Professional Documents
Culture Documents
I. Mitosis: 1) Introduction:: Phases of Mitosis Pictures
Uploaded by
nhiuyenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
I. Mitosis: 1) Introduction:: Phases of Mitosis Pictures
Uploaded by
nhiuyenCopyright:
Available Formats
I.
MITOSIS:
1) Introduction:
Mitosis produces two daughter cells that are identical to the parent cell. This type of
cell division allows multicellar organism to grow and repair damaged tissue.
This event is divided into 4 phases:
Prophase: Condensation of chromosomes. The nuclear disappears and the spindle
apparatus forms. After that, chromosome will attaches to the spindle.
Metaphase: Chromosomes are condensed and become aligned in to one row at
equatorial plate of the spindle.
Anaphase: sister chromatids of duplicated chromosome separate and are pulled to
two opposite poles of the spindle.
Telophase: The chromosomes relax again. The spindle apparatus breaks down and
nuclear membrane is formed again.
In this practical, we will observe different phases of mitosis under the microscope.
2) Procedure:
Use the prepared sample of dividing cells to identical which phases is occurring.
3) Results:
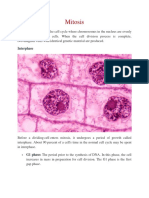
Phases of mitosis Pictures
Prophase: Chromosomes coil
and condense. The nuclear
membrane disappears and the
spindle apparatus forms. After
that, chromosome will attaches
to the spindle.
Prophase observed under objective lens 10X
Metaphase: Condensed
chromosomes will become
aligned in to one row at
equatorial plate of the spindle.
Metaphase observed under objective lens 10X
Anaphase: sister chromatids of
duplicated chromosome separate
and are pulled to two opposite
poles of the spindle
Anaphase observed under objective lens 10X
Telophase: The
chromosomes relax again. The
spindle apparatus breaks down
and nuclear membrane is formed
again.
Telophase observed under objective lens 10X
You might also like
- MitosisDocument3 pagesMitosisDirgantara Abdiel100% (1)
- Human Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsFrom EverandHuman Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Logan Mason Mitosis Flip NoteDocument1 pageLogan Mason Mitosis Flip NotelloganmmasonNo ratings yet
- English BiologyDocument3 pagesEnglish Biologyhannabelewicz09No ratings yet
- Gallo MitosisDocument7 pagesGallo Mitosisapi-310015223No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument32 pagesCell DivisionRhea GulayNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument8 pagesBiologyAya Makram Mohamed AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Observing Mitosis with Fluorescence MicroscopyDocument5 pagesObserving Mitosis with Fluorescence MicroscopyHans Jesper Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Inter Phase Is Followed by Mitosis. It Is The Nuclear Division Involves The Separation of Sister Chromatids. This Involves Four Stages NamelyDocument16 pagesInter Phase Is Followed by Mitosis. It Is The Nuclear Division Involves The Separation of Sister Chromatids. This Involves Four Stages NamelyKumaran JothiramNo ratings yet
- Agric QuizDocument3 pagesAgric QuizKelsy SalazarNo ratings yet
- Stages of Mitosis Cell DivisionDocument2 pagesStages of Mitosis Cell DivisionDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle: Mitosis and MeiosisDocument10 pagesCell Cycle: Mitosis and MeiosisdeepaNo ratings yet
- Interphase Prophase: ChromoDocument12 pagesInterphase Prophase: ChromoNkosi JupiterNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument5 pagesMITOSISdeepaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument28 pagesMitosis and MeiosisPriyanjali SainiNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Division Guide in 40 CharactersDocument28 pagesCell Cycle and Division Guide in 40 CharactersPriyanjali SainiNo ratings yet
- 14-Cell DivisionDocument9 pages14-Cell DivisionMaku MichaelNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument11 pagesCell DivisionDr Nicholas AdeNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4Document4 pagesExercise 4BARRIENTOS, MARIE NICOLENo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument19 pagesCell CycleMoffat KaprezzoNo ratings yet
- Biol Activity 5 Word2003Document16 pagesBiol Activity 5 Word2003Faith Jessica ParanNo ratings yet
- Mitosis, Meiosis I and IIDocument2 pagesMitosis, Meiosis I and IIYEO MING HUI MoeNo ratings yet
- Mitosis NoteDocument1 pageMitosis NoteRIVALS〆toxicNo ratings yet
- TEXT READINGS Chapter - 16Document6 pagesTEXT READINGS Chapter - 16tanusehdev17No ratings yet
- Meiosis Stages A Level BiologyDocument5 pagesMeiosis Stages A Level BiologyEimanNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument2 pagesMitosisKiMii EstebanNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionsDocument6 pagesCell DivisionsEuniceNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 5Document9 pagesLab Report 5buiiianna1995No ratings yet
- Class - X: Life Science Study Material: Cell DivisionDocument13 pagesClass - X: Life Science Study Material: Cell DivisionANIRBAN PALNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Cell Division Mitosis and MeiosisDocument87 pagesLesson 4 - Cell Division Mitosis and MeiosisHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- S4AE BiologyDocument51 pagesS4AE BiologyLeung BibiNo ratings yet
- Name:Cassy Lugak NO MATRIC:2018433928Document8 pagesName:Cassy Lugak NO MATRIC:2018433928CassyNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio (October 10, 2023)Document9 pagesGen Bio (October 10, 2023)Rhian Kassi Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Stages of MitosisDocument2 pagesStages of MitosisWONGNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument1 pageScienceRencyNo ratings yet
- MF009 4B Nuclear Division James L2Document29 pagesMF009 4B Nuclear Division James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: Mitosis and MeiosisDocument16 pagesCell Division: Mitosis and MeiosisMariane CarandangNo ratings yet
- Complete Cell-Cycle. INTERPHASE (Purple) MITOTIC PHASE (Light-Red)Document5 pagesComplete Cell-Cycle. INTERPHASE (Purple) MITOTIC PHASE (Light-Red)Camille Ann Faigao FamisanNo ratings yet
- Biology Mitosis Notes (O Level)Document9 pagesBiology Mitosis Notes (O Level)ojilongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Cell CycleDocument28 pagesChapter 6 Cell CyclefatimaNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle and How Cells DivideDocument41 pagesThe Cell Cycle and How Cells DivideSeleneblueNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument8 pagesMeiosisJohn Chiyu Garde-Labite Azuki100% (1)
- MitosisDocument7 pagesMitosisRishikesh BhintadeNo ratings yet
- CELL-CYCLE-BIOLOGYDocument7 pagesCELL-CYCLE-BIOLOGYjenifaNo ratings yet
- KODIGODocument64 pagesKODIGOcainglesgaeaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology NotesDocument21 pagesBiotechnology NotesRommel BauzaNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument2 pagesMitosisu20036929No ratings yet
- MODULE 3 - MitosisDocument3 pagesMODULE 3 - MitosisNicoleBenaguaNo ratings yet
- MITOSIS & MEIOSIS: Cell Division ProcessesDocument19 pagesMITOSIS & MEIOSIS: Cell Division ProcessesNeo RilloNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Mitosis and MeiosisDocument46 pages3.2 Mitosis and MeiosisAhmed AimanNo ratings yet
- Meiosis StagesDocument8 pagesMeiosis StagesAmelie BalibagonNo ratings yet
- Genetics: Cell Cycle Mitosis MeiosisDocument60 pagesGenetics: Cell Cycle Mitosis MeiosisPatches24 Patches24No ratings yet
- Structure of Chromosomes XRDocument16 pagesStructure of Chromosomes XRhrishikeshanil123No ratings yet
- What Is Meiosis?Document5 pagesWhat Is Meiosis?James DazNo ratings yet
- Copia de MITOSIS Texts FotoDocument2 pagesCopia de MITOSIS Texts FotoMarcos Nuñez CarreteroNo ratings yet
- BioA4 11. Cell Cycle and DivisionDocument7 pagesBioA4 11. Cell Cycle and Divisionthanks btNo ratings yet
- Interphase IDocument3 pagesInterphase IJJAMPPONG PSNo ratings yet
- Exp No 7 Meiosis in Onion Bud CellDocument3 pagesExp No 7 Meiosis in Onion Bud CellShadab AhmadNo ratings yet
- Modeling The Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument4 pagesModeling The Cell Cycle and MitosisFroilan Mae Olado CahaponNo ratings yet