Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial Question:: Solution. (I) No Load, Running As A Motor
Uploaded by
Umair AnsariOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial Question:: Solution. (I) No Load, Running As A Motor
Uploaded by
Umair AnsariCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial Question:
Q1- A 500-V D.C. shunt motor draws a line-current of 5 A on light-load. If armature resistance is 0.15 ohm and field
resistance is 200 ohms, determine the efficiency of the machine running as a generator delivering a load current of
40 Amps.
Solution. (i) No Load, running as a motor:
Input Power = 500 5 = 2500 watts
Field copper-loss = 500 2.5 = 1250 watts
Neglecting armature copper-loss at no load (since it comes out to be 2.5 0.15 = 1 watt), the balance
2
of 1250 watts of power goes towards no load losses of the machine running at rated speed. These losses
are mainly the no load mechanical losses and the core-loss.
(ii) As a Generator, delivering 40 A to load:
3
Output delivered = 500 40 10 = 20 kW Losses:
(a) Field copper-loss = 1250 watts
(b) Armature copper-loss = 42.5 0.15 = 271 watts
2
(c) No load losses = 1250 Watts Total
losses = 2.771 kW
Generator Efficiency = (20/22.771) 100 % = 87.83%
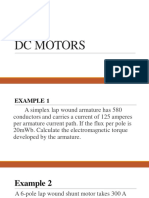
Q2- A 220-V, d.c. shunt motor takes 4 A at no-load when running at 700 r.p.m. The field resistance is 100 . The
resistance of armature at standstill gives a drop of 6 volts across armature terminals when 10 A were passed through
it. Calculate (a) speed on load (b) torque in N-m and (c) efficiency. The normal input of the motor is 8 kW.
You might also like
- Tutorial 6 DC MotorDocument1 pageTutorial 6 DC MotorparvathyNo ratings yet
- 12 A DC SeriesDocument6 pages12 A DC SeriesJose SurendranNo ratings yet
- DC GeneratorDocument24 pagesDC GeneratorRahmat Bagus ArdhiansyahNo ratings yet
- DC GeneratorDocument2 pagesDC GeneratorAravind Vinas100% (1)
- Electrical Machines TutorialsDocument6 pagesElectrical Machines TutorialsAllegro Presto ModeratoNo ratings yet
- Lecture9 Regulation and Effecieny of ElectomechnicalDocument23 pagesLecture9 Regulation and Effecieny of Electomechnicalahmedessamaee654No ratings yet
- Tutorial DC MachinesDocument2 pagesTutorial DC MachinesLucas LeeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial DC MachinesDocument2 pagesTutorial DC MachinesLucas LeeNo ratings yet
- DC GeneratorDocument23 pagesDC GeneratorEngr Danyal ZahidNo ratings yet
- Review Problems in DC MotorsDocument9 pagesReview Problems in DC MotorsFrancis Ilarde0% (1)
- Example 3: A 7.5-hp 120-V Series DC Motor Has An Armature Resistance of 0.2 Ohm and ADocument3 pagesExample 3: A 7.5-hp 120-V Series DC Motor Has An Armature Resistance of 0.2 Ohm and Ahakkı_aNo ratings yet
- Contoh SoalDocument24 pagesContoh SoalmbloexNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 - DC MotorsDocument2 pagesTutorial 4 - DC MotorsSmurf TanNo ratings yet
- 9A02308 Electrical Machines - IDocument4 pages9A02308 Electrical Machines - IsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 DC Machines IIDocument2 pagesTutorial 7 DC Machines IIAkshat SharmaNo ratings yet
- LEC - 12 (MCM Fundamentals)Document24 pagesLEC - 12 (MCM Fundamentals)zain malikNo ratings yet
- Addl Problems - DC MotorsDocument1 pageAddl Problems - DC MotorsSre VinodNo ratings yet
- DCDocument3 pagesDCAkhilesh Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- METU Electrical Engineering Homework on DC Generator and Motor AnalysisDocument2 pagesMETU Electrical Engineering Homework on DC Generator and Motor AnalysisFatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- Tutorials DC MachinesDocument1 pageTutorials DC MachinesMohd Rashid SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Hw4 Solutions 162Document10 pagesHw4 Solutions 162Rizky NandasmaraNo ratings yet
- Definition of A DC MotorDocument76 pagesDefinition of A DC MotorKiyoshi Jiro MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Template - MSE AC DC Machines - MSE2021Document2 pagesTemplate - MSE AC DC Machines - MSE2021NammmeeNo ratings yet
- EM II ProblemsDocument4 pagesEM II ProblemsTony StarkNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2tanaya.s.gadkariNo ratings yet
- Assignment (ELE3307)Document3 pagesAssignment (ELE3307)●●●●●●●1No ratings yet
- DC Motors Workout problems solvedDocument5 pagesDC Motors Workout problems solvedusreenivasNo ratings yet
- EE-3011 Assignment-1 and 2Document2 pagesEE-3011 Assignment-1 and 2Kartik GvrNo ratings yet
- DC Motor ExamplesDocument13 pagesDC Motor ExamplesAnonymous AFFiZn100% (1)
- Tutorial DCmachines PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial DCmachines PDFAmmar SafwtNo ratings yet
- Problems On Losses and Efficincy PDFDocument2 pagesProblems On Losses and Efficincy PDFPrajwal TripathyNo ratings yet
- TU3 DC-generatorDocument2 pagesTU3 DC-generatordsfsdf sdfdsNo ratings yet
- Training Machines2, Homework in Electrical MachinesDocument5 pagesTraining Machines2, Homework in Electrical MachinesNGOUNENo ratings yet
- Solving DC Motors Simple Torque Problems PDFDocument8 pagesSolving DC Motors Simple Torque Problems PDFRv EstebanNo ratings yet
- Solving DC Motors Simple Torque Problems PDFDocument8 pagesSolving DC Motors Simple Torque Problems PDFRv EstebanNo ratings yet
- EeeDocument10 pagesEeeConde Clint100% (1)
- EMF Assignment1Document5 pagesEMF Assignment1Ahtasham ArshadNo ratings yet
- R09 Set No. 2Document8 pagesR09 Set No. 2Eu AumentadoNo ratings yet
- Assingment No.1 EEE 306Document2 pagesAssingment No.1 EEE 306ashish mathurNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 & 2Document2 pagesTutorial 1 & 2lucasNo ratings yet
- Drill Problems On DC GeneratorsDocument4 pagesDrill Problems On DC GeneratorsJune Cedy BalsomoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial EMEC-I DC MachinesDocument1 pageTutorial EMEC-I DC MachinesRishi Kant SharmaNo ratings yet
- EE 435AL (6535) 3rd Exam, 2020-2021 - BERSABALDocument3 pagesEE 435AL (6535) 3rd Exam, 2020-2021 - BERSABALCegrow Ber BersabalNo ratings yet
- ECE 3810 Introduction To Power EngineeringDocument17 pagesECE 3810 Introduction To Power EngineeringAkif DharNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Question On DC MachinesDocument1 pageAssignment 1 Question On DC MachinesDeepti MishraNo ratings yet
- Problem 505Document44 pagesProblem 505Rinalyn-Oscar Gamboa Magtibay27% (11)
- Electrical Machines' SheetDocument2 pagesElectrical Machines' SheetAhmed HazemNo ratings yet
- Ener ConDocument5 pagesEner ConRey Del Castillo Luar Jr.0% (1)
- DC Shunt Generator and Motor ProblemsDocument3 pagesDC Shunt Generator and Motor ProblemsmahrusNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Roorkee EE - 101: Electrical Science Tutorial Sheet - 09Document1 pageDepartment of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Roorkee EE - 101: Electrical Science Tutorial Sheet - 09Bharat SinghNo ratings yet
- DC Motors: RLB EDocument6 pagesDC Motors: RLB Ehafiz_jaaffarNo ratings yet
- KNUST EE 172 Electrical Machines Exam QuestionsDocument9 pagesKNUST EE 172 Electrical Machines Exam QuestionsSamuel Kafui KwawukumeNo ratings yet
- R7210206-Electrical Machines - IDocument4 pagesR7210206-Electrical Machines - IsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- DC MOTORS COMPUTATION (Autosaved)Document11 pagesDC MOTORS COMPUTATION (Autosaved)ryan bhinogNo ratings yet
- D.c.-Machines ProblemesDocument9 pagesD.c.-Machines ProblemesMeesixNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines FundamentalsDocument8 pagesElectrical Machines FundamentalsUdayKiranNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Speed and Torque CalculationsDocument3 pagesDC Motor Speed and Torque CalculationsstanNo ratings yet
- Assignment I EEE 2214 ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Feb 2023 (2) (Original)Document1 pageAssignment I EEE 2214 ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Feb 2023 (2) (Original)Jimmy MachariaNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Turbulence ModelingDocument2 pagesTurbulence ModelingUmair AnsariNo ratings yet
- The AssessmentDocument3 pagesThe AssessmentUmair AnsariNo ratings yet
- EquationsDocument44 pagesEquationsUmair AnsariNo ratings yet
- Turbulent Flow Over A Backwardfacing StepDocument1 pageTurbulent Flow Over A Backwardfacing StepUmair AnsariNo ratings yet
- SeriesAndParallelWksht 2 PDFDocument8 pagesSeriesAndParallelWksht 2 PDFUmair AnsariNo ratings yet
- SeriesAndParallelWksht 2 PDFDocument8 pagesSeriesAndParallelWksht 2 PDFUmair AnsariNo ratings yet
- Answers to Hydraulics QuestionsDocument39 pagesAnswers to Hydraulics QuestionsGertjan Duniceri100% (3)
- Turbulent Flow Over A Backwardfacing Step PDFDocument36 pagesTurbulent Flow Over A Backwardfacing Step PDFUmair AnsariNo ratings yet
- Material DerivativeDFSFSDFDocument5 pagesMaterial DerivativeDFSFSDFUmair AnsariNo ratings yet
- Thermal Simulation of Solar Distiller Units: Study of Heat & Mass TransferDocument32 pagesThermal Simulation of Solar Distiller Units: Study of Heat & Mass TransferUmair AnsariNo ratings yet
- Manual - Solutions-Electrical Machines, Drives and Power Systems 6th Ed. by WildiDocument109 pagesManual - Solutions-Electrical Machines, Drives and Power Systems 6th Ed. by WildiLeonardo Lira100% (3)
- Material derivativeDFSFSDF PDFDocument2 pagesMaterial derivativeDFSFSDF PDFUmair AnsariNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Mechanical AnalysisDocument19 pagesDynamic Mechanical AnalysisUmair AnsariNo ratings yet
- Theodore Wildi - Electrical Machines, Drives and Power Systems Sixth Edition (Instructor's Manual)Document14 pagesTheodore Wildi - Electrical Machines, Drives and Power Systems Sixth Edition (Instructor's Manual)Umair Ansari100% (1)
- Steam TablesDocument16 pagesSteam TablesSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Material DerivativeDocument2 pagesMaterial DerivativeUmair AnsariNo ratings yet
- TurbomachinertDocument20 pagesTurbomachinertgavin_d265No ratings yet
- Special DistributionsDocument72 pagesSpecial DistributionsUmair AnsariNo ratings yet
- Steam TablesDocument16 pagesSteam TablesSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Special DistributionsDocument52 pagesSpecial DistributionsUmair AnsariNo ratings yet
- Special DistributionsDocument52 pagesSpecial DistributionsUmair AnsariNo ratings yet
- EquationsDocument44 pagesEquationsUmair AnsariNo ratings yet
- Warm Up Statements Converse Angles TheoremsDocument8 pagesWarm Up Statements Converse Angles TheoremsUmair AnsariNo ratings yet
- EquationsDocument44 pagesEquationsUmair AnsariNo ratings yet
- What is the Reynolds NumberDocument3 pagesWhat is the Reynolds NumberUmair AnsariNo ratings yet
- TS-SET Physical Sciences Exam GuideDocument3 pagesTS-SET Physical Sciences Exam GuideUmair AnsariNo ratings yet