Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2 Answers PDF
Uploaded by
KajaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2 Answers PDF
Uploaded by
KajaCopyright:
Available Formats
2 Answers to end-of-chapter questions
1 B [1]
2 A [1]
3 B [1]
4 B [1]
5 A [1]
6 C [1]
7 B [1]
8 A [1]
9 C [1]
10 C [1]
Structured questions
11 a A – epidermis [1]
B – parenchyma [1]
C – phloem/vascular [1]
D – xylem/vascular [1]
Good representation with all the tissues [2]
Actual size [1]
Correct proportions of tissue layers [1]
c Actual size = size of specimen / magnification
Actual size = 65 mm / 120
= 0.5417 mm or 541.7 μm Correct calculation with working [2]
Biology for CAPE Original material © Cambridge University Press 2011 1
d Tissues of root: epidermal, cortex, vascular [1]
• Epidermal – some epidermal cells form root hairs in order to
increase the surface area of the root for absorption [1]
• Cortex – made up mainly parenchyma tissue which is used to
store starch as an energy reserve. Water can move through
cortex without entering cells on its way to the xylem [1]
• Vascular tissues – made up of phloem tissue and xylem tissue
Phloem: Transports organic nutrients / sucrose by mass flow [1]
Xylem: Transports water and minerals from roots to leaves;
provides mechanical support to the plant [1]
12 a i A – cell wall
B – chloroplast
C – nucleus
D – nucleolus 7 correct [4]
E – cell membrane 5–6 correct [3]
F – mitochondrion 3–4 correct [2]
G – central vacuole 1–2 correct [1]
ii Cell wall, chloroplast, central vacuole 2 identified [1]
iii Presence of centrioles / microvilli / glycogen granules / cilia and
flagella / many small vacuoles / lysosomes
Absence of starch grains / cell wall / chloroplasts or Identification of presence or
plastids / central vacuole absence of two cell structures [2]
b Magnification = length of scale bar / actual length
= 37 mm × 1000
100
= × 370 [1]
c A – Holds cell firm / prevents cell from bursting / provides strength
to cell / allows the passage of substances e.g. water, gases / maintains
turgor pressure
B – Site of photosynthesis / traps light energy and produces
carbohydrates / contains chlorophyll which traps light energy to
produce ATP, oxygen and carbohydrates
C – Controls the activities of cell / contains DNA which codes for 1 correct function
proteins or enzymes which control cellular activities for each organelle [3]
D – Synthesis of ribosomal RNA / makes ribosomes / contains DNA 3 correct [2]
used to code for RNA 1–2 correct [1]
d Advantages of electron microscope
• high resolution (400 times better than light microscope)
• high magnification possible (× 300 000) 2 points [1]
Disadvantages of electron microscope
• black and white image produced
• coloured dyes cannot be used to identify different structures
• preparation of specimen may produce distortions 2 points [1]
Biology for CAPE Original material © Cambridge University Press 2011 2
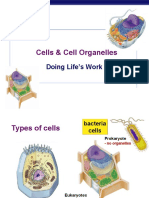
13 a Prokaryotes
• no true nucleus
• circular DNA without histones
• cell wall made of peptidoglycan
• no chloroplasts or mitochondria
• mainly unicellular
• small ribosomes (70S / 20 nm)
• simple flagella 2 points [2]
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes
• DNA
• ribosomes present
• cell membrane
• cytoplasm 2 points [2]
Eukaryotes
• true nucleus
• linear DNA with histones
• cell walls in plants made of cellulose
• chloroplasts
• mitochondria
• large ribosomes (80S / 30 nm)
• complex flagella
• ER present
• membranous organelles
• mainly multicellular 2 points [2]
b i
cell wall
circular DNA
cytoplasm
plasmid
ribosome
Drawing [2]
Drawing showing generalised structure of a bacterium 2 labels [1]
Total [3 marks]
Biology for CAPE Original material © Cambridge University Press 2011 3
ii
Good drawing [2]
Drawing of a mitochondrion 2 labels [1]
Total [3 marks]
c Folds of the inner membrane or cristae protrude into the interior of the
mitochondrion. [1]
Biology for CAPE Original material © Cambridge University Press 2011 4
Essay questions
14 a i Typical animal cell
cell membrane
mitochondrion
centriole
nucleus
nucleolus
cytoplasm
rough endoplasmic
reticulum
Golgi body
smooth endoplasmic
reticulum
lysosome
ribosome
• Surrounded by flexible cell membrane made up of phospholipids
and proteins
• Cytoplasm – gel-like, mostly water, metabolic reactions occur
here, cytoskeleton present
• Nucleus separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane; with
nucleolus
• Mitochondrion – double membrane, inner membrane convoluted;
for aerobic respiration
• RER – network of membranous flattened sacs with ribosomes
• Ribosomes – can be found free in the cytoplasm or on RER;
synthesis of proteins
• SER – tubular membranous sacs; lipid synthesis, detoxification
• Golgi body - membranous sacs which are continuously formed at
one end and bud off at other end; chemically modifies and
packages proteins
• Lysosomes – small membranous sacs with digestive enzymes
formed by budding Golgi body Diagram [1]
• Centrioles – pair of short microtubules, used for spindle 1 mark for each
formation during cell division point in detail [max 5]
Biology for CAPE Original material © Cambridge University Press 2011 5
ii Animal cell compared to plant cell
• no cell wall
• no chloroplasts / plastids
• no large permanent vacuole / tonoplast
• smaller (10–100 μm)
• has centrioles
• microvilli in some cells
• cilia / flagella in some cells
• lysosomes usually present
• contains glycogen as storage molecule instead of starch Any 3 points [3]
b
RER – has ribosomes which make
SER – synthesis of lipids proteins; proteins pass down the
and steroids; cisternae which isolate them from the
detoxification cytoplasm
secretory
vesicles –
contain
enzymes
which are
released by
exocytosis
lysosomes –
bud off the Golgi
body; contain
hydrolytic
enzymes which
degrade
bacteria, food,
old organelles ribosomes –
translate mRNA
into proteins
Golgi body –
chemically modifies Diagram [1]
proteins; add sugars to Annotations 1 mark each [max 6]
proteins
15 a Organ – collection of different tissues which performs a specialised function
Roots made up of three tissues: epidermis, cortex, vascular tissue. [1]
• Epidermal – some epidermal cells form root hairs in order to increase the surface
area of the root for absorption
• Cortex – made up mainly of parenchyma tissue which is used to store starch as an
energy reserve. Water can move through cortex without entering cells on its way to
the xylem
Cortex also contains the endodermis which contains cells with lignin and suberin /
Casparian strip; controls uptake of water
and pericycle which has lignin / mechanical support
• Vascular tissues – made up of phloem tissue and xylem tissue.
Phloem transports organic nutrients / sucrose by mass flow
Xylem transports water and minerals from roots to leaves; provides mechanical
support to the plant
Biology for CAPE Original material © Cambridge University Press 2011 6
Functions of root:
• Absorbs water and minerals from the soil
• Acts as a site for food storage
• Supports the plant
All the tissues work together to bring about these functions 7 points well described [7]
b i Organism that is symbiotic within another organism [2]
ii Evidence
• Both are about the same size as bacterial cells / prokaryotes
• Both have circular DNA (as prokaryotes) which lies free in stroma or matrix
• Both contain 70S or 20 nm ribosomes as prokaryotes
• Both have a pair of membranes surrounding them. The inner membrane has
similarities to membranes of prokaryotes
• Both reproduce by binary fission before the whole eukaryote cells divides by
mitosis 5 points [5]
16 a Advantages of electron microscope
• better resolution (0.5 nm)
• higher magnification (×300 000)
• can use SEM to study the surface of structures to give a 3D
image 3 points well described [3]
b
Feature Prokaryotes Eukaryotes
cell wall always present, made up only in plants, made of
of peptidoglycan cellulose
size 0.5–10 μm 10–100 μm
packaging DNA circular, not DNA linear, coiled around
of DNA associated with histones histones
protein • on free ribosomes • on ribosomes which can be
synthesis free or attached on RER; Any 12 points
• 70S or 20 nm • 80S or 30 nm [12]
Biology for CAPE Original material © Cambridge University Press 2011 7
You might also like
- Unit 2 Chapter 11 AnswersDocument7 pagesUnit 2 Chapter 11 AnswersLeeanaNo ratings yet
- 6 Answers To End-Of-Chapter QuestionsDocument6 pages6 Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questionsalyss ramdathNo ratings yet
- 9 Answers To End-Of-Chapter QuestionsDocument7 pages9 Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questionsalyss ramdathNo ratings yet
- Extra Practise Answers To Practise Questions Not On Test Topic 2 Cells 1 HourDocument7 pagesExtra Practise Answers To Practise Questions Not On Test Topic 2 Cells 1 HouremmaNo ratings yet
- Cells Practice AnswersDocument12 pagesCells Practice Answers晁海瀚No ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet Answerkey Grade 9Document5 pagesRevision Worksheet Answerkey Grade 9lenora.fernandes-smchsNo ratings yet
- Homework Marking Scheme 1.1: A: Cell Structure and B: VirusesDocument1 pageHomework Marking Scheme 1.1: A: Cell Structure and B: VirusesMikeNo ratings yet
- AS & A Level Biology Workbook AnswersDocument56 pagesAS & A Level Biology Workbook Answersღ꧁Lizzy X Roxiie꧂ღ100% (2)
- 5 Answers To End-Of-Chapter QuestionsDocument8 pages5 Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questionsalyss ramdathNo ratings yet
- Biology For CAPE Unit 1 Chapter 3 Answers PDFDocument8 pagesBiology For CAPE Unit 1 Chapter 3 Answers PDFGerrald RamoutarNo ratings yet
- GrammerDocument15 pagesGrammermaxking1246No ratings yet
- Mark First Response On Each Line Only: ACCEPT Nucleus, Membrane / Envelope ACCEPT Mitochondria DO NOT ACCEPT NucleousDocument2 pagesMark First Response On Each Line Only: ACCEPT Nucleus, Membrane / Envelope ACCEPT Mitochondria DO NOT ACCEPT NucleousBeaNo ratings yet
- Igcse Biology Coursebook 4th Ed AnswersDocument1 pageIgcse Biology Coursebook 4th Ed Answershanyawhurmzi1712No ratings yet
- 0610 s10 QP 22Document16 pages0610 s10 QP 22Nana_Banana_94No ratings yet
- F.3 First Term Revision Exercise For Christmas ANSDocument3 pagesF.3 First Term Revision Exercise For Christmas ANSjonas hoNo ratings yet
- 10TH Grade S.a-1 Question PaperDocument4 pages10TH Grade S.a-1 Question PaperManu DeviNo ratings yet
- Name: - Class: - DateDocument6 pagesName: - Class: - DateKaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- Class 9 - BIOLOGY - SET ADocument6 pagesClass 9 - BIOLOGY - SET AAnoushka GhoshNo ratings yet
- Cells Test - Whole Chapter - Nov 2022 - AnswersDocument3 pagesCells Test - Whole Chapter - Nov 2022 - AnswersDavid LeechNo ratings yet
- Skema Trial 2014 Batu PahatDocument25 pagesSkema Trial 2014 Batu PahatKavinesh GanesanNo ratings yet
- AS Biology Cell Structure Classified Questions Paper 1Document101 pagesAS Biology Cell Structure Classified Questions Paper 1ADEEL AHMAD100% (1)
- 6 Answers To End-Of-Chapter QuestionsDocument9 pages6 Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questionsalyss ramdath100% (1)
- SAT-1 Grade-06 Science QP 20-21Document15 pagesSAT-1 Grade-06 Science QP 20-21VANSHIKA AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions Chapter 7: Animal NutritionDocument2 pagesAnswers To End-Of-Chapter Questions Chapter 7: Animal NutritionRNo ratings yet
- heD58pOiJCRj9FJwHIcP 1 7Document7 pagesheD58pOiJCRj9FJwHIcP 1 7ajbros1223No ratings yet
- Science checkpoint questions for grade 6Document17 pagesScience checkpoint questions for grade 6Snikitha SiddavatamNo ratings yet
- Test 11b Full Syllabus Latest Pattern Test 2Document5 pagesTest 11b Full Syllabus Latest Pattern Test 2Hardik ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Biology For CAPE Chapter 2 AnswersDocument7 pagesBiology For CAPE Chapter 2 AnswersFiveLimaRomeo100% (4)
- Cell - The Unit of Life - Others - ICSE 9B - Cells - TestDocument2 pagesCell - The Unit of Life - Others - ICSE 9B - Cells - TestVivaan GandhiNo ratings yet
- U2 C12 AnswersDocument6 pagesU2 C12 Answersalyss ramdathNo ratings yet
- Particles and Waves Summary Notes 1Document4 pagesParticles and Waves Summary Notes 1Vanessa PassarelloNo ratings yet
- Revised GCSE SCI Double Award Unitised REVISED Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard MayJune Series 2018 27294Document6 pagesRevised GCSE SCI Double Award Unitised REVISED Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard MayJune Series 2018 27294Nora TuckNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 April 2017Document20 pagesPaper 1 April 2017Aries SaepanNo ratings yet
- 05 1113 01 5RP AFP tcm143-409121Document20 pages05 1113 01 5RP AFP tcm143-409121ashrafbestaNo ratings yet
- S9 End-Of-Year AnswersDocument5 pagesS9 End-Of-Year AnswersMoganoni MogaNo ratings yet
- S7 Mid-Year Test AnswersDocument3 pagesS7 Mid-Year Test AnswersShweta Bhasker.No ratings yet
- Science Checkpoint Revision Sheet Year 8Document6 pagesScience Checkpoint Revision Sheet Year 8Mark ZuckerburgNo ratings yet
- Structure Answer BiologyDocument9 pagesStructure Answer BiologySanjeefKumrIINo ratings yet
- IB CHEMISTRY 1ed TR End of Chapter Test AnsDocument22 pagesIB CHEMISTRY 1ed TR End of Chapter Test AnsKelvin ChoyNo ratings yet
- Class 8 - General Science - Periodic Test - 1 Key Answers ChemistryDocument2 pagesClass 8 - General Science - Periodic Test - 1 Key Answers ChemistryAries AANo ratings yet
- November 05 II MSDocument7 pagesNovember 05 II MSVarun PanickerNo ratings yet
- F.3 1st Term Bio Exam (16-17) - TV ShortDocument2 pagesF.3 1st Term Bio Exam (16-17) - TV Shortjonas hoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure 1 MSDocument10 pagesCell Structure 1 MSFelicia TTTNo ratings yet
- Science Paper 1: Stage 9Document16 pagesScience Paper 1: Stage 9Dazai KinnieNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in Animals NCERT Line by LineDocument13 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals NCERT Line by Linerajshelke2799No ratings yet
- Cells - Basic Units of LifeDocument12 pagesCells - Basic Units of LifeMani Kumaresan Janarthanavel (Scss)No ratings yet
- Paper 4 (A) (I) IGCSE Biology (Time - 30 Mins)Document12 pagesPaper 4 (A) (I) IGCSE Biology (Time - 30 Mins)Hisham AlEnaiziNo ratings yet
- NEURAL21Document44 pagesNEURAL21g1307No ratings yet
- Ant Colony Optimization: Presented by:VISHAL RAJDocument51 pagesAnt Colony Optimization: Presented by:VISHAL RAJVISHAL RAJNo ratings yet
- 5129 w12 Ms 22 PDFDocument7 pages5129 w12 Ms 22 PDFBrendon MuriraNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY 0610/4: Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate NumberDocument14 pagesBIOLOGY 0610/4: Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate NumbersybejoboNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Secondary Checkpoint - Science (1113) April 2018 Paper 2Document20 pagesCambridge Secondary Checkpoint - Science (1113) April 2018 Paper 2Linh Nguyễn KhánhNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Cell The Basic Unit of Life Test 01Document1 page9 Science Cell The Basic Unit of Life Test 01NAVEEN DHIMANNo ratings yet
- P1 Oct 2018 PDFDocument20 pagesP1 Oct 2018 PDFalishaNo ratings yet
- Answers To Exam-Style Questions: Topic 1 Topic 2Document9 pagesAnswers To Exam-Style Questions: Topic 1 Topic 2Mahnoor ShahidNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Alkaline Earth Metabolism in Adult Man: A Report Prepared by a Task Group of Committee 2 of the International Commission on Radiological ProtectionFrom EverandAlkaline Earth Metabolism in Adult Man: A Report Prepared by a Task Group of Committee 2 of the International Commission on Radiological ProtectionNo ratings yet
- Bio DrawingsDocument2 pagesBio DrawingsKajaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Questions AnswersDocument49 pagesMCQ Questions AnswersKajaNo ratings yet
- Investigative Project: Biology ProposalDocument3 pagesInvestigative Project: Biology ProposalKajaNo ratings yet
- Caribbean Examinations Council: MinutesDocument9 pagesCaribbean Examinations Council: MinutesPaul RobertoNo ratings yet
- The MeningesDocument2 pagesThe MeningesKajaNo ratings yet
- C4Hs02 CH20 C4H60z CH (C) C4Hs02 2 (D) C H 0: Which The Pairs Is 3. Compo - Und Which Shows Both Cis-TransDocument9 pagesC4Hs02 CH20 C4H60z CH (C) C4Hs02 2 (D) C H 0: Which The Pairs Is 3. Compo - Und Which Shows Both Cis-TransPaul RobertoNo ratings yet
- Federal Syllabus: St. Mary High SchoolDocument27 pagesFederal Syllabus: St. Mary High SchoolKajaNo ratings yet
- BBC Access For Students FinalDocument2 pagesBBC Access For Students FinalKajaNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer Treatment and Complications GuideDocument4 pagesCervical Cancer Treatment and Complications GuideKajaNo ratings yet
- Mark Twain QuotesDocument1 pageMark Twain QuotesBen ChongNo ratings yet
- Biology SBA #1: Kadeen GrahamDocument7 pagesBiology SBA #1: Kadeen GrahamKajaNo ratings yet
- C Hemp 12012Document10 pagesC Hemp 12012KajaNo ratings yet
- U2 c8 AnswersDocument8 pagesU2 c8 Answerstrudy-annNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution ResultsDocument1 pageWater Pollution ResultsKajaNo ratings yet
- LololDocument2 pagesLololKajaNo ratings yet
- Biology For CAPE Unit 1 Chapter 8 AnswersDocument5 pagesBiology For CAPE Unit 1 Chapter 8 AnswersFiveLimaRomeo100% (2)
- Lecture I - Respiration and Photosynthesis Version 1Document4 pagesLecture I - Respiration and Photosynthesis Version 1KajaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Answers PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 12 Answers PDFKajaNo ratings yet
- Lecture III - Matter and Energy Flow Recycling in The EnvironmentDocument10 pagesLecture III - Matter and Energy Flow Recycling in The Environmentshubham kumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture I - Respiration and Photosynthesis Version 1Document15 pagesLecture I - Respiration and Photosynthesis Version 1soumya123No ratings yet
- 101 Chapter 5Document2 pages101 Chapter 5KajaNo ratings yet
- PhyspdDocument1 pagePhyspdKajaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 12 - Visual Arts (Reference List)Document3 pagesUNIT 12 - Visual Arts (Reference List)KajaNo ratings yet
- St. Mary High School Meeting Minutes Feb 16 2016Document1 pageSt. Mary High School Meeting Minutes Feb 16 2016KajaNo ratings yet
- 10 - Chapter 5 PDFDocument24 pages10 - Chapter 5 PDFKajaNo ratings yet
- Miguel Street: Rtlaptfu TTDocument38 pagesMiguel Street: Rtlaptfu TTKaja100% (1)
- Topic 4 - EnergeticsDocument2 pagesTopic 4 - EnergeticsKajaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes 2.1 NotesDocument10 pagesChemistry Notes 2.1 NotesOsama Bin AmerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Genetic EngineeringDocument13 pagesLecture 9 - Genetic EngineeringazwelljohnsonNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Cell StructureDocument8 pagesStudent Exploration: Cell StructureMishaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Components of The Cell II (Subcellular Organelles)Document20 pages1.3 Components of The Cell II (Subcellular Organelles)Alexa Julienne RazNo ratings yet
- Cell organelles and their functionsDocument8 pagesCell organelles and their functionsSean CaloyloyNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of Life Cell (Prashant Kirad)Document17 pagesFundamental Unit of Life Cell (Prashant Kirad)chinkavarshavedNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Lam Nguyen - Worksheet - Plant Animal CellsDocument2 pagesKami Export - Lam Nguyen - Worksheet - Plant Animal Cellsapi-552399149No ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Cell The Unit of LifeDocument78 pagesLesson 6 Cell The Unit of LifeShriya RameshNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity #1 The Cell (1) (1) 2Document3 pagesLaboratory Activity #1 The Cell (1) (1) 2Kim VenturaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Cell StructureDocument37 pagesChapter 1 Cell StructureNawafNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BC SC Probe 8Document36 pagesChapter 1 BC SC Probe 8api-265180883No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument9 pagesCell Structure and Cell OrganisationVictoria PetrusNo ratings yet
- BME2106 Lecture+1.+Fundamentals+of+Molecules+and+CellsDocument67 pagesBME2106 Lecture+1.+Fundamentals+of+Molecules+and+CellsshanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Faculty Midterm Exam Human Physiology 1Document1 pagePharmacy Faculty Midterm Exam Human Physiology 1starvationNo ratings yet
- Little Girl Lost: A Case Study On Defective Cellular OrganellesDocument7 pagesLittle Girl Lost: A Case Study On Defective Cellular OrganellesClarissa CaroNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and FunctionsDocument4 pagesCell Parts and FunctionsAnonymous Dtsv6ySI100% (1)
- Guyton & Hall Physiology Review, 3e-2Document275 pagesGuyton & Hall Physiology Review, 3e-2Rawan Chakas100% (13)
- Question Bank For UPSCDocument64 pagesQuestion Bank For UPSCsidheart4uNo ratings yet
- 100 Concepts - MCBDocument316 pages100 Concepts - MCBNisreen SalameNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet - CellDocument2 pagesActivity Sheet - CellBettina Sanchez100% (1)
- Unit 1 Cell Biology Practice 1: (72 Marks)Document17 pagesUnit 1 Cell Biology Practice 1: (72 Marks)Rita LimNo ratings yet
- What You Are Expected To Learn: Science Ii Cell Structure and Function What This Module Is AboutDocument19 pagesWhat You Are Expected To Learn: Science Ii Cell Structure and Function What This Module Is AboutBia Aranilla MijaresNo ratings yet
- Pathology Biochemical and Molecular Basis of Some Mendelian DisordersDocument5 pagesPathology Biochemical and Molecular Basis of Some Mendelian DisordersAmna Baig0% (1)
- STEM Genbio11 q1 SLM Mod Cell-Structures-and-FunctionsDocument28 pagesSTEM Genbio11 q1 SLM Mod Cell-Structures-and-FunctionsLouie BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Cells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesDocument34 pagesCells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesJeffrey100% (1)
- Cells and OrganellesDocument38 pagesCells and OrganellesLUIS RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Biology Quiz: Cell Structure, Organ Systems, Evolution & MoreDocument32 pagesBiology Quiz: Cell Structure, Organ Systems, Evolution & MoreChrisshalyn Sy PinedaNo ratings yet
- Khan Academy Eukaryotic Cells QuestionsDocument3 pagesKhan Academy Eukaryotic Cells QuestionsLoraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document50 pagesLecture 1AMRAPALI SANTOSH PAWARNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Worksheet KEYDocument2 pagesCell Organelles Worksheet KEYmike_92457% (58)
- The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument137 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of LifeSudarshan S KNo ratings yet
- PASCA PT3 2016 BIOLOGY: Cell Structure and FunctionDocument3 pagesPASCA PT3 2016 BIOLOGY: Cell Structure and FunctionSjk TRNo ratings yet