Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abstract & Conclusion The Acid Ionization Constant, Ka
Uploaded by
najihahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abstract & Conclusion The Acid Ionization Constant, Ka
Uploaded by
najihahCopyright:
Available Formats
Abstract
The acid ionization constant, Ka, is a quantitative measure of the strength of
an acid a solution and commonly expressed in units of mol/L. For reference, there
are table of Ka values for weak acids to identify the acid based on the value of Ka
and pKa.
This experiment examined is to determine the value of Ka and identify the
unknown acid solution. To obtain an unknown weak acid, 15mL of 0.1M unknown
acid solution diluted with 90mL of distilled water. Titration was done by adding 1mL
by 1mL of NaOH to the diluted unknown acid to achieve standardized of NaOH
solution. The experiment was repeated three times to achieve accurate and precise
graph from the recorded data.
The equivalence point can be found on the graph plotted which is pH versus
volume of sodium hydroxide, NaOH. By plotting the titration curve, we managed to
find the equivalence point and half-equivalence point that give the volume of NaOH
and pH value. The equivalence point of the graph is 19.69 mL with 8.53
corresponding pH. The half-equivalence point of the graph is 9.845 mL with 5.2
corresponding pH. The pH value of the half-equivalence point is used as pKa and
lastly to calculate the Ka.
2 methods of calculation have been applied to calculate the value for Ka. The
first method is by using graph whereas the second is by using the initial pH of the
unknown acid solution. The value of Ka for the first is 6.3096 x 10-6 whereas for
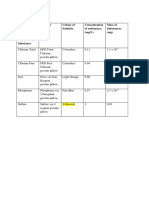
the second method is 2.453 x 10-8. The unknown acid solution had been identified as
pyridine with theoretical value Ka of 5.90x10-6.
The percentage error is calculated for determining the precision of your
calculations. For the first and the second method, the percentage error is 6.9424%
and 99.2792%. Therefore, the value of Ka by using the first method is more accurate
than method 2 due to lower percentage error.
Conclusion
As a conclusion, the value of Ka had been determined and the unknown acid
solution was identified. By plotting the graph of volume of NaOH(mL) versus pH
value, the equivalence point was obtained which is 19.69 mL with corresponding pH
of 8.53. From this point, the half-equivalence point was determined as 9.845 mL with
corresponding pH of 5.2. The pH value of half-equivalence point was then used to
calculate the Ka for the first method to determine the value of Ka and identify the
unknown solution which is by using the graph. The Ka value obtain from the first
method is 6.3096 x 10-6 and the unknown solution was identified as pyridine by
theoretical value Ka of 5.90x10-6.
As for the second method, by using the average of initial pH value , Ka was
calculated which is 4.253 X 10⁻⁸ M and identified as Hypochlorous Acid. The
percentage error obtained from the first method is 6.9424% whereas for the second
method is 99.2792%. Hence, the value of Ka from the first method is more accurate
compared to the second method. The unknown acid is identified as pyridine and the
value of Ka is 6.3096 x 10-6.
Determine Ka using Intial Ph of the Unknown Acid Solution
Reference
(Budgets, n.d.)Budgets, U. (n.d.). Appendix 1: Normality Appendix 2: Propagation of
Uncertainty and Uncertainty Budgets Appendix 3: Single-Sided Normal
Distribution Appendix 4: Critical Values for the, 1067–1102.
https://www.academia.edu/35240273/CHE485_-
_Lab_Report_on_Determination_of_The_Ka_Value_Of_A_Weak_Acid_2017_
Syahiirah, N. (2017). CHE485 - Lab Report on Determination of The Ka Value Of A Weak Acid (2017).
25.
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Xiangshui Chemical Factory's ExplosionDocument21 pagesXiangshui Chemical Factory's ExplosionnajihahNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Calculation Report 2Document4 pagesCalculation Report 2najihahNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Lab 4 ObjDocument1 pageLab 4 ObjnajihahNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Abstract & Conclusion The Acid Ionization Constant, KaDocument3 pagesAbstract & Conclusion The Acid Ionization Constant, KanajihahNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- MY Template - Fake NewsDocument4 pagesMY Template - Fake NewsnajihahNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Lab Report: Membrane Separation 1.0 AbstractDocument1 pageLab Report: Membrane Separation 1.0 AbstractnajihahNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Abstract For Exp 2Document1 pageAbstract For Exp 2najihahNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Surprising Benefits of Bitter Melon For DiabetesDocument41 pagesSurprising Benefits of Bitter Melon For DiabetesnajihahNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Level Process Control SystemDocument10 pagesLevel Process Control SystemnajihahNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Lab Report (Distillation)Document10 pagesLab Report (Distillation)najihahNo ratings yet
- Lab Report (Distillation)Document10 pagesLab Report (Distillation)najihahNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Co2 Concentration (M) Vs Time (Min)Document2 pagesCo2 Concentration (M) Vs Time (Min)najihahNo ratings yet
- Heat CalculationDocument4 pagesHeat CalculationnajihahNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Lab Report LLE LatestDocument7 pagesLab Report LLE Latestnajihah50% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Intro, Theory & RefDocument7 pagesIntro, Theory & RefnajihahNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- PC Experiment - Pressure, Temperature, Flow and LevelDocument15 pagesPC Experiment - Pressure, Temperature, Flow and LevelnajihahNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 ObjDocument1 pageLab 4 ObjnajihahNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Lab Report SOAPS AND DETERGENTDocument17 pagesLab Report SOAPS AND DETERGENTnajihahNo ratings yet
- For The Second Experiment, Part B, Molarity (Part B)Document1 pageFor The Second Experiment, Part B, Molarity (Part B)najihahNo ratings yet
- Level Process Control SystemDocument10 pagesLevel Process Control SystemnajihahNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Lab Report On Preparation of Soap and Properties Comparison With Synthetics DetergentDocument1 pageLab Report On Preparation of Soap and Properties Comparison With Synthetics DetergentnajihahNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Intro, Theory & RefDocument7 pagesIntro, Theory & RefnajihahNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 - Results & CalculationDocument2 pagesLab 5 - Results & CalculationnajihahNo ratings yet
- Equivalence PointDocument2 pagesEquivalence PointnajihahNo ratings yet
- Abstract For Exp 2Document1 pageAbstract For Exp 2najihahNo ratings yet
- Cyber CrimeDocument4 pagesCyber CrimenajihahNo ratings yet
- Conclusion & RecommendationDocument2 pagesConclusion & RecommendationnajihahNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- For The Second Experiment, Part B, Molarity (Part B)Document1 pageFor The Second Experiment, Part B, Molarity (Part B)najihahNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Reaction (Temperature)Document8 pagesLab Report Reaction (Temperature)najihahNo ratings yet
- Análisis de Textura en Frutas CongeladasDocument9 pagesAnálisis de Textura en Frutas CongeladasJORGENo ratings yet
- Jenbacher: Determining The Initial PH Value (Iph) of Used Lubrication Oil As Defined in Ti 1000-0099BDocument2 pagesJenbacher: Determining The Initial PH Value (Iph) of Used Lubrication Oil As Defined in Ti 1000-0099BArîfNo ratings yet
- Canning of Fish: Name: T.L.V.Peiris University of Sri JayawardenapuraDocument5 pagesCanning of Fish: Name: T.L.V.Peiris University of Sri JayawardenapuraLaksilu Viduraga PeirisNo ratings yet
- My FilesDocument18 pagesMy Filesjake dionisioNo ratings yet
- Module c7 Further Chemistry Scheme of Work and Lesson PlanDocument25 pagesModule c7 Further Chemistry Scheme of Work and Lesson PlanHendri Dwi PangestuNo ratings yet
- Chem 140.1 Laboratory Report 7Document3 pagesChem 140.1 Laboratory Report 7JM BoylesNo ratings yet
- Content of Unsaturated Fats Measured by The Iodine Number in Coconut and Sunflower Oil After BeingDocument13 pagesContent of Unsaturated Fats Measured by The Iodine Number in Coconut and Sunflower Oil After BeingMM DomìN8RNo ratings yet
- (Agm'Zemó Àmë' (JH$ ZM - XDHR B'Îmm 11 DR) Chemistry Practical Notebook Standard XiDocument114 pages(Agm'Zemó Àmë' (JH$ ZM - XDHR B'Îmm 11 DR) Chemistry Practical Notebook Standard Xibbtbadal100% (1)
- Metakaolin - Measuring The Total Quantity of Fixed Calcium Hydroxide (Chapelle Test Modified) Referring To The French Norm NF P 18-513, Annexe ADocument2 pagesMetakaolin - Measuring The Total Quantity of Fixed Calcium Hydroxide (Chapelle Test Modified) Referring To The French Norm NF P 18-513, Annexe Atomelo100% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Titration of Acetic Acid in Vinegar: CHEM 122L General Chemistry Laboratory Revision 1.4Document16 pagesThe Titration of Acetic Acid in Vinegar: CHEM 122L General Chemistry Laboratory Revision 1.4Nur Najwa YunusNo ratings yet
- Chemical Analysis of Sodium Chloride Test Methods For E534 PDFDocument6 pagesChemical Analysis of Sodium Chloride Test Methods For E534 PDFafifatul jannahNo ratings yet
- 1 Complexation TitrationDocument124 pages1 Complexation TitrationayukiwaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Titrimetric AnalysisDocument4 pagesExperiment 4: Titrimetric AnalysisBianca VirtudasoNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Transition Metals Variable Oxidation States QsDocument37 pages2.5 Transition Metals Variable Oxidation States QsJesulayomi BolajiNo ratings yet
- Gross Heat in Petroleum Coke: Instrument: AC600Document2 pagesGross Heat in Petroleum Coke: Instrument: AC600Alfredo MarcanoNo ratings yet
- Jenkins Quantitative ChemistryDocument496 pagesJenkins Quantitative ChemistryMaster Of BlankNo ratings yet
- Titration Sample ProblemDocument8 pagesTitration Sample ProblemPaulAcademicsNo ratings yet
- D21T050 RM TitraLab86x GB PDFDocument244 pagesD21T050 RM TitraLab86x GB PDFmuszeres.petrikNo ratings yet
- 20) Complexometric TitrationDocument47 pages20) Complexometric TitrationCzarina Angelli AnastacioNo ratings yet
- Possible Viva Questions Ak 4Document3 pagesPossible Viva Questions Ak 4akshat1aps100% (1)
- Determination of Soil Nutrients (NPK) Using Optical Methods: A Mini ReviewDocument16 pagesDetermination of Soil Nutrients (NPK) Using Optical Methods: A Mini ReviewDr-Amit Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Practical of Chemistry PDFDocument377 pagesPractical of Chemistry PDFrajesh971No ratings yet
- Measurements and ErrorsDocument89 pagesMeasurements and Errorselsiesaveena96No ratings yet
- 200L BCM Practical Past QuestionsDocument13 pages200L BCM Practical Past Questionsdajisafe829No ratings yet
- Acid and Base Titration Lab ReportDocument5 pagesAcid and Base Titration Lab Reportapi-350496922No ratings yet
- Percentage Purity of Lime StoneDocument2 pagesPercentage Purity of Lime StoneNitinSrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Discussion Chem 26.1Document48 pagesPost Lab Discussion Chem 26.1Coleen SalvadorNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Titrations Questions With AnswersDocument12 pagesGCSE Chemistry Titrations Questions With AnswersMahdi AssadNo ratings yet
- Carbonato de Calcio PDFDocument7 pagesCarbonato de Calcio PDFEMERSONNo ratings yet
- Coconut ProductDocument8 pagesCoconut ProductTHONG LAMNo ratings yet
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsFrom EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo ratings yet
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)