoxicillin 1g PO q8h
and trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole. Fluoroquinolones are effective or amoxicillin-clavulanate 2g PO q12h or
against atypical agents and Haem. Influenzae.
• Respiratory fluoroquinolone (eg, levofloxacin 750mg PO
The prevalence of penicillin-resistant Strep. pneumoniae, which daily or moxifloxacin 400mg PO daily)
accounts for over 25 percent of pneumococcal isolates in some
• Comorbidities present (eg, alcoholism, bronchiectasis/
areas of the United States and for higher rates in other areas of the
cystic fibrosis, COPD, IV drug user, post influenza, asplenia,
world [23-25]. Alternative drugs are limited because of resistance to
diabetes mellitus, lung/liver/renal diseases):
trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole, macrolides, and cephalosporins.
Most strains have intermediate resistance to penicillin, and • Levofloxacin 750mg PO q24h or
uncomplicated pneumonia caused by these strains may be treated with
• Moxifloxacin 400mg PO q24h or
high doses of penicillin or selected cephalosporins, such as cefaclor
or cefotaxime [24]. Mortality due to pneumococcal pneumonia Combination of a beta-lactam (amoxicillin 1g PO q8h or
involving resistant strains is similar to that for pneumonia involving amoxicillin-clavulanate 2g PO q12h or ceftriaxone 1g IV/IM q24h
sensitive strains, even when the treatment includes penicillins or or cefuroxime 500mg PO BID) plus a macrolide (azithromycin or
cephalosporins [25]. clarithromycin)
Most patients with no bacteriologic diagnosis have infections Duration of therapy: minimum of 5 days, should be afebrile for
involving atypical agents such as legionella species, Mycop. 48-72 hours, or until afebrile for 3 days; longer duration of therapy
pneumoniae, or Chl. pneumoniae. This assumption accounts for may be needed if initial therapy was not active against the identified
the frequent use of macrolides for pneumonia, although studies in pathogen or if it was complicated by extrapulmonary infections.
outpatients show that macrolides and beta-lactam agents are equally Inpatient, non-ICU:
effective in adult outpatients with pneumonia [26]. Legionella is
an important pulmonary pathogen that requires treatment with • Levofloxacin 750mg IV or PO q24h or
a macrolide or fluoroquinolone, and applies only to hospitalized • Moxifloxacin 400mg IV or PO q24h or
patients [27].
• Combination of a beta-lactam (ceftriaxone 1g IV q24h or
Adults with community-acquired pneumonia should receive cefotaxime 1g IV q8h or ertapenem 1g IV daily or ceftaroline
treatment with antibiotic agents selected according to the results 600mg IV q12h) plus azithromycin 500mg IV q24h
of microbiologic studies of sputum and blood cultures. For young
adults treated as outpatients, the oral administration of a macrolide • Duration of therapy: minimum of 5 days, should be afebrile for
(erythromycin, clarithromycin, or azithromycin) or doxycycline; 48-72 hours, stable blood pressure, adequate oral intake, and
for patients older than 25, oral amoxicillin or an oral cephalosporin room air oxygen saturation of greater than 90%; longer duration
is also acceptable. For adults over 60 and those with coexisting may be needed in some cases.
illnesses who are treated as outpatients: oral cephalosporin or Inpatient, ICU:
amoxicillin; for patients with penicillin allergy, oral macrolide or
doxycycline. For hospitalized patients: Second- or third-generation Severe COPD:
cephalosporin (cefuroxime, cefotaxime, or ceftriaxone) with or • Levofloxacin 750mg IV or PO q24h or
without erythromycin, given parenterally; parenteral therapy should
continue until the patient has been afebrile for more than 24 hours • Moxifloxacin 400mg IV or PO q24h or
and oxygen saturation exceeds 95 percent [28]. • Ceftriaxone 1g IV q24h or ertapenem 1g IV q24h plus
Several medical-specialty professional societies have suggested azithromycin 500mg IV q24h
that combination therapy with a β-lactam plus a macrolide or If gram-negative rod pneumonia (Pseudomonas) suspected, due
doxycycline or monotherapy with a “respiratory quinolone” (i.e., to alcoholism with necrotizing pneumoniae, chronic bronchiectasis/
levofloxacin, gatifloxacin, moxifloxacin, or gemifloxacin) are optimal tracheobronchitis due to cystic fibrosis, mechanical ventilation,
first-line therapy for patients hospitalized with community-acquired febrile neutropenia with pulmonary infiltrate, septic shock with
pneumonia [29]. Combination antibiotic therapy achieves a better organ failure:
outcome compared with monotherapy, and it should be given in the
following subset of patients with CAP: outpatients with comorbidities • Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5g IV q6h or 3.375g IV q4h or 4-h
and previous antibiotic therapy, nursing home patients with CAP, infusion of 3.375g q8h or
hospitalized patients with severe CAP, bacteremic pneumococcal • Cefepime 2g IV q12h or
CAP, presence of shock, and necessity of mechanical ventilation [30].
• Imipenem/cilastatin 500mg IV q6h or meropenem 1 g IV q8h or
Empiric therapeutic regimens for CAP are outlined below,
including those for outpatients with or without comorbidities, • If penicillin allergic, substitute aztreonam 2g IV q6h plus
intensive care unit (ICU) and non-ICU patients, and penicillin- • Levofloxacin 750mg IV q24h or
allergic patients [31].
• Moxifloxacin 400mg IV or PO q24h or
Outpatient:
• Aminoglycoside (gentamicin 7mg/kg/day IV or tobramycin 7mg/
• No comorbidities/previously healthy; no risk factors for kg/day IV)
drug-resistant S pneumoniae:
• Add azithromycin 500mg IV q24h if respiratory fluoroquinolone
• Azithromycin 500mg PO one dose, then 250mg PO daily for not used
4 d or extended-release 2g PO as a single dose
Duration of therapy: 10-14 days
or
If concomitant with or post influenza:
• Clarithromycin 500mg PO bid or extended-release 1000mg
PO q24h or • Vancomycin 15mg/kg IV q12h or linezolid 600 mg IV bid plus
Akter et al. Int J Respir Pulm Med 2015, 2:2 ISSN: 2378-3516 • Page 3 of 5 •
You might also like
- Pulmonary Infection GuidelinesDocument16 pagesPulmonary Infection GuidelinesFawad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Internal-Abdominal-infection-Treatment-ProtocolDocument9 pagesInternal-Abdominal-infection-Treatment-Protocolhatem newishyNo ratings yet
- Acute Pyelonephritis Treatment GuidelinesDocument4 pagesAcute Pyelonephritis Treatment GuidelinesPeter InocandoNo ratings yet
- Manage Community PneumoniaDocument6 pagesManage Community PneumoniaAlfa RidziNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia ADULTDocument6 pagesPneumonia ADULTSebastian TjuwatjaNo ratings yet
- WFBMC Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Treatment Guide For AdultsDocument2 pagesWFBMC Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Treatment Guide For AdultsAlmas Safina KauserNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For First-Line Empirical Antibiotic Therapy in AdultsDocument1 pageGuidelines For First-Line Empirical Antibiotic Therapy in AdultsAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- Anti Malarial Drugs by Salaria AnamikaDocument10 pagesAnti Malarial Drugs by Salaria AnamikaSalaria Anamika100% (1)
- Management of CommunityDocument1 pageManagement of CommunityTrixie Anne GamotinNo ratings yet
- Glenda AnehDocument4 pagesGlenda AnehglendaNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument22 pagesPneumoniaEmmaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of PneumoniaDocument7 pagesPharmacology of PneumoniaGomedi WuNo ratings yet
- Clin Phar NursDocument107 pagesClin Phar NursTadela MengashaNo ratings yet
- CPG Typhoid Fever 2017Document11 pagesCPG Typhoid Fever 2017Tam Adrian Aya-ayNo ratings yet
- CAP Guidance 2020 Revision Final UpdatedDocument11 pagesCAP Guidance 2020 Revision Final UpdatedNeerajaNo ratings yet
- Farmakoterapi Pada SepsisDocument36 pagesFarmakoterapi Pada SepsisNathaniaNo ratings yet
- Management of Healthcare-Associated Pneumonia (HCAP) in AdultsDocument3 pagesManagement of Healthcare-Associated Pneumonia (HCAP) in Adultstheseus5No ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument17 pagesPneumoniaamrokhalefa21No ratings yet
- Community Acquiredandhospital Acquiredpneumonia1Document29 pagesCommunity Acquiredandhospital Acquiredpneumonia1api-610938913No ratings yet
- 2RS. 3 PneumoniaDocument33 pages2RS. 3 PneumoniaMuath AlqarniNo ratings yet
- Habits Are Some of The Strategies RecommendedDocument30 pagesHabits Are Some of The Strategies Recommendedmd.dascalescu2486No ratings yet
- Septic ShockDocument35 pagesSeptic Shockphd0780No ratings yet
- Guideline For The Management of Community-Acquired PneumoniaDocument11 pagesGuideline For The Management of Community-Acquired PneumoniaCarlos VSNo ratings yet
- EVMS Critical Care COVID-19 ProtocolDocument23 pagesEVMS Critical Care COVID-19 ProtocoldarwinNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired Pneumonia: - Hafsah GhazaliDocument19 pagesCommunity Acquired Pneumonia: - Hafsah GhazaliloribyseaNo ratings yet
- Guideline for Diagnosing and Managing Acute PharyngitisDocument7 pagesGuideline for Diagnosing and Managing Acute PharyngitisRezki AnurNo ratings yet
- Sepsis and Septic Shock Management Guidelines 2019: Insp. Dr. Sunder Chapagain Nepal APF Hospital KathmanduDocument33 pagesSepsis and Septic Shock Management Guidelines 2019: Insp. Dr. Sunder Chapagain Nepal APF Hospital KathmanduKHAIRUL REDZUANNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics Community Acquired Pneumonia: Isimijola OpeyemiDocument30 pagesPediatrics Community Acquired Pneumonia: Isimijola OpeyemiFavourNo ratings yet
- Antifungal GuidelineDocument2 pagesAntifungal GuidelinedamondouglasNo ratings yet
- IDSA - Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis and Pyelonephritis in WomenDocument6 pagesIDSA - Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis and Pyelonephritis in WomenIcewizard EugeoNo ratings yet
- Antimikroba Dan Antiviral Pada Abdominal CompaintDocument86 pagesAntimikroba Dan Antiviral Pada Abdominal CompaintYulia KasihNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: Recent Evidence Based UpdatesDocument30 pagesPneumonia: Recent Evidence Based UpdatesAli AzamNo ratings yet
- CL Difficile ColitisDocument4 pagesCL Difficile ColitisAnonymous ZUaUz1wwNo ratings yet
- Icu Antibiotic GuidelinesDocument4 pagesIcu Antibiotic GuidelinesTia MonitaNo ratings yet
- Tavanic 5mgmlsolution SPCDocument16 pagesTavanic 5mgmlsolution SPCanchizNo ratings yet
- Antiprotozoal Drugs: Halia Wanadiatri, DR., M.SiDocument34 pagesAntiprotozoal Drugs: Halia Wanadiatri, DR., M.SiBaiqLinaAnggrianNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Treatment Adults Complicated Intra-abdominal InfectionsDocument2 pagesGuidelines Treatment Adults Complicated Intra-abdominal InfectionsluckevNo ratings yet
- TREATING OBSTETRIC/GYNECOLOGIC INFECTIONSDocument3 pagesTREATING OBSTETRIC/GYNECOLOGIC INFECTIONSHarshit RastogiNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycosides: Pharmacology, Therapeutic Uses, and Adverse EffectsDocument24 pagesAminoglycosides: Pharmacology, Therapeutic Uses, and Adverse EffectsMarieNo ratings yet
- Antibiotka PicuDocument4 pagesAntibiotka Picusunu rachmat100% (1)
- Medicine RotatationbookletDocument20 pagesMedicine RotatationbookletJanelle JosephsNo ratings yet
- Management of CAP in Adults - Ontario GovernmentDocument2 pagesManagement of CAP in Adults - Ontario GovernmentSukhvir AujlaNo ratings yet
- FluconazolecapmylanDocument20 pagesFluconazolecapmylanМомир МатовићNo ratings yet
- Sumit Bhutani: Neutropenic FeverDocument46 pagesSumit Bhutani: Neutropenic Feversumit240677No ratings yet
- Pharma-URO-CYCLIC LIPOEPETIDES (Vancomycin)Document6 pagesPharma-URO-CYCLIC LIPOEPETIDES (Vancomycin)Hussein AlhaddadNo ratings yet
- Penatalaksanaan CAPDocument31 pagesPenatalaksanaan CAPushagi-chanNo ratings yet
- Fluconazole: ErthromycinDocument7 pagesFluconazole: ErthromycinAseel AlsheeshNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Agents in UTIDocument12 pagesAntimicrobial Agents in UTITobias AlanNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument58 pagesAntibioticsKamal GhimireNo ratings yet
- Camp General Servillano A Aquino, 2301 San Miguel, Tarlac CityDocument9 pagesCamp General Servillano A Aquino, 2301 San Miguel, Tarlac CityRuffa FriasNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Community Pharmacy Training Summer 2018/2019Document23 pagesAntibiotics: Community Pharmacy Training Summer 2018/2019Anfal MNo ratings yet
- Hospital Acquiered PneumoniaDocument14 pagesHospital Acquiered PneumoniaAnonymous ZUaUz1wwNo ratings yet
- Drug of Treatment For Meningitis: Penicillin Cefotaxime ResistantDocument5 pagesDrug of Treatment For Meningitis: Penicillin Cefotaxime ResistantNama BestNo ratings yet
- PCAP Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument33 pagesPCAP Diagnosis and TreatmentRenette UyNo ratings yet
- Pocket Guide June2013 PDFDocument2 pagesPocket Guide June2013 PDFSergeyGruntov100% (1)
- HIV Infection - Opportunistic InfectionsDocument21 pagesHIV Infection - Opportunistic InfectionszawadiNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Treatment GuidelinesDocument26 pagesCOVID-19 Treatment GuidelinesStonefalconNo ratings yet
- Consortium ProtocolDocument16 pagesConsortium Protocolthe kingfishNo ratings yet
- Concise Guide to Clinical Dentistry: Common Prescriptions In Clinical DentistryFrom EverandConcise Guide to Clinical Dentistry: Common Prescriptions In Clinical DentistryNo ratings yet
- Tonsilitis - PDF Eng 2Document7 pagesTonsilitis - PDF Eng 2Ermanto D'PhytoxzNo ratings yet
- Study of Heart Rate Variability in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia - A Hospital-Based StudyDocument3 pagesStudy of Heart Rate Variability in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia - A Hospital-Based Studydwi-148502No ratings yet
- Study of Heart Rate Variability in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia - A Hospital-Based StudyDocument3 pagesStudy of Heart Rate Variability in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia - A Hospital-Based Studydwi-148502No ratings yet
- Rhinitis PDFDocument5 pagesRhinitis PDFbrendaNo ratings yet
- Journal Otitis Media (THT - KL)Document6 pagesJournal Otitis Media (THT - KL)dwi-148502No ratings yet
- Journal of Forensic and Legal MedicineDocument4 pagesJournal of Forensic and Legal Medicinedwi-148502No ratings yet
- Antropologi Forensik: Dr. Taufik Hidayat, M.SC, SP.FDocument46 pagesAntropologi Forensik: Dr. Taufik Hidayat, M.SC, SP.FRuslan KamilNo ratings yet
- Journal of Forensic and Legal MedicineDocument4 pagesJournal of Forensic and Legal Medicinedwi-148502No ratings yet
- Antropologi Forensik: Dr. Taufik Hidayat, M.SC, SP.FDocument46 pagesAntropologi Forensik: Dr. Taufik Hidayat, M.SC, SP.FRuslan KamilNo ratings yet
- Jurding PDFDocument8 pagesJurding PDFCHenyLeeNo ratings yet
- Tonsilitis - PDF Eng 2Document7 pagesTonsilitis - PDF Eng 2Ermanto D'PhytoxzNo ratings yet
- Pharyngitis, Diagnosis and Empiric Antibiotic Treatment ConsiderationsDocument7 pagesPharyngitis, Diagnosis and Empiric Antibiotic Treatment ConsiderationsIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Meningitis in Children Study Reveals High Case Fatality RatesDocument6 pagesMeningitis in Children Study Reveals High Case Fatality Ratesdwi-148502No ratings yet
- CommunityDocument10 pagesCommunitydwi-148502No ratings yet
- JournalDocument1 pageJournaldwi-148502No ratings yet
- Journal Siklus Anak 5Document5 pagesJournal Siklus Anak 5dwi-148502No ratings yet
- Journal of Forensic and Legal MedicineDocument4 pagesJournal of Forensic and Legal Medicinedwi-148502No ratings yet
- Bps Pendapatan Per Kapita SumbarDocument2 pagesBps Pendapatan Per Kapita Sumbardwi-148502No ratings yet
- Investigating Diphtheria Outbreak: A Qualitative Study in Rural AreaDocument4 pagesInvestigating Diphtheria Outbreak: A Qualitative Study in Rural Areadwi-148502No ratings yet
- Skripsi Obesitas Baru PDFDocument138 pagesSkripsi Obesitas Baru PDFdwi-148502No ratings yet
- Jounal Siklus Anak 5 PDFDocument5 pagesJounal Siklus Anak 5 PDFdwi-148502No ratings yet
- Journal Pneumonia 1Document1 pageJournal Pneumonia 1dwi-148502No ratings yet
- Evolution of MedicineDocument6 pagesEvolution of MedicineAssignmentLab.comNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology AT GLIMPSE PDFDocument252 pagesPharmacology AT GLIMPSE PDFBiswarup Das100% (1)
- Antibiotics: Classification and ExamplesDocument39 pagesAntibiotics: Classification and ExamplesV G Viju KumarNo ratings yet
- Daftar HargaDocument49 pagesDaftar HargaHabib BadruzzamanNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- Detection of Methicillin Resistance in Staphylococcus Species From Clinical SamplesDocument6 pagesDetection of Methicillin Resistance in Staphylococcus Species From Clinical SamplesOpenaccess Research paperNo ratings yet
- Bovine Mastitis SVDocument62 pagesBovine Mastitis SVSatyavrat SinghNo ratings yet
- 5 Sar CephalosporinsDocument17 pages5 Sar CephalosporinsGitasetya NingrumNo ratings yet
- Nurse Round - AugmentinDocument15 pagesNurse Round - AugmentinkyokeungkennethNo ratings yet
- Effect of Dietary Chitosan On Non-Specific Immune Response and Growth of Cyprinus Carpio Challenged With Aeromonas HydrophilaDocument9 pagesEffect of Dietary Chitosan On Non-Specific Immune Response and Growth of Cyprinus Carpio Challenged With Aeromonas HydrophilaSajid Dijas100% (1)
- The Risk For Endocarditis in Dental PracticeDocument9 pagesThe Risk For Endocarditis in Dental PracticeisanreryNo ratings yet
- Generic Menu CardDocument13 pagesGeneric Menu CardCarissa Villaver100% (2)
- Aminoglycosides and SulfonamidesDocument35 pagesAminoglycosides and SulfonamidesPhoenixNo ratings yet
- Highly Effective Against EsblDocument9 pagesHighly Effective Against Esblgaurav rawalNo ratings yet
- History of Antimicrobial Agents & Resistant BacteriaDocument6 pagesHistory of Antimicrobial Agents & Resistant BacteriaAnurrag KumarNo ratings yet
- Shahid 2009Document15 pagesShahid 2009Priyankan MajumderNo ratings yet
- 6 - Application of Bacillus Spp. Isolated From The Intestine of Black Tiger Shrimp (Penaeus Monodon Fabricius From Natural Habitat For Control Pathogenic Bacteria in Aquaculture-1Document8 pages6 - Application of Bacillus Spp. Isolated From The Intestine of Black Tiger Shrimp (Penaeus Monodon Fabricius From Natural Habitat For Control Pathogenic Bacteria in Aquaculture-1Nguyen Van MinhNo ratings yet
- A. Sediaan Tablet Dan Kapsul No Obat Dan KekuatanDocument13 pagesA. Sediaan Tablet Dan Kapsul No Obat Dan KekuatanrismaNo ratings yet
- MCP AbxDocument34 pagesMCP AbxShynne RPhNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Chemistry GuideDocument23 pagesMedicinal Chemistry Guidemurugs92No ratings yet
- DSP 02 Juli 2022Document32 pagesDSP 02 Juli 2022Pa RusdiyatNo ratings yet
- Guideline On Setting Specifications For Related Impurities in AntibioticsDocument15 pagesGuideline On Setting Specifications For Related Impurities in AntibioticsArmando SaldañaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Antibacterial Agents: Systemic Drugs For Infectious DiseasesDocument43 pagesSystemic Antibacterial Agents: Systemic Drugs For Infectious DiseasesJolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- Practice Guidelines For The Management of Infectious DiarrheaDocument21 pagesPractice Guidelines For The Management of Infectious DiarrheaJose Alfredo Cruz HernandezNo ratings yet
- Desensitization ProtocolsDocument28 pagesDesensitization ProtocolsAnonymous 9dVZCnTXSNo ratings yet
- Oxoid 2012-13Document84 pagesOxoid 2012-13Athar AbbasNo ratings yet
- EUCAST 2012 Oral Cephalosporin GuidanceDocument2 pagesEUCAST 2012 Oral Cephalosporin GuidanceSayantan BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy Mcqs For Preparation - PakMcqsDocument7 pagesChemotherapy Mcqs For Preparation - PakMcqsMohammed AbdelazizNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Stewardship Metrics How Do You Measure Up KuperDocument41 pagesAntibiotic Stewardship Metrics How Do You Measure Up KuperCarlos Espinoza CobeñasNo ratings yet