Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Deber 4
Uploaded by
Geovanny SatamaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Deber 4
Uploaded by
Geovanny SatamaCopyright:
Available Formats
Cálculo Diferencial e Integral Andrea Ayala
Módulo II: Funciones
Deber 4
1. Grafique las siguientes funciones:
⎧ − 2 x − 1 si x < 1
y=⎨
a) 4x - 3y - 7 = 0 b) 5x – 2y + 10 = 0 c) ! ⎩(3 x − 15)/ 2 si x ≥ 1
⎧ − 2 si x < 0
⎪
y = ⎨ x − 2 si 0 ≤ x < 4 ⎧− x 2 − 4 x − 2 si x < −1
⎪ 2 si x ≥ 4 y=⎨
d) ! ⎩ e) ! ⎩ x 2 si x ≥ −1
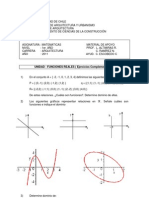
2. Asocia a cada gráfica su ecuación:
5
2 c) y = − x
a) y = −3 x + 5 b) y = ( x + 2 ) 3 d) y = −4 x 2
I) II)
! !
III) IV)
! !
3. Si f(x) = 3x – 2, entonces f(h+1) – f(h-1) es:
4. Si f(x) = 3x – 1, ¿cuál es el valor de f(-1)?
Cálculo Diferencial e Integral Andrea Ayala
5. Halle el dominio de:
1 1
f ( x) = f ( x) =
c) ! f ( x) = 2 x − 4
2
a) ! x−2 b) ! x −1
x −1
f ( x) = 4 2 5 2
d) ! x2 − 4 e) ! f ( x) = 16 − x f) ! f ( x) = x − 1
x
2
f ( x) =
g) ! f ( x) = 3x + 1 h) ! ln( x − 1)
6. Dadas las funciones f (x) = x ² - 3, y g(x) = x + 3, definir:
a) (f - g)(1/3) b) (f * g) (5) c) (f o g) (x)
7. Dadas las funciones f(x) = x ² + 1, y g(x) = 3x - 2, calcular:
a) (g o f) (x) b) (f o g) (x) c) (g o f) (1) + (f o g) (-1)
f ( x + h) − f ( x )
8. Si f(x) = 2+x3, entonces el valor de h es:
10. Sean las funciones f(x) = 3 x + 1, y g(x) = 2 x - 4.
a) (f + g)(-3) b) (f / g) (3) d) ( f o f ) (1)
3x + 4
f ( x) =
11. Encontrar el dominio y el rango de la función ! 2x − 1 .
You might also like
- La ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesFrom EverandLa ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesNo ratings yet
- TP 2-2021Document1 pageTP 2-2021DamarisNo ratings yet
- TallerdefuncionesDocument2 pagesTallerdefuncionesJose CaraguayNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio Sobre FuncionesDocument4 pagesEjercicio Sobre FuncionesAnthony Manuel0% (2)
- Guía de Reforzamiento: Funciones Electivo IV MedioDocument3 pagesGuía de Reforzamiento: Funciones Electivo IV MedioAndrés EspinozaNo ratings yet
- TP Funciones v2303Document5 pagesTP Funciones v2303Fernando TeselmanNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio Sobre FuncionesDocument3 pagesEjercicio Sobre FuncionesJean Carlos HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Cur 2 001 CD Ejercicios Funciones 002Document2 pagesCur 2 001 CD Ejercicios Funciones 002Emmanuel JimenezNo ratings yet
- Taller 4Document2 pagesTaller 4ELIZABETH CRUZ VALENCIANo ratings yet
- Práctica 6 - 6ABC (Derivadas e Integrales)Document5 pagesPráctica 6 - 6ABC (Derivadas e Integrales)Im BlueeNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio Sobre FuncionesNGLDocument3 pagesEjercicio Sobre FuncionesNGLluis maury perez guzmanNo ratings yet
- Introducción A La Matemática - EjercitaciónDocument22 pagesIntroducción A La Matemática - EjercitaciónLucas SosaNo ratings yet
- PD3 Mef1 2024-0Document4 pagesPD3 Mef1 2024-0The milfs fuckerNo ratings yet
- Dimaromo - Taller 1Document2 pagesDimaromo - Taller 1Karen BermudezNo ratings yet
- 4ºA Hoja Tema10Document1 page4ºA Hoja Tema10MaribelNo ratings yet
- Guia Derivadas Guia de Derivadas y Sus FormulasDocument10 pagesGuia Derivadas Guia de Derivadas y Sus FormulasPAOLA RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Representacion de FuncionesDocument2 pagesEjercicios Representacion de FuncionesOlaia Rodríguez LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Guía Funciones 2019 PDFDocument9 pagesGuía Funciones 2019 PDFKamila ToledoNo ratings yet
- Funciones 2Document9 pagesFunciones 2Ana CuentalNo ratings yet
- Calculo. Practico 1Document4 pagesCalculo. Practico 1Gabriel B ArzabeNo ratings yet
- Bolet N 2 Funciones Con Soluci n1525890370550Document3 pagesBolet N 2 Funciones Con Soluci n1525890370550Marcelino FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Calculo. Practico 1-1Document4 pagesCalculo. Practico 1-1soldelatorre0No ratings yet
- Guia Derivada 1Document7 pagesGuia Derivada 1SebastiánNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio Sobre Funciones MODIFDocument1 pageEjercicio Sobre Funciones MODIFJan P�rez FelizNo ratings yet
- Práctico 2 - 2018. FuncionesDocument8 pagesPráctico 2 - 2018. FuncionesmicaelakorecNo ratings yet
- Taller 4 Operaciones, Compuesta e InversaDocument2 pagesTaller 4 Operaciones, Compuesta e InversaOctavioNo ratings yet
- Lista de Exercícios Cálculo 1Document5 pagesLista de Exercícios Cálculo 1Ana IsaNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios DerivadasDocument8 pagesEjercicios DerivadasAngeln Calsin CariNo ratings yet
- Guia de Ejercicios FuncionesDocument5 pagesGuia de Ejercicios FuncionesSchlomits JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Taller FuncionesDocument3 pagesTaller Funcionesbmx.nico2018No ratings yet
- DerivadaDocument5 pagesDerivadagasty45No ratings yet
- Taller 1 Calculo DiferencialDocument4 pagesTaller 1 Calculo DiferencialFelicity GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Taller 1 Calculo DiferencialDocument4 pagesTaller 1 Calculo DiferencialangieNo ratings yet
- Pract. de DerivadasDocument4 pagesPract. de Derivadasjose andrade vargasNo ratings yet
- Mat6ActAcreditación1erCuatrimestre (2023)Document2 pagesMat6ActAcreditación1erCuatrimestre (2023)Samanta AlbanesiNo ratings yet
- PR Actico 7: Introducci Onalc Alculo - Ii Semestre 2022Document2 pagesPR Actico 7: Introducci Onalc Alculo - Ii Semestre 2022AlexJuanNo ratings yet
- Practica 7Document8 pagesPractica 7vegaNo ratings yet
- Guia Complementaria FuncionesDocument4 pagesGuia Complementaria FuncionesPilar Ascuy RochaNo ratings yet
- Matematicas Taller Examen FinalDocument3 pagesMatematicas Taller Examen FinalAnonymous aIE9TQNo ratings yet
- DerivadasDocument5 pagesDerivadasaaaNo ratings yet
- Lista 3 CalculoDocument7 pagesLista 3 CalculoMaria Amelia Melo RualesNo ratings yet
- Taller Funciones UdDocument2 pagesTaller Funciones Udandres felipe galindo duquinoNo ratings yet
- MatematicasDocument2 pagesMatematicasAlex CariagaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledAnibalGTXNo ratings yet
- Práctico III Funciones y Gráficas I-2023Document3 pagesPráctico III Funciones y Gráficas I-2023MALDONADO ARRAYASA JOHN JOSIASNo ratings yet
- Funciones Reales EjerciciosDocument7 pagesFunciones Reales EjerciciosRoimer SolorzanoNo ratings yet
- Practica 3 Exponencial LogaritmosDocument4 pagesPractica 3 Exponencial LogaritmosEsteban BallerNo ratings yet
- Guia 01 DerivadasDocument10 pagesGuia 01 DerivadascfloresahumadaNo ratings yet
- AP-MACS1-ejercicios Tema4 Funciones P20170120Document2 pagesAP-MACS1-ejercicios Tema4 Funciones P20170120Mª del Mar Arques MolinaNo ratings yet
- Laboratorio 11 - Tipos de Funciones, Función Compuesta.Document2 pagesLaboratorio 11 - Tipos de Funciones, Función Compuesta.Romy DanaisNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio Sobre funcionesNGLDocument3 pagesEjercicio Sobre funcionesNGLDarlin MartinesNo ratings yet
- Tarea VII - Derivadas y AplicacionesDocument1 pageTarea VII - Derivadas y AplicacionesDelmi Walkiri Leonardo Vásquez33% (3)
- Actividad Vii - Unidad IV Ms 2019Document1 pageActividad Vii - Unidad IV Ms 2019Carmen LunaNo ratings yet
- Actividad Vii - Unidad IV Ms 2019Document1 pageActividad Vii - Unidad IV Ms 2019Odalis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Practica 1Document6 pagesPractica 1Cris LomasNo ratings yet
- Consolidación U9Document2 pagesConsolidación U9gema_gamez2830No ratings yet
- 5-Derivadas-Guia Cálculo I - FIng Práctica 08Document3 pages5-Derivadas-Guia Cálculo I - FIng Práctica 08Nerak ZilramNo ratings yet
- TP 3 - 2022Document4 pagesTP 3 - 2022Francisco PretzNo ratings yet
- Taller 1Document2 pagesTaller 1Daniela camero lunaNo ratings yet
- Lab IIDocument14 pagesLab IIGeovanny SatamaNo ratings yet
- CV 00138700 20201005110710Document1 pageCV 00138700 20201005110710Geovanny SatamaNo ratings yet
- Capacidad de Canal en Redes Móviles 5G - Sistemas de ComunicacionesDocument15 pagesCapacidad de Canal en Redes Móviles 5G - Sistemas de ComunicacionesGeovanny SatamaNo ratings yet
- Practica 4 Filtros Con ADSDocument10 pagesPractica 4 Filtros Con ADSGeovanny SatamaNo ratings yet
- Practica2. Repaso Conceptos BásicosDocument5 pagesPractica2. Repaso Conceptos BásicosGeovanny SatamaNo ratings yet
- Experimento 2 Laboratorio de Ondas Electromagn Ticas N2Document15 pagesExperimento 2 Laboratorio de Ondas Electromagn Ticas N2Geovanny SatamaNo ratings yet
- Practica 6Document8 pagesPractica 6Geovanny SatamaNo ratings yet
- Taller 3Document1 pageTaller 3Geovanny SatamaNo ratings yet
- Informe ReadyDocument6 pagesInforme ReadyGeovanny SatamaNo ratings yet
- Pre Lab4Document6 pagesPre Lab4Geovanny SatamaNo ratings yet
- Tema 8. Gráfica de FuncionesDocument5 pagesTema 8. Gráfica de FuncionesGeovanny SatamaNo ratings yet
- Practica 6. Campo MagnéticoDocument10 pagesPractica 6. Campo MagnéticoGeovanny SatamaNo ratings yet
- Segundo Lab Fis 2Document7 pagesSegundo Lab Fis 2Geovanny SatamaNo ratings yet
- FISII-02 (Permitividad)Document3 pagesFISII-02 (Permitividad)Geovanny SatamaNo ratings yet
- Primer Lab Fis 2Document7 pagesPrimer Lab Fis 2Geovanny SatamaNo ratings yet
- Reporte de Testigo ExpertoDocument15 pagesReporte de Testigo ExpertoGeovanny SatamaNo ratings yet
- Deber 5Document2 pagesDeber 5Geovanny SatamaNo ratings yet
- FactorizacionDocument6 pagesFactorizacionJuan Javier de Lira MartinezNo ratings yet
- Complejos TEORÍA+EJERCICIOSDocument10 pagesComplejos TEORÍA+EJERCICIOSCristina LopezNo ratings yet
- 10 DiagonalizacionDocument23 pages10 DiagonalizacionNery ChiroqueNo ratings yet
- Álgebra MultilinealDocument4 pagesÁlgebra MultilinealDavid MurilloNo ratings yet
- Cuadro SinopticoDocument3 pagesCuadro SinopticoYamid Navea0% (1)
- Funciones Exponenciales y LogaritmicasDocument3 pagesFunciones Exponenciales y LogaritmicasAdriana Lucía Gualy VargasNo ratings yet
- MAT 2.2. Cuádricas en El Proyectivo (Castellón, UMA)Document45 pagesMAT 2.2. Cuádricas en El Proyectivo (Castellón, UMA)elduqueeconomicoNo ratings yet
- de La Semana 09Document29 pagesde La Semana 09Juan Miguel Aquije IncaNo ratings yet
- M 766 TPS1 2022-1Document3 pagesM 766 TPS1 2022-1undibal rivasNo ratings yet
- Tarea 5 Algebra LinealDocument9 pagesTarea 5 Algebra LinealOscar VazquezNo ratings yet
- I Festival de Habilidades Matematicas PdvsaDocument3 pagesI Festival de Habilidades Matematicas PdvsaTamara TorresNo ratings yet
- Recursamiento Calculo DiferencialDocument3 pagesRecursamiento Calculo DiferencialJULIO ALEXIS LABRA HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document4 pagesLab 4Sherly RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Guía de Trabajos Prácticos Aplicaciones Derivadas AMIDocument21 pagesGuía de Trabajos Prácticos Aplicaciones Derivadas AMIFlorencia JasaNo ratings yet
- Tarea 06 CalculoDocument8 pagesTarea 06 CalculoradhamesNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Métodos Matemáticos de La Física IIDocument2 pagesEjercicios Métodos Matemáticos de La Física IIAbraham McNo ratings yet
- Logaritmos PropiedadesDocument14 pagesLogaritmos PropiedadesCARLO VARGAS GONZALEZ100% (1)
- Libro Representación Gráfica de Funciones PDFDocument316 pagesLibro Representación Gráfica de Funciones PDFJorge Pibaque0% (1)
- Monografía de FuncionesDocument39 pagesMonografía de FuncionesYEFERSON WILMER QUISPE CERDANo ratings yet
- 02) Potencias y RadicalesDocument16 pages02) Potencias y Radicalesramirodecristo2No ratings yet
- AlgebraDocument7 pagesAlgebraPerez Moreno Francis LeonelaNo ratings yet
- Guía #4 Funciones (Función Lineal y Afín)Document5 pagesGuía #4 Funciones (Función Lineal y Afín)alberNo ratings yet
- Análisis de Sistemas Usando LDRDocument16 pagesAnálisis de Sistemas Usando LDRFernando PadillaNo ratings yet
- Grupo 3 Cable Colgante 1Document18 pagesGrupo 3 Cable Colgante 1Dennys MonteroNo ratings yet
- Operaciones de Funciones - PrácticaDocument6 pagesOperaciones de Funciones - PrácticaElias Abel Rodriguez Jaime100% (1)
- Folleto de Esa Materia :VDocument195 pagesFolleto de Esa Materia :VheyNo ratings yet
- Guía de Estudio MA1035Document14 pagesGuía de Estudio MA1035Daemi AlejoNo ratings yet
- Laboratorio 3 CaldDocument12 pagesLaboratorio 3 CaldEdward ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio Teorema de FubiniDocument5 pagesEjercicio Teorema de FubiniDeiby Casanova LopezNo ratings yet