Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cancer Is A Group of Diseases Involving Abnormal: Helicobacter Pylori
Uploaded by
Sayeda AlinaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cancer Is A Group of Diseases Involving Abnormal: Helicobacter Pylori
Uploaded by
Sayeda AlinaCopyright:
Available Formats
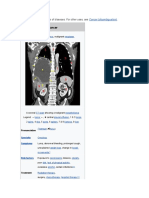
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread
to other parts of the body.[2][8] These contrast with benign tumors, which do not
spread.[8] Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough,
unexplained weight loss and a change in bowel movements.[1] While these symptoms may indicate
cancer, they can also have other causes.[1] Over 100 types of cancers affect humans.[8]
Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths.[2] Another 10% are due to obesity,
poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol.[2][9][10] Other factors include certain
infections, exposure to ionizing radiation and environmental pollutants.[3] In the developing world,
15% of cancers are due to infections such as Helicobacter pylori, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human
papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).[2] These
factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes of a cell.[11] Typically, many genetic changes are
required before cancer develops.[11] Approximately 5–10% of cancers are due to inherited genetic
defects from a person's parents.[12] Cancer can be detected by certain signs and symptoms
or screening tests.[2] It is then typically further investigated by medical imaging and confirmed
by biopsy.[13]
Many cancers can be prevented by not smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, not drinking too
much alcohol, eating plenty of vegetables, fruits and whole grains, vaccination against certain
infectious diseases, not eating too much processed and red meatand avoiding too
much sunlight exposure.[14][15] Early detection through screening is useful for cervical and colorectal
cancer.[16]The benefits of screening in breast cancer are controversial.[16][17] Cancer is often treated
with some combination of radiation therapy, surgery, chemotherapy and targeted therapy.[2][4] Pain
and symptom management are an important part of care.[2]Palliative care is particularly important in
people with advanced disease.[2] The chance of survival depends on the type of cancer and extent of
disease at the start of treatment.[11] In children under 15 at diagnosis, the five-year survival rate in
the developed world is on average 80%.[18] For cancer in the United States, the average five-year
survival rate is 66%.[5]
In 2015, about 90.5 million people had cancer.[6] About 14.1 million new cases occur a year (not
including skin cancer other than melanoma).[11] It caused about 8.8 million deaths (15.7%
of deaths).[7] The most common types of cancer in males are lung cancer, prostate cancer, colorectal
cancer and stomach cancer.[19] In females, the most common types are breast cancer, colorectal
cancer, lung cancer and cervical cancer.[11] If skin cancer other than melanoma were included in total
new cancer cases each year, it would account for around 40% of cases.[20][21] In children, acute
lymphoblastic leukemia and brain tumorsare most common, except in Africa where non-Hodgkin
lymphoma occurs more often.[18] In 2012, about 165,000 children under 15 years of age were
diagnosed with cancer.[19] The risk of cancer increases significantly with age, and many cancers
occur more commonly in developed countries.[11] Rates are increasing as more people live to an old
age and as lifestyle changes occur in the developing world.[22] The financial costs of cancer were
estimated at $1.16 trillion USD per year as of 2010.[2
You might also like
- "Cancer 101: What You Need to Know About Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention"From Everand"Cancer 101: What You Need to Know About Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention"No ratings yet
- Cancer Is A Group of Diseases Involving AbnormalDocument1 pageCancer Is A Group of Diseases Involving AbnormalСергей МалайNo ratings yet
- Cancer, Also Known As A: Malignant Tumor NeoplasmDocument1 pageCancer, Also Known As A: Malignant Tumor Neoplasmdian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- Definitions: Helicobacter PyloriDocument3 pagesDefinitions: Helicobacter PylorifranklinNo ratings yet
- Article About CancerDocument4 pagesArticle About CancerMohammad 08No ratings yet
- CancerDocument6 pagesCancersujithasNo ratings yet
- Idiopathy and CancerDocument130 pagesIdiopathy and CancerNinthCircleOfHellNo ratings yet
- Who IntDocument4 pagesWho IntTrisna Bagus FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument5 pagesCancerJessica DiasNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument23 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentMoinak GuhaNo ratings yet
- Cancer / : (Listen)Document2 pagesCancer / : (Listen)Pearl Canaya PeñafloridaNo ratings yet
- Causes of CancerDocument4 pagesCauses of CancerMonil ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Key Facts: The ProblemDocument6 pagesKey Facts: The Problemriza kurniaNo ratings yet
- Biology Project Draft PDFDocument21 pagesBiology Project Draft PDFkarthikeya kakarlapudiNo ratings yet
- Cancer (From WHO, World Health Organisation) : Key FactsDocument5 pagesCancer (From WHO, World Health Organisation) : Key FactsAfini Exo KNo ratings yet
- Album Types of Cancer: Name: Ghina Raquel Funes Euceda Grade: 7thDocument5 pagesAlbum Types of Cancer: Name: Ghina Raquel Funes Euceda Grade: 7thgloria velasquezNo ratings yet
- Cancer: Key FactsDocument4 pagesCancer: Key FactsAndriyani Indah KusumaDewiNo ratings yet
- Cancer: Key FactsDocument6 pagesCancer: Key FactsKARL PASCUANo ratings yet
- Cancer: Dr. Sonkar V KDocument64 pagesCancer: Dr. Sonkar V KVenkatramana SonkarNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet N°297 Updated February 2015: CancerDocument4 pagesFact Sheet N°297 Updated February 2015: CancerkristinNo ratings yet
- Major Public Health & Lifestyle Issues in IndiaDocument15 pagesMajor Public Health & Lifestyle Issues in IndiakomalNo ratings yet
- Cancer Is A Group of Diseases Involving AbnormalDocument1 pageCancer Is A Group of Diseases Involving AbnormalMada AdamNo ratings yet
- What Is CancerDocument15 pagesWhat Is CancerroggesterNo ratings yet
- Cancer: Done By: Lana Shabsough Samira Owdeh Supervised By: Prof. Farouq Al ShakhatrehDocument30 pagesCancer: Done By: Lana Shabsough Samira Owdeh Supervised By: Prof. Farouq Al ShakhatrehLana ShabsoughNo ratings yet
- Molecular Carcinogenesis 2017Document91 pagesMolecular Carcinogenesis 2017yuslipahNo ratings yet
- Bio Final DraftDocument5 pagesBio Final Draftfrozan s naderiNo ratings yet
- Principios de OncologiaDocument14 pagesPrincipios de Oncologiaangie18No ratings yet
- Cancer Management Blueprint FINAL 27 MARCH 2008Document165 pagesCancer Management Blueprint FINAL 27 MARCH 2008Gan Tzyh KeongNo ratings yet
- Author: Section Editors: Deputy EditorDocument44 pagesAuthor: Section Editors: Deputy EditorYdeli DetanNo ratings yet
- Key FactsDocument1 pageKey Factsdhruvdesai24No ratings yet
- Problem Statement WORLD Cancer Afflicts All Communities WorldwideDocument30 pagesProblem Statement WORLD Cancer Afflicts All Communities Worldwidesalma0430100% (2)
- Pancreatic CancerDocument2 pagesPancreatic CancerKyle AndrewNo ratings yet
- Cancer WHO 2011Document17 pagesCancer WHO 2011Chiara GuidottiNo ratings yet
- Cancer For DummiesDocument26 pagesCancer For DummiesrkdivyaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Influences in Cancer Aetiology: John A. Newby BSC & C. Vyvyan Howard MB, CHB, PHD, FrcpathDocument59 pagesEnvironmental Influences in Cancer Aetiology: John A. Newby BSC & C. Vyvyan Howard MB, CHB, PHD, FrcpathSaad MotawéaNo ratings yet
- Worldwide Burden of Colorectal Cancer: A ReviewDocument5 pagesWorldwide Burden of Colorectal Cancer: A ReviewRomário CerqueiraNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument24 pagesCancermiltynethouseNo ratings yet
- Cancer, Also Known As ADocument4 pagesCancer, Also Known As AMarc Lorenz DucusinNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Medicine in CancerDocument25 pagesBehavioral Medicine in CancerOVIDIU-IULIAN BOBEINo ratings yet
- English Final CoursDocument223 pagesEnglish Final CourspopeataNo ratings yet
- Lecture On BREAST CANCER 2021Document5 pagesLecture On BREAST CANCER 2021Krisheille Amano MirandaNo ratings yet
- Cancer (Causes)Document5 pagesCancer (Causes)Abhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Cancer Presentation1Document50 pagesCancer Presentation1AnishaNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument6 pagesCancerRajiv FurtadoNo ratings yet
- Mcglynn 2020Document23 pagesMcglynn 2020Luluil MunirohNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic CancerDocument26 pagesPancreatic CancerJesus RFNo ratings yet
- Cancer Epidemiology - NCDEDocument6 pagesCancer Epidemiology - NCDEFirly Azra GhassanieNo ratings yet
- Sample RORLDocument25 pagesSample RORLLj BerganioNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project ON Cancer: BY D.Dhanus H Xii-IdDocument20 pagesBiology Investigatory Project ON Cancer: BY D.Dhanus H Xii-IddhanushNo ratings yet
- ESMO Clinical PracticeDocument13 pagesESMO Clinical PracticePati MuresanNo ratings yet
- Sourav Bio3Document7 pagesSourav Bio3manojoram709No ratings yet
- المستندDocument3 pagesالمستندعبدالرحمن الشهريNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument1 pageCancerNithyababuNo ratings yet
- MALIGNANCYDocument47 pagesMALIGNANCYAsmi MohamedNo ratings yet
- Epidem Cancer ColorectalDocument5 pagesEpidem Cancer ColorectalAna MîndrilăNo ratings yet
- The Status of Colorectal Cancer Care in The Netherlands: Past, Present and FutureDocument6 pagesThe Status of Colorectal Cancer Care in The Netherlands: Past, Present and FutureIlija TripkovićNo ratings yet
- Epi of Oral CancerDocument294 pagesEpi of Oral CancerHansa KunduNo ratings yet
- Thrumurthy 2016Document12 pagesThrumurthy 2016SidiqrifNo ratings yet
- QQQQQQQQQQQQQDocument21 pagesQQQQQQQQQQQQQكاظم طارقNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 1Document18 pagesJurnal 1YTNo ratings yet
- Role of Bank Regulation On Bank Performance: Evidence From Asia-Pacific Commercial BanksDocument25 pagesRole of Bank Regulation On Bank Performance: Evidence From Asia-Pacific Commercial BanksSayeda AlinaNo ratings yet
- Presentation File: Introduction To ComputingDocument4 pagesPresentation File: Introduction To ComputingSayeda AlinaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Inc.: Business AnalysisDocument5 pagesMicrosoft Inc.: Business AnalysisSayeda AlinaNo ratings yet
- 6TTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTDocument10 pages6TTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTSayeda AlinaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Drug BaseDocument263 pagesClinical Drug BaseJackie MoonNo ratings yet
- PCA Pump Vs FentanylDocument1 pagePCA Pump Vs FentanylJanaNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases For InternsDocument60 pagesInfectious Diseases For InternsMaya SwariNo ratings yet
- MethottexateDocument104 pagesMethottexateFarha Elein KukihiNo ratings yet
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Review ArticleDocument13 pagesIdiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Review ArticleMr. LNo ratings yet
- Myotonic Dystrophy 2017Document8 pagesMyotonic Dystrophy 2017Ully BatubaraNo ratings yet
- Outcomes in Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery An UpdatedDocument10 pagesOutcomes in Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery An UpdatedNofia AlistaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes y Embarazo ADA 2023Document13 pagesDiabetes y Embarazo ADA 2023Efrain FernandoNo ratings yet
- Tetanus Neonatorum LectureDocument11 pagesTetanus Neonatorum LectureJackNo ratings yet
- Precautions - Isolation Precautions - Guidelines Library - Infection Control - CDCDocument6 pagesPrecautions - Isolation Precautions - Guidelines Library - Infection Control - CDCKomite PPI RSUDPCNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument39 pagesAcute PancreatitisGloria KikiNo ratings yet
- MINI International Neuropsychiatric Schedule: Clinical Utility and Patient AcceptanceDocument4 pagesMINI International Neuropsychiatric Schedule: Clinical Utility and Patient AcceptanceRafael MartinsNo ratings yet
- Hip Arthroplasty in Lokoja PPT 2Document16 pagesHip Arthroplasty in Lokoja PPT 2asi basseyNo ratings yet
- OS 216 - Myelodysplastic SyndromesDocument5 pagesOS 216 - Myelodysplastic Syndromesx_xtattooedx_x1636100% (1)
- 3 Workbook - A Miracle RescueDocument3 pages3 Workbook - A Miracle RescueDiego JavierNo ratings yet
- Cancer Colon and Rectum (Wardah)Document23 pagesCancer Colon and Rectum (Wardah)WardahAliNo ratings yet
- Emergency Department Bronchiolitis Care Guideline: Inclusion CriteriaDocument3 pagesEmergency Department Bronchiolitis Care Guideline: Inclusion CriteriaPatricia KoikyNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument2 pagesSpina BifidaTracy100% (2)
- WHO Classification of Head and Neck TumoursDocument349 pagesWHO Classification of Head and Neck TumoursdrAlbertoVV100% (2)
- Von Willebrand DiseaseDocument9 pagesVon Willebrand DiseaserandyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16 IEN of The Lower Genital TractDocument16 pagesLecture 16 IEN of The Lower Genital TractCharisse Angelica MacedaNo ratings yet
- Bonus BTR CompiledDocument373 pagesBonus BTR Compiledbhaskarjya58No ratings yet
- Brain Injury: Closed (Blunt) Brain Injury Occurs When The Head Accelerates and ThenDocument7 pagesBrain Injury: Closed (Blunt) Brain Injury Occurs When The Head Accelerates and Thencute_tineeNo ratings yet
- Assesment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goal Nursing Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssesment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goal Nursing Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDickson,Emilia Jade100% (1)
- Journal Reading FixDocument20 pagesJournal Reading FixElsa MayoraNo ratings yet
- CKD EsrdDocument83 pagesCKD EsrdRita Lakhani100% (1)
- HOPI in History TakingDocument5 pagesHOPI in History TakingKumar KP100% (1)
- Regulations - Addressing Complaints - Student1Document13 pagesRegulations - Addressing Complaints - Student1danushaNo ratings yet
- Multipel Vulnus IncisivumDocument11 pagesMultipel Vulnus IncisivumDeaz CressendoNo ratings yet
- 233271689-Grabovoi-Numbers 240202 020626Document6 pages233271689-Grabovoi-Numbers 240202 020626fun fit fat fineNo ratings yet
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (32)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- The Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeFrom EverandThe Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesFrom EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1412)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyFrom EverandThe Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (170)
- Forever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellFrom EverandForever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellNo ratings yet
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (254)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (60)