Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Question Bank of CAD
Uploaded by
shailuCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Question Bank of CAD
Uploaded by
shailuCopyright:
Available Formats
QUESTION BANK OF COMPUTER AIDED DESIGN
UNIT-1
1. What are the benefits of computer aided design?
2. Discuss the major elements of computer aided design.
3. Explain graphics software.
4. What do you mean by output primitives?
5. Describe windowing and clipping technique used in computer graphics.
6. Make a table of important design phase.
7. What are Cad tools to support various design phases?
7. Differentiate between Random and Raster Scan display.
8. What do you mean by graphics standard? Enlist graphics standard and explain any one in brief.
9. What is difference between CAD and CAM irrespective of manufacturing consideration.
10. Explain the application of computer aided design.
UNIT-2
1. Explain the working principle of LCD.
2. Describe the Translation, Rotation and Scaling.
3. Describe the shearing and reflection.
4. Rotate a triangle A (0, 0), B (1, 1), C (5, 2) by 450 about the origin.
5. Explain the working of CRT with neat sketch and how pixels are generated. Differentiate CRT with flat panel display.
6. What is geometric transformation?
7. Find the reflection matrix when the axis of reflection is given by y = 5x. Also determine the reflection of point (7,3) about the axis.
8. Explain the LED and plasma display.
9. Find the coordinate of triangle (1,2),(1,4) and (3,3) after scaling 3 units in x direction and 2 unit in y direction.
10. Find the coordinate of point (3,5) when rotated about 45 degree with respect to origin.
UNIT-3
1. Explain the advantage of using parametric curve over non parametric curve.
2. Generate a Bezier curve passing through control points (2, 0), (5, 4), (6, 3) and (4, 3).
3. Discuss Bresenham’s line algorithm. And also discuss DDA algorithm.
4. Discuss Mid point circle algorithm. Create a circle whose centre is at (5, 10) and radius is 10 units by using mid point circle algorithm.
5. What do you mean by the order of continuity?
6. Briefly discuss the generation of 2-D curves. What are the difficulties of using non parametric curve. What advantages does a parametric curve offer for
representing curve.
7. Briefly discuss the Bezier curve, its blending function and properties.
8. Briefly discuss the B-spline curve, its blending function and properties
9. What do you understand by interpolation approximation?
10. Determine and plot the blending functions for Hermite spline. What are the limitations of Hermite curve? How they are removed?
UNIT-4
1.What do you understand by geometric model?
2. Explain boundary representation technique.
3. What do you mean by quadric surfaces?
4. What do you mean by Superquadric surfaces?
5. Write down the two applications Pro/E.
6. Distinguish between solid and surface modeling.
7. Explain various parametric continuity conditions.
8. Explain RGB and CMYK colour models.
9. Explain constructive solid geometry. What is the role of Primitives and Boolean operation in CSG?
10. What do you understand by Blobby objects, explain with figure?
UNIT-4
1. Define element stiffness matrix.
2. What error may be in FEM solution?
3. What is the difference between local coordinates and natural coordinates?
4. Explain the following : i. Solidworks ii. Catia iii. AutoCAD
5. Describe the steps involve in analysis of physical system by FEM.
6. Design element and global stiffness matrix for a spring system by FEA.
7. A tapering round bar is fixed at one end and a tensile load of 1000 N is applied at the other end as given in the figure. Take modulus of elasticity =3x105 MPa.
Find global stiffness matrix and displacement considering it as 4 elementss
8. Design element and global stiffness matrix for a bar system by FEA.
9. A simple plane truss is made of two identical bars (with E, A and L) and loaded as shown in figure .Find: displacement at node 2 and stresses in each bar.
10. For the beam shown in figure find the deflection and rotation at node 2 and node 3 and reactions.
Load = 50 kN, spring constant k= 200kN/m, length of each section L= 3 m, E =210 GPa, I = 2x10-4m4
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- How 50 Million People Are Changing the WorldDocument5 pagesHow 50 Million People Are Changing the WorldCTRCTR0% (1)
- Anatomy 090819Document30 pagesAnatomy 090819Vaishnavi GourabathiniNo ratings yet
- PPC2000 Association of Consultant Architects Standard Form of Project Partnering ContractDocument5 pagesPPC2000 Association of Consultant Architects Standard Form of Project Partnering ContractJoy CeeNo ratings yet
- Canna DispensariesDocument35 pagesCanna DispensariesWaf Etano100% (1)
- Book of Lost Spells (Necromancer Games)Document137 pagesBook of Lost Spells (Necromancer Games)Rodrigo Hky91% (22)
- 123Document2 pages123shailuNo ratings yet
- Rameshwaram Institute of Technology & Management LucknowDocument1 pageRameshwaram Institute of Technology & Management LucknowshailuNo ratings yet
- Ratan TataDocument14 pagesRatan Tatashruti.dhond3251100% (1)
- B. Tech.: Printed Pages - 2 RME-502Document2 pagesB. Tech.: Printed Pages - 2 RME-502shailuNo ratings yet
- Practical Brief (योगा मक सं त) : Print (ंट कर)Document1 pagePractical Brief (योगा मक सं त) : Print (ंट कर)shailuNo ratings yet
- Rameshwaram Institute of Technology & ManagementDocument4 pagesRameshwaram Institute of Technology & ManagementshailuNo ratings yet
- MS-II Lab ManualDocument18 pagesMS-II Lab ManualdibyenindusNo ratings yet
- Historical Source Author Date of The Event Objective of The Event Persons Involved Main ArgumentDocument5 pagesHistorical Source Author Date of The Event Objective of The Event Persons Involved Main ArgumentMark Saldie RoncesvallesNo ratings yet
- EDIBLE VACCINES: A COST-EFFECTIVE SOLUTIONDocument21 pagesEDIBLE VACCINES: A COST-EFFECTIVE SOLUTIONPritish SareenNo ratings yet
- 2.7.3 Lab Use Steganography To Hide Data Answer KeyDocument3 pages2.7.3 Lab Use Steganography To Hide Data Answer KeyVivek GaonkarNo ratings yet
- Snorkeling: A Brief History and Guide to This Underwater AdventureDocument3 pagesSnorkeling: A Brief History and Guide to This Underwater AdventureBernadette PerezNo ratings yet
- Recent Developments in Ultrasonic NDT Modelling in CIVADocument7 pagesRecent Developments in Ultrasonic NDT Modelling in CIVAcal2_uniNo ratings yet
- Institutional Competency Assessment Instrument (ICAI)Document12 pagesInstitutional Competency Assessment Instrument (ICAI)Bea EtacNo ratings yet
- The Case of Ataraxia and Apraxia in The Development of Skeptic THDocument11 pagesThe Case of Ataraxia and Apraxia in The Development of Skeptic THeweNo ratings yet
- Current Developments in Testing Item Response Theory (IRT) : Prepared byDocument32 pagesCurrent Developments in Testing Item Response Theory (IRT) : Prepared byMalar VengadesNo ratings yet
- Science SimulationsDocument4 pagesScience Simulationsgk_gbuNo ratings yet
- Management and Breeding of Game BirdsDocument18 pagesManagement and Breeding of Game BirdsAgustinNachoAnzóateguiNo ratings yet
- Ifatsea Atsep Brochure 2019 PDFDocument4 pagesIfatsea Atsep Brochure 2019 PDFCondor GuatonNo ratings yet
- Remembrance 23 Names PDFDocument1 pageRemembrance 23 Names PDFJennifer ThuncherNo ratings yet
- WBC Study Reveals God's NatureDocument11 pagesWBC Study Reveals God's NatureSherwin Castillo DelgadoNo ratings yet
- LM385Document14 pagesLM385vandocardosoNo ratings yet
- PA2 Value and PD2 ValueDocument4 pagesPA2 Value and PD2 Valueguddu1680No ratings yet
- Reasons Why Coca Cola Has A Large Market Share in Kenya and The WorldDocument9 pagesReasons Why Coca Cola Has A Large Market Share in Kenya and The WorldAludahNo ratings yet
- Reading in Philippine History (Chapter 3)Document14 pagesReading in Philippine History (Chapter 3)AKIO HIROKINo ratings yet
- Preparatory Lights and Perfections: Joseph Smith's Training with the Urim and ThummimDocument9 pagesPreparatory Lights and Perfections: Joseph Smith's Training with the Urim and ThummimslightlyguiltyNo ratings yet
- Process of Producting High Carbon Ferro ChromeDocument5 pagesProcess of Producting High Carbon Ferro ChromeSantosh Kumar MahtoNo ratings yet
- 1651 EE-ES-2019-1015-R0 Load Flow PQ Capability (ENG)Document62 pages1651 EE-ES-2019-1015-R0 Load Flow PQ Capability (ENG)Alfonso GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Sight Reduction Tables For Marine Navigation: B, R - D, D. SDocument12 pagesSight Reduction Tables For Marine Navigation: B, R - D, D. SGeani MihaiNo ratings yet
- Mini Centre CatalogDocument26 pagesMini Centre CatalogJohn EarleyNo ratings yet
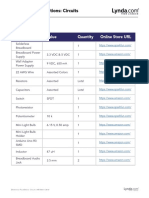
- Electronics Foundations - Basic CircuitsDocument20 pagesElectronics Foundations - Basic Circuitsccorp0089No ratings yet
- Strata KT Office OpportunityDocument41 pagesStrata KT Office OpportunitySanskar SurekaNo ratings yet
- Self Healing Challenge - March 2023 Workshop ThreeDocument16 pagesSelf Healing Challenge - March 2023 Workshop ThreeDeena DSNo ratings yet