Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Operation of a positive clamping circuit
Uploaded by
Nayinala Satya Kiran0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesSem paper
Original Title
15EC201J_4_sem (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSem paper
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesOperation of a positive clamping circuit
Uploaded by
Nayinala Satya KiranSem paper
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
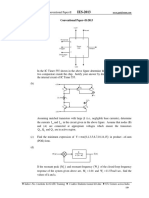
ii. What is a clamper? Discuss the operation of a positive clamping circuit with the help of Reg. No.
circuit diagram and wave forms.
31. a. Sketch the input and output characteristics of common collector configuration and explain B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2018
the operation. 1st to 6rh Semester
(oR) 15EC2O1J _ ELECTRON DEVICES
b.i. Derive the operating point of a CE transistor amplifier that uses potential divider bias. (For the candidates admitted during the academic year 2015 - 2A16 onwards)
Note:
ii. Determine the operating point for the circuit of a potential divider bias arrangement with (i) Part - A should be answered in OMR sheet within frst 45 minutes and OMR sheet should be handed
Rt=39Ko-, R2=3.9 KQ., Rc =10 Kg>,Vcc=2V, f =fiO and Rp =1.5 Kf). (ii)
over to hall invigilator at the end of 45s minute.
Part - B and Part - C should be answered in answer booklet.
32. a. Explain the construction, operation and V-I characteristics of P-channel E-MOSFET.
Time: Three Hours Max. Marks: 100
(oR)
b. Derive and determine the Vgg, Ip, Vpg, Vgand Vp for the self-bias configuration of PART-A(20x1=20Marks)
Answer ALL Questions
D-MOSFET if IDSS =8 mA, Rs =1 KO, VDD =20 V, IOe=2.6 mA, RD =33 KA,
The most commonly used semiconductor is
k=lMel andVp=-6V. 1.
(A) Germanium (B) Silicon
(C) Carbon (D) Sulphur
***r<*
2. The tum on voltage of germanium diode is Voit.
(A)
0.7 (B) 0.3
(c) 1 (D) 0.1
3. The reverse current in a diode is of the order of
(A) kA (B) mA
(c) pA (D) A
4. When we apply reverse bias to ajunction diode, it
(A) Lowers the potential barrier (B) Raises the potential barrier
(C) Greatly increases the minority carrier (D) Greatly increases the majority carrier
curent current
5. APD's are preferred over PIN diodes because of
(A) Speed of operation (B) Higher sensitivity
(C) Largerbandwidth (D) Larger power handling capacity
6. When the reverse bias voltage of a varactor diode increases, its
(A) Capacitance decreases (B) Leakage current decreases
(C) Negative resistance increases (D) Depletion region decreases
7 . What type of diode is commonly used in electronic tuners in TVs?
(A) Varactor (B) Schottlqy
(c) LED (D) Gunn
8. The normal operating region for aZener diode is the
(A) Forward-bias region (B) Reverse-biasregion
(C) Zero-crossingregion (D) Reverse-breakdownregion
Page 4 of 4 23MA1-6/15EC20iJ Page I of4 23MA1-6/15EC201J
9. Efficiency of a centre tapped fulIwave rectifier is PART-B(5x4:20Marks)
(A) 40.6% (B) 8r.2% Answer ANY FM Questions
(c) 3s.8% (D) 8r.7%
21. List out the applications of PN junction diode.
10. Voltage multipliers are circuits best used to produce
(A) Low voltage and low current (B) Low voltage 22. Draw diode equivalent model for PN junction diode under forward and reverse bias.
and high cunent
(C) High voltage and low current (D) High voltage and high current 23. Explain the principle behind the laser diode with a neat sketch.
24. Write the significance of graded doping in step recovery diode.
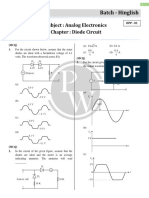
11. A circuit that removes positive or negative parts of waveform is called
(A) Clamper (B) Clipper 25. Write a short note on precision half wave rectifier.
(C) Rectifier (D) Regulator
26. Draw a CE transistor h-parameter model and define forward current ratio.
12. Calculate the average DC voltage in a half wave rectifier with V* = 32.5 V 27. Write the operation of MOSFET as switch.
(A) 20Y (B) 10.3 v
(c) e.s v (D) 20.s v PART - C (5 x 12 = 60 Marks)
Answer ALL Questions
13. What is the current gain for a common base configuration where
In:4.2mA and Ic=4mA? 28. a.i. A silicon PN junction has a reverse saturation current of 40 nA at a temperature of 300 K.
(A) 0.es (B) 16.8
Calculate the junction curtent when the applied voltage is (4 Marks)
(c) 1.05 (D) 0.2
(1) 0.7 V forward bias
(2) 10 V reverse bias
14. In a transistor, base current is about of emitter current. ii. With the help of a neat sketch, explain the operation of PN junction diode in forward and
(A) 2s% (B) 20% reveres bias. (8 Marks)
(c) 3s% (D) s%
(oR)
b. Draw and explain energy band structure of PN diode with relevant equations.
1 5. If the value of o is 0.9, then value of B is
(A) e (B) 0.9 29. a. Discuss the different types of junction breakdown that can occur in a reverse biased diode.
(c) e00 (D) 90 Sketch the circuit symbol for a Zener diode and briefly explain its operation. Show that the
Zener diode can be used as a voltage regulator.
16. Hybrid n model is for analysis. (oR)
(A) Low frequency (B) Mid frequency b. Describe the construction and operation of IMPATT diode with relevant diagrams and also
(C) High frequency (D) Zero frequency mgntion its applications.
30. a. Explain the operation of bridge rectifier circuit and sketch the input and output waveforms.
t7. Common drain configuration used as
(A) Voitage amplifier (B) Current amplifier
List its advantages and disadvantages.
(C) Impedance matching circuits (D) Voltage regulator (oR)
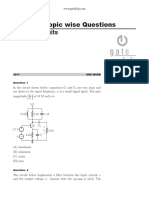
b.i. Determine the output waveform for the network shown below.
18. Threshold voltage of N-channel enhanced-MOSFET is
(A) Zerc (B) Low negative
(C) High negative (D) Positive
19. The effective channel lenglh of a MOSFET in saturation decreases with increases in
(A) Gate voltage (B) Drain voltage
(C) Source voltage (D) Body voltage
20. CMOS stands for
(A) Common MOS (B) Coherent MOS
(C) Cathode MOS (D) Complementary MOS
Page2 of 4 23MAr-6t15EC201J Page 3 of4 23MA1-6/1sEC201J
You might also like
- Runyes Autoclave - Service ManualDocument21 pagesRunyes Autoclave - Service Manualvoica andreea67% (15)
- B. List - : Will (Or) How TwoDocument2 pagesB. List - : Will (Or) How TwoSarvesh SinghNo ratings yet
- FLRX If (C) V RR (B) : ExaminationDocument2 pagesFLRX If (C) V RR (B) : ExaminationJerry SinghNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document2 pagesPaper 1subhaNo ratings yet
- 成功大學電機所電子學考古題98 107大破解Document40 pages成功大學電機所電子學考古題98 107大破解game davidNo ratings yet
- ET1006 - 1718S2Exam With AnsDocument12 pagesET1006 - 1718S2Exam With AnsfastNo ratings yet
- 15EC203J 4 SemDocument2 pages15EC203J 4 SemUttam NeelapureddyNo ratings yet
- ET1006 1617S1Exam Paper With AnswersDocument14 pagesET1006 1617S1Exam Paper With AnswersfastNo ratings yet
- NK C SI R: Current Electricity, Basic Home Work Sheet-5Document2 pagesNK C SI R: Current Electricity, Basic Home Work Sheet-5RohanNo ratings yet
- Network Practice Sheet 1 & 2 CHDocument23 pagesNetwork Practice Sheet 1 & 2 CHPAWAN KUMAR MAURYANo ratings yet
- ET1006 - 1617S2Exam With AnswersDocument12 pagesET1006 - 1617S2Exam With AnswersfastNo ratings yet
- Practice 3Document9 pagesPractice 3ayu afNo ratings yet
- BJT Amplifier Design and AnalysisDocument9 pagesBJT Amplifier Design and Analysisayu afNo ratings yet
- ET1006 1920S1Exam AnswersDocument13 pagesET1006 1920S1Exam AnswersfastNo ratings yet
- End Semester Exam BEEE Question Paper 2022-23Document3 pagesEnd Semester Exam BEEE Question Paper 2022-23erbviubNo ratings yet
- ET1006 - 1819S1Exam AnsDocument12 pagesET1006 - 1819S1Exam AnsfastNo ratings yet
- EC Solutions Topicwise Examination Questions NetworksDocument67 pagesEC Solutions Topicwise Examination Questions NetworksMallik's ChannelNo ratings yet
- Ae53 Ac53 At53Document4 pagesAe53 Ac53 At53M Taher BamyaniNo ratings yet
- (A) Define (I) Electric Field.: Physics Paper 2 Sf026/2 PSPM Semester 2 Session 2015/2016 1Document13 pages(A) Define (I) Electric Field.: Physics Paper 2 Sf026/2 PSPM Semester 2 Session 2015/2016 1Voon Chen WeiNo ratings yet
- Network Theory SolutionsDocument159 pagesNetwork Theory SolutionsSrijan DwivediNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 2-NOV23 - CH-1-2-3 - Nov22Document14 pagesQUIZ 2-NOV23 - CH-1-2-3 - Nov22MUHAMMAD NUR AMNI KHARIMANNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - P.SDocument5 pagesCurrent Electricity - P.SAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Fitjee Paper Class 10 ElectrcityDocument4 pagesFitjee Paper Class 10 ElectrcityKeerthivasav 12No ratings yet
- Current Electricity-02-Objective SolvedDocument9 pagesCurrent Electricity-02-Objective SolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- GATE 2009 Electrical Engineering Question PaperDocument15 pagesGATE 2009 Electrical Engineering Question PaperArjun MudlapurNo ratings yet
- DPP 3Document11 pagesDPP 3mstudy1009No ratings yet
- Measurement (Ques - Ch3 - Measurements of RLC)Document23 pagesMeasurement (Ques - Ch3 - Measurements of RLC)madivala nagarajaNo ratings yet
- EC-Conventional Paper-II Key PointsDocument6 pagesEC-Conventional Paper-II Key PointsDIGITAL BUSINESSNo ratings yet
- 03-MP, GP and AssertionDocument10 pages03-MP, GP and AssertionRNo ratings yet
- Phy3622 11 Nor 2018Document5 pagesPhy3622 11 Nor 2018Jay KayyNo ratings yet
- Diode Circuit - DPP 01 (Of Lec 06)Document5 pagesDiode Circuit - DPP 01 (Of Lec 06)devdipika992434No ratings yet
- Analog 2018Document3 pagesAnalog 2018Aparajita NathNo ratings yet
- 131101-2 Gtu 3rd Sem PaperDocument4 pages131101-2 Gtu 3rd Sem PaperShailesh SankdasariyaNo ratings yet
- OP AMP AssignmentDocument8 pagesOP AMP AssignmentPradeep ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Model Paper AnalysisDocument12 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Model Paper AnalysisanithaNo ratings yet
- 37Document7 pages37padhi8480No ratings yet
- IES - Electronics Engineering - Electronic Measurement and InstrumentationDocument58 pagesIES - Electronics Engineering - Electronic Measurement and InstrumentationUsha RaniNo ratings yet
- Lightning Current Test On Radars and Similar StructuresDocument4 pagesLightning Current Test On Radars and Similar StructuresZainal KadirNo ratings yet
- ET1006 - 1820 - Exam With AnswersDocument12 pagesET1006 - 1820 - Exam With AnswersfastNo ratings yet
- Digital Pulse and Circuits Exam QuestionsDocument8 pagesDigital Pulse and Circuits Exam QuestionsKota divyasreeNo ratings yet
- B.tech Power Electronics (E-309)Document2 pagesB.tech Power Electronics (E-309)Parag RaoNo ratings yet
- Applied ElectronicsDocument2 pagesApplied ElectronicsShish DattaNo ratings yet
- JEE Main - 5 - JEE 2023 - PaperDocument15 pagesJEE Main - 5 - JEE 2023 - PaperDevansh GoelNo ratings yet
- Part - A (Physics) : Jee Main 2019 - 9 April - Morning Shift MathongoDocument37 pagesPart - A (Physics) : Jee Main 2019 - 9 April - Morning Shift Mathongorohit574No ratings yet
- Question PaperDocument2 pagesQuestion PaperVidit NaithaniNo ratings yet
- 13-Comp-2012-13-14-15-Aits Pt+otDocument6 pages13-Comp-2012-13-14-15-Aits Pt+otShreyaNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits: GATE EC Topic Wise QuestionsDocument50 pagesAnalog Circuits: GATE EC Topic Wise Questionsdeepthi1993100% (1)
- JEE II Exam Question Bank for AC EngineersDocument44 pagesJEE II Exam Question Bank for AC EngineersLokesh Ujjainia UjjainiaNo ratings yet
- AAI ATC - Previous Year Physics QuesDocument14 pagesAAI ATC - Previous Year Physics Quesarmaan626742No ratings yet
- Ehv Q1Document2 pagesEhv Q1sanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- 03-MP, GP and AssertionDocument9 pages03-MP, GP and AssertionWillis ChekovNo ratings yet
- Selected Problems Ch2Document8 pagesSelected Problems Ch2AhmadNo ratings yet
- MST EX-504 PE PaperDocument1 pageMST EX-504 PE Papersagar manjrekarNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Oct-Nov 2019Document7 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Oct-Nov 2019Venkata LalithaNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Level 1 and 2 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 pagesCurrent Electricity Level 1 and 2 Multiple Choice QuestionsDevansh DuhanNo ratings yet
- MCQ Questions Analog Circuits (EC-405)Document15 pagesMCQ Questions Analog Circuits (EC-405)Ankit KapoorNo ratings yet
- Nodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Instrumentation Engineering 2006Document23 pagesNodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Instrumentation Engineering 2006Meet PatelNo ratings yet
- Code: 20A02101TDocument2 pagesCode: 20A02101Tkurubamailagani ravaliNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Microcomputer and System BUSDocument25 pagesMicrocomputer and System BUSRocky Samrat100% (1)
- MPPT Algorithm PDFDocument8 pagesMPPT Algorithm PDFakilaNo ratings yet
- Op and Tech-Gen2 Mnl-000003Document52 pagesOp and Tech-Gen2 Mnl-000003Salazar HCNo ratings yet
- Answer Section B and C and Paper 3Document21 pagesAnswer Section B and C and Paper 3Adnan ShamsudinNo ratings yet
- Lecture5 Chapter2 - Positive and Negative LogicDocument11 pagesLecture5 Chapter2 - Positive and Negative LogicAyesha HussainNo ratings yet
- TIC106DDocument1 pageTIC106DMauricio BurgosNo ratings yet
- Engineering Division: FF/HART ConfigurationDocument34 pagesEngineering Division: FF/HART ConfigurationJorge Pérez FrisanchoNo ratings yet
- SF-2001-SureFire II High Energy Igniter (English) 2020-12-17Document24 pagesSF-2001-SureFire II High Energy Igniter (English) 2020-12-17akash kurheNo ratings yet
- Analog transmission methodsDocument8 pagesAnalog transmission methodsAnonymous gUjimJKNo ratings yet
- George Trinkaus Magnetic Amplifiers PDFDocument2 pagesGeorge Trinkaus Magnetic Amplifiers PDFjwarswolves0% (1)
- DGPS Trimble BD950Document2 pagesDGPS Trimble BD950aitopesNo ratings yet
- Panel Csi-Cs6p-220-250 PDFDocument2 pagesPanel Csi-Cs6p-220-250 PDFfranchisca9999No ratings yet
- 2 Capacitance ObjectiveDocument16 pages2 Capacitance ObjectiveSiddharth PandabNo ratings yet
- 0651 24 System 10 Generic Manual 09 18Document57 pages0651 24 System 10 Generic Manual 09 18Siva Raman MurugesanNo ratings yet
- TD Docomo IntegrationDocument3 pagesTD Docomo IntegrationVishal SuryawaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 State Space AnalysisDocument22 pagesChapter 8 State Space AnalysisAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics PowerpointDocument16 pagesBasic Electronics PowerpointEarle Sean MendozaNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument21 pagesPDFThuso SebinaNo ratings yet
- Lightning Arrester Modeling Using Atp-Emtp: Trin Saengsuwan and Wichet ThipprasertDocument4 pagesLightning Arrester Modeling Using Atp-Emtp: Trin Saengsuwan and Wichet ThipprasertgumilarNo ratings yet
- Alto Mistral 6000 PWR SM PDFDocument33 pagesAlto Mistral 6000 PWR SM PDFmundomusicalmeriaNo ratings yet
- ReferencesDocument3 pagesReferencesKUHENDRAN A/L RAVANDRANNo ratings yet
- TeSys K Control Relay 4 NO 24V DC Data SheetDocument2 pagesTeSys K Control Relay 4 NO 24V DC Data Sheetsherub wangdiNo ratings yet
- Teradyne Hastings Vacuum Gage BrochrureDocument2 pagesTeradyne Hastings Vacuum Gage Brochrurekp83No ratings yet
- En 301 489-1-17 - Msd30ag - 2017-03Document24 pagesEn 301 489-1-17 - Msd30ag - 2017-03Manohar T MNo ratings yet
- s66698 138URecPrtrDocument36 pagess66698 138URecPrtrPeter SamuelNo ratings yet
- Monopole & Dipole Antennas LabDocument8 pagesMonopole & Dipole Antennas LabSharjeel AsifNo ratings yet
- GSSI UtilityScanDFBrochure PDFDocument2 pagesGSSI UtilityScanDFBrochure PDFJoel AlonzoNo ratings yet
- 3GPP TS 36.101: Technical SpecificationDocument223 pages3GPP TS 36.101: Technical SpecificationsomberriNo ratings yet
- CEPT Novice 1Document26 pagesCEPT Novice 1Ster RncNo ratings yet