Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cyanotic Congenital Heart Disease
Uploaded by
Ziyad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
353 views1 pageCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
353 views1 pageCyanotic Congenital Heart Disease
Uploaded by
ZiyadCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Cyanotic Congenital Heart Disease
Etiology Epid. Clinical Manifestations Imaging Studies Treatment Comments
TOF 10% (m/c Cyanosis, Pulmonary stenosis murmur, ECG: RAD, RVH Rx hypoxia: O2 (minimal benefit), Coronary anomalies present in 5%
cyanotic single S2 & RV impulse (LSB), hypoxic CXR: “boot-shaped” heart knee-chest position (squat, of TOF patients
CHD) (Tet) spells (restless, agitated, crying) VR), morphine sulfate, Natural hx is progression and
unconsciousness, convulsions, phenylephedrine ( SVR). worsening of PS and cyanosis
hemiparesis, death. Cyanotic spell: Surgery (complete, Subacute beacterial endocarditis
risk of cerebral TE, cerebral abscess palliative shunt surgery for prophylaxis indicated until 6 m
complex TOF) after repair & for residual VSDs.
TOGA 5% VS intact: Cyanosis, quiet tachypnea, ECG: RAD, RVH Prostaglandin E1 Most common cyanotic lesion
single S2, no murmur CXR: pulmonary vascularity, Balloon atrial septostomy present in newborn period
VSD: less cyanosis, signs of HF, cardiac shadow “egg on Complete surgical repair: Atrial Depends on presence of ASD,
palpable left & right ventricular string” switch within 2 w of life. VSD, PDA for survival
impulses, loud VSD murmur, single S2 Echo: transposition, mixing
TCA 2% Infant severely cyanotic, single S2, ECG: LVH, superior QRS axis VS intact: PE1 until surgery, or VSD Hypoplastic right ventricle
frequently no murmur (VSD murmur, (between 0 & -90°) Surgery staged (3): subclavian AP Depends on PDA or VSD for
diastolic murmur over mitral valve) CXR: normal-mildly enlarged shunt (Blalock-Taussig survival
cardiac silhouette, PBF procedure), 2-stage procedure
(biD Glenn, Fontan)
TA <1% Cyanosis, HF, PVR, tachypnea, cough, ECG: combined ventricular Anticongestive medication Left and right ventricle empty into
bounding peripheral pulses. hypertrophy, cardiomegaly Surgical repair: VSD closure, a single trunk that then divides
Single S2, SEC, systolic murmur (LSB) CXR: pulmonary blood, conduit between RV & PA
displaced PA
Echo: VSD, origin of PA
TAPVR 1% Infants without obstruction: minimal Iw/oO: ECG: RV volume Surgery: common pulmonary vein
cyanosis, asymptomatic, hyperactive overload. CXR: cardiomegaly, is opened into the left atrium
RV impulse (LUSB), mid-diastolic PBF
murmur (LLSB), poor growth. IwO: ECG: RAD, RVH, CXR:
Infants with obstruction: cyanosis, pulmonary edema (similar to
marked tachypnea, signs of RSHF HMB or pneum.)
(hepatomegaly), no murmur.
HLHS 1% HF, weak to absent pulses, single loud ECG: RVH, LV forces PE1, correct acidosis, supportive Most common cause of death
S2, no heart murmur, minimal CXR: right sided enlargement, Surgical repair (staged): Norwood, from cardiac defects in the first
cyanosis, low CO, grayish color of skin pulmonary venous congestion bidirectional Glenn and Fontan month of life
& edema procedures. Failure of development of mitral or
Echo: small left side of heart, aortic valve or aortic arch
hyoplastic ascending aorta Dependent on right-to-left
shunting at DA for survival
TOF, Tetralogy Of Fallot; TOGA, Transposition Of The Great Arteries; TCA, Tricuspid Atresia; TA, Truncus Arteriosus; TAPVR, Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return; HLHS, Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
You might also like
- 14 - Toronto Notes 2011 - GynecologyDocument52 pages14 - Toronto Notes 2011 - GynecologyZiyad100% (4)
- Fluid Management in PediatricsDocument3 pagesFluid Management in PediatricsZiyadNo ratings yet
- Acyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument2 pagesAcyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseZiyad100% (1)
- "Most Common's" in Pediatric CardiologyDocument1 page"Most Common's" in Pediatric CardiologyZiyadNo ratings yet
- Typical CSF Findings in Pediatric MeningitisDocument1 pageTypical CSF Findings in Pediatric MeningitisZiyadNo ratings yet
- EndometriosisDocument1 pageEndometriosisZiyad100% (1)
- Prenatal Assessment of FetusDocument1 pagePrenatal Assessment of FetusZiyadNo ratings yet
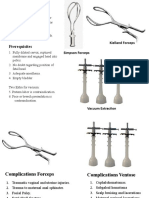
- Instruments & IndicationsDocument11 pagesInstruments & IndicationsZiyad100% (2)
- Urinary IncontinenceDocument1 pageUrinary IncontinenceZiyad100% (1)
- Thyroid DiseaseDocument1 pageThyroid DiseaseZiyadNo ratings yet
- Obstetric BleedingDocument1 pageObstetric BleedingZiyadNo ratings yet
- BreechDocument1 pageBreechZiyadNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- NCM 102Document22 pagesNCM 102Yessamin100% (2)
- Cardiac Arrhythmias I: Atrioventricular Conduction Disturbances and BradyarrhythmiasDocument73 pagesCardiac Arrhythmias I: Atrioventricular Conduction Disturbances and Bradyarrhythmiasiman firmansyahNo ratings yet
- Echocardiography A Practical Guide For Reporting and Interpretation, Third EditionDocument251 pagesEchocardiography A Practical Guide For Reporting and Interpretation, Third EditionJoao da Costa100% (1)
- Ventricular Septal DefectDocument11 pagesVentricular Septal DefectFajar YuniftiadiNo ratings yet
- s.3 Biology Transport in Plants and Animals NotesDocument40 pagess.3 Biology Transport in Plants and Animals Notesgeofreyvybz95No ratings yet
- ATPL (H) Human Performance and LimitationsDocument117 pagesATPL (H) Human Performance and LimitationsRebaz Jamal AhmedNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 LECTURE Hemodynamics Understanding The Basic Principles 2021 For Canvas UpdatedDocument59 pagesNCM 118 LECTURE Hemodynamics Understanding The Basic Principles 2021 For Canvas UpdatedPollen Siega BunalNo ratings yet
- AnestesiDocument11 pagesAnestesiAnonymous 8w9QEGNo ratings yet
- Equipment and Monetring CPB PDFDocument10 pagesEquipment and Monetring CPB PDFBasantkumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Organon of Medicine and Principles of Homoeopathic Philosophy & PsychologyDocument40 pagesOrganon of Medicine and Principles of Homoeopathic Philosophy & PsychologyAmit BangiaNo ratings yet
- Inotropes and Vasoconstictor PackageDocument25 pagesInotropes and Vasoconstictor PackageYoussef MokdadNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument12 pagesJurnalFKWNo ratings yet
- Cath Lab PreparationDocument158 pagesCath Lab PreparationBat ManNo ratings yet
- Bio 202 - Exam 1 (Part 2)Document6 pagesBio 202 - Exam 1 (Part 2)GretchenNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument80 pagesBiologyAmp100% (5)
- Cardiovascular History Taking and Physical ExaminationsDocument35 pagesCardiovascular History Taking and Physical ExaminationsEndalk AsfawNo ratings yet
- Vasodilators and The Treatment of Angina PectorisDocument24 pagesVasodilators and The Treatment of Angina PectorisKriselda May TorioNo ratings yet
- PEDIA - Cardio (Esguerra) PDFDocument9 pagesPEDIA - Cardio (Esguerra) PDFMedisina101No ratings yet
- Task 2: Physiological Exercise and Physical Activity: To Transport Nutrients, Gases and Waste Products Around The BodyDocument2 pagesTask 2: Physiological Exercise and Physical Activity: To Transport Nutrients, Gases and Waste Products Around The Bodyjohn paul PatronNo ratings yet
- Simulation Scenarios PDFDocument59 pagesSimulation Scenarios PDFryan24No ratings yet
- BRN 301-400 PediDocument46 pagesBRN 301-400 PediJoyzoeyNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument16 pagesCirculatory SystemHarinder KaurNo ratings yet
- PhysiologyDocument31 pagesPhysiologyraza20No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument9 pagesCirculatory SystemKyla Mae JinonNo ratings yet
- Martini The HeartDocument64 pagesMartini The HeartEvan PermanaNo ratings yet
- Minimally Invasive Cardiac Output Monitors: Kate E Drummond MBBS FANZCA Edward Murphy MBBS FANZCADocument6 pagesMinimally Invasive Cardiac Output Monitors: Kate E Drummond MBBS FANZCA Edward Murphy MBBS FANZCApankaj88gmcNo ratings yet
- Sample Transes 2Document11 pagesSample Transes 2Sophia SalamatNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0021915018315259 Main PDFDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0021915018315259 Main PDFElson TavaresNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure: Pediatrics 2Document11 pagesCongestive Heart Failure: Pediatrics 2Rea Dominique CabanillaNo ratings yet
- Atrial Systole: The End of DiastoleDocument9 pagesAtrial Systole: The End of DiastoleSophia MahboobNo ratings yet