Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Name: Vince John B. Sevilla NCP Conference N-31
Uploaded by
Vince John Sevilla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesncp con wat
Original Title
ncpcon
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentncp con wat
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesName: Vince John B. Sevilla NCP Conference N-31
Uploaded by
Vince John Sevillancp con wat
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Name: Vince John B.
Sevilla NCP CONFERENCE N-31
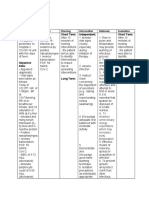
ASSESSMENT NURSING OBJECTIVES/EVAL NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOS UATION CRITERIA
IS
Independent: Independent: Short Term: after 8 hours
S: Risk for Short term: Within 8 1. Assess the general condition of the patient 1. To note any alterations regarding the of nursing interventions,
infection r/t hours of nursing 2. Focused assessment on abdomen . patient’s condition and to identify the the patient was able to
tissue interventions the 3. Observe for localize sign of infection. prioritized problem. identify ways to prevent
destruction patient will be able 4. Review of lab studies. 2. To have a thorough assessment on following or reduce risk of
O: secondary identify ways to 5. Assess for use of medication that may cause areas in the lower abdomen. infection
to inguinal prevent or reduce risk immunosuppression. 3. To know where the microorganism may enter - Goal met
-with 4 days hernia of infection and create infection. Long Term: after 3 days
incision site at repair 6. Monitor temperature of pt. 4. Very low WBC count may indicate a severe of nursing interventions,
inguinal area. Long term: Within 3 7. Assist with measures to facilitate gas exchange. risk for infection. the patient was able to be
days of nursing (positioning Semi-fowlers) 5. Antineoplastic agents, corticosteroids, and so free from developing an
-warm upper interventions the
lower on, can reduce immunity infection throughout her
patient will be able to 8. Demonstrate Coughing exercise such as direct or 6. Hyperthermia indicates present of infection. hospitalization
extremities be free from controlled coughing through splinting. 7. To promote comfort when standing , sitting - Goal met
developing an 9. Demonstrate Breathing Exercise such Inspiratory, and lying.
-WBC 11.5
infection throughout Diaphragmatic, Pursed Lip Breathing. 8. The most convenient way to remove most
increased
his hospitalization 10. Demonstrated proper hand washing to patient and secretions is coughing.
-Neutrophils SO 9. Deep breathing, on the other hand, promotes
9.87 increased 11. Maintain adequate hydration, stand, or sit to void if oxygenation before controlled coughing.
necessary 10. To prevent such infections.
-unchanged 12. Provide a clean and well ventilated environment 11. To eliminate toxic substances from our body,
dressing 4 days so they can be excreted through urine and/or
Health Teachings: sweat.
12. To minimize the possibility of infection
13. Advise adequate rest periods 13. Pulse oximetry values are used to assess the
14. Emphasize constant and proper personal care patient’s need for oxygen and administer
15. Encourage intake of foods rich in protein and supplemental oxygen as prescribed
vitamin C. Health Teachings:
16. Encourage patient adequate fluid intake 14. To promote healing and restoration of energy
17. Encourage Patient to limit visitor 15. Patients and SO can spread infection from
18. Teach the patient or SO the importance of avoiding one part of the body to another –
contact with individuals who have infection or colds. handwashing reduces these risks.
19. Teach patient to avoid touching the incision site. 16. Helps support the immune system
20. Instructed pt to avoid wetting the dressing. responsiveness.
21. teach the patient to take antibiotics as prescribed. 17. Fluids promote diluted urine and frequent
Dependent: emptying of bladder – reducing the stasis of
22. Administer antibiotics, as indicated urine, in turn, reduces risk for bladder
infection or urinary tract infection.
18. Restricting visitation reduces the
transmission of pathogens.
19. To prevent entry of microorganism
20. Wet areas causes the microorganism
multiply fast
21. To provide information about nebulizing
22. Antibiotics work best when a constant blood
level is maintained which is done when
medications are taken as prescribed.
Dependent:
23. Antibiotics hinder or kill susceptible
bacterias
Collaborative:
24. For curative measres
You might also like
- Suctioning ChecklistDocument7 pagesSuctioning Checklistacademic purposesNo ratings yet
- Faye Abdellahs TheoryDocument44 pagesFaye Abdellahs TheoryMaria Kathleen ArrofoNo ratings yet
- Forro Intestinal Obstruction-2Document4 pagesForro Intestinal Obstruction-2Shiehan Mae ForroNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Short TermDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Short TermLorie May GuillangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - BeDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan - BeMart UrsuNo ratings yet
- 1F Procedure Guide (CAUSIN)Document12 pages1F Procedure Guide (CAUSIN)CAUSIN, Lance Matthew,No ratings yet
- Intervensi Ispa Dan Oma FixDocument5 pagesIntervensi Ispa Dan Oma FixRizki ArifNo ratings yet
- NCP and Fdar Wk2 Sarscov-19Document4 pagesNCP and Fdar Wk2 Sarscov-19Jamaica Malicdem0% (1)
- Cholecystectomy Nursing Care Plan: Risk For InfectionDocument1 pageCholecystectomy Nursing Care Plan: Risk For InfectionBesael BaccolNo ratings yet
- Assisting With A Liver BiopsyDocument8 pagesAssisting With A Liver BiopsyCharLie BlackNo ratings yet
- NCP Case Pre Nichole SarioDocument2 pagesNCP Case Pre Nichole SarioJoule PeirreNo ratings yet
- University of The East: Assessmen T Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesUniversity of The East: Assessmen T Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationPATRICIA JEANNE JABIANNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term: Independent: Short TermDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term: Independent: Short TermDYNA GISELLE ROMERONo ratings yet
- NCP (Baluyot Jason Lee) Group17Document3 pagesNCP (Baluyot Jason Lee) Group17Jasonlee BaluyotNo ratings yet
- Assesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha Suazo100% (1)
- Chicken Pox N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesChicken Pox N C P BY BHERU LALBheru Lal100% (1)
- OB - NCP (Episiotomy)Document3 pagesOB - NCP (Episiotomy)eosNo ratings yet
- Risk For Infection: Objective: - Fever - Lower Back Pain - Pain in Urinating For 1 WeekDocument8 pagesRisk For Infection: Objective: - Fever - Lower Back Pain - Pain in Urinating For 1 WeekJamie HaravataNo ratings yet
- Checklist Using Nasopharengeal and Oropharengeal SuctioningDocument4 pagesChecklist Using Nasopharengeal and Oropharengeal SuctioningKristine Louise JavierNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nusing Checklist: Conams Wesleyan University Philippines 2020-2021Document4 pagesMedical-Surgical Nusing Checklist: Conams Wesleyan University Philippines 2020-2021eliza luisNo ratings yet
- APPENDICITISDocument15 pagesAPPENDICITISTiffany AdriasNo ratings yet
- NCP Case Analysis GastritisDocument7 pagesNCP Case Analysis GastritisSteffi GolezNo ratings yet
- Incentive SpirometryDocument3 pagesIncentive SpirometryJocel Mae OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Fundal Height MeasurementDocument3 pagesFundal Height MeasurementJoseph Hechanova AsenjoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Diarrhea & VomitingDocument4 pagesFluid Volume Deficit R/T Diarrhea & Vomitingjisoo100% (3)
- HTP HemoptysisDocument10 pagesHTP HemoptysisみずNo ratings yet
- 2ND Exam Part 2Document5 pages2ND Exam Part 2SajeebChandraNo ratings yet
- Seizure ChecklistDocument3 pagesSeizure ChecklistBALIWANG, MARCOS JR. G.No ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal of Care Outcome Criteria Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal of Care Outcome Criteria Interventions and Rationale EvaluationMariah Angela PonceNo ratings yet
- Assisting The Patient During The Lumbar Puncture DefinitionDocument3 pagesAssisting The Patient During The Lumbar Puncture DefinitionSHAINA CADALINNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance-Nursing Care Plan For COPDDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance-Nursing Care Plan For COPDRnspeakcom100% (1)
- DULNUANDocument2 pagesDULNUANJB tindonganNo ratings yet
- Romero, Deinielle Ingrid M. (Hiv)Document8 pagesRomero, Deinielle Ingrid M. (Hiv)Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- NCP ER DoneDocument3 pagesNCP ER DonejozaiaNo ratings yet
- Dnrle Influenza NCPDocument3 pagesDnrle Influenza NCPEna RodasNo ratings yet
- NCPsDocument6 pagesNCPshdjndijriifNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - Perioperative Nursing Activity and ExerciseDocument11 pagesWeek 7 - Perioperative Nursing Activity and ExerciseMiss VinaNo ratings yet
- 11 SurgeriesDocument11 pages11 SurgeriesJanely EstreraNo ratings yet
- Status AsthmaticusDocument6 pagesStatus AsthmaticusMae Azores100% (1)
- Cefazolin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCefazolin Drug StudyAj GoNo ratings yet
- Nursing BulletsDocument65 pagesNursing Bulletsjoan olanteNo ratings yet
- LIVER CIRRHOSIS - SeminarrDocument12 pagesLIVER CIRRHOSIS - Seminarrعمار ياسرNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lorma Colleges Con Template Related Learning ExperienceDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lorma Colleges Con Template Related Learning ExperiencePauline GarciaNo ratings yet
- Rle Procedure StudyDocument4 pagesRle Procedure StudyMyangel LoiseNo ratings yet
- Cap Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesCap Nursing Care PlanCharlene Grace ReginoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanJasonlee BaluyotNo ratings yet
- Oro-Nasopharyngeal SuctioningDocument3 pagesOro-Nasopharyngeal SuctioningMichelle SatairapanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan2Document13 pagesNursing Care Plan2Nna ANn CastleNo ratings yet
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressDocument2 pagesAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- Micro Lab#24Document2 pagesMicro Lab#24رجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis (1) (1) .Finalgid NiyaDocument30 pagesNursing Diagnosis (1) (1) .Finalgid NiyaReadcast EFNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: NOC: Swallowing Status Goal: NIC: SwallowingDocument10 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: NOC: Swallowing Status Goal: NIC: SwallowingSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- April 1999 Paper 1 Clinical Nursing Essay - Type Test Items: Scenario 1 Item 1Document10 pagesApril 1999 Paper 1 Clinical Nursing Essay - Type Test Items: Scenario 1 Item 1Aaron WallaceNo ratings yet
- Case Study (DS)Document3 pagesCase Study (DS)Erica DumriqueNo ratings yet
- NCP InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP InfectionHasna LisnaNo ratings yet
- Romero, Deinielle Ingrid M. (Pulmo)Document3 pagesRomero, Deinielle Ingrid M. (Pulmo)Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Volume 1Document2 pagesVolume 1roxybiscanteNo ratings yet
- BDH NCP Medical FormDocument9 pagesBDH NCP Medical FormRegie CanoNo ratings yet
- Activity Intolerance R/T Imbalance Between Oxygen Supply and DemandDocument2 pagesActivity Intolerance R/T Imbalance Between Oxygen Supply and DemandVince John SevillaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Skills: Blood Transfusion/ Iv TherapyDocument6 pagesNursing Skills: Blood Transfusion/ Iv TherapyVince John SevillaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearanc e Related To Airway Obstruc Tion Secondary To Trauma and Tissue DamageDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearanc e Related To Airway Obstruc Tion Secondary To Trauma and Tissue DamageVince John SevillaNo ratings yet
- Dengue FeverDocument3 pagesDengue FeverVince John SevillaNo ratings yet
- Breathing PatternDocument4 pagesBreathing PatternVince John SevillaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument6 pagesPathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseVince John Sevilla100% (2)
- NCP DiarrheaDocument2 pagesNCP DiarrheaVince John SevillaNo ratings yet
- Nursing. COPAR Aims To Transform The Apathetic, Individualistic and Voiceless Poor Into Dynamic, Participatory and Politically Responsive CommunityDocument6 pagesNursing. COPAR Aims To Transform The Apathetic, Individualistic and Voiceless Poor Into Dynamic, Participatory and Politically Responsive CommunityVince John SevillaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascul Ar Agent Calcium Channel Blocker Antihyperten Sive Agent Tablet 2.5mg, 5mg, 10mg Patient Dosage 5 MG ODDocument1 pageCardiovascul Ar Agent Calcium Channel Blocker Antihyperten Sive Agent Tablet 2.5mg, 5mg, 10mg Patient Dosage 5 MG ODVince John SevillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Classificati On Dosage Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesDrug Classificati On Dosage Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesVince John SevillaNo ratings yet
- Red Font - Abnomal: Physical AssessmentDocument5 pagesRed Font - Abnomal: Physical AssessmentVince John SevillaNo ratings yet
- Valproic Acid DrugstudyDocument2 pagesValproic Acid DrugstudyVince John SevillaNo ratings yet
- Post-Operative Nursing Care Plan # 1Document14 pagesPost-Operative Nursing Care Plan # 1Vince John SevillaNo ratings yet
- Uterine Fibroids ReportDocument3 pagesUterine Fibroids ReportVince John SevillaNo ratings yet
- Psychological Stressors of The College Students of Father Saturnino Urios University I: Profile Age: Sex: Female Program: AccountancyDocument5 pagesPsychological Stressors of The College Students of Father Saturnino Urios University I: Profile Age: Sex: Female Program: AccountancyVince John SevillaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPVince John SevillaNo ratings yet
- OPD Network ListDocument354 pagesOPD Network ListSHAIKH ABDUL AZIZ salim bashaNo ratings yet
- Human Diseases A Systemic Approach 8th Edition-Páginas-15-26Document12 pagesHuman Diseases A Systemic Approach 8th Edition-Páginas-15-26Karime LopezNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Alternative System of MedicineDocument37 pagesLesson Plan On Alternative System of MedicineSagiraju Srinu100% (3)
- Social Policy For Effective Practice A Strengths Approach Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesSocial Policy For Effective Practice A Strengths Approach Ebook PDFcarolyn.kemper626100% (39)
- Christian Health Association of Malawi: Application Form A. Personal InformationDocument2 pagesChristian Health Association of Malawi: Application Form A. Personal InformationAnonymous 5Q2f2n4No ratings yet
- (Medical Radiology) Lluís Donoso-Bach, Giles W. L. Boland - Quality and Safety in Imaging-Springer International Publishing (2018)Document187 pages(Medical Radiology) Lluís Donoso-Bach, Giles W. L. Boland - Quality and Safety in Imaging-Springer International Publishing (2018)Piotr JankowskiNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspects of Medical RecordsDocument14 pagesLegal Aspects of Medical Recordsneeta rajesh bhide50% (4)
- Efficacy and Safety of Paliperidone Palmitate Eca ADocument14 pagesEfficacy and Safety of Paliperidone Palmitate Eca AMaria Fernanda AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol CalpolDocument1 pageParacetamol Calpolunkown userNo ratings yet
- Manchikanti 2015Document14 pagesManchikanti 2015Jose PerezNo ratings yet
- MLGP MacArthur FinalDocument47 pagesMLGP MacArthur Finalcatherine joy macalosNo ratings yet
- Out of Synch ChildDocument1 pageOut of Synch ChildChristine ButtkusNo ratings yet
- Chiropractic Marketing: Market Segmentation & Growth StrategyDocument11 pagesChiropractic Marketing: Market Segmentation & Growth StrategySubhashis Priyadarshi Sahoo100% (1)
- Norms, Policies and Protocols of Pediatric CareDocument49 pagesNorms, Policies and Protocols of Pediatric CareSivabarathy86% (14)
- Body Mass Index Form Medical Exam CoqcDocument1 pageBody Mass Index Form Medical Exam CoqcPaulo Justin Tabangcora OropillaNo ratings yet
- Brochures Super MBADocument24 pagesBrochures Super MBAVirat TiwariNo ratings yet
- Healy World Flyer Wellbeing en USDocument1 pageHealy World Flyer Wellbeing en USAllan Emmanuel Lopez MarquezNo ratings yet
- PALLIATIVE RadiationDocument13 pagesPALLIATIVE RadiationFeras OskanNo ratings yet
- Rubric - Nursing Clinical NURS 316Document5 pagesRubric - Nursing Clinical NURS 316louradelNo ratings yet
- Conduct of LaborDocument8 pagesConduct of LaborChristine Evan HoNo ratings yet
- Extension Function of HEIsDocument14 pagesExtension Function of HEIsJuvy MojaresNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Recreation Leadership and Prog - RobinDocument625 pagesTherapeutic Recreation Leadership and Prog - RobinBrandiBassett100% (8)
- CV of DoctorDocument1 pageCV of DoctorBobby Jatt0% (1)
- AHTDP RTMS Resistant Depression UofCDocument162 pagesAHTDP RTMS Resistant Depression UofCGurpreet CharaNo ratings yet
- Health Belief ModelDocument5 pagesHealth Belief Modeldanimon1984No ratings yet
- Major Challenges in The Health Sector in BangladeshDocument13 pagesMajor Challenges in The Health Sector in Bangladesh12-057 MOHAMMAD MUSHFIQUR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Head & Neck Surgery-Vol 2 Lore & Medina PDFDocument848 pagesAtlas of Head & Neck Surgery-Vol 2 Lore & Medina PDFroata cristian100% (3)
- Domperidone For Increasing Breast Milk Supply 260219 PDFDocument2 pagesDomperidone For Increasing Breast Milk Supply 260219 PDFANneNo ratings yet
- Guidelines PDFDocument6 pagesGuidelines PDFSunil JainNo ratings yet
- Universal Health Coverage of Bangladesh - Analysis Through The Framework of Alford's Theory of Structural Interests in Health Care PPT 28 PresentedDocument30 pagesUniversal Health Coverage of Bangladesh - Analysis Through The Framework of Alford's Theory of Structural Interests in Health Care PPT 28 PresentedRashed ShukornoNo ratings yet