Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 4 Bio Vocab
Uploaded by
Pranav Menon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageCell WallOutside surfaces of plant, fungi, and bacteria cells. Made of cellulo se. Channel ProteinProtiens that form channels; allows small water-soluble molecul es to pass through. ConcentrationNumber of molecules in a given unit of volume. Concentration GradientDiffernece in concentration between on region and anothe r.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCell WallOutside surfaces of plant, fungi, and bacteria cells. Made of cellulo se. Channel ProteinProtiens that form channels; allows small water-soluble molecul es to pass through. ConcentrationNumber of molecules in a given unit of volume. Concentration GradientDiffernece in concentration between on region and anothe r.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageChapter 4 Bio Vocab
Uploaded by
Pranav MenonCell WallOutside surfaces of plant, fungi, and bacteria cells. Made of cellulo se. Channel ProteinProtiens that form channels; allows small water-soluble molecul es to pass through. ConcentrationNumber of molecules in a given unit of volume. Concentration GradientDiffernece in concentration between on region and anothe r.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
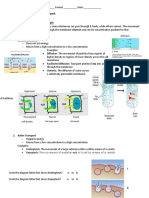
Chapter 4 Vocabulary
Active Transport- Exchange of materials inside cell membrane using ATP.
Carrier Protein- Proteins with binding sites that can grab certain molecules. Ch
anges shape to move molecule.
Cell Wall- Outside surfaces of plant, fungi, and bacteria cells. Made of cellulo
se.
Channel Protein- Protiens that form channels; allows small water-soluble molecul
es to pass through.
Concentration- Number of molecules in a given unit of volume.
Concentration Gradient- Differnece in concentration between on region and anothe
r.
Cytoplasm- Fluid like enviornment containing all the cell's contents, save the n
ucleus.
Desmosome- Junctions that hold adjacent cells together with proteins and carbohy
drates.
Differentially Permeable- Allow some molecules to pass, but hold others at bay.
Diffusion- Movement of molecules from an area of high to low concentration.
Endocytosis- Surrounds molecule in a vesicle into the cytoplasm.
Exocytosis- Reverse of endocytosis.
Facilitated Diffusion- Passive transport with the use of transport proteins.
Fluid- Matter with the ability to flow.
Fluid Mosaic Model- Cell membrane model created in '72 by S.J. Singer and G.L. N
icolson.
Gap Junction- Cell-to-cell channels that allow hormonal and material transfer.
Glycoprotein- Proteins with carbohydrates attatched to them in the bilayer.
Gradient- Physical differnence between two areas that causes molecule movement.
Hypertonic- Net movement is out of the cell (water).
Hypotonic- Net movement is into the cell (water).
Isotonic- Net movement is equal (water)
Middle Lamella- layer made of pectin.
Osmosis- Diffusion of water (passive).
Passive Transport- Transport without expenditure of ATP.
Phagocytosis- Use of pseudopodia to bring large particles into the cell.
Phospholipid Bilayer- Main part of the cell membrane; fluid, yet solid. Flexible
.
Pinocytosis- Cell brings fluid into itself.
Plasma Membrane- Outer membrane of the cell. Three main functions:
1. Separate cell from fluid.
2. Regulate material exchange.
3. Communicate with other cells.
Plasmodesma- Connection holes in plant cell walls that allow communication, etc.
Primary Cell Wall- First layer of cellulose; original cell wall.
Pseudopod- Extensions of surface membrane.
Receptor Mediated Endocytosis- Concentrates only needed amounts of molecules int
o a cell.
Receptor Protein- Triggers responses in cell after certain molecules arrive at b
onding site.
Recognition Protein- Serve as identity tags at cell surface.
Secondary Cell Wall- 2nd Wall generated from secreted calcium and cellulose.
Simple Diffusion- Diffusion of nonpolar, small particles.
Tight Junction- Protein bands literally fuse cell membranes together.
Transport Protein- Regulate the movement of hydrophilic molecules through the me
mbrane.
Vesicle- Membranous sac used for transport.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Action PotentialDocument12 pagesAction PotentialArooj FatimaNo ratings yet
- EE3BB3 Homework2 SolnsDocument6 pagesEE3BB3 Homework2 SolnsKashif AbbasNo ratings yet
- Neet Pyq Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument4 pagesNeet Pyq Cell - The Unit of LifeAyush DuttaNo ratings yet
- File 1195Document86 pagesFile 1195yNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Lectures 4 & 5 Q'sDocument6 pagesExam 1 Lectures 4 & 5 Q'sBlaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 General Biology 1Document23 pagesModule 5 General Biology 1Glenn Capcap Jr.No ratings yet
- Biological Membranes 1 QPDocument12 pagesBiological Membranes 1 QParvibainNo ratings yet
- Hematologi dan Kimia Bulan September-Oktober 2021Document46 pagesHematologi dan Kimia Bulan September-Oktober 2021Fernando PkpNo ratings yet
- Cell Handwritten NotesDocument20 pagesCell Handwritten NotesNavya MehtaNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling - Biology in FocusDocument8 pagesCH 5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling - Biology in FocusYou MeaniesNo ratings yet
- (Notes) Cell MembraneDocument5 pages(Notes) Cell MembraneSiva Letchumi SelvanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketDocument9 pagesUnit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketShannon ErdmanNo ratings yet
- Lipids and Proteins in Biological MembranesDocument20 pagesLipids and Proteins in Biological Membranescarlette11No ratings yet
- Biochemistry Concepts and Connections 1St Edition Appling Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument27 pagesBiochemistry Concepts and Connections 1St Edition Appling Test Bank Full Chapter PDFElizabethRuizrxka100% (11)
- Endocytosis and ExocytosisDocument2 pagesEndocytosis and ExocytosisALPEREZ, GRACE LYN C.No ratings yet
- Cell City Analogy 06Document2 pagesCell City Analogy 06alek22No ratings yet
- 4.the Golgi ApparatusDocument3 pages4.the Golgi ApparatusSabina MaharjanNo ratings yet
- 11 Transport in Plants - PPT - PPSXDocument4 pages11 Transport in Plants - PPT - PPSXrohit singhNo ratings yet
- Hodgkin Huxley Neuron ModelDocument9 pagesHodgkin Huxley Neuron ModelSomnath SandeepNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Drug Absorption From The GITDocument15 pages2.2 Drug Absorption From The GITCari MosehuusNo ratings yet
- Biological MembranesDocument5 pagesBiological MembranesMohammed RagabNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: I) Ii) Iii)Document4 pagesWorksheet: I) Ii) Iii)Jin MingNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Diffusion Active - Transport+studentDocument35 pagesOsmosis Diffusion Active - Transport+studentMetaknight360 LiveNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane and Transport ColoringDocument3 pagesCell Membrane and Transport ColoringTeresa GonzNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Outline - Chapter 5Document6 pagesAP Biology Outline - Chapter 5Omar LopezNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument105 pagesTransport MechanismMAY FULGENCIONo ratings yet
- Bubbles Lab ReportDocument8 pagesBubbles Lab ReportARNI SENGUPTA100% (1)
- Cytoplasm By: Prof. Dr. Suzi H. Ibrahim Lectures 1,2&3Document58 pagesCytoplasm By: Prof. Dr. Suzi H. Ibrahim Lectures 1,2&3eman el saeedNo ratings yet
- Plasma MembraneDocument40 pagesPlasma Membraneshaffan ula prasetyoNo ratings yet
- Active Transport, Endocytosis, and ExocytosisDocument3 pagesActive Transport, Endocytosis, and ExocytosisCherifa AbdallahNo ratings yet