Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Life Sciences Dbe NSC Grade 12 Supplementary Past Exam Papers 2016 p1 Marking Guidelines
Uploaded by
Malaiya the MelioristOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Life Sciences Dbe NSC Grade 12 Supplementary Past Exam Papers 2016 p1 Marking Guidelines
Uploaded by
Malaiya the MelioristCopyright:
Available Formats
NATIONAL
SENIOR CERTIFICATE
GRADE 12
LIFE SCIENCES P1
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2016
MEMORANDUM
MARKS: 150
This memorandum consists of 10 pages.
Copyright reserved Please turn over
Life Sciences/P1 2 DBE/Feb.–Mar. 2016
NSC – Memorandum
PRINCIPLES RELATED TO MARKING LIFE SCIENCES
1. If more information than marks allocated is given
Stop marking when maximum marks is reached and put a wavy line and 'max' in the
right-hand margin.
2. If, for example, three reasons are required and five are given
Mark the first three irrespective of whether all or some are correct/ incorrect.
3. If whole process is given when only a part of it is required
Read all and credit the relevant part.
4. If comparisons are asked for but descriptions are given
Accept if the differences/similarities are clear.
5. If tabulation is required but paragraphs are given
Candidates will lose marks for not tabulating.
6. If diagrams are given with annotations when descriptions are required
Candidates will lose marks.
7. If flow charts are given instead of descriptions
Candidates will lose marks.
8. If sequence is muddled and links do not make sense
Where sequence and links are correct, credit. Where sequence and links are
incorrect, do not credit. If sequence and links become correct again, resume credit.
9. Non-recognised abbreviations
Accept if first defined in answer. If not defined, do not credit the unrecognised
abbreviation but credit the rest of the answer if correct.
10. Wrong numbering
If answer fits into the correct sequence of questions but the wrong number is given,
it is acceptable.
11. If language used changes the intended meaning
Do not accept.
12. Spelling errors
If recognisable, accept the answer, provided it does not mean something else in Life
Sciences or if it is out of context.
13. If common names are given in terminology
Accept, provided it was accepted at the national memo discussion meeting.
14. If only the letter is asked for but only the name is given (and vice versa)
Do not credit.
Copyright reserved Please turn over
Life Sciences/P1 3 DBE/Feb.–Mar. 2016
NSC – Memorandum
15. If units are not given in measurements
Candidates will lose marks. Memorandum will allocate marks for units separately.
16. Be sensitive to the sense of an answer, which may be stated in a different way.
17. Caption
All illustrations (diagrams, graphs, tables, etc.) must have a caption.
18. Code-switching of official languages (terms and concepts)
A single word or two that appear(s) in any official language other than the learners'
assessment language used to the greatest extent in his/her answers should be
credited if it is correct. A marker that is proficient in the relevant official language
should be consulted. This is applicable to all official languages.
19. Changes to the memorandum
No changes must be made to the memoranda without consulting the provincial
internal moderator who in turn will consult with the national internal moderator (and
the Umalusi moderators where necessary).
20. Official memoranda
Only memoranda bearing the signatures of the national internal moderator and the
Umalusi moderators and distributed by the National Department of Basic Education
via the provinces must be used.
Copyright reserved Please turn over
Life Sciences/P1 4 DBE/Feb.–Mar. 2016
NSC – Memorandum
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 1.1.1 C
1.1.2 D
1.1.3 C
1.1.4 B
1.1.5 B
1.1.6 C
1.1.7 A
1.1.8 D
1.1.9 B
1.1.10 A (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 1.2.1 Vivipary/Viviparous
1.2.2 Centrioles/Centrosome
1.2.3 Geotropism/Gravitropism
1.2.4 Carbon footprint
1.2.5 Puberty
1.2.6 Stimulus
1.2.7 Grommets
1.2.8 Pinna (8 x 1) (8)
1.3 1.3.1 B only
1.3.2 Both A and B
1.3.3 B only
1.3.4 None (4 x 2) (8)
1.4 1.4.1 (a) A - penis (2)
(b) E - testes (2)
1.4.2 (a) D and E (2)
(Mark first TWO only)
(b) B and C (2)
(Mark first TWO only) (8)
1.5 1.5.1 (a) E (1)
(b) A (1)
(c) C (1)
1.5.2 F - motor neuron (2)
1.5.3 D to E (1)
(6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
Copyright reserved Please turn over
Life Sciences/P1 5 DBE/Feb.–Mar. 2016
NSC – Memorandum
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
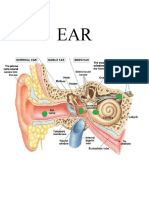
2.1 2.1.1 (a) Round window (1)
(b) Cochlea (1)
2.1.2 Cristae (1)
2.1.3 (a)
- Impulses from the cochlea cannot be transmitted to the brain
- and therefore hearing will not occur (2)
2.1.4 (b)
- Part A will not be able to vibrate
- The round window will not absorb the sound waves from the
cochlea
- and hearing will be affected (Any 2) (2)
(7)
2.2 - Mucus in the middle ear
- will lead to the blockage of the Eustachian tube
- which will not be able to equalise the pressure in the middle ear
- resulting in pressure on the tympanic membrane
- that may cause the tympanic membrane to burst
- leading to hearing loss (Any 4) (4)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
Life Sciences/P1 6 DBE/Feb.–Mar. 2016
NSC – Memorandum
2.3 2.3.1
Graph to show the relationship between ages of women and
the percentage of pregnancies per month
30
25 24
Pregnancies per month
25
20 18
(%)
15
10 6
5 2
0
22 28 34 40 46
Ages of women (years)
Mark allocation of the graph
Criteria Mark Allocation
Correct type of graph drawn for the
1
pregnancies per month only
Title of graph including the two
variables (Age of women and 1
pregnancies per month)
Correct label and unit for X-axis
1
and Y-axis
Correct scale for X-axis and Y-axis 1
Drawing of the graph 0: No points plotted correctly
1: 1 to 4 points plotted correctly
2: All 5 points plotted correctly
NOTE:
If axes are transposed: marks will be lost only for labelling of X-axis and Y-axis
(6)
2.3.2 The older the women, the higher the chances of having
miscarriages
OR
The younger the women, the lower the chances of having
miscarriages (2)
2.3.3 50% x 12 = 6
OR
50 x 12 = 6
100 (2)
(10)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
Life Sciences/P1 7 DBE/Feb.–Mar. 2016
NSC – Memorandum
2.4.1 2.4.1 - As a result of the blocked Fallopian tube
- the sperm cannot reach the ovum
- therefore fertilisation cannot take place (Any 2) (2)
2.4.2 (a) FSH/follicle stimulating hormone (1)
(Mark first ONE only)
(b) Oestrogen (1)
(Mark first ONE only)
2.4.3 - A zygote is formed
- which divides by mitosis
- forming a ball of cells
- called the morula
- which further divides to form a hollow ball of cells (Any 4) (4)
2.4.4 - Progesterone levels would fall
- The endometrium would no longer be maintained
- A miscarriage would occur (3)
(11)
2.5 2.5.1 Metaphase I (1)
2.5.2 - Crossing over has taken place
- and genetic material was exchanged (2)
2.5.3 Anaphase II (1)
2.5.4 - The spindle fibres contract
- The centromeres split
- and pull the daughter chromosomes/chromatids
- to the opposite poles of the cells
- Cytokinesis begins (Any 3) (3)
2.5.5 Testes/seminiferous tubules (1)
(Mark first ONE only) (8)
[40]
Copyright reserved Please turn over
Life Sciences/P1 8 DBE/Feb.–Mar. 2016
NSC – Memorandum
QUESTION 3
3.1 3.1.1 (a) ADH/antidiuretic hormone (1)
(b) Hypothalamus/Pituitary gland (1)
(c) Kidneys (1)
3.1.2 - An increase in ADH causes the walls of the kidney tubules
- to become more permeable to water
- More water is reabsorbed
- and the blood volume increases
- Less urine is produced
- and the urine is more concentrated (Any 4) (4)
(7)
3.2 3.2.1 Pancreas (1)
3.2.2 Insulin A Insulin B
Glucose uptake peaks at a Glucose uptake peaks at
higher level/around lower level/around
7 mg/kg/min 1 mg/kg/min
All glucose uptake occurs in a Glucose uptake is gradual/
short period of time/the first sustained over a period of
5 hours 24 hours
The initial uptake of glucose rises The initial uptake of glucose
rapidly to a maximum within the rises slowly to the maximum
first few hours over 5 hours
A
TABULATION IS NOT REQUIRED (Any 2 x 2) (4)
(Mark first TWO only) (5)
3.3 3.3.1 (a) Amount of thyroxin (1)
(b) Body weight (1)
3.3.2 - Same number of rats in each group
- All rats were of the same species
- All groups were investigated for the same period of time
- All rats were the same gender
- All groups were weighed after the same interval (Any 3) (3)
(Mark first THREE only)
3.3.3 Group A (1)
3.3.4 - Low thyroxin levels
- will lead to low metabolic rate
- Therefore the energy from the diet is used very slowly
- and more organic compounds are stored (Any 3) (3)
3.3.5 Group B (1)
3.3.6 - These rats have high levels of thyroxin in their blood
- therefore pituitary gland will not be stimulatedto secrete TSH (2)
(12)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
Life Sciences/P1 9 DBE/Feb.–Mar. 2016
NSC – Memorandum
3.4 3.4.1 - Poor infrastructure
- Climate change
- Wastage
- Pollution of water sources (Any 2) (2)
(Mark first TWO only)
3.4.2 - The need of water for irrigation will be reduced (1)
3.4.3 - Decreased production
- will lead to loss of profit (2)
3.4.4 - More revenue for fixing poor infrastructure/building dams
- Less water wastageby individuals and companies (2)
(Mark first TWO only) (7)
3.5 3.5.1 (a)
- Invasive alien plants reduce food security
- since they grow rapidly and invade land
- that could be used to grow crops (3)
(b)
- Invasive alien plants reduce water availability
- since they use more water (2)
3.5.2 (a)
- The new organism may become a pest itself/it may feed on
indigenous plants instead of the targeted alien plant
- since no natural enemy for it was brought into the area (2)
(b)
- Some parts that are left behind
- can regrow/will cost more money to remove them again (2)
(9)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
Copyright reserved Please turn over
Life Sciences/P1 10 DBE/Feb.–Mar. 2016
NSC – Memorandum
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
Plant stems response to unilateral light
- Plant stems response to light is positively phototropic
- Auxins
- produced in the tip of the stem
- move away from unilateral light
- so that there is a high concentration of auxins on the darker side
- which stimulates growth/cell division/cell elongation
- The low concentration of auxins on the side exposed to light
- inhibits growth
- This uneven growth
- causes the stem to bend towards the light Max 7
How humans receive and interpret light stimuli
- Light enters the eye
- through the cornea
- which refracts the light
- It then passes through the aqueous humour
- and the pupil
- The size of the pupil is adjusted by the iris
- to regulate the amount of light that enters the eye
- The light then passes through the lens
- which also refracts the light
- It then passes through the vitreous humour
- and reaches the retina
- which has the photoreceptors/rods and cones which convert the light stimulus
into a nerve impulse Max 10 (10)
Content: (17)
Synthesis: (3)
(20)
ASSESSING THE PRESENTATION OF THE ESSAY
Relevance Logical sequence Comprehensive
All information provided is Ideas arranged in a logical/ Answered all aspects required by
relevant to the question cause-effect sequence the essay in sufficient detail
All the information provided is All the information regarding At least the following points
relevant to plant stems' how plant stems respond to should be included:
response to unilateral light and unilateral light and how - Plant response to unilateral
how humans receive and humans receive and interpret light (4/7)
interpret light stimuli. light stimuli are arranged in a - How humans receive and
logical manner. interpret light stimuli (7/10)
No irrelevant information.
1 mark 1 mark 1 mark
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Copyright reserved
You might also like
- Life Sciences P1 May-June 2016 Memo EngDocument12 pagesLife Sciences P1 May-June 2016 Memo EngIviweNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 Nov 2016 Memo EngDocument9 pagesLife Sciences P1 Nov 2016 Memo EngOlerato NtsimaneNo ratings yet
- Senior Certificate Examinations: Life Sciences P1 2017 Marking GuidelinesDocument10 pagesSenior Certificate Examinations: Life Sciences P1 2017 Marking GuidelinestshilidzimbauNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 May-June 2022 MG EngDocument8 pagesLife Sciences P1 May-June 2022 MG EngDariusNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 May-June 2021 MG EngDocument9 pagesLife Sciences P1 May-June 2021 MG EngDariusNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 Feb-March 2017 Memo EngDocument12 pagesLife Sciences P2 Feb-March 2017 Memo Engmpumelelosibeko5No ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 May-June 2019 Memo EngDocument13 pagesLife Sciences P2 May-June 2019 Memo Engpaballomogopodi09No ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 Feb-March 2018 Memo EngDocument12 pagesLife Sciences P1 Feb-March 2018 Memo Engpearllwandle4No ratings yet
- Life Sciences p1 Feb March 2015 Memo Eng PDFDocument11 pagesLife Sciences p1 Feb March 2015 Memo Eng PDFSgush MageshNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 May-June 2021 MG EngDocument13 pagesLife Sciences P2 May-June 2021 MG Engrethabile.lepediNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 May-June 2023 MG EngDocument9 pagesLife Sciences P1 May-June 2023 MG EngkemibokiNo ratings yet
- LIFE SCIENCES P1 GR11 MEMO NOV2019 - English LatestDocument9 pagesLIFE SCIENCES P1 GR11 MEMO NOV2019 - English LatestScrëen SavëRNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 Nov 2023 MG EngDocument10 pagesLife Sciences P1 Nov 2023 MG EngOlerato NtsimaneNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 Nov 2022 MG EngDocument10 pagesLife Sciences P1 Nov 2022 MG Engmunyaifhatuwani364No ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 Nov 2016 Memo EngDocument12 pagesLife Sciences P2 Nov 2016 Memo EngjoyNo ratings yet
- 2018 - Life Sciences p1 MemoDocument10 pages2018 - Life Sciences p1 MemoZaydaan JassiemNo ratings yet
- Life Science P1 Memo 2014Document10 pagesLife Science P1 Memo 2014UNATHI SIZWE MAKHOKHOBANo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 Nov 2017 Memo EngDocument11 pagesLife Sciences P2 Nov 2017 Memo Engsiyandazondi621No ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 Nov 2021 MG EngDocument13 pagesLife Sciences P2 Nov 2021 MG Engthembalihlemvundla7No ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 Nov 2023 MG EngDocument11 pagesLife Sciences P2 Nov 2023 MG EngOlerato NtsimaneNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 Nov 2021 MG EngDocument12 pagesLife Sciences P2 Nov 2021 MG EngAmahleNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 May-June 2023 MG EngDocument11 pagesLife Sciences P2 May-June 2023 MG Engmauricetteisasi3No ratings yet
- NSC Life Science Grade 12 June 2022 P1 and MemoDocument23 pagesNSC Life Science Grade 12 June 2022 P1 and MemoMatsiri ImmanuelNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences p2 Gr11 Memo Nov 2019 - EnglishDocument12 pagesLife Sciences p2 Gr11 Memo Nov 2019 - EnglishaaliyamosavelNo ratings yet
- KZN - Grade 12 LFSC MG P1 - Final Sept 2023Document9 pagesKZN - Grade 12 LFSC MG P1 - Final Sept 2023Wandile TembeNo ratings yet
- National Senior Certificate: Grade 12Document11 pagesNational Senior Certificate: Grade 12Josia XebeyiNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 Feb-March 2018 Memo EngDocument11 pagesLife Sciences P2 Feb-March 2018 Memo EngjoyNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences p1 Nov 2019 Memo North WestDocument10 pagesLife Sciences p1 Nov 2019 Memo North Westmasegomvubu27No ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 Nov 2020 Memo EngDocument12 pagesLife Sciences P2 Nov 2020 Memo Englindort00No ratings yet
- LIFE SCIENCES P1 GR12 MEMO SEPT2023 - EnglishDocument11 pagesLIFE SCIENCES P1 GR12 MEMO SEPT2023 - Englishptvzd5qjzbNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 Marking Memo FDocument10 pagesLife Sciences P1 Marking Memo FPBS SibandaNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 May-June 2019 Memo EngDocument10 pagesLife Sciences P1 May-June 2019 Memo Engbalfourlibone440No ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 12 Trial 2021 p2 and MemoDocument27 pagesLife Sciences Grade 12 Trial 2021 p2 and Memobusiswamavimbela06No ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 May-June 2022 MG EngDocument11 pagesLife Sciences P2 May-June 2022 MG EngDariusNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences GR 11 MEMODocument11 pagesLife Sciences GR 11 MEMOAnathiey Certified Jnr.No ratings yet
- NW GR 10 LFSC P1 Eng Memo Nov 2019 1Document9 pagesNW GR 10 LFSC P1 Eng Memo Nov 2019 1tshelostsheksNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences p2 Nov 2017 MemoDocument11 pagesLife Sciences p2 Nov 2017 MemoMidyondzi ngobeniNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 Eng MemoDocument12 pagesLife Sciences P1 Eng MemoabingdadeNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences p1 Memo Gr11 Nov 2020 Eng DDocument10 pagesLife Sciences p1 Memo Gr11 Nov 2020 Eng Dmokoenakoketso018No ratings yet
- Wa0009Document8 pagesWa0009secondsphiwokuhleNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 Feb-March 2013 Version 1 Memo EngDocument9 pagesLife Sciences P2 Feb-March 2013 Version 1 Memo EngDrAzTikNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 Nov 2018 FINALMemo Eng.Document9 pagesLife Sciences P1 Nov 2018 FINALMemo Eng.PBS SibandaNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 GR 10 Exemplar Memo EngDocument8 pagesLife Sciences P1 GR 10 Exemplar Memo EngstephanseggsyNo ratings yet
- LFSC G10 Topic Test 2 Memo Chemistry of LifeDocument5 pagesLFSC G10 Topic Test 2 Memo Chemistry of LifengonyoloilisoNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Test MemoDocument4 pagesMeiosis Test MemoMaciaNo ratings yet
- LFSC Grade 10 P2 MEMO ENG FinalDocument11 pagesLFSC Grade 10 P2 MEMO ENG FinalLucky Jr MonobeNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 Nov 2011 Memo Eng Version 2 FinalDocument12 pagesLife Sciences P1 Nov 2011 Memo Eng Version 2 Finalbellydanceafrica9540No ratings yet
- Life Sciences-P1-March-2009-MemoDocument12 pagesLife Sciences-P1-March-2009-MemoOlerato NtsimaneNo ratings yet
- National Senior Certificate: Grade 12Document12 pagesNational Senior Certificate: Grade 12dlaladlalaNo ratings yet
- Scicent SQ U2 5-6 SetA Final eDocument4 pagesScicent SQ U2 5-6 SetA Final esteve LNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Marking Memorandum Common Test: JUNE 2019Document11 pagesLife Sciences Marking Memorandum Common Test: JUNE 2019EXISTING FOR DOGSNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Test 1 MemoDocument5 pagesReproduction Test 1 MemoMaciaNo ratings yet
- gr12 Life Sciences p1 English Sep 2022 Possible AnswersDocument14 pagesgr12 Life Sciences p1 English Sep 2022 Possible Answersapi-202349222No ratings yet
- Paper 6 June 2000Document3 pagesPaper 6 June 2000MSHNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences GR 11 MEMODocument8 pagesLife Sciences GR 11 MEMOAnathiey Certified Jnr.No ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 Nov 2011 Memo Eng Version 2 FinalDocument12 pagesLife Sciences P2 Nov 2011 Memo Eng Version 2 Finalbellydanceafrica9540No ratings yet
- LFSC 2020 Gr10 Memo Nov Decmopani East DistrictDocument6 pagesLFSC 2020 Gr10 Memo Nov Decmopani East Districtdeveloping habit and lifestyle of praise and worshNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Bio 2 Trial Perak 2007 BIOLOGY SPM PAPERDocument11 pagesMark Scheme Bio 2 Trial Perak 2007 BIOLOGY SPM PAPERhasimahazitNo ratings yet
- Trump Rally SpeechesDocument185 pagesTrump Rally SpeechesMalaiya the MelioristNo ratings yet
- Daily Routines - WorksheetDocument1 pageDaily Routines - WorksheetMalaiya the MelioristNo ratings yet
- InheritanceDocument1 pageInheritanceMalaiya the MelioristNo ratings yet
- 150 Foreign Expressions To Inspire You by Mark NicholDocument7 pages150 Foreign Expressions To Inspire You by Mark NicholMalaiya the MelioristNo ratings yet
- Stuck On So Long A Letter: Senegalese Women's Writings and The Specter of Mariama Bà by Marame Gueye East Carolina University, USADocument30 pagesStuck On So Long A Letter: Senegalese Women's Writings and The Specter of Mariama Bà by Marame Gueye East Carolina University, USAMalaiya the MelioristNo ratings yet
- Ent and OptalmologyDocument138 pagesEnt and OptalmologyFan Eli100% (3)
- Maintenance and Continuity of LifeDocument43 pagesMaintenance and Continuity of LifeCik Puan FaridahNo ratings yet
- Sensory SystemDocument51 pagesSensory SystemsureshdassNo ratings yet
- Animal Diversity-I: (Tutor Marked Assignment)Document16 pagesAnimal Diversity-I: (Tutor Marked Assignment)Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- HearingDocument8 pagesHearingapi-445117811No ratings yet
- Экзам.тесты ИГ 4курс ЛОРDocument98 pagesЭкзам.тесты ИГ 4курс ЛОРканизаNo ratings yet
- Psych Chap 4+5Document26 pagesPsych Chap 4+5lmaoheartsNo ratings yet
- Genetics of Hearing Loss DR NayyarDocument56 pagesGenetics of Hearing Loss DR NayyarSuprit SnNo ratings yet
- HearingDocument15 pagesHearingdisha mangeNo ratings yet
- Ultimate HPL-LAMHADERDocument29 pagesUltimate HPL-LAMHADERATPL 2016No ratings yet
- 1 - Principles of Hearing Aid AudiologyDocument350 pages1 - Principles of Hearing Aid AudiologyCarlos GoodwinNo ratings yet
- A&P Chapter 9 SensesDocument19 pagesA&P Chapter 9 SensesJeong song parkNo ratings yet
- Human ExceptionalityDocument46 pagesHuman ExceptionalityhapsariindreyNo ratings yet
- 2010 Book NanoneuroscienceDocument290 pages2010 Book NanoneuroscienceValentina SotoNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Sense OrgansDocument39 pagesUnit 8 Sense OrgansBasant RajNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy Final Flashcards - QuizletDocument17 pagesNeuroanatomy Final Flashcards - QuizletFaten AklanNo ratings yet
- Histology of Ear and EyeDocument2 pagesHistology of Ear and EyeAnny Alvrz100% (1)
- Pathogenesis of Hearing LossDocument6 pagesPathogenesis of Hearing LossYogi HadityaNo ratings yet
- Utilities 3Document530 pagesUtilities 3Ojhi Gonzales SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Human Ear: (Or Phono Receptor Organ)Document32 pagesHuman Ear: (Or Phono Receptor Organ)Sampada GautamNo ratings yet
- Anatomy EarDocument20 pagesAnatomy EarRod HilalNo ratings yet
- Audio and Video Coding PDFDocument72 pagesAudio and Video Coding PDFPrometheus QueenNo ratings yet
- 2° Tricellular Tight Junctions in The Inner Ear Review Article Ya Elegido 21-1 para 2do ParcialDocument5 pages2° Tricellular Tight Junctions in The Inner Ear Review Article Ya Elegido 21-1 para 2do ParcialGabriela V SuarezNo ratings yet
- ENT EEE by Dr. Manisha Budhiraja 5th Edition - UnlockedDocument448 pagesENT EEE by Dr. Manisha Budhiraja 5th Edition - UnlockedArbin PanjaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab Reviewer Midterm 1st SemDocument26 pagesAnaphy Lab Reviewer Midterm 1st SemSeaniah Faith ApolonaNo ratings yet
- Tool Box Talk # 19 Hearing ProtectionDocument1 pageTool Box Talk # 19 Hearing Protectionsudeesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and Coordination Grade 11Document30 pagesNeural Control and Coordination Grade 11Dr. Remya RanjithNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves. - Sensory Organs - General MedicineDocument100 pagesCranial Nerves. - Sensory Organs - General MedicineHamdi AlaqalNo ratings yet
- ShivaSutras PDFDocument197 pagesShivaSutras PDFB GANAPATHY100% (6)
- Non Visual SensorsDocument2 pagesNon Visual Sensorsarhodes777No ratings yet
- Lower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8From EverandLower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionFrom EverandHow to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- AI and the Future of Education: Teaching in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandAI and the Future of Education: Teaching in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Nature-Based Learning for Young Children: Anytime, Anywhere, on Any BudgetFrom EverandNature-Based Learning for Young Children: Anytime, Anywhere, on Any BudgetRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How Do Cell Phones Work? Technology Book for Kids | Children's How Things Work BooksFrom EverandHow Do Cell Phones Work? Technology Book for Kids | Children's How Things Work BooksNo ratings yet
- Interactive Science Notebook: The Human Body WorkbookFrom EverandInteractive Science Notebook: The Human Body WorkbookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Interactive Notebook: Life Science, Grades 5 - 8From EverandInteractive Notebook: Life Science, Grades 5 - 8Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- STEM Labs for Physical Science, Grades 6 - 8From EverandSTEM Labs for Physical Science, Grades 6 - 8Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- How to Think Like a Lawyer--and Why: A Common-Sense Guide to Everyday DilemmasFrom EverandHow to Think Like a Lawyer--and Why: A Common-Sense Guide to Everyday DilemmasRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Nature Preschools and Forest Kindergartens: The Handbook for Outdoor LearningFrom EverandNature Preschools and Forest Kindergartens: The Handbook for Outdoor LearningRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet