Professional Documents
Culture Documents
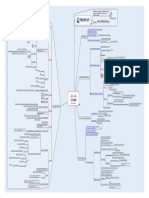
MindCert CISSP Cryptography MindMap
Uploaded by
jayarajanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MindCert CISSP Cryptography MindMap
Uploaded by
jayarajanCopyright:
Available Formats
Motivation and Study Techniques to help Cisco
you learn, remember, and pass your
CISSP
X.509 technical exams!
S/MIME CEH
More coming soon...
IDEA Confidentiality
RSA PGP Visit us www.mindcert.com
Key Exchange
Web of Trust not PKI
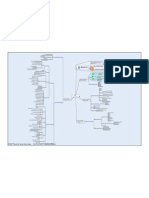
Between application and transport layers
Uses digital certs Art relating to encrypting and decrypting information
SSL/TLS Cryptography
Hidden to the user
Browser support Cryptanalysis Art relating to converting Ciphertext into plaintext without the secret key
AH IPSec
IPSec Encrypting data on the network
ESP Link Encryption L2TP
WAP
Wireless SSL
WTLS Security Layer Misc Security Applications End-to-end Encryption Encryption from source to system/Client to Server
Definitions
Uses SKIPJACK Denial of sending a message Non-repudiation
An embedded chip Repudiation
Escrow Key stored in two places Clipper Traffic Analysis Inference of information from analysis of traffic
For government to spy on you! Generation of spurious data units
Traffic Padding
Two identical pads/keys
Work Factor Effort/Time needed to overcome a protective measure
Unbreakable
Pads can only be used once One time Pad
relies on physical storage of the pads Replace one letter with another one
Substitution Ciphers
Distribution a NIGHTMARE Monoalphabetic
Hiding text in a .JPG Uses more than one method
Hiding data in another format
Steganography History Transposition Ciphers Transposes the keys
Does not follow a common pattern
Issuing CA CA
Symmetric
SSL Server Encryption Categories Asymmetric
Types of Certificates Hash
For e-mail Personal
Older
Algorithmic
ActiveX Controls Software Publishers Secret algorithm
Systems Newer
The authenticating agency CA Fundamentals Keyed Systems Secrecy is provided by the key
The end user or device listed in the subject field of the X.509 certificate End Entity PKI Known algorithm
Strength of the algorithm
A public document containing the rules of the CA Certificate Policy Statement
Encryption Strength Secrecy of the keys
Terminology
The traceable history of parties who have vouched for this certificate Length of the key
Certification Path
A trusted body that can verify the authenticity of a person or host RA Uses the same key to encrypt and decrypt
Where clients store the Certificate Certificate Repository
CISSP Encrypts data in discrete blocks
Cryptography Data is padded if required
Block Block size usually 64 or 128 bytes long
An answer to the symmetric Key Distribution problem Verification
Ciphers Most popular method
Based on Public Keys and Private Key pairs
Plain text is encrypted with the Encrypts data bit by bit
Only receiver can decrypt it receivers public key
Confidentiality Stream Fastest
Cannot verify stream so not considered as secure as block mode
Authentication
56 bit Key
Hash provides integrity Then encrypted with private key to
create a Digital Signature Industry standard
Encryption with the Private signature
provides Authentication Provided by hashing Integrity Block Cipher
Combats MITM Attacks Diffusion and Confusion
NIST
160 Bits Uses SHA DSS Fast and simple
Single key distribution is problematic
Uses a shared secret to combine with the hash Problems
Faster than using asymmetric with the hash Can be cracked
Hashed Message Authentication Code (HMAC)
SHA HMAC Asymmetric/Public DES Cipher Block Chaining
Variants
MD5 HMAC Key Fundamentals Electronic Code Book
Operating Modes
S/MIME is used for secure emails Symmetric/Private Cipher Feedback
Faster than using the public/private key pair S/MIME Key Fundamentals Output Feedback
S/MIME uses session keys to encrypt the message
Provides confidentiality Spread the influence of a plain text character
Confusion
160 bit P Box
SHA
HASH
Symmetric Algorithms Conceals the statistical connection
128 bit between cipher and plain texts
MD5 Diffusion
HASH S Box
Based on Factoring two large prime numbers Algorithms 112 or 168 bit
RSA 3DES
DES but with two or three keys
Based on elliptic curve discreet logarithms
IDEA 128 bit
Faster than RSA ECC
movianVPN Great for PDAs Variable length
RC4
Blowfish 1-448 bit
Repeated use of a key makes it easier to crack
Both sender and receiver must have the same key Up to 256 bit
Key Distribution and Two Fish
Based on modular arithmetic Key Distribution
Can use DH Management Issues 128, 192, or 256 bit
Rijndael
AES
Supports smart cards and 32, 64 bit processors
NIST competition winner
CISSP Cryptography.mmap - 01/05/2008 - Andrew Mason
You might also like
- Real time network monitoring and incident detectionDocument1 pageReal time network monitoring and incident detectionZeeshan RanaNo ratings yet
- MindCert Cisco IPsec MindMap PDFDocument1 pageMindCert Cisco IPsec MindMap PDFzinzinNo ratings yet
- MindCert CEH Ethical Hacking MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert CEH Ethical Hacking MindMapgarbett294No ratings yet
- MindCert CISSP Physical Security MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert CISSP Physical Security MindMapbesmart2000100% (1)
- MindCert CISSP Application Development MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert CISSP Application Development MindMapjayarajanNo ratings yet
- MindCert CISSP Access Control MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert CISSP Access Control MindMapjayarajan100% (1)
- CISSP MindMapDocument66 pagesCISSP MindMapJuan Carlos Angarita C.100% (7)
- CISSP Chapter 1: Information Security Governance and Risk ManagementDocument60 pagesCISSP Chapter 1: Information Security Governance and Risk Managementjonty509No ratings yet
- Top 10 Tips for Passing the CISSP ExamDocument6 pagesTop 10 Tips for Passing the CISSP Examgriffin_ilinkNo ratings yet
- 008 Thor-Teaches-study-guide-CISSP-domain-1 - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)Document24 pages008 Thor-Teaches-study-guide-CISSP-domain-1 - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)LinuxPower100% (1)
- CISSP Mind Maps by Matheus PDF 1638358395Document10 pagesCISSP Mind Maps by Matheus PDF 1638358395Rodrigo Juan100% (1)
- Thor Teaches Study Guide CISSP Domain 7Document40 pagesThor Teaches Study Guide CISSP Domain 7babyNo ratings yet
- My Cissp Success Journey: (Lalit Kumar, CISSP, CISA, ISO 27001 LA, CEH, ITIL, DBA, System Admin)Document2 pagesMy Cissp Success Journey: (Lalit Kumar, CISSP, CISA, ISO 27001 LA, CEH, ITIL, DBA, System Admin)Abdul MalikNo ratings yet
- MindCert Cisco IPsec MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert Cisco IPsec MindMapcpawan_69No ratings yet
- CISSP exam questions on physical securityDocument58 pagesCISSP exam questions on physical securityIvan MartinezNo ratings yet
- CISSP ExqsDocument20 pagesCISSP Exqssentoubudo1647No ratings yet
- Thor Teaches Study Guide CISSP Domain 8Document30 pagesThor Teaches Study Guide CISSP Domain 8baby100% (1)
- 7 Types Hard CISSP Exam QuestionsDocument6 pages7 Types Hard CISSP Exam QuestionsIndarko WiyogoNo ratings yet
- CISSP Combined NotesDocument59 pagesCISSP Combined NotesAnonymous 9d1jFv100% (4)
- CISM - Cybrary TrainingDocument2 pagesCISM - Cybrary TrainingRAJESH SNo ratings yet
- EC-Council Certified Security Analyst Standard RequirementsFrom EverandEC-Council Certified Security Analyst Standard RequirementsNo ratings yet
- CEH Quick Review GuideDocument55 pagesCEH Quick Review GuideAnonymous Y6jSgL100% (1)
- Thor Teaches Study Guide CISSP Domain 6Document11 pagesThor Teaches Study Guide CISSP Domain 6babyNo ratings yet
- CISSP Study PlanDocument1 pageCISSP Study PlanAnonymous RA353CNo ratings yet
- CISSP Mem AidDocument4 pagesCISSP Mem Aidsandra072353100% (2)
- CISSP Quiz QuestionsDocument7 pagesCISSP Quiz Questionsthejoker2055100% (1)
- CISSP Certification - Types of Exam QuestionsDocument1 pageCISSP Certification - Types of Exam QuestionsHakim Moi-meme100% (1)
- Cissp WeekDocument159 pagesCissp Weekrcb023100% (1)
- 0-CISSP Flash Cards Draft 6-6-2010Document126 pages0-CISSP Flash Cards Draft 6-6-2010Maurício SilvaNo ratings yet
- CEH Notes Cybrary PDFDocument34 pagesCEH Notes Cybrary PDFJashan Singh100% (1)
- How Muhammad Cracked His CISSP ExamDocument3 pagesHow Muhammad Cracked His CISSP ExamSayed Ashraf Husaini KaziNo ratings yet
- CISSP Certification Study Guide for Sampat Ray, CISSP, CCSK, CPISI, ISO 27001 LADocument13 pagesCISSP Certification Study Guide for Sampat Ray, CISSP, CCSK, CPISI, ISO 27001 LAsampat rayNo ratings yet
- Oscp PreparationDocument39 pagesOscp Preparationnoc_31380% (5)
- 2023+CISSP+Domain+1+Study+Guide+by+ThorTeaches Com+v4 0Document33 pages2023+CISSP+Domain+1+Study+Guide+by+ThorTeaches Com+v4 0somkumar1100% (2)
- CISSP Study NotesDocument11 pagesCISSP Study NotesCISSPInspired100% (1)
- CISSP Cheat SheetsDocument1 pageCISSP Cheat SheetsRajaram K.VNo ratings yet
- Ec-Council Testinises 312-50v11 Exam Question 2021-Jun-26 by Bartholomew 131q VceDocument18 pagesEc-Council Testinises 312-50v11 Exam Question 2021-Jun-26 by Bartholomew 131q VceYazid BenjamaâNo ratings yet
- Covers All 8 CISSP Exam Domains in One GuideDocument82 pagesCovers All 8 CISSP Exam Domains in One GuidePremdeepakHulagbaliNo ratings yet
- Ebook - CISSP - Domain - 03 - Security Architecture and EngineeringDocument279 pagesEbook - CISSP - Domain - 03 - Security Architecture and EngineeringNOAH ABALONDENo ratings yet
- CISSP CertifiedDocument76 pagesCISSP Certifiedfai100% (2)
- CISSP Referenced The Reddit Forum WeeklyDocument2 pagesCISSP Referenced The Reddit Forum WeeklySakil MahmudNo ratings yet
- CISSP preparation guide and resourcesDocument2 pagesCISSP preparation guide and resourcesDavid WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Bootcamp NotesDocument28 pagesBootcamp Notessandra072353No ratings yet
- CISSP Cheat Sheet Domain 3Document1 pageCISSP Cheat Sheet Domain 3Zainulabdin100% (4)
- CISSP Plan Part 1 Convert to Notecards 1298 TermsDocument64 pagesCISSP Plan Part 1 Convert to Notecards 1298 TermsbabuNo ratings yet
- Comptia Casp Certification: Cram GuideDocument9 pagesComptia Casp Certification: Cram GuideNuria CantosNo ratings yet
- CISSP How To Pass TrainingDocument713 pagesCISSP How To Pass TrainingJose RiveraNo ratings yet
- CISSP Cheat Sheet Domain 1-2Document1 pageCISSP Cheat Sheet Domain 1-2Xaxtsu LungNo ratings yet
- CISSP NotesDocument2 pagesCISSP NotesafeeshNo ratings yet
- SSCP / Cissp Notes I Used To PassDocument43 pagesSSCP / Cissp Notes I Used To Passmilo_andy100% (4)
- CISSP Exam Prep Questions, Answers & Explanations: 1500+ CISSP Practice Questions with SolutionsFrom EverandCISSP Exam Prep Questions, Answers & Explanations: 1500+ CISSP Practice Questions with SolutionsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (7)
- Asset Attack Vectors: Building Effective Vulnerability Management Strategies to Protect OrganizationsFrom EverandAsset Attack Vectors: Building Effective Vulnerability Management Strategies to Protect OrganizationsNo ratings yet
- Kelly Handerhan’s CISSP Exam Review QuestionsDocument89 pagesKelly Handerhan’s CISSP Exam Review QuestionsAnonymous 9d1jFvNo ratings yet
- Pass4sure CISSPDocument28 pagesPass4sure CISSPRhiannon44450% (2)
- CySA+ CS0-002 Cheat SheetDocument31 pagesCySA+ CS0-002 Cheat SheetShurjo Ali100% (3)
- Key Tables, Charts and Flows For SSCP - CISSPDocument45 pagesKey Tables, Charts and Flows For SSCP - CISSPKevin HuangNo ratings yet
- EC Council Certified Incident Handler A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionFrom EverandEC Council Certified Incident Handler A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNo ratings yet
- The SSCP Prep Guide: Mastering the Seven Key Areas of System SecurityFrom EverandThe SSCP Prep Guide: Mastering the Seven Key Areas of System SecurityNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity Leadership: Powering the Modern OrganizationFrom EverandCybersecurity Leadership: Powering the Modern OrganizationNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - The RPA Business Analyst - Role, Skills and ChallengesDocument5 pagesLesson 2 - The RPA Business Analyst - Role, Skills and ChallengesjayarajanNo ratings yet
- UiPath Licensing - Platform ComponentsDocument2 pagesUiPath Licensing - Platform ComponentsjayarajanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - What Is A Process. The RPA PerspectiveDocument6 pagesLesson 1 - What Is A Process. The RPA PerspectiveJhady BolivarNo ratings yet
- Comic Book - Calvin and Hobbes - Yukon Ho 1987-1988 PDFDocument293 pagesComic Book - Calvin and Hobbes - Yukon Ho 1987-1988 PDFamrinderNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - The RPA Journey and The BA's RoleDocument3 pagesLesson 3 - The RPA Journey and The BA's RolejayarajanNo ratings yet
- ESP8266 Tutorial - How To Control Anything From The Internet! - DIY HackingDocument8 pagesESP8266 Tutorial - How To Control Anything From The Internet! - DIY HackingjayarajanNo ratings yet
- UiPath Licensing - Recommended Setup and License DistributionDocument3 pagesUiPath Licensing - Recommended Setup and License DistributionjayarajanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Prepare RPADocument12 pagesLesson 4 - Prepare RPAichaz22No ratings yet
- UiPath Licensing - Licensing ModelsDocument3 pagesUiPath Licensing - Licensing ModelsjayarajanNo ratings yet
- UiPath Licensing - Standalone LicensesDocument2 pagesUiPath Licensing - Standalone LicensesjayarajanNo ratings yet
- Calvin and Hobbes CollectionDocument541 pagesCalvin and Hobbes Collectiondevesh_200367% (3)
- Lesson 1 - What Is A Process. The RPA PerspectiveDocument6 pagesLesson 1 - What Is A Process. The RPA PerspectiveJhady BolivarNo ratings yet
- EC2029-DIP Important Question PDFDocument7 pagesEC2029-DIP Important Question PDFjayarajanNo ratings yet
- EC2029-R08Mayjun 13 PDFDocument3 pagesEC2029-R08Mayjun 13 PDFjayarajanNo ratings yet
- EC2029 R08 AprilMay 15Document3 pagesEC2029 R08 AprilMay 15jayarajanNo ratings yet
- EC2029 R08 MayJune 14 PDFDocument2 pagesEC2029 R08 MayJune 14 PDFjayarajanNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 1768Document84 pagesLab Manual 1768jayarajanNo ratings yet
- EC2029 R08NovDec 13 PDFDocument2 pagesEC2029 R08NovDec 13 PDFjayarajanNo ratings yet
- CS2204 Adc V+ QBDocument4 pagesCS2204 Adc V+ QBjayarajanNo ratings yet
- Arduino ManualDocument40 pagesArduino ManualDaniela Cardenas LuboNo ratings yet
- Israel and The 1948 WarDocument3 pagesIsrael and The 1948 WarjayarajanNo ratings yet
- ARM Processor Embedded Systems DesignDocument6 pagesARM Processor Embedded Systems Designjayarajan0% (1)
- WidgetDocument8 pagesWidgetjayarajanNo ratings yet
- Arthashastra of Chanakya - EnglishDocument614 pagesArthashastra of Chanakya - EnglishHari Chandana K83% (6)
- Group Discussion With AnswersDocument4 pagesGroup Discussion With AnswersjayarajanNo ratings yet
- Mindcert Cissp BCP MindmapDocument1 pageMindcert Cissp BCP MindmapjayarajanNo ratings yet
- Class 6-8 Maths and Science QuestionsDocument17 pagesClass 6-8 Maths and Science QuestionsRakesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Robo Pica E30Document88 pagesRobo Pica E30montri_lpk1728100% (1)
- MindCert CISSP Law MindMap PDFDocument1 pageMindCert CISSP Law MindMap PDFprog_man_0101No ratings yet
- Voucher Hotspot - Jagonet - Outdoor Paket 1 Jam 2000 Up 719 09.06.22Document2 pagesVoucher Hotspot - Jagonet - Outdoor Paket 1 Jam 2000 Up 719 09.06.22MADAN本No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Environment Virtual Machine Vulnerability and Its Proposed SolutionsDocument9 pagesCloud Computing Environment Virtual Machine Vulnerability and Its Proposed SolutionsRajni ManushendraNo ratings yet
- Hacking Talk With Trishneet Arora PaperbackDocument4 pagesHacking Talk With Trishneet Arora Paperbackaw8040% (5)
- A Cybersecurity Checklist For StartupsDocument5 pagesA Cybersecurity Checklist For Startupsaristoteles_cerberus2409No ratings yet
- Project Final Year On Password Management SystemDocument52 pagesProject Final Year On Password Management SystemAyeah Godlove25% (4)
- Draft Witness StatementDOCDocument1 pageDraft Witness StatementDOCMarcus RobathanNo ratings yet
- Department of The Navy: Chief Information Officer 1000 Navy Pentagon WASHINGTON DC 20350-1000Document3 pagesDepartment of The Navy: Chief Information Officer 1000 Navy Pentagon WASHINGTON DC 20350-1000FedScoopNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Privacy Protection in Blockchain SystemDocument13 pagesA Survey On Privacy Protection in Blockchain SystemHafiz Muhammad Azeem SarwarNo ratings yet
- A Light and Secure Healthcare Blockchain For IoT Medical DevicesDocument5 pagesA Light and Secure Healthcare Blockchain For IoT Medical DevicesDivya KandpalNo ratings yet
- IOT (Internet of Things) SecurityDocument41 pagesIOT (Internet of Things) SecurityaksdafNo ratings yet
- Author Accounts Update Sheet (Hamid SEO)Document50 pagesAuthor Accounts Update Sheet (Hamid SEO)Abdullah0% (1)
- Future Generation Computer SystemsDocument17 pagesFuture Generation Computer SystemsSuresh ChavhanNo ratings yet
- IA Security and AssuranceDocument9 pagesIA Security and AssuranceMike Tanhueco100% (3)
- Exploit Pdfka TrojanDocument2 pagesExploit Pdfka TrojanTerriNo ratings yet
- Enhancing System SecurityDocument5 pagesEnhancing System Security9e0 c0No ratings yet
- What Is Cyber Security? Definition & Best PracticesDocument7 pagesWhat Is Cyber Security? Definition & Best PracticesA.No ratings yet
- Lecture 02 - Information Security Threats and AttacksDocument26 pagesLecture 02 - Information Security Threats and AttacksCarlitos MandalaNo ratings yet
- Comparision of AES 128, 192 and 256 Bit Algorithm For Encryption and Description FileDocument5 pagesComparision of AES 128, 192 and 256 Bit Algorithm For Encryption and Description FileARIQ KHOIRINo ratings yet
- Threats, Vulnerabilities, and AttacksDocument9 pagesThreats, Vulnerabilities, and AttacksJohn Hector SaynoNo ratings yet
- Anti Passback (ZD2F20)Document3 pagesAnti Passback (ZD2F20)ANaNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Introduction To Computer Security PDFDocument19 pagesUnit - I Introduction To Computer Security PDFJayesh DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- AWS Security ChecklistDocument2 pagesAWS Security ChecklistwiredfrombackNo ratings yet
- The RSA AlgorithmDocument31 pagesThe RSA AlgorithmbyprasadNo ratings yet
- Lab13 - Bruteforce - and - Password - CrackingDocument13 pagesLab13 - Bruteforce - and - Password - CrackingSaw GyiNo ratings yet
- Cloud Security Assessment Report Template (July 2020)Document23 pagesCloud Security Assessment Report Template (July 2020)Ah ChaiNo ratings yet
- Sap Security Resume 2Document4 pagesSap Security Resume 2Surya NandaNo ratings yet
- Cat Exams Out of 70Document20 pagesCat Exams Out of 70Bashir DestinNo ratings yet
- Final PPT 2nd ReviewDocument18 pagesFinal PPT 2nd ReviewsaranNo ratings yet
- XDR Kill Chain - Full Attack VisibilityDocument4 pagesXDR Kill Chain - Full Attack VisibilityramramNo ratings yet
- Offensive Security: Penetration Test Report For Internal Lab and ExamDocument12 pagesOffensive Security: Penetration Test Report For Internal Lab and Examnobuyuki100% (1)