Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fluid Mechancs
Uploaded by
Twizer Lebaleng0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesfluid mechanics
Original Title
fluid mechancs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesFluid Mechancs
Uploaded by
Twizer LebalengYou are on page 1of 4
=
Faculty of Engineering and Technology
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical Engineering Degree
‘COURSE CODE ‘COURSE TITLE:
e323 | thermodynamic t
EXAMINATION SERIES:
| 20" May, 2013 ‘APRIL/MAY 2013
[TIME AWOWeD: READING TIM MAK, MARKS:
I 2 Hours 10 minutes 3.00
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
| 4. This paper contains 4questions,
2. ‘This paper has 2 pages excluding the cover page.
3. Ansiver ALL FOUR QUESTIONS.
4. The marks for each question are indicated []
|S. Alllsketches should be clear and in good proportion.
| 6. Answers should show sufficient working steps to indicate the solution method used.
7. Any additional examination material is tobe placed in the answer book end must indicate
‘leary the question number, full name and the student 10 number.
INSTRUCTIONS TO INVIGILATORS
1. Provide
‘Thermodynamic and Transport Properties of Fluids: SI Units
By G. F.C. Roger and Y. R. Mayhew.
| 2. Psychrometric chart
| 3. Teble A-17
4. Programmable calculators are not allowed.
Question 1
(a) Air at 10°C and 80 kPa enters the diffuser of 2 jet engine steadily with a velocity of 200 m/s. The
inlet area of the diffuser is 0.4m*. The air leaves the diffuser with a velocity that is very small
compared with the inlet velocity.
i, Determine the mass flow rate of the air . [6]
ii, Using information on table A-17, calculate the temperature of the air leaving the diffuser.
(10)
iii. Using sketches show the difference between a diffuser and a nozzle. [4]
(b) Calculate the entropy change when I kg of air is throttled from 10bars to 2 bi 5]
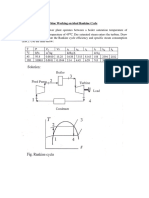
Question 2
In a steam turbine plant 20 kg/s is supplied to a high-pressure turbine at 80 bars and 450°C, and
expansion within this turbine is to 15 bars with an isentropic efficiency of 87%. After exhausting from
the high-pressure turbine, the steam is reheated at constant pressure to 400°C before passing to the low-
pressure turbine where in it expands to the condenser pressure of 0.05 bars with an isentropic efficiency
of 78%.
i. Sketch the cycle on T-s coordinates {5}
Neglecting the feed pump work transfer, calculate the followings:
ii. The power output of the plant (10)
iii, The thermal efficiency (s]
iv. The efficiency of the Camot cycle operating between the same steam saturated
temperature limits (51
Question 3
(@) A gas turbine unit has a pressure ratio of 10/1 and 2 maximum cycle temperature of 700°C. The
isentropic efficiencies of the compressor and turbine are 0.82 and 0.85, respectively. The air
enters the compressor at 15°C and at the rate of 15 kg/s.
(sketch a labeled T-s diagram 1
(ii) show the equations that determine the actual exit temperature of the compressor
and the turbine. Is)
(b) (i) Whet is brake and indicated power referring to internal combustion engines. (4)
(i) A single-cylinder gas engine working on a four-stroke cyele is required to develop brake
power of 20 kW,and mechanical efficiency of 80%, when running at 300 rev/min. The mean
effective pressure is to be 600 KN/m* and the stroke = 114 x bore, Determine the necessary
cylinder diameter. {10}
(c) A fuel (coal) consists of 80% carbon, 4.6% hydrogen, 3% oxygen, and the remainder ash. Find
the theoretical mass of air required per kg of fuel. BI
Question 4
(@) Explain briefly what is an air-conditioning system l4
(0) In an ammonia refrigeration plant, the refrigerant enters the compressor as a dry saturated vapour
at 2.908 bar abs. Afier isentropic compression, the refrigerant leaves the compressor at 9.722 bar
abs and no undercooling of the condensed liquid.
() sketch and label an ideal cycle on a T-s diagram 2)
Determine
Gi) the temperature of the refrigerant after compression (to the nearest degree) [4]
(iii) the dryness fraction of the vapour entering the evaporator. Rl
(iv) the coefficient of performance (COP),. BI
(©) The readings taken in a room fiom a sling psychrometer give a dry and a wet bulb temperature of
25°C and 20°C respectively. Using a psychrometric chart, taking the atmospheric pressure as
1.01325 bar, determine:
(@ the specific humidity, RI
(Gi) the relative humidity, BI
Gi) the dew poim, PI
(iv) the specific volume of mixture, 2]
(v) the specific enthalpy of the mixture. 2]
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- 1008national Report (Agriculture) - BotswanaDocument7 pages1008national Report (Agriculture) - BotswanaTwizer LebalengNo ratings yet
- Challenges of Agricultural Technology Transfer and Productivity Increase in The SudanDocument16 pagesChallenges of Agricultural Technology Transfer and Productivity Increase in The SudanTwizer LebalengNo ratings yet
- Book 2Document3 pagesBook 2Twizer LebalengNo ratings yet
- Book 2Document3 pagesBook 2Twizer LebalengNo ratings yet
- Numerical PDFDocument1 pageNumerical PDFTwizer LebalengNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 SlidesDocument8 pagesLesson 9 SlidesTwizer LebalengNo ratings yet
- Literature review on tillage implements in BotswanaDocument3 pagesLiterature review on tillage implements in BotswanaTwizer LebalengNo ratings yet
- TITLE Gear Box OverhaulDocument7 pagesTITLE Gear Box OverhaulTwizer LebalengNo ratings yet
- Mixtures of Ideal GasesDocument21 pagesMixtures of Ideal GasesTwizer LebalengNo ratings yet
- Rankine PDFDocument3 pagesRankine PDFTwizer LebalengNo ratings yet
- University of Botswana Faculty of Engineering and Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering MMB 312 - Tutorial #1Document2 pagesUniversity of Botswana Faculty of Engineering and Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering MMB 312 - Tutorial #1Twizer LebalengNo ratings yet
- 3 Analytical Kinematics PDFDocument13 pages3 Analytical Kinematics PDFTwizer LebalengNo ratings yet
- Nozzle EtcDocument21 pagesNozzle EtcTwizer LebalengNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Exp 8 CHM420Document15 pagesExp 8 CHM420Nur Faizatul Atiqah100% (1)
- Spell Names: 1d10 Spell Name Template 1d10 Spell Name TemplateDocument2 pagesSpell Names: 1d10 Spell Name Template 1d10 Spell Name TemplateSage HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Arlon 300XT - Data - SheetDocument5 pagesArlon 300XT - Data - Sheetseeralan_1986No ratings yet
- Class9 NSO 2017 SetB - SolutionsDocument15 pagesClass9 NSO 2017 SetB - SolutionsAmbica JainNo ratings yet
- GRB Physical Chemistry IIT JEE 3Document995 pagesGRB Physical Chemistry IIT JEE 3Natanael CarmoNo ratings yet
- Glossary - Gas Encyclopedia Air Liquide - Air Liquide - InglesDocument6 pagesGlossary - Gas Encyclopedia Air Liquide - Air Liquide - Inglesvmpp222No ratings yet
- Tinuvin P - BASFDocument2 pagesTinuvin P - BASFsriNo ratings yet
- FIITJEE Phase Test (JEE-Advanced) Physics, Chemistry & MathematicsDocument13 pagesFIITJEE Phase Test (JEE-Advanced) Physics, Chemistry & MathematicsAman AntilNo ratings yet
- Government Approves Shifting of LG Polymers IndustryDocument2 pagesGovernment Approves Shifting of LG Polymers Industrysrinivas gowdNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Analyses of Banisteriopsis Caapi and Psychotria ViridisDocument7 pagesPhytochemical Analyses of Banisteriopsis Caapi and Psychotria ViridisHector QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Deconstruct and Design ExemplarDocument5 pagesDeconstruct and Design ExemplarTNo ratings yet
- An Investigation of Copper Pitting Corrosion and Pinhole LeaksDocument8 pagesAn Investigation of Copper Pitting Corrosion and Pinhole LeaksLEONARDO DAVID DONADO PALACIONo ratings yet
- 1280a4-8310-43c1 Rev F1Document31 pages1280a4-8310-43c1 Rev F1Stephen LowNo ratings yet
- Lab Report CHM301Document15 pagesLab Report CHM301NURFATHIHA ARFANo ratings yet
- Applications in HPLC in Pharmaceutical AnalysisDocument9 pagesApplications in HPLC in Pharmaceutical AnalysisSnoAbuAlSamedNo ratings yet
- Prelims: Test SeriesDocument75 pagesPrelims: Test SeriesAnil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Paper Chromatography Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesPaper Chromatography Literature Reviewafdtuaerl100% (1)
- Bchem 455 - Module 3Document42 pagesBchem 455 - Module 3WilliamNo ratings yet
- Nabl 400Document579 pagesNabl 400Team Labs LaboratoryNo ratings yet
- IFFCO Phulpur Training ReportDocument34 pagesIFFCO Phulpur Training ReportROSHAN KUMAR GUPTANo ratings yet
- Biochem CH 24 Amino Acid BiosynthesisDocument6 pagesBiochem CH 24 Amino Acid BiosynthesisSchat ZiNo ratings yet
- 09 - Air Conditioning SystemsDocument12 pages09 - Air Conditioning Systems郝帅No ratings yet
- Droste Chapter 2-3Document43 pagesDroste Chapter 2-3Kirito KazutoNo ratings yet
- Chap 2. Acid-Base Equilibrium&titrationDocument86 pagesChap 2. Acid-Base Equilibrium&titrationNgọc Việt NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Nanomaterials 09 01197Document6 pagesNanomaterials 09 01197RadhikaGuptaNo ratings yet
- 13.5 DNA Structure and Protein Synthesis (Biology Only) 2020 StudentsDocument55 pages13.5 DNA Structure and Protein Synthesis (Biology Only) 2020 StudentsBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- 2020-11 Product Data Sheet LiOH TG CMP PDFDocument5 pages2020-11 Product Data Sheet LiOH TG CMP PDFSergey GlazzNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xii-Chemistry-Qb-Ans-Anil-13. AminesDocument9 pagesHsslive-Xii-Chemistry-Qb-Ans-Anil-13. AminesSneha Rose BennyNo ratings yet
- IB DP Chemistry 1Document74 pagesIB DP Chemistry 1Zheng JoeyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument23 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectManikandan sNo ratings yet